Status determination of benzodiazepines
On this page
How to use this page
This guidance document provides a general overview of how Health Canada determines the status for benzodiazepines under the CDSA. Please note that this guidance is subject to change upon availability of new scientific evidence. It bears emphasis that this document is published for informational purposes only. It is not a comprehensive account of how status decisions are made, and is not a substitute for status decisions made by the Science Division of the Office of Legislative and Regulatory Affairs.
This document should be read in conjunction with relevant sections of the CDSA and its regulations. In the case of any discrepancies between this document and the legislation, the latter shall prevail.
In order to ensure the accurate status of any substance of interest, please contact: status-demandedestatut@hc-sc.gc.ca.
About benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are depressant drugs that slow down brain activity and produce sedative and calming effects and can be used to treat people with conditions such as anxiety, panic attacks, sleep disorders and seizures. Benzodiazepines are only legally available by prescription and should only be consumed as recommended by a physician.
Problematic use of benzodiazepines can cause substance use disorder, overdose and even death, and are especially dangerous when consumed with alcohol and other drugs.
There are 34 benzodiazepines currently listed explicitly under item 18 in Schedule IV of the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act (CDSA) under the heading "Benzodiazepines, their salts and derivatives". However, some benzodiazepines are captured under other listings, such as flunitrazepam, which is currently listed under item 20 of Schedule I, and clotiazepam which is listed under item 12 of Schedule IV. Additionally, clozapine and olanzapine are benzodiazepines that are excluded from the CDSA but are regulated as prescription drugs under the Food and Drug Regulations.
Many structurally similar substances also have the potential to induce psychoactive and toxic effects similar to benzodiazepines. Health Canada's position is that these substances are also controlled as they belong to the benzodiazepine chemical class.
Substances classified as benzodiazepines under the CDSA
In order to determine whether a substance belongs to the benzodiazepine class, and therefore controlled under the CDSA, a benzodiazepine core structure has been defined. This core structure captures substances that are chemically related as well as potentially psychoactive. The core benzodiazepine structure in this document is based on the structural elements of the benzodiazepines currently listed under the CDSA. The core structure is further validated using currently available scientific information related to benzodiazepines, including structure-activity relationships and pharmacological activity.
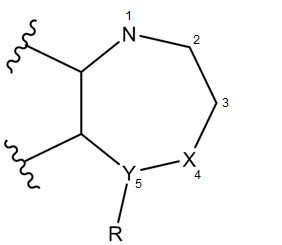
Figure 1 - Text description
The benzodiazepine core structure includes a skeleton consisting of a diazepine ring fused with a 5- or 6-membered aromatic ring, whether or not substituted, adjacent to position 1 of the diazepine ring. A 6-membered ring (R), whether or not substituted, must be attached at position 5 of the diazepine ring, with the exception of a piperazine ring. Benzodiazepines with a piperazine ring at position 5 are excluded from this core structure. The two nitrogen (N) atoms on the diazepine ring must be present in either the 1,4- (X) or 1,5- (Y) positions; any other positions of the two nitrogen atoms are excluded from this core structure. Further substitutions can be made on positions 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5, including an additional fused ring.
- Second nitrogen (N) atom on position 4 or 5
- X and Y - if there is a nitrogen (N) atom in one position, the other must be a carbon (C) atom
- Any 5- or 6-membered aromatic ring fused to the diazepine ring; adjacent to position 1, including any further substitutions on fused aromatic ring
- R is a 6-membered ring attached to position 5 (e.g. phenyl, pyridine, cyclohexen-1-yl, etc.), optionally mono- or poly-substituted
See "Exclusions" for exceptions to this rule - Any further substitutions on positions 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, including an additional fused ring
Exclusions:
- Nitrogen atoms on positions other than 1,4 and 1,5
- Substances with a piperazine ring at position 5 (i.e. R = piperazine)
The core structure may be relied upon to determine whether a substance belongs to the benzodiazepine class. If the substance is captured within the outlined core structure above, it is captured under item 18 of Schedule IV to the CDSA.
Page details
- Date modified: