Departmental Performance Report
For the period ending
March 31, 2015
Citizenship and Immigration Canada
ISSN 2368-593X
Table of Contents
- Minister’s Message
- Section I: Organizational Expenditure Overview
- Organizational Profile
- Organizational Context
- Strategic Outcomes and Program Alignment Architecture
- Organizational Priorities
- About CIC’s Risks
- Risk Analysis
- Actual Expenditures
- Alignment of Spending with the Whole-of-Government Framework
- Departmental Spending Trend
- Estimates by Vote
- Canada’s Immigration Plan for 2014
- Section II: Analysis of Programs by Strategic Outcome
- Strategic Outcome 1: Migration of permanent and temporary residents that strengthens Canada’s economy
- Strategic Outcome 2: Family and humanitarian migration that reunites families and offers protection to the displaced and persecuted
- Strategic Outcome 3: Newcomers and citizens participate in fostering an integrated society
- Strategic Outcome 4: Managed migration that promotes Canadian interests and protects the health, safety and security of Canadians
- Program 5.1: Internal Services
- Section III: Supplementary Information
- Section IV: Organizational Contact Information
- Appendix: Definitions
Minister's Message
As the new Minister of Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship, I am pleased to present the Departmental Performance Report for 2014–2015.
Canada is the country it is today thanks to the entrepreneurial spirit of those who have chosen to make their lives here. We will continue to advance our humanitarian tradition while drawing the best from around the world to help build a nation that is economically, socially and culturally prosperous, and continuing to ensure the safety and security of Canadians.
In the coming year we will renew and expand Canada’s refugee resettlement program—with an immediate focus on the Syrian crisis. By balancing compassion and economic opportunity for all, our efforts will contribute to attracting talented people from around the world while recognizing that diversity can bring both economic and social rewards.
I look forward to building on the many successes of the Department outlined in the report. These include the launch of the new Express Entry system in January 2015, enhancing client service, and strengthening Canada’s humanitarian tradition of welcoming refugees. We will reflect Canadians’ open, accepting, and generous nature in our immigration policies and in our approach to welcoming those seeking refuge from conflict and war. When we come together to help those in need and to welcome newcomers who want to build a better Canada, we build stronger communities and a stronger country.
A robust, effective, and efficient immigration system is critical to Canada’s long-term success and I look forward to working with departmental officials, my provincial and territorial counterparts, and our partners and stakeholders to make Canada’s immigration system the best it can be.
Although responsibility for the Multiculturalism Program has been transferred to the Minister of Canadian Heritage, I am also proud to report on the Program’s achievements for 2014–2015.
The departmental accomplishments in the last year would not have been possible without the hard work of dedicated employees in offices across Canada and at our missions abroad. I have every confidence we will continue to succeed on all fronts.
Minister of Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship
Section I: Organizational Expenditure Overview
Organizational Profile
Minister: John McCallum
Deputy Head: Anita Biguzs
Ministerial Portfolio:
Citizenship and Immigration Footnote i
Department: Department of Citizenship and Immigration
Statutory and Other Agencies: Citizenship Commission, Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada
Crown Corporation: Canadian Race Relations Foundation
Enabling Instruments: Section 95 of the Constitution Act, 1867, the Citizenship Act, the Immigration and Refugee Protection Act (IRPA), the Canadian Multiculturalism Act Footnote ii and the Canadian Passport Order.
Year Established: 1994
Organizational Context
Raison d’être
In the first years after Confederation, Canada’s leaders had a powerful vision: to connect Canada by rail and make the West the world’s breadbasket as a foundation for the country’s economic prosperity. This vision meant quickly populating the Prairies, leading the Government of Canada to establish its first national immigration policies. Immigrants have been a driving force in Canada’s nationhood and its economic prosperity—as farmers settling lands, as workers in factories fuelling industrial growth, as entrepreneurs and as innovators helping Canada to compete in the global economy.
Responsibilities
Citizenship and Immigration Canada (CIC) selects foreign nationals as permanent and temporary residents whose skills contribute to Canadian prosperity.
The Department maintains Canada’s humanitarian tradition by welcoming refugees and other people in need of protection, thereby upholding its international obligations and reputation.
CIC develops Canada’s admissibility policy, which sets the conditions for entering and remaining in Canada. It conducts, in collaboration with its partners, the screening of potential permanent and temporary residents to protect the health, safety and security of Canadians. CIC is also responsible for the issuance and control of Canadian passports, which facilitate the travel of Canadians abroad.
Lastly, the Department builds a stronger Canada by helping all newcomers settle and integrate into Canadian society and the economy, and by encouraging and facilitating Canadian citizenship.
To achieve its goals, CIC offers many of its services on the CIC Web site, as well as at 25 in-Canada points of service and 61 points of service in 52 countries. CIC also partners with other federal government departments to administer its many programs. For instance, CIC works with Service Canada and Canada Post for the delivery of most passport services through these departments’ respective 153 and 43 in-Canada locations. Additionally, CIC’s services and programs are delivered through contract or grant and contribution agreements. As of March 31, 2015 there were 132 visa application centres in 94 countries, 145 application support centres within the United States of America, and a panel physicians’ network operating around the world.
Strategic Outcomes and Program Alignment Architecture
- Strategic Outcome 1: Migration of permanent and temporary residents that strengthens Canada’s economy
- Program 1.1: Permanent Economic Residents
- Sub-Program 1.1.1: Federal Skilled Workers
- Sub-Program 1.1.2: Federal Skilled Tradespersons
- Sub-Program 1.1.3: Quebec Skilled Workers
- Sub-Program 1.1.4: Provincial Nominees
- Sub-Program 1.1.5: Live-in Caregivers
- Sub-Program 1.1.6: Canadian Experience Class
- Sub-Program 1.1.7: Federal Business Immigrants
- Sub-Program 1.1.8: Quebec Business Immigrants
- Program 1.2: Temporary Economic Residents
- Sub-Program 1.2.1: International Students
- Sub-program 1.2.2: Temporary Foreign Workers
- Program 1.1: Permanent Economic Residents
- Strategic Outcome 2: Family and humanitarian migration that reunites families and offers protection to the displaced and persecuted
- Program 2.1: Family and Discretionary Immigration
- Sub-Program 2.1.1: Spouses, Partners and Children Reunification
- Sub-Program 2.1.2: Parents and Grandparents Reunification
- Sub-Program 2.1.3: Humanitarian and Compassionate and Public Policy Considerations
- Program 2.2: Refugee Protection
- Sub-Program 2.2.1: Government-Assisted Refugees
- Sub-Program 2.2.2: Privately Sponsored Refugees
- Sub-Program 2.2.3: Visa Office Referred Refugees
- Sub-Program 2.2.4: In-Canada Asylum
- Sub-Program 2.2.5: Pre-removal Risk Assessment
- Program 2.1: Family and Discretionary Immigration
- Strategic Outcome 3: Newcomers and citizens participate in fostering an integrated society
- Program 3.1: Newcomer Settlement and Integration
- Sub-Program 3.1.1: Settlement
- Sub-Sub-Program 3.1.1.1: Language Training
- Sub-Sub-Program 3.1.1.2: Community and Labour Market Integration
- Sub-Program 3.1.2: Grant to Quebec
- Sub-Program 3.1.3: Immigration Loan
- Sub-Program 3.1.4: Resettlement Assistance Program
- Sub-Program 3.1.1: Settlement
- Program 3.2: Citizenship for Newcomers and All Canadians
- Sub-Program 3.2.1: Citizenship Awareness
- Sub-Program 3.2.2: Citizenship Acquisition, Confirmation and Revocation
- Program 3.3: Multiculturalism for Newcomers and All Canadians
- Sub-Program 3.3.1: Multiculturalism Awareness
- Sub-Program 3.3.2: Federal and Public Institutional Multiculturalism Support
- Program 3.1: Newcomer Settlement and Integration
- Strategic Outcome 4: Managed migration that promotes Canadian interests and protects the health, safety and security of Canadians
- Program 4.1:Health Protection
- Sub-Program 4.1.1: Health Screening
- Sub-Program 4.1.2: Medical Surveillance Notification
- Sub-Program 4.1.3: Interim Federal Health
- Program 4.2: Migration Control and Security Management
- Sub-Program 4.2.1: Permanent Resident Status Documents
- Sub-Program 4.2.2: Visitors Status
- Sub-Program 4.2.3: Temporary Resident Permits
- Sub-Program 4.2.4: Fraud Prevention and Program Integrity Protection
- Sub-Program 4.2.5: Global Assistance for Irregular Migrants
- Program 4.3: Canadian Influence in International Migration and Integration Agenda
- Program 4.4: Passport
- Program 5.1: Internal Services (Supports all Strategic Outcomes)
- Program 4.1:Health Protection
Organizational Priorities
In 2014–2015, CIC identified the following three priorities:
Priority: Emphasizing people management
TypeFootnote iii: Ongoing
Strategic Outcomes: SO 1, 2, 3, 4—Enabling
Summary of Progress
In its commitment to create a workplace conducive to a resilient, productive and innovative workforce that delivers effective programs and services to Canadians, CIC pursued several key human resources management initiatives, including:
- Implementing the Treasury Board Directive on Performance Management
- A training program was successfully developed and launched to facilitate the implementation of the new Treasury Board Directive, which sets out guidelines for managing employee performance within the public service. It consisted of online training, information sessions and other support activities for nearly 2,000 managers and employees.
- To prepare for the launch of the talent management component of the Directive on Performance Management, tools and guidelines for talent management and career development were developed for managers and employees. In addition, support was provided to managers by putting performance improvement plans in place.
- Review panels, along with a governance structure, were established. Review panel roles included: compliance; case management oversight; program oversight; and direction. CIC exceeded the Public Service average for completion rates for mid-year and year-end employee performance reviews.
- Integrating human resources planning with corporate planning
- A human resources (HR) planning framework was developed to outline an approach for CIC to align its human resources activities with its business goals.
- An improved web-based HR dashboard was launched in the third quarter which supports corporate planning by better aligning HR planning with business planning via up-to-date HR demographics.
- A more comprehensive HR planning process was introduced and aligned with CIC’s integrated business planning process. The new HR planning approach was implemented across all sectors and branches and will improve CIC’s work environment and enable its work force to adapt to the evolution of its programs and services.
- Streamlining HR processes
- In 2013–2014, CIC completed the core components of the government-wide Common Human Resources Business Process project, which provided a common approach for efficiently managing people across the Public Service of Canada.
- In 2014–2015, CIC continued to improve and refine its HR processes and tools, allowing managers to more effectively manage the work force while strengthening the strategic partnership with HR professionals. This included:
- establishment of a Strategic Work Force Management Steering Committee, chaired by the Associate Deputy Minister, to work with departmental senior executives and HR Branch leadership to review and develop effective planning, management and business processes in HR;
- completion of a comprehensive review of staffing processes and implementation of the recommendations;
- creation of the Express Lane Staffing team and the implementation of new HR tools to streamline and expedite low-risk staffing processes;
- collaboration of HR and Financial Management branches to initiate the integration of the staffing and salary forecasting processes to support better resource planning; and
- continued improvements to payroll administration, including preparations for the transition to a modernized pay system (Phoenix) and the transition to a centralized Public Service Pay Centre.
- Supporting the Disability Management Initiative
- The Disability Management Initiative has now been included as part of the broader Government of Canada Workplace Wellness and Productivity Strategy, which looks to update and align all the policies, processes, services, roles, responsibilities and accountabilities required to enhance employee wellness and productivity. CIC continued to support TBS in the implementation of this strategy.
- CIC continued to manage disability cases and data was tracked and monitored. Progress in the management of long-term disability appears to be yielding results, as the average length of long-term sick leave without pay has decreased from 20 months at the end of 2012, to 13.2 months at the end of 2014.
- Implementing the employment equity and official languages corporate action plans
- CIC’s Diversity and Employment Equity Champion worked closely with the Diversity and Employment Equity Advisory Committee to establish a new Action Plan for 2015–2018.
- The new Action Plan will address the challenges outlined in the 2014 Public Service Employee Survey results for CIC, as well as continue to support an inclusive and supportive workplace and reflect the priorities and strategies identified in the Human Resources Management Plan.
- The 2013–2016 Official Languages Action Plan was updated to address some Blueprint 2020 priorities.
- Following the new governance structure that was implemented during 2013–2014, regular meetings occurred quarterly to discuss items such as the progress of the 2013–2016 Action Plan and the results of the 2014 Public Service Employee Survey.
Priority: Improving/modernizing client service
Type: Ongoing
Strategic Outcomes: SO 1, 2, 3, 4—Enabling
Summary of Progress
CIC has continued to modernize its services and improve the experience of its clients. By putting clients’ needs at the forefront, CIC aims to enhance the performance and effectiveness of Canada’s immigration, settlement, citizenship and passport programs. In 2014–2015, the Department made significant progress in the improvement and modernization of its services, including:
- Developing a Service Excellence Agenda
- In 2014–2015, CIC moved toward an increasingly integrated, modernized and centralized working environment. The Department has also placed a renewed focus on client service improvement. In 2014–2015, CIC introduced a Departmental Service Excellence Agenda focused on five client service goals based on industry best practices and clients’ expectations. These goals are:
- easy-to-use programs and services;
- timely service;
- up-to-date case status information;
- clear communication; and
- access to a mechanism for clients to relate service feedback.
- The Department has already achieved some of these goals. For example, in November 2014, CIC launched a client feedback mechanism that allows clients to submit comments, compliments and complaints about CIC’s services. This mechanism enables the Department to collect, analyze and generate reports on feedback received and at the same time respond to feedback and track responses made through its centralized database. Clients now have access to a single webform that can be used for feedback relating to multiple lines of business. Since November 2014, CIC has been gathering, monitoring and analyzing the feedback received through the client feedback mechanism in order to identify and address opportunities to improve our services.
- A client service satisfaction survey was conducted in early 2015 in order to gain a clearer understanding of clients’ expectations and experiences as well as to evaluate the impact of modernization efforts. The information will be used to improve existing services and inform the design of new ones.
- In 2014–2015, CIC moved toward an increasingly integrated, modernized and centralized working environment. The Department has also placed a renewed focus on client service improvement. In 2014–2015, CIC introduced a Departmental Service Excellence Agenda focused on five client service goals based on industry best practices and clients’ expectations. These goals are:
- Increasing access to online services
- CIC has been upgrading its technical infrastructure and processes to provide clients with the ease and convenience of self-service through its Web site, suite of e-services and paperless processing. The launch of Express Entry, formerly known as Expression of Interest, in January 2015 is a recent example of a faster, more flexible and responsive system where candidates in most economic streams benefit from online applications with the intent to reduce processing times to six months or less. The four key economic streams eligible for Express Entry are:
- Federal Skilled Workers Program;
- Federal Skilled Trades Program;
- Canadian Experience Class; and
- A portion of the Provincial Nominee Program.
- In 2014–2015, much progress was made in laying the ground work for the Integrated Network Project, which aims to transform the processing network by:
- improving the client experience;
- leveraging the use of technology;
- streamlining the application processes; and
- strengthening program integrity.
- CIC has been upgrading its technical infrastructure and processes to provide clients with the ease and convenience of self-service through its Web site, suite of e-services and paperless processing. The launch of Express Entry, formerly known as Expression of Interest, in January 2015 is a recent example of a faster, more flexible and responsive system where candidates in most economic streams benefit from online applications with the intent to reduce processing times to six months or less. The four key economic streams eligible for Express Entry are:
- Decommissioning of the Field Operations Support System and Expanding the Global Case Management System (GCMS)
- CIC successfully completed the replacement of its Field Operations Support System, an electronic database for important immigration information, in December 2014. The information and functionalities contained in this system are now available in GCMS. In 2014–2015, CIC also made progress in the replacement of the Passport Program’s Integrated Retrieval Information System with expanded functions in GCMS.
- GCMS has moved the Department to a more centralized and virtual business model by providing staff with access to more complete applicant information in one place, improved file tracking, better reporting and fraud detection, and the capacity to move work and files around the globe electronically.
Priority: Promoting management accountability and excellence
Type: Ongoing
Strategic Outcomes: SO 1, 2, 3, 4—Enabling
Summary of Progress
CIC continues to build a strong, high-performing institution that is nimble, connected, engaged and ready to face new challenges. In 2014–2015, CIC focused on streamlining its tools and processes, as well as promoting management excellence through learning events, strategic procurement, compliance and risk management. These activities supported the achievement of this priority and included the following:
- Improving oversight of internal services by strengthening governance practices and processes
- The Department develops and monitors an annual Integrated Corporate Plan that aligns deliverables and resources to advance priorities, while considering environmental and organizational contexts, risks and resources. In 2014–2015, CIC continued to work towards more integrated business and financial planning and reporting to support senior management decision making.
- In 2014–2015, CIC reviewed its security requirement (security in contracting) and its procurement intake process to simplify its processes. Implementation of feasible changes will be carried out in 2015–2016.
- CIC revised its Asset Management Framework to ensure more responsible control of and reporting on government assets.
- CIC updated its Integrated Risk Management Framework and Policy to improve the effectiveness of risk management within the Department. Risk management capacity across the Department was further reinforced through improved support and communication; this in turn strengthens the Department’s capacity to recognize and adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
- CIC undertook a comprehensive review of the Business Continuity Plan and the Business Impact Assessment in 2014–2015. Streamlining the Business Continuity and Emergency Program enabled the Department to continue key activities without interruption during unforeseen events such as the October 2014 Parliament Hill shooting.
- Additionally, CIC successfully deployed the data loss prevention program, which reduces the risk of data loss for the Department by restricting the ability to transfer data from the CIC network to portable storage devices.
- Aligning CIC’s environmental activities to meet the targets in the 2013–2016 Federal Sustainable Development Strategy
- The Department continued to work towards achieving the environmental targets of the 2013–2016 Federal Sustainable Development Strategy.
- In February 2015, CIC participated in the Evaluation of Environment Canada Activities in support of the Federal Sustainable Development Strategy and Canadian Environmental Sustainability Indicators. The Department developed a Sustainable Development Communication Plan and Communiqué to engage employees on green initiatives, such as reducing paper consumption.
- Detailed results on CIC’s environmental targets can be found in the Departmental Sustainable Development Strategy supplementary information table.
- Building on best practices for project management to strengthen the return on investment for CIC projects
- To strengthen the return on investment for CIC projects, the Department continued to work with its project managers to better define business outcomes and measurement criteria.
- In 2014–2015, the Department strengthened project management governance to ensure compliance with Treasury Board project management policies and standards as well as departmental project management directives, standards and best practices.
- In 2014–2015, the Department launched a three-tiered Project Management Certification Program that offers a structured curriculum for CIC employees. The program leverages the Blueprint 2020 objective of building a work force of the future, and offers modules that will assist employees in acquiring the project management competency levels needed to manage projects with different levels of complexity.
About CIC’s Risks
Program Integrity
Because the financial, social and economic stakes involved in immigration and the value placed on Canadian travel documents are so high, all of CIC’s lines of business are potential targets of attempted fraud or other abuse. Compromises to the integrity of CIC’s programs could have far-reaching impacts, including legal challenges, threats to public health and safety, and damage to CIC and Canada’s domestic and international reputations. In 2014–2015, CIC continued to prioritize the integrity of its programs through improved information sharing, wider implementation of biometric screening, enhanced passport security and design and increased efficiencies in the system.
Natural Disasters/Emerging Events
CIC’s broadly dispersed network of personnel and infrastructure is at risk from terrorism, political unrest, natural disasters or war. These events can also lead to unpredictable migration flows, as those affected flee from danger or find themselves dispossessed. Any of these situations may require Canada’s intervention and specialized supports for resettlement or emergency or temporary passports for Canadians for repatriation. CIC recognizes the importance of contingency planning and working closely with its national and international partners, which enabled it to respond quickly and efficiently to a number of events in 2014–2015, including temporary closure of three embassies, the Ebola crisis and the assisted departure of Canadians and eligible persons from Gaza.
Program and Service Delivery
CIC’s strategic direction, as well as its day-to-day activities, is influenced by emerging events, the Canadian and global economic, social and political realities, and shifting migration trends. The scope and pace of change in every line of business over the past several years challenges the Department’s ability to adapt quickly and efficiently. CIC continues to deliver the highest immigration levels plan in recent history. Implementing significant changes to its program and service delivery frameworks and leveraging innovative technology is enabling the Department to remain a flexible, nimble and responsive organization.
Partnership Management
Jurisdiction over immigration is shared between federal, provincial and territorial governments. CIC increasingly relies on partners and stakeholders to support policy and program development, as well as to deliver its internal and external services. Insufficient partner and stakeholder capacity or buy-in, and competing priorities, could have a negative impact on the Department’s ability to achieve its strategic outcomes and support the Government’s agenda. CIC supports its partnerships with robust governance and oversight mechanisms, proactive collaboration and consistent service delivery across all business lines.
Risk Analysis
| Risk | Risk Response StrategyFootnote iv | Link to Program Alignment Architecture |
|---|---|---|
Program integrity |
To mitigate this risk, CIC:
|
|
Natural Disasters / Emerging Events |
|
|
Program and service delivery |
|
|
Partnership Management |
|
|
Actual Expenditures
| 2014–15 Main Estimates |
2014–15 Planned Spending |
2014–15 Total Authorities Available for Use |
2014–15 Actual Spending (authorities used) |
Difference (actual minus planned) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,385,441,063 | 1,385,441,063 | 1,886,944,419 | 1,360,751,108 | -24,689,955 |
| 2014–15 Planned |
2014–15 Actual |
2014–15 Difference (actual minus planned) |
|---|---|---|
| 5,886 | 6,011 | 125 |
| Strategic Outcomes, Programs and Internal Services | 2014–15 Main Estimates |
2014–15 Planned Spending |
2015–16 Planned Spending |
2016–17 Planned Spending |
2014–15 Total Authorities Available for Use | 2014–15 Actual Spending (authorities used) |
2013–14 Actual Spending (authorities used) |
2012–13 Actual Spending (authorities used) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Outcome 1: Migration of permanent and temporary residents that strengthens Canada’s economy | |||||||||
| 1.1 Permanent Economic Residents | 80,799,944 | 80,799,944 | 99,145,934 | 52,512,010 | 82,234,006 | 81,907,913 | 79,311,818 | 40,200,532 | |
| 1.2 Temporary Economic Residents | 34,918,556 | 34,918,556 | 24,278,038 | 24,062,558 | 30,945,774 | 28,817,691 | 20,831,035 | 20,617,661 | |
| Subtotal | 115,718,500 | 115,718,500 | 123,423,972 | 76,574,568 | 113,179,780 | 110,725,604 | 100,142,853 | 60,818,193 | |
| Strategic Outcome 2: Family and humanitarian migration that reunites families and offers protection to the displaced and persecuted | |||||||||
| 2.1 Family and Discretionary Immigration | 46,863,229 | 46,863,229 | 37,572,058 | 37,980,719 | 39,810,239 | 39,557,058 | 44,096,198 | 48,674,101 | |
| 2.2 Refugee Protection | 35,205,049 | 35,205,049 | 30,059,852 | 20,357,936 | 31,249,238 | 29,926,000 | 28,698,237 | 30,301,402 | |
| Subtotal | 82,068,278 | 82,068,278 | 67,631,910 | 58,338,655 | 71,059,477 | 69,483,058 | 72,794,435 | 78,975,503 | |
| Strategic Outcome 3: Newcomers and citizens participate in fostering an integrated society | |||||||||
| 3.1 Newcomer Settlement and Integration | 1,002,954,353 | 1,002,954,353 | 1,014,017,140 | 1,014,602,101 | 1,015,688,908 | 1,010,190,212 | 970,807,076 | 950,739,681 | |
| 3.2 Citizenship for Newcomers and All Canadians | 109,789,678 | 109,789,678 | 68,062,779 | 67,270,183 | 83,594,979 | 82,983,275 | 62,517,787 | 46,583,524 | |
| 3.3 Multiculturalism for Newcomers and All Canadians | 13,208,032 | 13,208,032 | 13,049,066 | 11,521,963 | 10,976,878 | 6,771,604 | 9,793,615 | 15,120,234 | |
| Subtotal | 1,125,952,063 | 1,125,952,063 | 1,095,128,985 | 1,093,394,247 | 1,110,260,765 | 1,099,945,091 | 1,043,118,478 | 1,012,443,439 | |
| Strategic Outcome 4: Managed migration that promotes Canada's interests and protects the health, safety, and security of Canadians | |||||||||
| 4.1 Health Protection | 58,356,894 | 58,356,894 | 63,217,689 | 61,803,321 | 57,867,068 | 31,042,845 | 38,115,873 | 59,616,808 | |
| 4.2 Migration Control and Security Management | 84,966,649 | 84,966,649 | 124,537,482 | 120,437,839 | 115,658,136 | 104,056,335 | 93,642,100 | 76,410,491 | |
| 4.3 Canadian influence in international migration and integration agenda | 8,156,032 | 8,156,032 | 5,177,541 | 5,284,973 | 5,898,735 | 5,896,698 | 5,616,646 | 3,282,924 | |
| 4.4 PassportFootnote v | -254,192,238 | -254,192,238 | -202,153,477 | -208,677,357 | 177,230,530 | -287,387,229 | -206,332,014 | – | |
| Subtotal | -102,712,663 | -102,712,663 | -9,220,765 | -21,151,224 | 356,654,469 | -146,391,351 | -68,957,395 | 139,310,223 | |
| Internal Services Subtotal | 164,414,885 | 164,414,885 | 187,702,906 | 180,737,881 | 235,789,928 | 226,988,706 | 231,596,325 | 231,778,110 | |
| Total | 1,385,441,063 | 1,385,441,063 | 1,464,667,008 | 1,387,894,127 | 1,886,944,419 | 1,360,751,108 | 1,378,694,696 | 1,523,325,468 | |
Planning assumptions and forecasts, including FTEs, as reported in our planned spending, change over the course of the period between the time they are developed and the time actual resource usage is reported in the DPR. The difference between starting number (planned spending), which was developed in late 2013, and the actual usage is due to various factors such as changes in priorities and operational activities. CIC is continuously improving its planning and HR strategies in order to minimize its resources.
In 2014–2015, an overall amount of $1,360.7 million was spent by CIC, compared with planned spending of $1,385.4 million in the 2014–2015 Main Estimates, for an overall variance of $24.7 million. This is a result of a surplus in the Passport Program of $33.2 million and by less-than-anticipated spending related to $28.6 million in fee returns for cancelled Federal Skilled Worker applications. These surpluses were offset by a deficit of $13.4 million in grants and contributions before Supplementary Estimates funding, the reimbursement of fees ($9.5 million) for cancelled Immigrant Investor Program applications, year-end adjustments of $8.6 million, and a deficit in operating expenditures of $5.6 million before in-year funding was provided through Supplementary Estimates, as well as other adjustments.
Total authorities available for use increased during the year by $501.5 million from planned spending of $1,385.4 million to $1,886.9 million. This change is related to an increase in the Passport Program’s spending authority of $431.4 million (comprised of an in-year authority increase of $254.2 million and $177.2 million available from previous years), in-year funding adjustments of $40.5 million (which include the carry forward and salary funding adjustments) and another $39.6 million provided through the Supplementary Estimates for initiatives such as the Canada-Quebec Accord, Express Entry, increased functionality for CIC’s GCMS, and an advertising campaign on services for newcomers. These increases in spending authority were offset by year-end adjustments related to statutory items for an amount of approximately $10.0 million.
Actual spending was lower than total authorities available by $526.1 million. The Passport Program’s portion associated with this difference is $464.6 million, resulting from a surplus of $287.4 million in 2014–2015 which is added to its previous surplus of $177.2 million. These surpluses will fund the anticipated deficit forecast during the second half of the 10-year business cycle of the Passport Program where it is anticipated that the volume will be reduced significantly due to the shift to the 10-year passport.
A total of $51.3 million in operating expenditures was not used in 2014–2015. Among the most significant factors explaining this positive variance is the reduction in costs related to the Interim Federal Health Program, explained mainly by a reduction in the volume of the program’s claims from 469,000 in 2013–2014 to 364,000 in 2014–2015. Funds related to the Beyond the Border Action Plan have been reprofiled to next year. In addition, for various reasons, costs for initiatives such as the government advertising campaign on services to newcomers, the Temporary Foreign Workers Program Reform and Express Entry were lower than anticipated.
The decrease in planned spending for the Permanent Economic Residents Program starting in 2016–2017 is due to the termination of the statutory funding profile in 2015–2016 that supported the return of fees for terminated applications. Reduction in planned spending for the Refugee Protection Program is mainly attributable to the sunsetting of funding for a ministerial reviews and intervention pilot for the In-Canada Asylum Program, as well as a potential transfer of responsibilities, and associated funding, to the Immigration and Refugee Board for the Pre-removal Risk Assessment function.
Lastly, a positive variance of $10.2 million in grants and contributions was achieved and is mainly attributable to lower than planned expenditures in the Settlement Program and the Multiculturalism Program.
Alignment of Spending with the Whole-of-Government Framework
Alignment of 2014–2015 Actual Spending with the Whole-of-Government Framework (dollars)
| Strategic Outcome | Program | Spending Area | Government of Canada Outcome | 2014–15 Actual Spending |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migration of permanent and temporary residents that strengthens Canada’s economy | 1.1 Permanent Economic Residents | Economic Affairs | Strong Economic Growth | 81,907,913 |
| 1.2 Temporary Economic Residents | Economic Affairs | Strong Economic Growth | 28,817,691 | |
| Family and humanitarian migration that reunites families and offers protection to the displaced and persecuted | 2.1 Family and Discretionary Immigration | Social Affairs | A diverse society that promotes linguistic duality and social inclusion | 39,557,058 |
| 2.2 Refugee Protection | International Affairs | A safe and secure world through international engagement | 29,926,000 | |
| Newcomers and citizens participate in fostering an integrated society | 3.1 Newcomer Settlement and Integration | Social Affairs | A diverse society that promotes linguistic duality and social inclusion | 1,010,190,212 |
| 3.2 Citizenship for Newcomers and All Canadians | Social Affairs | A diverse society that promotes linguistic duality and social inclusion | 82,983,275 | |
| 3.3 Multiculturalism for Newcomers and All Canadians | Social Affairs | A diverse society that promotes linguistic duality and social inclusion | 6,771,604 | |
| Managed migration that promotes Canadian interests and protects the health, safety and security of Canadians | 4.1 Health Protection | Social Affairs | Healthy Canadians | 31,042,845 |
| 4.2 Migration Control and Security Management | Social Affairs | A safe and secure Canada | 104,056,335 | |
| 4.3 Canadian Influence in International Migration and Integration Agenda | International Affairs | A safe and secure world through international engagement | 5,896,698 | |
| 4.4 Passport | International Affairs | A safe and secure world through international engagement | -287,387,229 |
Total Spending by Spending Area (dollars)
| Spending Area | Total Planned Spending | Total Actual Spending |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Affairs | 115,718,500 | 110,725,604 |
| Social Affairs | 1,316,138,835 | 1,274,601,329 |
| International Affairs | -210,831,157 | -251,564,531 |
| Government Affairs | – | – |
Departmental Spending Trend
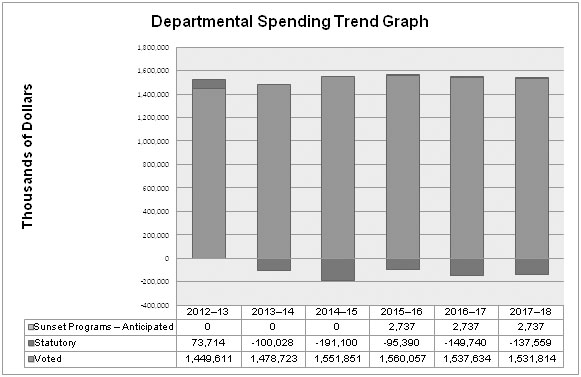
Text version: Departmental Spending Trend Graph
| Fiscal Year | Sunset Programs - Anticipated | Statutory | Voted |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012–2013 | 0 | 73,714 | 1,449,611 |
| 2013–2014 | 0 | -100,028 | 1,478,723 |
| 2014–2015 | 0 | -191,100 | 1,551,851 |
| 2015–2016 | 2,737 | -95,390 | 1,560,057 |
| 2016–2017 | 2,737 | -149,740 | 1,537,634 |
| 2017–2018 | 2,737 | -137,559 | 1,531,814 |
The trend in CIC spending has been primarily affected by the integration of the Passport Program, which was included in 2013–2014 under the statutory items starting July 2, 2013. It is anticipated that Passport will generate a surplus during the first years of its 10-year business cycle, offsetting the overall spending picture for the Department.
Between 2012–2013 and 2014–2015, the Department experienced increased spending in voted items (Operating and Grants and Contribution expenditures). These increases were mostly related to Beyond the Border initiatives and the implementation of core initiatives such as biometrics, citizenship reforms and obligations with our partners.
Sunset funding did not have a material impact on the overall spending trend.
Estimates by Vote
For information on CIC’s organizational votes and statutory expenditures, consult the Public Accounts of Canada 2015 on the Public Works and Government Services Canada Web site.
Canada’s Immigration Plan for 2014
Canada’s approach to managed migration emphasizes human capital as key to long-term economic success and, unlike many other countries, Canada plans annually for the number of permanent immigrants that are welcomed in the country.
The immigration levels set out in Canada’s immigration plan for 2014 reflect the important role of immigration in supporting Canada’s economic growth and prosperity. Further details can be found in the Annual Report to Parliament on Immigration, 2014.
| Immigrant Category | 2014 Plan Admissions Ranges | Number Admitted in 2014 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||
| Federal Skilled Workers Footnote vii | 41,500 | 47,800 | 38,701 |
| Federal Business | 6,000 | 7,400 | 4,464 |
| Canadian Experience Class | 14,000 | 15,000 | 23,786 |
| Caregiver Footnote viii | 14,400 | 17,500 | 17,692 |
| Provincial Nominee | 44,500 | 47,000 | 47,628 |
| Quebec-selected Skilled Workers | 26,000 | 27,000 | 28,922 |
| Quebec-selected Business | 5,000 | 5,500 | 3,896 |
| Subtotal Economic Class: Principal Applicants | – | – | 78,107 |
| Subtotal Economic Class: Spouses and Dependants | – | – | 86,982 |
| Total Economic | 151,400 | 167,200 | 165,089 |
| Spouses, Partners and Children Footnote ix | 45,000 | 48,000 | 45,389 |
| Parents and Grandparents | 18,000 | 20,000 | 18,150 |
| Other Family Class | – | – | 3,122 |
| Total Family | 63,000 | 68,000 | 66,661 |
| Protected Persons in Canada and Dependents Abroad | 11,000 | 12,000 | 10,976 |
| Government-assisted Refugees | 6,900 | 7,200 | 7,573 |
| Blended Visa Office Referred Refugees | 400 | 500 | 177 |
| Privately Sponsored Refugees | 4,500 | 6,500 | 4,560 |
| Public Policy–Federal Resettlement Assistance | 200 | 300 | 8 |
| Public Policy–Other Resettlement Assistance | 100 | 200 | 800 |
| Humanitarian and Compassionate Considerations | 2,500 | 3,000 | 4,528 |
| Total Humanitarian | 25,600 | 29,700 | 28,622 |
| Permit Holders | 0 | 100 | 31 |
| Category not stated Footnote x | – | – | 1 |
| Grand Total | 240,000 | 265,000 | 260,404 |
Section II: Analysis of Programs by Strategic Outcome
Strategic Outcome 1: Migration of permanent and temporary residents that strengthens Canada’s economy
CIC plays a significant role in fostering Canada’s economic development. By promoting Canada as a destination of choice for innovation, investment and opportunity, CIC encourages talented individuals to come to Canada and to contribute to our prosperity. Canada’s immigration program is based on non-discriminatory principles—foreign nationals are assessed without regard to race, nationality, ethnic origin, colour, religion or gender. Those who are selected to immigrate to Canada have the skills, education, language competencies and work experience to make an immediate economic contribution.
CIC’s efforts, whether through policy and program development or processing applications for various programs, result in several hundred thousand new permanent residents each year. Under the 2008 amendments to the Immigration and Refugee Protection Act (IRPA) the Minister for Citizenship and Immigration Canada has the authority to issue instructions establishing priorities for processing certain categories of applications. In that regard, the Department analyzes and monitors its programs to ensure they are responsive to emerging labour market needs.
CIC also facilitates the hiring of foreign nationals by Canadian employers on a temporary basis and implements a number of initiatives to attract and retain international students.
Benefits for Canadians
Immigration continues to have a significant influence on Canadian society and economic development. Permanent residents who arrive in Canada every year enhance Canada’s social fabric, contribute to labour market growth and strengthen the economy. Changes that modernize and improve the immigration system not only strengthen the integrity of the Permanent Economic Residents Program but also benefit Canada by targeting skills Canadian employers need and admitting qualified individuals more quickly.
Temporary foreign workers (TFWs) help generate growth for a number of Canadian industries by meeting short-term and acute needs in the labour market that are not easily filled by the domestic labour force. International students contribute economically as consumers and enrich the fabric of Canadian society through their diverse experiences and talents. Some temporary workers and international students represent a key talent pool to be retained as immigrants.
Performance Analysis
| Performance Indicator | Target | 2014–15 Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Rank within the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) of employment rate for all immigrants | ≤ 5 | 4 |
According to OECD figures, Canada’s employment rate of the foreign-born rose to 71% in 2013 (the most recent year for which OECD data is available), which is an increase from 2012 and the highest employment rate since 2008. Canada rose from sixth to fourth place among OECD countries.
The following programs and sub-programs support this Strategic Outcome:
Program 1.1: Permanent Economic Residents
Rooted in objectives outlined in IRPA, the focus of this program is on the selection and processing of immigrants who can support the development of a strong and prosperous Canada, in which the benefits of immigration are shared across all regions of Canada. The acceptance of qualified permanent residents helps the government meet its economic objectives, such as building a skilled work force, addressing immediate and longer-term labour market needs, and supporting national and regional labour force growth. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.1.1: Federal Skilled Workers
The Federal Skilled Worker (FSW) Program is the Government of Canada's main selection system for skilled immigration. The goal of the program is to select highly-skilled immigrants who will make a long-term contribution to Canada's national and structural labour market needs, in support of a strong and prosperous Canadian economy. The program uses a points system to identify prospective immigrants with the ability to economically establish in Canada, based on their human capital (education, skilled work experience, language skills, etc.), with a minimum language threshold and a third-party foreign educational credential assessment prior to application. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.1.2: Federal Skilled Tradespersons
The Federal Skilled Trades (FST) Program is intended to attract skilled tradespersons needed to meet labour demands in specific industries across the country and who want to become permanent residents based on being qualified in a skilled trade. In contrast with the FSW Program’s points-based selection, the FST Program operates on a streamlined pass/fail basis with four mandatory criteria including: a minimum language threshold; a valid offer of employment in Canada or a certificate of qualification from a province or territory in a qualifying skilled trade; at least two years of work experience in the occupation within the last five years; and meeting the employment requirements set out in the National Occupational Classification system. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.1.3: Quebec Skilled Workers
The Canada-Quebec Accord specifies that the province of Quebec is solely responsible for the selection of applicants destined to the province of Quebec. Federal responsibility under the Accord is to assess an applicant’s admissibility and to issue permanent resident visas. The Quebec Skilled Workers (QSW) Program uses specific criteria to identify immigrants with the human capital and skills needed to economically establish in Quebec. Similar to the FSW Program, the QSW Program assesses applicants according to their age, education, work experience, language proficiency (in French) and enhanced settlement prospects (previous education or work experience in Canada, or a confirmed job offer). The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.1.4: Provincial Nominees
The Provincial Nominee (PN) Program supports the Government of Canada’s objective for the benefits of immigration to be shared across all regions of Canada. Bilateral immigration agreements are in place with all provinces and territories except Nunavut and Quebec, Footnote xi conferring on their governments the authority to identify and nominate for permanent residence immigrants who will meet local economic development and regional labour market needs, and who wish to settle in that specific province or territory. As part of the nomination process, provincial and territorial governments assess the skills, education and work experience of prospective candidates to ensure that nominees can make an immediate economic contribution to the nominating province or territory. CIC retains the final selection authority and verifies that nominees can economically establish in Canada and meet all admissibility requirements before issuing permanent resident visas. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.1.5: Live-in Caregivers Footnote xii
The Live-in Caregiver Program allows persons residing in Canada to employ qualified foreign workers in private residences to provide care for children, elderly persons or persons with a disability. Eligible applicants come to Canada as temporary foreign workers (TFWs), subject to their employer obtaining a neutral or positive labour market opinion (LMO) from Employment and Social Development Canada. The LMO considers whether a Canadian or permanent resident is available and the wage and working conditions being offered Footnote xiii. The critical component of the Live-in Caregiver Program distinguishing it from the general pool of TFWs is the requirement for the caregiver to reside in their place of employment. The Live-in Caregiver Program is also unique in that foreign workers arriving in Canada under the program are eligible to apply for permanent residence after two years or 3,900 hours of full-time employment within four years of their arrival in Canada. They are granted permanent residence as part of the live-in caregiver category of the Economic Class, with established room under the annual levels plan. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.1.6: Canadian Experience Class
The Canadian Experience Class was introduced in 2008 as a path to permanent residence for those with eligible work experience in Canada, usually obtained as a result of temporary residence as a foreign worker or international student. The program is complementary to the FSW Program but uses simplified criteria, including eligible skilled Canadian work experience and a minimum level of proficiency in English or French. The program provides a streamlined and usually faster route to permanent residence for those who have already established themselves in skilled work in Canada. This allows Canada to retain talented workers who have already contributed to the Canadian economy. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.1.7: Federal Business Immigrants
This program admits to Canada those with the experience and skills to support, through their investment, entrepreneurship or self-employment, the development of a strong and prosperous economy. Immigrant investors bring business capital to Canada while entrepreneurs contribute to economic development through enterprise and employment creation. Self-employed persons hold the intention and ability to be self-employed in Canada in such fields as athletics, cultural activities and farming, thereby making a contribution to specified activities in our economy. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.1.8: Quebec Business Immigrants
The Canada-Quebec Accord specifies that the province of Quebec is solely responsible for the selection of applicants destined to the province of Quebec. Federal responsibility under the Accord is to assess an applicant’s admissibility and issue permanent resident visas. This program seeks to attract experienced investors, entrepreneurs and self-employed persons to the province of Quebec, to support the development of a strong and prosperous economy in Quebec. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs Footnote xiv | 304 | 507 | 203 | ||
| Spending | 80,799,944 | 80,799,944 | 82,234,006 | 81,907,913 | 1,107,969 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1.1: Federal Skilled Workers | FTEs | 127 | 222 | 95 |
| Spending | 61,284,746 | 44,055,935 | -17,228,811 | |
| 1.1.2: Federal Skilled Tradespersons | FTEs | 2 | 1 | -1 |
| Spending | 212,507 | 647,866 | 435,359 | |
| 1.1.3: Quebec Skilled Workers | FTEs | 39 | 58 | 19 |
| Spending | 4,342,021 | 5,131,214 | 789,193 | |
| 1.1.4: Provincial Nominees | FTEs | 48 | 46 | -2 |
| Spending | 5,261,536 | 5,327,161 | 65,625 | |
| 1.1.5: Live-in Caregivers | FTEs | 50 | 115 | 65 |
| Spending | 5,551,781 | 9,323,829 | 3,772,048 | |
| 1.1.6: Canadian Experience Class | FTEs | 22 | 50 | 28 |
| Spending | 2,429,081 | 4,424,254 | 1,995,173 | |
| 1.1.7: Federal Business Immigrants | FTEs | 11 | 12 | 1 |
| Spending | 1,154,040 | 12,485,078 | 11,331,038 | |
| 1.1.8: Quebec Business Immigrants | FTEs | 5 | 3 | -2 |
| Spending | 564,233 | 512,576 | -51,657 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 1.1 was slightly higher than planned spending due to a combination of operating and statutory expenditures. On the operational front, the increase was mainly attributable to expenses related to funding for Express Entry that were not included at the planning stage and other higher-than-anticipated operating costs. This increase was offset by a less-than-projected fee return stemming from the cancellation of applications for the FSW Program. The deficit (higher actual spending than planned spending) in the Federal Business Immigrants Program is explained by the fee return that took place in 2014–2015 for cancelled Federal Immigrant Investor and Federal Entrepreneur applications that were not identified in the 2014–2015 Main Estimates.
Performance Results – Program 1.1 and Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| The benefits of immigration are shared across all regions of Canada | Percentage of new permanent residents who land outside of the Montréal, Toronto and Vancouver census metropolitan areas (CMAs) | > 50% | 45.9% |
| Economic immigrants support the long-term economic goals of Canada | Employment earnings relative to the Canadian average, five years after landing | 100% | 115% |
| Percentage growth in labour force attributed to economic migration | > 42% | 66% |
The percentage of new permanent residents who landed outside of Canada’s three largest CMAs increased from 42.1% in 2013 to 45.9% in 2014. This increase is a small departure from recent trends, as this number has ranged between 40 and 42% for the past three years.
Economic permanent resident principal applicants are selected for their ability to become economically established in Canada. Average entry employment earnings for these applicants are well above the average of all immigrants and are on par with or surpass the Canadian average three years after landing. Permanent economic residents also have greater labour market attachment, as measured by the incidence of employment earnings one year after landing.
Immigration is increasingly accounting for most labour force growth in Canada. This growth in turn contributes to increased overall economic activity and greater tax revenue to support services for all Canadians.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal skilled workers (FSWs) support the long-term economic goals of Canada | FSW principal applicants' incidence of employment relative to the Canadian average, five years after landing | +15% | +12.6% |
| Percentage of FSWs earning at or above the Canadian average, five years after landing | ≥ 35% | 40.7% | |
| Rate of social assistance for FSW principal applicants, five years after landing | ≤ 5% | 2.9% |
In 2012, 78.2% of FSWs claimed employment earnings five years after landing, a figure that is 12.6% higher than the Canadian average of 65.6%. Footnote xv Although below target, this difference between FSW employment and the Canadian average increased slightly from 11.3% in 2011.
In 2012, approximately 41% of FSWs showed employment earnings at or above the Canadian average five years after landing, well exceeding the target of 35%.
The rate of FSWs on social assistance five years after landing was 2.9% for the 2012 tax year, which is a decrease from 3.7% in 2011. It is also lower than the Canadian average of 5.9% for the same period.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal skilled tradespersons (FSTs) support the long-term economic goals of Canada | FST principal applicants' incidence of employment relative to the Canadian average, five years after landing | TBD – once data for sufficient years since landing is available | Not yet Available. |
| Percentage of FSTs earning at or above the Canadian average, five years after landing | TBD – once data for sufficient years since landing is available | Not yet Available. | |
| Rate of social assistance for FST principal applicants, five years after landing | TBD – once data for sufficient years since landing is available | Not yet Available. |
In January 2013, the FST Program was launched to facilitate the immigration of skilled tradespersons in response to the growing demand in certain industry sectors. This program emphasizes practical training and work experience, which are key to the employability of skilled tradespersons.
As the Program was launched less than three years ago, no FSTs have been in Canada for a sufficient period of time to obtain baseline or other performance data on their economic outcomes.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quebec-selected skilled workers (QSWs) contribute to the growth of the labour force of the province | QSW principal applicants' incidence of employment, in Quebec, relative to the province's average, five years after landing | TBD | 17.7% |
| Successful QSW applicants are admitted to Quebec | Number of admissions to Quebec | 26,000–27,000 | 28,922 |
In 2012, 82.5% of QSWs showed employment earnings five years after landing, a figure 17.7% higher than the Quebec average of 64.8%. This difference between QSW employment and the Quebec average increased slightly from 16.9% in 2011.
In 2014, a total of 28,922 admissions were destined to Quebec. This is slightly (7%) above the target range of 26,000-27,000.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial nominees (PNs) support the long-term economic goals of Canada | Percentage of PN principal applicants earning at or above the Canadian average, five years after landing | ≥25% | 37.8% |
| PNs support the long-term economic goals of the province or territory of nomination | PN principal applicants' incidence of employment, in their province or territory of nomination, relative to that province or territory's incidence of employment earnings, five years after landing | ≥ +10% | 11% |
| PNs contribute to the shared benefits of immigration in regions of Canada | Percentage of PNs landing outside of Toronto and Vancouver CMAs (excludes Quebec and QSWs) | ≥ 90% | 85.7% |
In 2012, 37.8% of PNs showed employment earnings at or above the Canadian average five years after landing, well exceeding the target of 25%.
In 2012, PNs show incidence of employment in all provinces on average approximately 11% higher than the incidence of employment of Canadians in all provinces. This result is not surprising, given that the PN Program targets regional labour market shortages and many PNs have a job offer at the time of nomination.
The percentage of PNs who landed outside of Canada’s three largest CMAs increased from 83.3% in 2013 to 85.7% in 2014. While not achieving the 90% target, this figure is nearly 30% higher than the rate for all new permanent residents, and represents a significant contribution to more regionally balanced immigration patterns.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Successful live-in caregiver permanent resident applicants and their family members are admitted to Canada | Number of admissions | 14,400–17,500 | 17,692 |
In 2014, live-in caregiver admissions were 17,692, exceeding the target range by 192 admissions, or 1.1%. This is a significant increase from 8,784 admissions in 2013, and reflects efforts on the part of CIC to reduce its overall inventory of live-in caregiver applicants.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporary residents transition to permanent residence in support of the long-term economic goals of Canada | Canadian Experience Class (CEC) principal applicants' incidence of employment relative to the Canadian average, five years after landing | TBD – once data for sufficient years since landing is available | 21.6% Footnote xvi |
| Percentage of CEC principal applicants with employment earnings at or above the Canadian average, five years after landing | TBD – once data for sufficient years since landing is available | 46.6% Footnote xvi | |
| Rate of social assistance for CEC principal applicants, five years after landing | TBD – once data for sufficient years since landing is available | 0.3% Footnote xvi |
In 2012, 87.2% of CEC principal applicants claimed employment earnings three years after landing, a figure that is 21.6% higher than the Canadian average of 65.6%. Approximately 47% of CEC principal applicants showed employment earnings at or above the Canadian average in the same period, and their rate of social assistance five years after landing was 0.3% for the 2012 tax year, well below the Canadian average of 5.9%.
Results for CEC participants are the strongest as compared to all other classes of permanent economic residents for which these statistics are available. This is largely because the CEC Program targets skilled individuals who have demonstrated an ability to integrate into the Canadian labour market through prior work experience.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Successful applicants to the Federal Business Immigrants Program are admitted to Canada | Number of admissions | 6,000–7,400 | 4,464 |
In 2014, the number of federal business immigrant admissions was 4,464, which is 25.6% below the target range of 6,000 to 7,400. The immigrant investor and entrepreneur backlog was eliminated in 2014, which resulted in fewer overall cases to process.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Successful Quebec-selected Business Immigrant applicants are admitted to Quebec | Number of admissions destined to Quebec | 5,000–5,500 | 3,896 |
In 2014, CIC processed 3,896 Quebec Business Immigrant admissions, falling short of achieving the target range by 1,104 admissions, or 22.1%. The Department is continuing to work bilaterally with Quebec to address known issues, and remains committed to processing Quebec Business Immigrants in accordance with the province’s published targets, and ensuring that these individuals meet all federal program requirements.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on the Permanent Economic Residents Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Launch of Express Entry
- On January 1, 2015, the Government of Canada launched Express Entry, a new application management system that targets highly skilled immigrants in the Federal Skilled Workers (1.1.1), Federal Skilled Tradespersons (1.1.2), a portion of Provincial Nominees (1.1.4), and the Canadian Experience Class (1.1.6) programs. Express Entry is designed to more quickly and efficiently welcome economic class immigrants who best meet Canada’s labour market needs.
- Under the previous application approach, applicants for permanent economic residence were processed on a paper-based first-come, first-served basis. This resulted in long inventories of applicants to be processed, and did not guarantee that Canada accepted the best possible candidates to meet its labour market needs in a timely manner.
- With Express Entry, potential candidates participate in a two-step process. First, they submit an online profile to determine if they meet the minimum entry requirements (e.g., language ability, education, Canadian work experience, registration with Job Bank), after which they are placed into the Express Entry pool. Candidate profiles can remain in the pool for up to 12 months during which time they are ranked against other profiles in the pool and may be invited to apply for permanent residence. In such cases, the Department will process most applications in six months.
- Express Entry is also aligned with CIC’s client service goals: an online wizard improves ease of use by helping prospective candidates self-assess their eligibility to submit an Express Entry profile; the six-month service standard in 80% of cases ensures timely processing of applications; candidates in the Express Entry pool can update their information as their circumstances change; and the system is designed to keep candidates clearly informed about the status of their applications. Footnote xvii
- During the first three months of operation (to March 31, 2015), there were six rounds of invitations to apply for permanent residence, with 6,851 invitations to apply for permanent residence issued through Express Entry. Invitations were issued to foreign nationals eligible for all four of the participating immigration programs, and approximately 75% of the individuals who received an invitation submitted a complete application for permanent residence.
- As of March 31, 2015, there were over 25,000 eligible foreign nationals in the Express Entry pool. While no candidate had been admitted to Canada through Express Entry at that time, this is consistent with a processing time of approximately six months for permanent resident applications.
Reform of the Caregiver Program (1.1.5)
- In November 2014, the Live-in Caregivers Program was reformed and two new pathways for caregivers were launched. The reforms acknowledge the valuable contribution that caregivers make to Canadian families and the economy, as well as their potential vulnerability to abuse by employers.
- Changes to the program include ending the requirement for caregivers to live with the care recipients, providing eligible caregivers with two new pathways that will lead to permanent residence: one for those who have provided child care in a home, and one for those who have provided care for individuals with high medical needs. These changes also helped to reduce the existing backlog of caregivers applying for permanent residence by establishing an admissions target of 30,000 permanent resident caregivers in 2015.
- These reforms were intended to improve timely processing for caregivers and their family members applying for permanent residence, with a targeted six-month service standard in most cases, and better protect caregivers from workplace vulnerability and abuse by allowing them to live outside the home of their employers.
Evaluation of and Reforms to the Federal Business Immigrants Program (1.1.7)
- In June 2014, CIC released an Evaluation of the Federal Business Immigrants Program. The evaluation noted that the program was relevant to Canada’s economic objectives, and that there is a continuing need to attract business immigrants to Canada to foster job and business creation. However, the evaluation observed that the program had become less aligned over time with Government of Canada priorities for promoting innovation. The evaluation concluded that the program could benefit from major adjustments in order to increase the economic advantages of business immigration to Canada.
- Advancing reforms in this program, CIC launched the Immigrant Investor Venture Capital Pilot in January 2015, to complement its existing Start-up Visa Pilot Program. The pilot targets dynamic business people who want to make a real investment in the Canadian economy and integrate into the Canadian business community. Since requirements for the pilot are higher than the previous Immigrant Investor Program, it ensures that qualified participants have the necessary human capital and skills to integrate into Canadian society and provide maximum benefit to Canada.
Program 1.2: Temporary Economic Residents
Rooted in objectives outlined in IRPA, the focus of this program is to establish and apply the rules governing entry into Canada of TFWs and international students. Temporary economic migration enhances Canada’s trade, commerce, cultural, educational and scientific activities, in support of our overall economic and social prosperity. The selection and processing involve the issuance of temporary resident visas (TRVs), work permits and study permits to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.2.1: International Students
CIC supports a range of goals for immigration by managing the entry of international students to Canada. International students contribute to Canada’s educational and international competitiveness, and strengthen our educational institutions. International students are selected by these institutions according to their criteria, and CIC validates their presence in Canada to work and study by issuing study permits and, where necessary, visas, which allow them to obtain a Canadian education. CIC is responsible for ensuring that the proper documentation, financial and security requirements are met, including the bona fides, or honest intentions, of all applicants. In order to provide the opportunity of the benefit of Canadian work experience, work permits are issued to qualified international students under CIC’s On-Campus, Off-Campus and Co-op/Internship Work Permit components. Students who want to work in Canada after graduation can apply for a work permit under the Post-Graduation Work Permit component, which allows them to gain up to three years of valuable Canadian work experience. Some Post-Graduation Work Permit holders of work permits will also be eligible to apply for permanent residence under the Canadian Experience Class or other programs. The selection and processing involve the issuance of TRVs and study permits to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 1.2.2: Temporary Foreign Workers
TFW Program allows employers to hire foreign nationals on a temporary basis. The program contributes to the competitiveness and viability of Canadian businesses, since workers are recruited by employers or agencies to address labour or skill supply shortages. The federal government’s role is to manage the entry of foreign nationals to work, scrutinizing the job offer to ensure it is both consistent with our goals for economic immigration and has a neutral or positive effect on the Canadian labour market. In fulfilling this role, in order to hire a temporary worker some employers may require an LMO from Employment and Social Development Canada, which considers whether a Canadian or permanent resident is available and the wage and working conditions being offered. Once in possession of the LMO (if required), the applicant may then apply for the work permit at a mission abroad, at the port of entry (if eligible) or inside Canada (if eligible). The foreign national must meet all admissibility and eligibility requirements. There are a number of different streams under the TFW Program. One of these is the Live-in Caregiver Program, which allows persons residing in Canada to employ qualified foreign nationals to live and work in their private residence to provide care for children, the elderly and the disabled. The Seasonal Agricultural Worker component enables the hiring of workers from countries with these agreements with Canada. If an LMO is not required, such as for reciprocal employment exchanges, intra-company transfers, international agreements (including the North American Free Trade Agreement, bilateral youth exchange agreements and other exceptions), the foreign national applies directly to CIC for a work permit and visa, and CIC considers the genuineness of the job offer and ensures the foreign national meets all admissibility and eligibility requirements. The selection and processing involve the issuance of TRVs and work permits to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants. Footnote xviii
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 320 | 339 | 19 | ||
| Spending | 34,918,556 | 34,918,556 | 30,945,774 | 28,817,691 | -6,100,865 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2.1: International Students | FTEs | 96 | 82 | -14 |
| Spending | 11,430,323 | 7,655,506 | -3,774,817 | |
| 1.2.2: Temporary Foreign Workers | FTEs | 225 | 257 | 32 |
| Spending | 23,488,233 | 21,162,185 | -2,326,048 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 1.2 was lower than planned spending by $6.1 million and authorities were subsequently adjusted to fund other programs.
Performance Results – Program 1.2 and Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualified TFWs enter Canada | Number of TFW entries | 213,573Footnote xvi | 291,649 |
| Qualified international students enter Canada in support of Canada's goals for international education | Number of foreign student entries | 120,000Footnote xix | 211,949 |
In 2014, TFW entries, including entries under the new International Mobility Program (see additional performance information below), were 291,649, exceeding the target by 78,076. This higher-than-expected result reflects a change in data methodology.
In 2014, foreign student entries exceeded the target range by 91,949 admissions, representing an 89.4% increase in reported student entries from 2013. However, as with TFWs, this increase is largely a result of a change in data methodology at CIC and is not representative of such a large increase in foreign student entries. Using the updated methodology, the actual increase in foreign student entries from 2013 to 2014 was only 9.2%.
Previously, data methodologies assigned foreign nationals carrying more than one temporary permit to only one relevant category. As a result, some foreign students who also carried temporary work permits were not counted as student entries, or vice versa. The updated data methodology now assigns entries of foreign nationals carrying more than one temporary permit to both entry categories, resulting in increases in the counts of study permit and temporary foreign work permit holders.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| The skills of selected international students are retained through transition to permanent residence in support of long-term economic goals of Canada | Number of study permit holders transitioning to permanent residence under the Economic Class programs | 5,000–10,000Footnote xvi | 6,937 |
| International students have the opportunity to gain valuable Canadian work experience to complement their education | Number of work permits issued to international students | 62,000 | 63,021 |
| Provinces and territories designate educational institutions for the purposes of admitting international students, based on agreed-upon principles | Number of memorandums of understanding (MOUs) in place with provinces and territories to govern the quality of their designation of educational institutions for the purposes of admitting international students | 12 | 11 |
In 2014, a total of 6,937 international students transitioned to permanent residence through economic streams in Canada. This figure is within the historical target range and represents an increase of 21.7% over transitions made in 2013. Of those who transitioned into permanent residence, most did so through the PN Program (31.8%), followed by the FSW Program (23.4%).
In 2014, CIC issued 63,021 work permits to international students, which is less than 2% above the target range of 62,000. This represents a significant decrease from the 91,048 work permits issued to international students in 2013. However in 2014 CIC eliminated the requirement for international students to obtain a work permit for authorization to work off-campus which resulted in the observed decrease in issued work permits. Also note, that the criteria for work as part of a co-op or internship program were tightened – which would have contributed to the decrease.
The target for this indicator has been met. MOUs have been signed and are in place for all provinces and territories with the exception of Quebec. It was determined that an MOU with Quebec is not required, as the areas of responsibility for the oversight of educational institutions for the purpose of hosting international students is already articulated though the Canada-Quebec Accord.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| The skills of selected TFWs are retained through transition to permanent residence in support of long-term economic goals of Canada | Number of work permit holders transitioning to permanent residence under the economic class programs | 15,000–30,000Footnote xx | 46,520 |
| Percentage adherence rate to 14 calendar day service standard for responses to employers on exemptions from LMOs | ≥ 80% | 92% |
In 2014, a total of 46,520 temporary work permit holders transitioned to permanent residence under an economic class program, which is 55.1% above the target range.Footnote xxi TFWs are an important source of growth for Canada’s labour force, as their Canadian work experience improves overall integration.
In 2014–2015, 92% of applications for exemptions from LMOs were responded to within the 14 calendar day service period, exceeding the 80% target. As of June 2014, LMOs were replaced by labour market impact assessments, which require additional information and attestation from employer applications.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results for the Temporary Economic Residents Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Preparations for the Pan/ParaPan American Games (1.2)
- In 2014–2015, CIC worked closely with its Government of Canada partners and the Pan/ParaPan American Organizing Committee (Toronto 2015) to develop and implement the facilitated accreditation process for Games participants, also known as “Games Family Members.” This facilitated process was a key commitment in the bid Canada put forward to host the Games.
Reform and Growth of the International Student Program (1.2.1)
- 2014 marked a record year for the number of foreign students welcomed to study at Canadian institutions, with 211,979 student entries. The majority of these students came from China, India, South Korea, France and the United States. Foreign student graduates are an important source of growth for the Canadian economy; they can transition to Canadian permanent residents through the Canadian Experience Class Program, and typically have very strong outcomes both in terms of integrating into Canadian society and succeeding in the labour market.
- Changes to the International Student Program came into force on June 1, 2014. These changes:
- improve the integrity of the program by limiting study permits to applicants attending designated learning institutions, and by requiring that foreign students be actively pursuing their studies while in Canada; and
- introduce greater flexibility by allowing full-time international students to work part-time off campus, and full-time during school breaks. This flexibility to work allows international students more opportunities in the Canadian labour market and encourages transition from student to permanent resident through the Canadian Experience Class Program.
Reform of the Temporary Foreign Workers Program (1.2.2)
- Since 2012, the TFW Program has undergone a range of reforms to enhance program integrity, protect foreign workers from abuse, and ensure that Canadians are prioritized for labour market opportunities.
- On June 20 2014, the Government of Canada announced a range of reforms to overhaul the TFW Program, including the reorganization of the program into two separate types of foreign workers:
- The temporary foreign workers streamFootnote xxii now refers only to foreign nationals who enter Canada at the request of employers following a labour market impact assessment by Employment and Social Development Canada. The labour market impact assessment is a more rigorous assessment than the previous LMO, determining if there are Canadians available who could fill the employment need.
- The International Mobility Program stream does not include a requirement for a labour market impact assessment. Its objective is to advance Canada’s economic and national interest, rather than filling specific jobs identified by employers. This includes foreign graduates of Canadian schools, those authorized to work in Canada through agreements such as the North American Free Trade Agreement, International Experience Canada participants, and the spouses of skilled foreign workers.
- Additionally, the June 2014 reforms included enhanced oversight of both the TFW Program and International Mobility Program streams to prevent their misuse. Specifically, this included increases in the scope and number of on-site inspections, greater penalties for non-compliance, and improved information sharing among departments and agencies involved in monitoring, including provincial and territorial governments.
- A new fee of $230 – archived was introduced for employers hiring TFWs under the International Mobility Program.
Strategic Outcome 2: Family and humanitarian migration that reunites families and offers protection to the displaced and persecuted
CIC is committed to upholding Canada’s humanitarian tradition of reuniting families, resettling refugees and providing protection to those in need.
The Family Class, as set forth in IRPA, allows permanent residents and Canadian citizens to sponsor their immediate family members (i.e., their spouse, common-law or conjugal partner, and dependent children), as well as parents and grandparents, for immigration to Canada. The permanent resident or Canadian citizen must undertake to provide for the basic needs of their sponsored relative for a set period of time, depending on the nature of the relationship. This program facilitates family reunification while ensuring that there is no undue cost to the general public.
As a signatory to the 1951 Convention Relating to the Status of Refugees, the 1967 Protocol, and the Convention against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment, and further to provisions set forth in the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, Canada has international and domestic legal obligations to provide safe haven to individuals in need of protection. Canada meets these obligations through the in-Canada refugee status determination system. In addition, Canada partners with other countries and with international and civil society organizations to come to the aid of individuals in need of protection through resettlement. Every year, Canada resettles approximately one out of every 10 refugees resettled globally. CIC engages both domestic and international stakeholders to develop and implement timely, efficient and effective refugee protection policies and programs.
Benefits for Canadians
CIC plays a significant role in upholding Canada’s international and domestic obligations and reputation with regard to refugees and in promoting the Canadian values of openness, diversity, human rights and the rule of law. Through family sponsorship, CIC’s efforts enable Canadian citizens and permanent residents to reunite with family members.
The following programs and sub-programs support this Strategic Outcome:
Program 2.1: Family and Discretionary Immigration
CIC’s family and discretionary programs support the Government of Canada’s family reunification goals for immigration. The program objectives are to reunite family members and to allow for the processing of exceptional cases. Family Class provisions of IRPA enable Canadian citizens and permanent residents of Canada to apply to sponsor eligible members of the family class, including spouses and partners, dependent children, and parents and grandparents. Discretionary provisions in the legislation are used in cases where there are humanitarian and compassionate considerations or for public policy reasons. These discretionary provisions provide the flexibility to approve exceptional and deserving cases not anticipated in the legislation and to support the Government of Canada in its humanitarian response to world events and crises. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 2.1.1: Spouses, Partners and Children Reunification
The objective of this program is to grant permanent resident status to foreign nationals who are the sponsored spouses, partners and dependent children (including adopted children) of Canadian citizens and permanent residents. This supports the government’s objective to reunite close family members while ensuring that there is no undue cost to the general public. The sponsor, who is a permanent resident or Canadian citizen, is responsible for providing the basic needs of his or her spouse or partner for three years, and for their dependent children for up to 10 years. Processing involves determining the sponsor’s ability to meet the sponsorship obligations and verifying the bona fides of the relationships. Given the close family relationships involved, these family members are the highest priority for processing. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 2.1.2: Parents and Grandparents Reunification
The objective of this program is to grant permanent resident status to sponsored foreign nationals who are the parents and grandparents of Canadian citizens and permanent residents. This program makes it possible for Canadian citizens and permanent residents to be reunited with their extended family members, while ensuring that there is no undue cost to the general public. Sponsors must demonstrate that they can meet their sponsorship obligations, which include providing for the basic needs of their parents and grandparents for 10 years. Particular sponsorship requirements and a lower processing priority distinguish this category from the spouses, partners and dependent children category. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
Sub-Program 2.1.3: Humanitarian and Compassionate and Public Policy Considerations
The humanitarian and compassionate and public policy provisions of IRPA enable the Minister to address exceptional circumstances by granting an exception to certain criteria or obligations of the Act or by granting permanent residence. These discretionary provisions provide the flexibility to approve exceptional cases that were not envisioned in the legislation. An applicant’s circumstances are assessed on a case-by-case basis. The public policy provision is a discretionary tool designed to grant permanent or temporary resident status to individuals in similar circumstances, all of whom must meet eligibility criteria defined in the public policy. The selection and processing involve the granting of permanent residence to qualified applicants, as well as the refusal of unqualified applicants.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 424 | 438 | 14 | ||
| Spending | 46,863,229 | 46,863,229 | 39,810,239 | 39,557,058 | -7,306,171 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1.1: Spouses, Partners and Children Reunification | FTEs | 249 | 219 | -30 |
| Spending | 27,472,071 | 20,695,904 | -6,776,167 | |
| 2.1.2: Parents and Grandparents Reunification | FTEs | 72 | 109 | 37 |
| Spending | 7,942,856 | 9,224,349 | 1,281,493 | |
| 2.1.3: Humanitarian and Compassionate and Public Policy Considerations | FTEs | 104 | 110 | 6 |
| Spending | 11,448,302 | 9,636,805 | -1,811,497 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 2.1 was lower than planned spending by $7.3 million and authorities were subsequently adjusted to fund other programs.
Performance Results – Program 2.1 and Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canada reunites families and provides residence in Canada for deserving cases in exceptional circumstances | Number of admissions for total Family Class, humanitarian and compassionate grounds, and public policy grounds | 65,800–71,500Footnote xxiii | 71,997 |
In 2014, family and discretionary admissions were 71,997, exceeding the target range by 497 admissions, or 0.7%. This is a moderate decrease from 86,982 admissions in 2013, and is largely the result of a decrease in parents and grandparents admissions (see below).
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spouses, partners and children are admitted to Canada and reunited with their sponsor | Number of admissions | 45,000–48,000 | 48,511 |
| Reunification applications are processed within published service standards | Percentage adherence to the 12 month service standard for cases processed overseas | 80% | 65% |
In 2014, Canada supported family reunification with 48,511 admissions of spouses, partners and children, exceeding the target range by 511 admissions, or 1.1%. This is a slight decrease from 49,513 admissions in 2013.
In 2014, CIC adhered to its service standard for processing overseas reunification applications within 12 months in 65% of cases, falling short of the 80% target. This adherence rate was unchanged from that reported in 2013. CIC’s ability to achieve the targeted service standard is affected by a number of factors, including those beyond its control, such as incomplete applications and the need for additional information.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parents and grandparents are admitted to Canada and reunited with their sponsor | Number of admissions | 18,000–20,000 | 18,150 |
In 2014, parent and grandparent admissions were 18,150, which was within the target range for this program. This is a decrease from 32,322 admissions in 2013. Higher admission levels in 2012 and 2013, totalling 54,000 admissions, allowed CIC to re-open intake of applications for parents and grandparents in 2014; this new intake was limited to 5,000 new applications per year, so that the Department could continue to reduce the backlog of applications in this area while continuing to maintain a high number of admissions. Between 2011 and March 31, 2015, the inventory of parents and grandparents was reduced by 59%.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| On an exceptional basis, persons are admitted or are allowed to remain in Canada and acquire permanent resident status | Number of persons granted permanent resident status on humanitarian and compassionate or public policy grounds due to their exceptional circumstances | 2,800–3,500 | 5,336 |
In 2014, there were 5,336 admissions on humanitarian and compassionate or public policy grounds, exceeding the target by 1,836, or 52.5%. This is an increase from 5,140 admissions in 2013. A distinguishing feature of these categories is that applications may vary, depending on a range of circumstances beyond the forecasting capability of the Department. The high number of admissions was due largely to backlog reduction efforts, specifically in the humanitarian and compassionate immigration categories.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on the Family and Discretionary Immigration Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Changes to Protect the Vulnerable (2.1.1)
- In 2014–2015, the Government of Canada made changes to the Spouses, Partners and Children Reunification Program to help protect women in an immigration context:
- The Government of Canada worked on the changes to the Immigration and Refugee Protection Regulations, which have since come into force. These changes raise the minimum age of eligibility to immigrate to Canada as a spouse or partner from 16 to 18, and deny recognition of marriages in which one or both of the participants are not physically present at the ceremony, such as ceremonies conducted by proxy or from a distance via telecommunications.Footnote xxiv
Program 2.2: Refugee Protection
The Refugee Protection Program is in the first instance about saving lives and offering protection to the displaced and persecuted. One arm of the program starts overseas, where refugees and persons in refugee-like situations are selected by Canadian visa officers to be resettled as permanent residents to Canada. Flowing from Canada's international and domestic legal obligations, the in-Canada asylum system evaluates the claims of individuals seeking asylum in Canada and grants protected person status when a positive decision is rendered by the Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada.
Sub-Program 2.2.1: Government-assisted Refugees
Working closely with the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) or other referral agencies, Canadian visa officers within the Government-assisted Refugee (GAR) Program identify and select as permanent residents members of the Convention Refugees Abroad and Humanitarian-Protected Persons Abroad classes for resettlement in Canada when there is no other durable solution available within a reasonable period of time. The primary objective of the program is to affirm Canada’s humanitarian commitment to assist refugees in need of international protection through the provision of government assistance and to assist the countries hosting them through responsibility sharing.
Sub-Program 2.2.2: Privately Sponsored Refugees
The primary objective of the Privately Sponsored Refugees (PSR) Program is to affirm Canada’s commitment to providing durable solutions to more refugees than would otherwise be admitted under the GAR Program. Canadian visa officers select as permanent residents members of the Convention Refugees Abroad and Humanitarian-Protected Persons Abroad classes for resettlement in Canada who are referred by private sponsors. These private sponsors then provide the social, financial and emotional support to the refugees upon their arrival in Canada. The program is unique as it ensures an additional number of refugees are offered protection over and above those sponsored by the government.
Sub-Program 2.2.3: Visa Office Referred Refugees
Working closely with the UNHCR or other referral agencies, Canadian visa officers identify and select as permanent residents, members of the Convention Refugees Abroad and Humanitarian-Protected Persons Abroad classes for resettlement in Canada when there is no other durable solution available within a reasonable period of time. Refugees referred by the visa office are matched with a private sponsor and, upon arrival in Canada, receive six months of income support from the Government of Canada via the Resettlement Assistance Program (RAP) and six months of income support from their sponsor. Private sponsors also provide arrival and orientation services, temporary accommodation, and ongoing emotional and social support. The program is a unique public-private partnership that encourages faith-based, ethnocultural and other community organizations in Canada to play a larger role in offering durable solutions to refugees found to be in need of resettlement by the UNHCR or other referral agencies, supporting the objectives of both the Government-assisted Refugee and Private Sponsorship of Refugees programs.
Sub-Program 2.2.4: In-Canada Asylum
Flowing from Canada's international and domestic legal obligations, Canada's asylum system provides protection to persons fleeing persecution and risk of torture, risk to life, or risk of cruel treatment or punishment, by way of legislative and regulatory measures that enable Canada to meet those obligations. The program establishes fair and efficient procedures that uphold Canada’s respect for the human rights and fundamental freedoms of all human beings, while maintaining the overall integrity of the Canadian refugee protection system. Canada’s asylum system includes the determination of eligibility for referral to the Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada and the granting of protected person status to those determined by the Board to be Convention refugees or persons in need of protection. When appropriate, the system also provides for a pre-removal risk assessment (PRRA) to failed refugee claimants and others facing removal from Canada.
Sub-Program 2.2.5: Pre-removal Risk Assessment
In accordance with its commitment to the principle of non-refoulement, CIC offers a risk assessment before removing a person from Canada. Under IRPA, people who have been issued a removal order must formally apply to CIC for a PRRA. When a person has already had a refugee protection claim assessed by the Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada, only new evidence, such as evidence that demonstrates a sudden change in country conditions, is considered. While some persons whose applications are approved may benefit from a stay of removal, others whose applications are approved may become “protected persons” and may apply and be granted permanent resident status.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 319 | 339 | 20 | ||
| Spending | 35,205,049 | 35,205,049 | 31,249,238 | 29,926,000 | -5,279,049 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.2.1: Government-assisted Refugees | FTEs | 25 | 17 | -8 |
| Spending | 2,711,326 | 2,548,982 | -162,344 | |
| 2.2.2: Privately Sponsored Refugees | FTEs | 34 | 30 | -4 |
| Spending | 3,793,017 | 3,128,931 | -664,086 | |
| 2.2.3: Visa Office Referred Refugees | FTEs | 2 | 2 | – |
| Spending | 201,868 | 131,564 | -70,304 | |
| 2.2.4: In-Canada Asylum | FTEs | 186 | 172 | -14 |
| Spending | 20,547,835 | 14,655,033 | -5,892,802 | |
| 2.2.5: Pre-removal Risk Assessment | FTEs | 72 | 118 | 46 |
| Spending | 7,951,002 | 9,461,490 | 1,510,488 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 2.2 was lower than planned spending by $5.3 million. This was partly offset by a budget transfer from the Immigration and Refugee Board to cover a deficit (higher actual spending than planned spending) in the Pre-removal Risk Assessment Program. The overall surplus was realigned to other programs.
Performance Results – Program 2.2 and Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canada protects refugees in need of resettlement | Percentage of resettled refugees in the world that Canada resettles (dependent on actions of other countries) | 8–12% | 11.7% |
In 2014, Canada resettled 12,310 refugees. This is approximately 11.7% of the 105,200 refugees admitted for permanent resettlement through UNHCR worldwide. This is also a slight increase in refugee admissions over 2013, when Canada’s total resettlement was 12,186 persons. Canada resettles refugees through the assistance of the UNHCR or private sponsors.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| GARs granted protection through resettlement in Canada | Number of admissions | 6,900–7,200 | 7,573 |
In 2014, GAR admissions were 7,573, which exceeded the target range for this indicator by 373 admissions, or 5.2%. This is a moderate increase from 5,661 admissions in 2013.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSRs are granted protection through resettlement in Canada | Number of admissions | 4,500–6,500 | 4,560 |
| Number of private sponsors that have submitted an application within the past year | >300Footnote xxv | 341 |
In 2014, PSR admissions were 4,560, which was within target range for this indicator. This is a moderate decrease from 6,269 admissions in 2013.
In 2014, 341 sponsorship entities submitted an application for private refugee sponsorship, exceeding the target of 300.Footnote xxvi Strong private sponsor support is an essential component to success in the PSR Program.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visa office-referred refugees are granted protection through resettlement in Canada | Number of admissions | 400–500 | 177 |
| Number of private sponsors that have submitted an application within the past year | 40Footnote xxvii | 42 |
As part of Budget 2012, the Government shifted 1,000 resettlement spaces from the GAR Program to a new iteration of the Visa Office-referred Refugees Program—the Blended Visa Office-Referred (BVOR) Program. Under this new program, financial responsibility for these refugees is shared between the Government and private sponsors.
In 2014, BVOR admissions were 177, which fell short of the target range for this indicator by 223 admissions, or 55.8%. This is the first full fiscal year for the BVOR Program at CIC, and it is expected that admission levels will increase as the program continues to mature. The Department will continue with efforts to encourage uptake of the program.
Applications to participate in the BVOR Program were received from 42 unique private sponsors (sponsorship agreement holders) in 2014, slightly exceeding the target of 40.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decisions made on eligibility of in-Canada refugee claims are rendered within three working days | Percentage of decisions made on eligibility of refugee claims rendered within three working days | ≥ 97% | 98% |
| Protected persons in-Canada and their dependants abroad are admitted as permanent residents | Number of admissions | 11,000–12,000 | 10,973 |
In 2014, decisions on eligibility for in-Canada refugee claims were rendered within three working days in 98% of cases, exceeding the target of 97%. This is a slight increase from 2013, when 97.3% of decisions were rendered within three days.
In 2014, there were 10,973 admissions for refugees and their dependants landing in Canada, which fell short of the target range by 27 admissions, or 0.2%. This is a decrease from 11,863 admissions in 2013.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRRA decisions are made in compliance with IRPA | Percentage of PRRA decisions returned to CIC by the Federal Court for redetermination | < 1% | 0.12% |
| PRRA backlog is reduced | Percentage of PRRA backlog eliminated prior to transfer of the program to the Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada | 90% | 76.4% |
In 2014, PRRA decisions returned to CIC by the Federal Court accounted for only 0.12% of all decisions rendered. This is within the target of below 1%, and represents a slight increase from 2013, when 0.05% of PRRA decisions were returned to CIC by the Federal Court.
Since the creation of CIC’s backlog reduction offices in 2011, the backlog of PRRAs has been reduced from 7,350 to 1,732, or 76.4%. With the delay of the transfer of PRRA to the Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada (date to be determined), CIC continues to receive and process PRRA applications.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results for the Refugee Protection Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Commitment to Victims of Violence in Iraq and Syria (2.2.1–2.2.3)
- In response to the overwhelming humanitarian crisis stemming from the ongoing violence in Syria, in 2013 the Government of Canada began working with the UNHCR and private sponsors to welcome Syrian refugees fleeing the horrors of war. As of March 31, 2015, a total of 1,550 Syrians refugees were resettled in Canada.
- In 2014–2015, the Government of Canada initiated work towards meeting the goal of welcoming an additional 10,000 Syrian and 3,000 Iraqi refugees, and continues to work closely with the UNHCR and its private partners to this end.
Changes to the Designated Countries of Origin List (2.2.4)
- In 2012, new measures came into force for Canada’s asylum system. Changes included the development of a Refugee Appeal Division at the IRB, accelerated timelines and limited access to appeal measures for asylum claimants from Designated Countries of Origin, and changes to human smuggling and biometrics requirements.
- In 2014, asylum claims from Designated Countries of Origin were 75% lower than previous levels. Processing times have been reduced by 16 months compared to previous levels.
- In 2014–2015, five new countries were added to the Designated Countries of Origin list and a monitoring and de-designation framework was implemented.
Strategic Outcome 3: Newcomers and citizens participate in fostering an integrated society
Through the Canadian Multiculturalism Act, IRPA and the Citizenship Act, as well as a broader constitutional and legislative suite that includes the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, the Canadian Human Rights Act, the Official Languages Act and the Employment Equity Act among others, the Government of Canada is committed to facilitating the participation of all Canadians in the social, cultural, economic and civic spheres of Canadian society. Accordingly, the focus of this strategic outcome is on a “two-way street” approach that works with communities and Canadian institutions to assist individuals to become active, connected and productive citizens.
Working with a wide range of social supports, including other levels of government, voluntary sector and community partners, employers, school boards and others, CIC seeks to strengthen social integration by providing newcomers with tools to fully participate in the labour market; promoting social and cultural connections; encouraging active civic participation; and fostering a sense of the rights and responsibilities of Canadian citizenship.
Benefits for Canadians
Canadians enjoy a higher quality of life when citizens and newcomers actively participate in all aspects of society; contribute to a prosperous economy; and have a strong sense of civic pride and attachment.
The following programs and sub-programs support this Strategic Outcome:
Program 3.1: Newcomer Settlement and Integration
In accordance with the Canadian Multiculturalism Act, the Employment Equity Act and IRPA, programming is developed based on policies that support the settlement, resettlement, adaptation and integration of newcomers into Canadian society. All permanent residents are eligible for settlement and integration programs. Programming is delivered by third parties (including provincial and municipal governments, school boards and post-secondary institutions, settlement service organizations and other non-governmental actors, and the private sector) across the country.
Sub-Program 3.1.1: Settlement
Settlement refers to a short period (three to five years) of adaptation by newcomers during which the government provides support and services. Ultimately, the goal of integration is to encourage newcomers to be fully engaged in the economic, social, political and cultural life of Canada. CIC’s Settlement Program assists immigrants and refugees to overcome barriers specific to the newcomer experience, such as a lack of official language skills, limited knowledge of Canada and the recognition of foreign credentials. The program provides language learning services for newcomers, community and employment bridging services, settlement information, and support services that facilitate access to settlement programming. Also, through the Foreign Credentials Referral Office, the program provides information, path-finding and referral services to internationally trained individuals to have their credentials assessed quickly so they can find work in the fields in which they have been trained. Most services are designed and delivered by service provider organizations (SPOs); however, certain services (such as information provision) are delivered directly by CIC in Canada and overseas.
Sub-Sub-Program 3.1.1.1: Language Training
The ability of newcomers to communicate in one of Canada’s official languages has long been recognized as key to both the initial settlement and the longer-term integration of immigrants. Language learning services are intended to help newcomers develop sufficient linguistic communication skills (including literacy) to enable newcomers to function in Canadian society and contribute to the economy. Through the Settlement Program, CIC funds SPOs to deliver various language learning services for newcomers, including language assessment and official language instruction. This program uses transfer payment funding from the Settlement Program.
Sub-Sub-Program 3.1.1.2: Community and Labour Market Integration Services
Newcomers face a variety of barriers to integration, including the need for information and connections to social and economic networks. Settlement information, bridging and other support services including foreign credential referrals, attempt to address these barriers. SPOs are funded to design and deliver bridging services that facilitate newcomers’ connections to the labour market and the wider community. Through CIC offices and SPOs, the program also provides prospective immigrants and newcomers with access to settlement-related information so that they can make informed decisions about immigrating to and settling in Canada. The program also funds SPOs to offer services that improve newcomers’ access to settlement programming; these support services include childminding and transportation. Information on foreign credential recognition is provided in-person and by telephone on behalf of the Foreign Credentials Referral Office by Service Canada and through the CIC Web site to prospective immigrants overseas. This program uses transfer payment funding from the Settlement Program.
Sub-Program 3.1.2: Grant to Quebec
Under the Canada-Quebec Accord, signed in 1991, Canada has devolved settlement and resettlement responsibility to Quebec, with a grant that includes reasonable compensation for costs. The compensation to Quebec covers services for reception services and linguistic, cultural and economic integration services provided that they are equivalent to similar federal services in other parts of the country. An objective of the Accord is, among other things, the preservation of Quebec’s demographic importance within Canada and the integration of immigrants into that province in a manner that respects the distinct identity of Quebec. The Accord provides Quebec with exclusive responsibility for the selection of immigrants destined to the province (except for family reunification and asylum seekers in Canada) as well as the reception and linguistic and cultural integration of these immigrants (including resettlement of refugees). Under the Accord, Canada is responsible for defining overall immigration objectives, national levels, admissibility, selecting family category and asylum seekers in Canada, and citizenship. This program uses transfer payment funding from the grant for the Canada-Quebec Accord on Immigration.
Sub-Program 3.1.3: Immigration Loan
The Immigration Loan Program is a statutory program under IRPA. It ensures that some persons, otherwise unable to pay for the costs of transportation to Canada and medical admissibility exams, have access to a funding source. Assistance loans may also be approved for newcomers in need to cover initial settlement expenses such as rental and utilities deposits. The main target groups for the program are government-assisted refugees and privately-sponsored refugees. These individuals have undergone extreme hardship and most often have few personal resources and are therefore unable to access traditional lending institutions. Canadian visa officers authorize the transportation and admissibility loans and the International Organization for Migration arranges travel and medical exams for refugees and pays these costs. CIC reimburses them and the refugee reimburses CIC. Assistance loans are authorized by in-Canada officers. The interest-bearing loans are repayable in full and payment plans vary by the value of the loan and the recipients’ ability to repay while integrating.
Sub-Program 3.1.4: Resettlement Assistance Program
RAP provides direct financial support and immediate and essential services to RAP clients, including government-assisted refugees, privately-sponsored refugees in blended initiatives under the Visa Office Referred Refugee Program, and persons in refugee-like situations admitted to Canada under a public policy consideration, to meet their resettlement needs. In most cases RAP clients have undergone extreme hardship and may lack the social networks and the financial resources to assist in addressing the needs associated with becoming established in a new country. Income support is administered directly by CIC to RAP clients for up to 12 months if the RAP client’s income is insufficient to meet his or her own needs and the needs of any accompanying dependents. In some cases, RAP clients also receive start-up allowances for expenses related to furniture and other household supplies. Immediate and essential services are supported through contributions to SPOs in all provinces in Canada except Quebec, which delivers similar settlement services through the Canada-Quebec Accord. RAP services include, but are not limited to, port of entry services, assistance with temporary accommodations, assistance opening a bank account, life skills training, orientation sessions, and links to settlement programming and mandatory federal and provincial programs. This program uses transfer payment funding from RAP.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 361 | 315 | -46 | ||
| Spending | 1,002,954,353 | 1,002,954,353 | 1,015,688,908 | 1,010,190,212 | 7,235,859 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1.1: Settlement | FTEs | 302 | 251 | -51 |
| Spending | 621,572,779 | 599,227,991 | -22,344,788 | |
| 3.1.1.1: Language Training Footnote xxviii | FTEs | – | 62 | Not Applicable (N/A) |
| Spending | – | 273,937,022 | N/A | |
| 3.1.1.2: Community and Labour Market Integration Services | FTEs | – | 189 | N/A |
| Spending | – | 325,290,969 | N/A | |
| 3.1.2: Grant to Quebec | FTEs | 4 | – | -4 |
| Spending | 320,457,088 | 340,568,000 | 20,110,912 | |
| 3.1.3: Immigration Loan | FTEs | 13 | 13 | – |
| Spending | 1,450,623 | 2,299,181 | 848,558 | |
| 3.1.4: Resettlement Assistance Program | FTEs | 41 | 51 | 10 |
| Spending | 59,473,863 | 68,095,040 | 8,621,177 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 3.1 was higher than planned spending by $7.2 million, primarily due to higher-than-projected expenditures for the delivery of RAP, as a result of CIC exceeding the lower end of its GAR target range by 10%, as well as an increase in the transfer to Quebec under the Canada-Quebec Accord. Overall spending for Settlement services was lower than projected, primarily due to planned activities not materializing. Total authorities increased by $12.7 million compared with planned spending, primarily due to the increase to the Canada-Quebec Accord transfer.
Performance Results – Program 3.1, Sub-Programs and Sub-Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| NewcomersFootnote xxix contribute to Canada's economic, social and cultural development | Percentage difference of labour market participation of immigrants residing in Canada less than five years in comparison with the Canadian-born | > -3% Footnote xxx | -1.1% |
| Percentage difference of newcomers who performed unpaid volunteer work in comparison with the Canadian-born | > -10% Footnote xxxi | -5.4% | |
| Percentage difference of internationally trained immigrants working at occupational skill levels that match their education levels within the first five years of arrival in Canada in comparison with the Canadian-born educated in Canada | 24.5% | 24.5% |
In 2014–2015, the labour market participation rate for new immigrants was 1.1% less than for the Canadian-born, Footnote xxxii which was within the target rate for this indicator. This difference increased slightly from 2013–2014, when the participation rate was 0.7% less for new immigrants than for the Canadian-born.
Results from the 2013 General Social Survey on Social Identity revealed that the gap between newcomers and the Canadian-born has narrowed with regard to volunteering: 5.4% fewer newcomers reported volunteering than did Canadian-born respondents, in comparison with the results shown in the 2008 General Social Survey on Social Networks which reported a 13.1% difference. The rate of volunteerism is viewed as a measurement of the degree to which newcomers are participating and thus integrating into Canadian Society.
The third indicator is taken from the 2011 National Household Survey. It shows that when examining whether people are working at an occupational skill level that matches their education levels, there is a 24.5 percentage point difference between those who are internationally trained immigrants who landed in Canada within the last five years and the Canadian-born who are educated in Canada. As the National Household Survey is undertaken only every five years, the 2011 data provides the most recent information on this indicator.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clients make informed decisions about life in CanadaFootnote xxxiii | Percentage of clients who are able to make informed decisions about life in Canada | TBD | N/A |
| Clients use official languages to function and participate in Canadian society | Percentage of clients who use official languages to function and participate in Canadian society | TBD | N/A |
| Clients participate in society | Percentage of clients who participate in society | TBD | N/A |
Data for these indicators was to be obtained from a Settlement Client Outcomes Survey. However, due to unforeseen delays the data is not available for 2014–2015. In the absence of the survey results, the number of clients who accessed services is used as proxy, as is Canada’s recent ranking from the Migrant Integration Policy Index.
In 2014–2015, a total of 355,670 clients used at least one settlement service. Of these, 262,911 clients accessed information and orientation services, 107,400 clients received language training, and 41,541 clients used community connection services. The usage of these services by clients helped enable them to make informed decisions, participate in society and use official languages.
The most recent Migrant Integration Policy Index, published by the Migration Policy Group and the Barcelona Centre for International Affairs, ranks Canada sixth overall in terms of its policy and practices in integrating newcomers. Canada was also ranked: first in anti-discrimination policies; fourth in family reunification and education policies; and eighth in terms of access to nationality.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clients learn official language skills for adapting to Canadian society | Annual number of clients who complete a Language Instruction for Newcomers to Canada (LINC) level | 18,000 | 20,220 |
| Annual number of clients at higher LINC levels (5–7) | 16,000 | 18,904 |
In 2014–2015, a total of 20,220 clients completed either a LINC level, or a Canadian language benchmark level.Footnote xxxiv This exceeded the target by 2,220 clients, or 12.3%.
Additionally, 18,904 clients either began or completed a French or English language speaking or listening course at a higher LINC level (5–7), or their Canadian Language Benchmark equivalent (6–8) in 2014–2015. This exceeded the target by 2,904 clients, or 18.2%
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clients gain knowledge of life in Canada | Percentage of clients who are knowledgeable about life in Canada | TBD | N/A |
| Clients acquire skills to function in the Canadian work environment | Percentage of clients who acquire skills to function in the Canadian work environment | TBD | N/A |
Data for these indicators was to be obtained from a Settlement Client Outcome Survey. However, due to unforeseen delays the data is not available for 2014–2015. In the absence of survey results, the number of clients who accessed services is used as proxy. The usage of these services helped to enable clients to gain knowledge of Canada and acquire skills to function in the work environment.
As indicated in 3.1.1, a total of 262,911 clients accessed information and orientation services, which helped clients to increase their knowledge of life in Canada on specific topics, such as official documents (133,079 clients); community connections information (113,481 clients) education (93,311 clients); overview of Canada (70,791 clients); health and related services (72,980 clients); money and finance (70,269 clients); housing (43,488 clients); rights and freedoms (45,866 clients); and Canadian law and justice (46,368 clients).
In 2014–2015, a total of 31,342 clients accessed employment services targeted to their specific needs. For example, 27,243 accessed short-term services, such as networking opportunities and employment counselling, and 4,759 clients used long-term services including developing work skills, seeking jobs, receiving mentoring and preparing for licensure/certification. These services helped enable clients to acquire the skills they need to function in the Canadian work environment.
Lastly, community connection services allowed 24,249 to participate in community based events. In addition, 24,574 clients were matched with members of the community to further facilitate their participation in society.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quebec provides settlement and integration services to newcomers in the province that are comparable to services provided across Canada | Frequency of Comité Mixte meetingsFootnote xxxv | 1 | 1 |
The annual Comité Mixte meeting was held on September 11, 2014, with members of CIC and their counterparts in the Government of Quebec. Officials approved a comparison of national and Quebec services at the meeting, to be updated on an annual basis. Beginning in 2016–2017 this comparison will be available as a performance indicator for the Grant to Quebec.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individuals in need receive and repay immigration loans | Proportion of resettled refugee principal applicants (landed) that receive immigration loans | 100% | 91% |
| Percentage of loan recipients who repay their immigration loans within the original prescribed loan period | TBD | 75% |
In 2014, 91% of principal applicant refugees who landed in Canada received immigration loans. While this fell short of the target, it represents an increase from 2013 when 87.6% of refugees who landed in Canada received immigration loans.
In 2014, 75% of immigration loan recipients repaid their loans within the original prescribed loan period. The target for this indicator will be finalized once the current evaluation of this program is completed. Collectively, including those recipients who exceed the allotted timeframe to pay off their loans, 91% of the value of all loans is paid.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| GARs have access to CIC settlement services | Percentage of GARs outside Quebec who access settlement services within six months after arrival, where CIC manages the delivery of settlement services | ≥ 85% | 89% |
| GARs have their immediate and essential needs met | Percentage of GARs, outside of Quebec, who report that their immediate and essential resettlement needs were met by the RAP services | 80% | N/A |
For the first indicator, in 2014–2015, the uptake of CIC settlement services by GARs within six months of arrival was 89%. This exceeded the target by 4%.
Data for the second indicator was to be obtained from a Settlement Client Outcomes Survey. However, due to unforeseen delays the data for 2014–2015 is not available. In the absence of this data, results from a previous survey were used as a proxy.
Fiscal year 2011–2012 was the last time a survey of RAP clients was conducted. At that time, 92% of survey respondents indicated that RAP services helped them to get what they needed in terms of resettlement services.
CIC continues to fund services that meet the immediate and essential needs of GARs and other RAP clients, and to ensure that the services are timely, accessible and useful. CIC also ensures that RAP clients are made aware of settlement services early in the integration process so that they can benefit from services, such as language training and employment-related services. As shown in the first indicator, 89% of GARs accessed settlement services so it can be assumed that their immediate and essential needs are being met.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on the Newcomer Settlement and Integration Program, other specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Expansion of Pre-Arrival Services to Better Integrate Newcomers Early
- CIC provides a number of settlement orientation services for newcomers prior to their departure for Canada. These services involve some combination of orientation workshops, individual counselling and online resources. Preliminary results suggest that newcomers receiving these pre-arrival orientation services feel better prepared to look for jobs, are more likely to access settlement services once they have arrived and are better able to find employment that aligns with their existing work experience. These services are currently available to only a small portion of eligible newcomers however, as they are offered in a limited number of countries.
- In 2014–2015, CIC expanded pre-arrival services for newcomers coming to Canada. In support of this expansion, two calls for proposals were launched: one call targeted pre-arrival settlement information for new permanent economic residents, and the other targeted information and orientation for refugees coming to Canada. By expanding the availability of pre-arrival settlement services, CIC is improving its ability to integrate newcomers into the social, cultural and economic fabric of Canada.
Help for Newcomers to Find Work Aligned with their Skills and Education (3.1.1.2)
- As a member of the Foreign Qualification Recognition Working Group, CIC works closely with its federal partners, including Employment and Social Development Canada and Health Canada, as well as provincial and territorial governments, on the recognition of the foreign qualification of internationally trained individuals.
- In 2014, a new Action Plan renewed the Pan-Canadian Framework for the Assessment and Recognition of Foreign Qualification. The Action Plan includes the goal of improving the ability of foreign nationals to have their qualifications assessed prior to arriving in Canada, which would improve the ability of new permanent residents to obtain employment in occupations aligned with their education and work experience.
- CIC has developed an Alternative Career Approach, which is designed to assist internationally trained individuals in exploring alternative career pathways that are aligned to their skills and experience, but are not necessarily within a specific regulated profession. In 2014–2015, CIC funded and collaborated to facilitate 26 Alternative Career sessions, which connected approximately 2,445 internationally trained individuals with employers and regulators from a variety of industry sectors. Participation in these sessions resulted in new employment pathways as individuals and employers learned to match skills and experience, beyond credentials, with jobs. Immediate examples of success included an internationally trained doctor who obtained employment in a regional tissue bank and an internationally trained lawyer who found work as a research analyst.
- The Federal Internship for Newcomers program was created in response to a key barrier to labour market participation for newcomers—that of gaining relevant Canadian work experience. It is delivered in partnership with 22 immigrant serving organizations in Ottawa/Gatineau, the Greater Toronto Area and Vancouver/Victoria. In 2014–2015, the program received 1,271 applications. Following a rigorous screening and interviewing process, 156 candidates were placed into pools and 64 newcomers have received work placements to date. All candidates who received internships were paired with mentors and were invited to seven different training opportunities to further support their successful integration into the labour market. Based on annual surveys of hiring managers, employer satisfaction with candidates has been overwhelmingly positive.
Program 3.2: Citizenship for Newcomers and All Canadians
The purpose of the Citizenship Program is to administer citizenship legislation and promote the rights and responsibilities of Canadian citizenship. CIC administers the acquisition of Canadian citizenship by developing, implementing and applying legislation, regulations and policies that protect the integrity of Canadian citizenship and allow eligible applicants to be granted citizenship or be provided with a proof of citizenship. In addition, the program promotes citizenship, to both newcomers and the Canadian-born, through various events, materials and projects. Promotional activities focus on enhancing knowledge of Canada’s history, institutions and values, as well as fostering an understanding of the rights and responsibilities of Canadian citizenship.
Sub-Program 3.2.1: Citizenship Awareness
The Citizenship Awareness Program aims to enhance the meaning of Canadian citizenship for both newcomers and the Canadian-born and to increase a sense of belonging to Canada. Through knowledge of Canada’s history, institutions and values, as well as the rights and responsibilities associated with citizenship, newcomers and the Canadian-born are better equipped for active citizenship and can contribute to the development of an integrated society. The program undertakes various knowledge-building and promotional activities such as: citizenship ceremonies; citizenship reaffirmation ceremonies; Citizenship Week; Citation for Citizenship award; and, the distribution of citizenship educational publications (e.g. Discover Canada citizenship study guide, the Welcome to Canada guide). This program uses transfer payment funding from the grant for the Institute for Canadian Citizenship.
Sub-Program 3.2.2: Citizenship Acquisition, Confirmation and Revocation
Citizenship processing activities include interpreting and administering the Citizenship Act and Regulations, managing the naturalization process (whereby non-citizens become citizens), issuing proof of citizenship to those who are citizens by birth or by naturalization, and maintaining these records. The processing of Canadian citizenship helps newcomers fully participate in Canadian life and contributes to their successful integration into Canadian society. A person’s citizenship is revoked if it is found that they have obtained their citizenship fraudulently, by misrepresentation or by knowingly concealing information during the course of their immigration or citizenship application process. CIC reviews files where there are allegations of fraud and collects and analyzes information to determine if a recommendation to initiate revocation proceedings should be made to the Minister.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 999 | 1,029 | 30 | ||
| Spending | 109,789,678 | 109,789,678 | 83,594,979 | 82,983,275 | -26,806,403 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.2.1: Citizenship Awareness | FTEs | 53 | 20 | -33 |
| Spending | 6,083,159 | 2,805,190 | -3,277,969 | |
| 3.2.2: Citizenship Acquisition, Confirmation and Revocation | FTEs | 946 | 1,009 | 63 |
| Spending | 103,706,519 | 80,178,085 | -23,528,434 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 3.2 was lower than planned spending by $26.8 million as the implementation of the Strengthening Canadian Citizenship Act resulted in some operational efficiencies. As some planning assumptions also differed from the actual resource usage, unused authorities were subsequently adjusted to fund other programs.
Performance Results – Program 3.2 and Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canadian citizenship is a valued status | Take-up rates of citizenship among eligible newcomers | ≥ 75% | 85.6% |
| Percentage of applicants referred to a citizenship hearing to protect the integrity of citizenship | 5-10% Footnote xxxvi | 5% |
The 2011 National Household Survey reported that 85.6% of eligible newcomers took up citizenship, exceeding the 75% target. New figures for this indicator will be available following completion of the 2016 National Household Survey.
In 2014, 5% of citizenship applicants were referred to a hearing as part of ongoing program integrity oversight of the Citizenship Program. This is in line with historical targets.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citizenship responsibilities and privileges are promoted to newcomers and established Canadians | Percentage of enhancedFootnote xxxvii citizenship ceremonies held in partnership with community or external organizations | ≥ 15% | 13% |
| Percentage of applicants who write and pass the written citizenship knowledge test | 80-85% Footnote xxvii | 90% | |
| Number of printed Discover Canada guides distributed | ≥ 250,000 | 92,688 |
In 2014–2015, 13% of citizenship ceremonies were enhanced in partnership with community or external organizations. By working with community partners to enhance ceremonies, CIC strives to make citizenship ceremonies more accessible to the public, encourages the taking-up of citizenship among eligible newcomers, and provides an opportunity for community members to contribute to and participate in an important nation-building experience. While this is slightly less than the target of 15%, it should be noted that the Department delivered 85 more enhanced citizenship ceremonies in 2014–2015 than the previous year. Two factors that contributed to falling short of this target were the increased focus on processing targets to eliminate application backlogs and the implementation of new citizenship legislation. Both of these priorities led to the delivery of 1,100 more citizenship ceremonies in 2014–2015 than in 2013–2014, which accounted for the drop in percentage of enhanced ceremonies.
In 2014, over 90% of applicants passed the written citizenship knowledge test. Discover Canada, the official citizenship study guide used by newcomers to prepare for the citizenship test, had lower distribution levels in 2014–2015, with 92,688 print copies distributed. However, the guide was downloaded 583,219 times in 2014–2015. While distribution of Discover Canada continued in print format in 2014–2015, efforts are underway in the Department to encourage the use of the downloaded electronic version of the guide.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applications for proofs and grants are processed | Total number of decisions for grants | 144,747–160,531Footnote xxxviii | 288,625 |
| Total number of decisions for proofs | ≥ 38,000 | 58,010 |
In 2014–2015, a total of 288,625 citizenship grant decisions, which provide citizenship for newcomers, were rendered, exceeding the target by 128,094, or 80%. This also represents a 57.4% increase over grant decisions in 2013–2014.
Decisions regarding proof of citizenship, which confirms status for existing citizens, reached 58,010 in 2014–2015. This exceeded the target by 20,010 decisions, or 52.6%, and represented a 12% increase over 2013–2014 figures.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on the Citizenship Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Reduction of Backlogs and Improvement of Service Times for Citizenship Applications
- On June 19, 2014, the Strengthening Canadian Citizenship Act received Royal Assent and became law. Some changes came into effect immediately, including the fast-tracking of citizenship for members of the Canadian Armed Forces, improved clarity on the limit on citizenship for those born abroad, and a shift in decision-making authority for discretionary citizenship grants to the Minister of Citizenship and Immigration.
- Additional changes were brought into force on August 1, 2014, including a new decision model. Under the new model, decision making changed from a three-step process to a single-step process in most cases, thereby eliminating review duplication and increasing efficiency. CIC officers now decide all aspects of grant cases except where they believe that the applicant does not meet the residence requirement. Such cases are referred to citizenship judges on a transitional basis for decision.
- The new process is helping to improve the timeliness of application processing and improve client service. In 2014–2015, a total of 288,625 citizenship grant decisions were taken, almost 80% higher than the target. As of March 31, 2015, the backlog of applications older than 12 months was reduced by 58%, and it is expected that it will be entirely eliminated in 2016.
Strengthening the Integrity of the Citizenship Program
- While the Strengthening Canadian Citizenship Act improved the overall efficiency of citizenship processing, it also included amendments to the Citizenship Act to extend citizenship to additional “lost Canadians” born before 1947, when the first Canadian Citizenship Act came into effect. Other provisions were designed to strengthen attachment to Canada and improve the integrity of the Citizenship Program, including:
- new requirements to have been physically present in Canada for four of the last six years, to have filed Canadian income taxes and to intend to reside in Canada;
- the expansion of age ranges for those required to demonstrate official language proficiency, and be tested on knowledge of Canadian history, values, citizenship responsibilities;Footnote xxxix and
- strengthened offences and penalties for fraud, controls on citizenship consultants and prohibitions for foreign criminality.
- In 2014–2015, the Government of Canada began the system, program and regulatory changes to finalize the implementation of these remaining Strengthening Canadian Citizenship Act provisions for their coming into force in 2015.
Program 3.3: Multiculturalism for Newcomers and All Canadians
The Multiculturalism Program is the principal means of carrying out the Minister’s responsibilities under the Canadian Multiculturalism Act for promoting the full and equitable participation of individuals and communities across Canada. Grants and contributions to not-for-profit organizations, the private sector, provincial and municipal governments, non-federal public institutions, and individuals seek to advance overarching program objectives. These objectives are to: build an integrated, socially cohesive society (through increasing intercultural and interfaith understanding, civic memory and pride, respect for core democratic values, and equality of opportunity to full participation in society and the economy); improve the responsiveness of institutions to the needs of a diverse population; and actively engage in discussions on multiculturalism, integration and diversity at the international level. Direct public outreach and promotional activities by the program primarily target young people. Further, the program assists federal partners to meet their obligations under the Act through its annual report to Parliament on its operation and the federal Multiculturalism Champions Network. It also engages with non-federal public institutions seeking to respond to diversity through the Federal-Provincial-Territorial Officials Responsible for Multiculturalism Issues. The program is the locus for Canada’s participation in international agreements and institutions with respect to anti-Semitism and Holocaust remembrance (through the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance).
Sub-Program 3.3.1: Multiculturalism Awareness
Multiculturalism awareness comprises a suite of policy, operational, and public engagement and promotional activities. In addition to developing policies that shape Canada's stance on diversity issues, project funding (grants and contributions) is disbursed to recipients (e.g., not-for-profit organizations, the private sector and individuals) seeking to address the program's overarching objective of building an integrated, socially cohesive society through promotion of intercultural/interfaith understanding, civic memory and pride, respect for core democratic values, and equal opportunity to full participation in society and the economy. Multiculturalism awareness also directs public outreach and promotional activities, primarily targeting young people, designed to engage newcomers and Canadians on multiculturalism, racism and discrimination issues. This program uses transfer payment funding from the grant in support of the Multiculturalism Program and contribution in support of the Multiculturalism Program.
Sub-Program 3.3.2: Federal and Public Institutional Multiculturalism Support
Federal and public institutional multiculturalism support efforts are directed towards improving the responsiveness of institutions to the needs of a diverse population. To assist federal institutions in meeting their obligations under the Canadian Multiculturalism Act, the program leads a Multiculturalism Champions Network which serves as a forum for discussing shared challenges, best practices, lessons learned and increasing awareness of tools available to institutions to help implement the Act. CIC develops the annual report on the operation of the Canadian Multiculturalism Act for tabling in Parliament, which fulfils the Minister’s obligations under the Act, and serves as an informative tool for institutions seeking best practices toward the implementation of the Act. Dialogue with provinces and related non-financial support is also provided through the Secretariat of the Network of Federal-Provincial-Territorial Network of Officials Responsible for Multiculturalism Issues. In addition, through Inter-Action, the program manages and disburses project funding (grants and contributions) to regional and municipal governments and non-federal public institutions. Lastly, the program fosters policy relationships and portfolio management of the Canadian Race Relations Foundation and the Global Centre for Pluralism. This program uses transfer payment funding from the grant in support of the Multiculturalism Program and contribution in support of the Multiculturalism Program.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 42 | 28 | -14 | ||
| Spending | 13,208,032 | 13,208,032 | 10,976,878 | 6,771,604 | -6,436,428 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3.1: Multiculturalism Awareness | FTEs | 38 | 25 | -13 |
| Spending | 12,705,957 | 6,112,655 | -6,593,302 | |
| 3.3.2: Federal and Public Institutional Multiculturalism Support | FTEs | 4 | 3 | -1 |
| Spending | 502,075 | 658,949 | 156,874 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 3.3 was lower than planned spending by $6.4 million, primarily due to lower than projected expenses in grants and contributions for the Inter-Action project stream.
Performance Results – Program 3.3 and Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Program participants are given information or tools to support an integrated society | Annual percentage of program respondents who report that they are more enabled to support an integrated society | ≥ 70% | N/AFootnote * |
Overall, the Multiculturalism Program achieved its expected results for 2014–2015.
Through activities funded or initiated by the program, participants (the Canadian public and targeted federal and public institutions) were given information and tools necessary to support an integrated society, were made aware of issues related to an integrated society, and were supported in fulfilling obligations to report on the operation of the Canadian Multiculturalism Act.
The Inter-Action Program provided initiatives that fostered intercultural/interfaith understanding, civic memory and pride, respect for core democratic values and a more integrated, socially cohesive society. Public outreach and promotional activities via the Internet helped ensure that program participants were given information and tools necessary to support an integrated society and made aware of issues related to an integrated, socially-cohesive society.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Program participants report an increased respect for Canada’s core democratic system and values | Annual percentage of program participants reporting increased respect for core democratic values | ≥ 70% | N/A |
| Program participants report a better understanding of a religious, ethnic, or cultural group that is different from their own | Annual percentage of program participants reporting increased intercultural/interfaith understanding | ≥ 70% | N/A |
In 2014–2015, CIC provided $1,891,008 in grant payments and $2,251,966 in contribution payments to support 194 events and various multiculturalism projects that fostered intercultural/interfaith understanding, civic memory and pride, respect for core democratic values and a more integrated, socially-cohesive society.
Black History Month, Asian Heritage Month and Komagata Maru campaigns resulted in more than 65,000 page views, over 46,000 views of videos and 17,339 downloads of posters and narratives. The Canada’s PanAm Hopefuls, Paul Yuzyk Awards for Multiculturalism , the Community Historical Recognition Program videos had in excess of 3,500 views.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal institutions report on their responsiveness to a diverse society | Percentage of respondents (federal institutions) who report on the operation of the Canadian Multiculturalism Act | ≥ 75% | 92% |
| Targeted institutions are supported | Participation rate of targeted institutions | ≥ 85% | 53% |
| Number of support or outreach activities provided to targeted institutions | ≥ 5 | 5 |
The percentage of federal institutions contributing to the Annual Report on the Multiculturalism Act exceeded the 75% target by 17% (92% or 130 of 142 federal institutions).
The Multiculturalism Program’s policy objectives are further ingrained into daily federal activities as more federal institutions participate in reporting activities. Furthermore, as the quality and quantity of initiatives showcased in the Report increase, so does the overall value of the report in highlighting best practices and a diversity of approaches.
Going forward, the program will review and assess current approaches and consider common themes to enhance delivery of multiculturalism policy objectives.
In 2014–2015, only 53% of targeted federal institutions participated in the Federal-Provincial-Territorial Network of Officials Responsible for Multiculturalism Issues. This fell short of the 85% target, and represents a 16% decrease in participation from last year.
The program achieved its objective of providing five outreach activities to support federal institutions with respect to their obligations under the Canadian Multiculturalism Act.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on the Multiculturalism Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Support for Multiculturalism in Canada
- Through Inter-Action, CIC’s Multiculturalism Grants and Contribution Program, the Department promotes and supports multiculturalism by funding community-based events that foster understanding across faiths and cultures, civic pride, and respect for democratic values. Inter-Action also provides funding for long-term, multi-year community building projects that foster a more integrated, socially cohesive society. In 2014–2015, CIC provided $1,891,008 in grant payments and $2,251,966 in contribution payments to support 194 events and various multiculturalism projects. Notable highlights included:
- In May 2014, the Vancouver Holocaust Centre Society for Education and Remembrance launched a survivor testimony project, with CIC funding of up to $300,380.
- In June 2014, funding up to $89,500 was announced for the Sikh Heritage Museum of Canada to create the “Lions of the Sea” exhibit, bringing the story of the Komagata Maru to life and allowing Canadians across the country to learn about its historical significance.
- In July 2014, the Canadian Race Relations Foundation launched a project, “Exploring Canadian Values through Culture, Faith and Identity”, with CIC funding of up to $2,161,396.
- In January 2015, funding of $1,459,728 was announced for the Canada Ukraine Foundation to fund the Holodomor National Awareness Tour to raise awareness among Canadians about the “terror-famine” in Ukraine, which resulted in the deaths of millions of people in the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1932–1933.
- In February 2015, Facing History and Ourselves’ Building Bridges launched its “Diverse Canadian Identities, Shared Civic Values” project with $360,280 in funding from CIC.
- On October 24, 2014, the winner of the 2014 Paul Yuzyk Award for Multiculturalism was announced. Tomas Avendaño was recognized in the Lifetime Achievement category for his efforts to establish the Multicultural Helping House Society and act as a bridge between Vancouver’s Filipino community and other cultural communities in the city. CIC supports the annual Paul Yuzyk award and in 2014–2015 worked to expand the award so that in 2015 it will include two new award categories, targeting youth and multiculturalism organizations.
- The Multiculturalism Program’s direct public outreach and promotional activities via the Internet (i.e., Black History Month, Asian Heritage Month, Remembering the Komagata Maru and Canada’s Pan Am Games Hopefuls) included historic overviews, the Canadian Black History Virtual Museum, a variety of videos, posters, games and quizzes. The Black History Month campaign received the highest number of visits relative to other campaigns in 2014–2015, and the posters and videos were the downloaded elements.
Strategic Outcome 4: Managed migration that promotes Canadian interests and protects the health, safety and security of Canadians
Canada welcomes thousands of permanent residents, temporary foreign workers, international students and visitors each year. CIC manages the movement of people within the context of a more responsive immigration system that benefits Canada’s economic, social and cultural development while at the same time protecting the health, safety and security of all Canadians. To manage health issues related to immigration, CIC develops and implements risk mitigation strategies in cooperation with the Public Health Agency of Canada, provinces and territories, and partner countries. Any residual public health risks regarding the transmission of infectious diseases are mitigated through medical surveillance of newly arrived permanent and temporary residents as required. To protect Canadians—and to ensure that the benefits of a more responsive immigration system are not undermined—CIC works with the Canada Border Services Agency, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police and the Canadian Security Intelligence Service to conduct appropriate background screening of both immigrants and temporary residents and to identify applicants who could pose a security risk to the country. CIC shares information with these organizations, fostering timely and effective delivery of its programs.
Internationally, migration and humanitarian issues continue to gain the attention of governments, bilateral and multilateral forums, non-governmental organizations, and academic and other research institutes. CIC plays an important role in framing and advancing international dialogues on migration and integration policy, refugee protection and governance. These dialogues explore the links between migration policy and development assistance, health, the environment, trade, and the movement of human capital. CIC works to develop and implement a strategic agenda on global migration and refugee protection, and to advance Canada’s policy and program priorities.
Benefits for Canadians
Growing international migration has increased the possibility of Canadians being exposed to disease outbreaks and infectious diseases. CIC and its partners in health management work to reduce the impact of identified risks on the Canadian population.
Policies and programs that affect the international movement of people—across Canada’s borders and outside them—have a direct bearing on the safety and security of Canada and Canadians at large, whether they are at home or travelling and conducting trade abroad. Strengthening Canada’s refugee programs and demonstrating continued leadership in refugee protection, human rights and the promotion of cultural diversity through active participation in various international and regional forums and partnerships support Canada’s broader contribution to a safe and secure world. Finally, coordinated and responsible sharing of information supports a fast response to threats to the safety and security of Canadians.
The following programs and sub-programs support this Strategic Outcome:
Program 4.1: Health Protection
This program aims to provide effective immigration health services to manage the health aspect of migrant access and settlement to Canada, and facilitate the arrival of resettled refugees to Canada and their integration while contributing to the protection of the health and safety of all Canadians and contributing to the maintenance of sustainable Canadian health and social services.
The program aims to evaluate health risks related to immigration and coordinate with international and Canadian health partners to develop risk management strategies and processes to assess the health of applicants wishing to immigrate to Canada. The strategies, processes and interventions are intended to reduce the impact of the risks identified on the health of Canadians and on Canada’s health and social services.
Sub-Program 4.1.1: Health Screening
This program aims to manage the health risks related to permanent and temporary residence according to the three grounds for inadmissibility under IRPA, which are (1) danger to public health, (2) danger to public safety and (3) excessive demand on health or social services.
The immigration medical examination (IME) is a tool used to screen for infectious diseases of public health significance in all applicants for permanent residence and certain applicants for temporary residence. The IME includes x-rays and lab tests that identify applicants who could pose health threats to Canadians or to the Canadian health and social systems. Those who are in good health are cleared for entry into Canada; those who are found with infectious disease are referred for treatment, where relevant, before admittance to Canada; those who are a danger to public health or public safety or are deemed to cause excessive demand on Canada’s health and social system are deemed inadmissible.
Sub-Program 4.1.2: Medical Surveillance Notification
Section 38(1) of IRPA sets danger to public to health as one key condition of inadmissibility to Canada. Applicants for temporary or permanent residence in Canada whose immigration medical assessments demonstrate that they may pose risks to public health require further health assessment and monitoring following their landing in Canada in order to ensure that they do not represent a danger to public health.
The Medical Surveillance Notification Program informs provincial and territorial public health authorities of applicants who require medical surveillance in order to ensure that the terms and conditions of landing are met.
Sub-Program 4.1.3: Interim Federal Health
The Interim Federal Health (IFH) Program provides temporary coverage of health-care costs. The target population includes resettled refugees, protected persons, refugee claimants, and persons detained under IRPA. In general, eligibility and level of coverage under the IFH Program are determined by the beneficiary’s status in Canada. The program offers five types of coverage: Expanded Health Coverage, Health-Care Coverage, Public Health or Public Safety Health-Care Coverage, coverage for the Immigration Medical Examination and coverage for detainees. Most beneficiaries receive Health-Care Coverage, which is a level of coverage similar to the coverage Canadians receive through their provincial/territorial health insurance plans. The program helps protect public health and public safety and supports the successful settlement of resettled refugees receiving government support. IFH Program beneficiaries with valid coverage access health services through registered health-care providers, who are reimbursed directly by the IFH claims administrator for covered services.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 69 | 53 | -16 | ||
| Spending | 58,356,894 | 58,356,894 | 57,867,068 | 31,042,845 | -27,314,049 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.1.1: Health Screening | FTEs | 39 | 33 | -6 |
| Spending | 4,281,252 | 5,409,299 | 1,128,047 | |
| 4.1.2: Medical Surveillance Notification | FTEs | 7 | 10 | 3 |
| Spending | 816,376 | 768,472 | -47,904 | |
| 4.1.3: Interim Federal Health | FTEs | 23 | 10 | -13 |
| Spending | 53,259,266 | 24,865,074 | -28,394,192 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 4.1 was lower than planned spending by $27.3 million. This is primarily due to lower-than-forecasted expenditures for the IFH Program, resulting from modifications to the program.
Performance Results – Program 4.1 and Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applicants for permanent or temporary residence who pose a risk to public health and/or public safety and/or may be reasonably expected to cause excessive demand on the Canadian social and/or health-care systems are identified | Percentage of applications refused for health reasons (public health, public safety or excessive demand) by visa officers over the number of medically inadmissible cases identified in the immigration medical assessment (IMA) Footnote xl process | 100% | 76.4% |
| Eligible clients receive coverage for health services under the IFH Program | Percentage of eligible clients who receive health coverage under the IFH Program | 100% | 99.7% |
In 2014, 76.4% of applications for permanent residence that were identified as inadmissible as part of the IMA were refused by visa officers for health reasons. This is below the target of 100% for this indicator, and is a slight decrease from 2013, when 80.2% of applications deemed inadmissible by the IMA were refused.
There are a number of reasons why medically inadmissible applicants may not be refused by visa officers. For example, some applicants satisfy the visa officer of their ability and intent to mitigate possible excessive demand that their medical conditions could pose on Canadian health and social services, and are subsequently not refused. In other cases, medically inadmissible applicants are accepted by visa officers on humanitarian and compassionate grounds. As well, others may withdraw their application when notified of medical inadmissibility.
From October 1, 2013 to September 30, 2014, of 11,458 eligible refugee claimants, 99.7% received an IFH Program eligibility certificate. Program officials reviewed all 35 cases where IFH eligibility certificates were not issued for eligible claimants and determined that these cases were due to incorrect coding or situations where clients had access to other health-care coverage, such as a provincial plan. These results are slightly higher than the previous year, when 99.6% of eligible claimants were determined to have received an eligibility certificate.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applicants for permanent and temporary residence who pose public health risks or public safety risks or are likely to create excessive demand on the Canadian health-care or social services systems are deemed inadmissible | Percentage of applicants identified as medically inadmissible based on health grounds (public health, public safety, or excessive demand) | 0.1% to 0.2% | 0.2% |
| Percentage of new cases of active tuberculosis found during an IMA over total number of IMAs | < 0.08% | 0.09% | |
| Percentage of new cases of inactive tuberculosis found during an IMA over total number of IMAs | 1.88%Footnote xli | 1.7% |
In 2014, of the 552,416 applicants who received an IMA, 1,126 were found to be inadmissible on medical grounds. This rate of inadmissibility is within the target rate and in line with results from 2013, when 0.21% of applicants were found to be inadmissible.
At the time of their immigration medical examination, 470 applicants were found to have active tuberculosis; all but nine of these were treated and their tuberculosis rendered inactive, with the remaining cases rendered inadmissible to Canada. An additional 9,426 cases of inactive pulmonary tuberculosis were identified for further medical surveillance.
The immigration medical examination/IMA process helps to identify applicants who may pose a danger to public health or public safety or may cause excessive demand on Canada’s health and social services system.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provincial and territorial public health authorities are notified, for the purposes of medical surveillance, of migrants who pose public health risks | Percentage of migrants identified as having inactive tuberculosis and/or adequately treated syphilis who landed in Canada and were reported to provincial or territorial health authorities | 100% | 99.2% |
| Percentage of identified cases of human immunodeficiency virus who landed in Canada and were reported to provincial or territorial health authorities (except for Nova Scotia and Nunavut - which elected to not receive the information) | 100% | 95.8% | |
| Percentage of clients who comply with the condition of provincial or territorial medical surveillance | 100% | 80.5% |
In 2014, of the 5,045 cases where CIC was informed of the landing and destination of a client with inactive tuberculosis or actively treated syphilis, the province was notified by CIC 99.2% of the time. In the remainder of cases (41), the address was missing from the client information received and the province could not be notified. This result, while short of the target of full notification, represents an improvement from 91.6% notification in 2013. It should be noted that, in May 2014, the requirement for surveillance of adequately treated syphilis was removed.
Similarly, in 2014, of the 475 clients identified with human immunodeficiency virus, 455, or 95.8%, were reported to provincial authorities. The remaining 20 cases where provincial health authorities were not informed are the result of a lack of residential address documentation. This result is a slight improvement over 2013, when 95.5% of clients with human immunodeficiency virus were reported to provincial health authorities.
Of the 5,796 individuals in need of medical surveillance who entered Canada between September 1, 2013 and August 31, 2014, CIC received confirmation of medical surveillance compliance from provinces and territories for 4,668 individuals. The remaining 1,128 individuals still have a status of non-compliance, which could be due to public health authorities being unable to locate the individuals, the lack of residential address in Canada, a failure by individuals to have self-reported or a delay in receiving a compliance report from the public health authority.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eligible clients receive health services that reduce risks to the health and safety of Canadians | Percentage of refugee claimants who received an immigration medical examination (IME)Footnote xlii | 100% | 96.3% |
| Percentage of IFH Program beneficiaries by coverage type who obtain health services that reduce risk to public health and public safety | Public Health or Public Safety Health-Care Coverage: 100% Expanded Health-Care Coverage: 45%Footnote xliii Health-Care Coverage: 75% Footnote xxxviii |
Public Health or Public Safety Health-Care Coverage: 100% Expanded Health-Care Coverage: 45.8% Health-Care Coverage: 75.3% |
In 2014, 96.3% of all eligible refugee claimants received an IME. Of the 3.7% who did not receive an IME, 2% abandoned or withdrew their claim for refugee status, and it is believed that the remaining 1.7% have left the country. While this result falls short of the 100% target, it represents an improvement over 2013, when 93% of eligible refugee claimants received an IME.
All eligible beneficiaries receive, at a minimum, coverage to treat diseases that pose a risk to public health or to treat conditions of public safety concern. From October 1, 2013 to September 30, 2014, 100% of the 3,625 beneficiaries eligible for Public Health and Public Safety Coverage, 45.8% of the 7,170 beneficiaries eligible for Expanded Health-Care Coverage, and 75.3% of the 18,446 beneficiaries eligible for Health-Care Coverage received services that reduced the risk to public health and public safety. The results reflect the projected targets and suggest no change or increased risk to public health or public safety.
CIC implemented changes to the IFHP – archived to comply with the July 4, 2014 Federal Court ruling. CIC will report on data and results going forward.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on the Health Protection Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Protection Against the Spread of Ebola
- In response to the Ebola outbreak in West Africa, CIC worked with federal and international partners to gather and share information on health risks, establish procedures and develop measures to protect the health and safety of Canadians. In October 2014, CIC temporarily stopped processing visa applications from foreign nationals who had been physically present in a country designated by the World Health Organization as having widespread transmission of the Ebola virus. However, during the same period of time, CIC continued to facilitate the arrival of resettled refugees from the Ebola-affected countries, while at the same time working with the Public Health Agency of Canada as well as provinces and territories to mitigate any risks that this might pose to the health of Canadians.
Improved Health Knowledge to Improve Programming
- In 2014–2015, CIC developed the Health Knowledge Framework to identify research priorities on migration health. The Department also engaged with public sector stakeholders and research partners to facilitate migrant health research. Further, CIC undertook analysis of various public health issues, such as immunization and pre-departure services. The research and analysis results will help inform the Health Protection Program as it faces a changing migration context.
Program 4.2: Migration Control and Security Management
This program aims to ensure the managed migration of foreign nationals and newcomers to Canada. As such, in accordance with IRPA and accompanying Regulations, CIC facilitates the travel of bona fide permanent residents, visitors, students and temporary workers while protecting the health, safety and security of Canadians by effectively managing migration access and controlling entry. This is accomplished through a variety of policy and operational measures, including visa policy interventions, anti-fraud measures, eligibility and admissibility criteria, negotiations of bilateral and multilateral information-sharing agreements and treaties, security updates to travel and immigration status documents, as well as revisions to identity management practices. Strategic partnership engagements with security and public safety-related departments are another essential component of this program.
Sub-Program 4.2.1: Permanent Resident Status Documents
In accordance with IRPA, CIC must process and issue to all permanent residents a secure status document for travel purposes. The permanent resident card serves as proof of permanent resident status in Canada and may be easily verified by commercial carriers and border officers. While the permanent resident card also meets international travel document standards, it is not a travel document. The Permanent Resident Status Documents Program makes it difficult to access Canadian territory fraudulently. The program establishes a mechanism to verify compliance with the residency requirement, provides permanent residents with a status document confirming their right to live, work and study in Canada, provides permanent residents with access to government services, and enables them to be recognized and processed quickly at the border, thereby enhancing border security. While not mandatory within Canada, the permanent resident card is required for all permanent residents as proof of their status when seeking to re-enter Canada on a commercial carrier. It contains security features to reduce the risk of fraud. Permanent residents who obtained their status under previous immigration legislation or those who wish to replace an expired, lost or stolen permanent resident card may obtain one upon application. Limited use travel documents are also issued by visa offices overseas to qualified permanent residents outside of Canada who do not have a valid permanent resident card, to facilitate return travel to Canada.
Sub-Program 4.2.2: Visitors Status
Under IRPA, all visitors to Canada require a temporary resident visa (TRV), except citizens of countries for which an exemption has been granted under the Regulations. A foreign national who wishes to come to Canada, and from a country for which a TRV is imposed, needs to apply at a Canadian Embassy abroad prior to travelling to Canada. The Visitors Status Program aims to ensure that each applicant is screened to determine whether they meet the entry requirements, including that they will abide by the terms and conditions of entry, and are not inadmissible to Canada. The screening of travellers requiring a TRV is carried out by CIC in cooperation with its federal security partners. Once individuals arrive in Canada, their status needs to be maintained, regardless of whether they needed a visa to enter the country.
The TRV is designed to prevent individuals who would abuse temporary entry from coming to Canada, and to facilitate the entry to Canada of genuine temporary residents. The requirement to obtain a TRV limits the number of immigration violations (e.g., refugee claims, no proper travel documents, not leaving Canada once the period of stay has expired, working illegally, etc.) and protects the health, safety and security of Canadians.
Sub-Program 4.2.3: Temporary Resident Permits
Persons seeking temporary residence in Canada who do not meet IRPA requirements are subject to refusal of a TRV abroad, denial of entry at ports of entry, or refusal of extensions inland. In some cases, however, there may be compelling reasons for an officer to issue a temporary resident permit (TRP) to allow a person who is otherwise inadmissible to enter or remain in Canada. Under the TRP Program, designated officers may issue these permits abroad, at a port of entry or in Canada, depending on the circumstances. Grounds for issuance of a TRP include, among others, inadmissibility due to medical reasons, criminality, reasons of security, infringement of human or international rights, or organized crime. TRPs are issued for a limited, often short, period of time and are subject to cancellation at any time. TRPs provide officers with the flexibility to address exceptional circumstances and, in so doing, maintain the integrity of Canada’s immigration program and protect the health, safety and security of Canadians.
Sub-Program 4.2.4: Fraud Prevention and Program Integrity Protection
Under this program, operational policy is developed and procedures are designed in order to maintain confidence in Canada’s citizenship and immigration system and to protect the safety and security of Canada while effectively delivering on economic and social objectives by selecting only those applicants that meet program requirements. Program integrity is achieved through case processing procedures that identify and refuse status to applicants who fail to meet eligibility and/or admissibility requirements, including fraud, and through referral of these cases for enforcement action where appropriate.
Identity management contributes to strengthened program integrity by ensuring that services are delivered to the correct individual, developing efficiencies across multiple business lines, and allowing CIC to streamline interactions with repeat clientele. Identity management involves the application of procedures to establish, fix and manage client identity across CIC operations and between key partners based on personal identifiers, identity documents and biometrics identifiers.
Sub-Program 4.2.5: Global Assistance for Irregular Migrants
The Global Assistance for Irregular Migrants (GAIM) Program provides transfer payments in the form of contributions to trusted international, intergovernmental and non-governmental organizations (such as the International Organization for Migration) to fund activities and support for intercepted irregular migrants, such as meeting basic needs, providing medical care, identifying migrants to be referred to the appropriate authorities for refugee status determination, and facilitating voluntary return and reintegration in the country of origin if determined not to be in need of protection. The GAIM Program responds to the need for Canada to have a permanent program to manage the consequences of disrupting human-smuggling activities believed to be destined for Canada. It is triggered when the Prime Minister’s Special Advisor on Human Smuggling identifies an event involving these activities and CIC agrees to implement the program. It also addresses the need for complementary activities that demonstrate Canada’s commitment to transit states and international partners that would otherwise be encumbered with the costs of unintended consequences arising from smuggling-prevention activities. Offers of capacity building and support in managing the consequences of successful prevention of human smuggling have been critical in securing bilateral cooperation from transit states. The GAIM Program reflects CIC’s role in Canada’s whole-of-government strategy to combat human-smuggling activities. The program uses transfer payment funding from the contribution in support of the GAIM Program.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 702 | 819 | 117 | ||
| Spending | 84,966,649 | 84,966,649 | 115,658,136 | 104,056,335 | 19,089,686 |
| Sub-Programs | Resource | Planned 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.2.1: Permanent Resident Status Documents | FTEs | 159 | 274 | 115 |
| Spending | 17,591,861 | 21,670,918 | 4,079,057 | |
| 4.2.2: Visitors Status | FTEs | 298 | 270 | -28 |
| Spending | 37,408,204 | 32,967,020 | -4,441,184 | |
| 4.2.3: Temporary Resident Permits | FTEs | 17 | 17 | – |
| Spending | 1,878,477 | 1,838,001 | -40,476 | |
| 4.2.4: Fraud Prevention and Program Integrity Protection | FTEs | 226 | 257 | 31 |
| Spending | 24,940,882 | 45,226,376 | 20,285,494 | |
| 4.2.5: Global Assistance for Irregular Migrants | FTEs | 1 | 1 | – |
| Spending | 3,147,226 | 2,354,020 | -793,206 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 4.2 was higher than planned spending by $19.1 million, primarily due to increased spending for fraud prevention, program integrity and biometrics as the management of the safety and security of Canadians remained among the top priorities for the Government. Specifically, this deficit (higher actual spending than planned spending) was the result of spending on various initiatives such as Electronic Travel Authorization, Entry/Exit (a Beyond the Border initiative) and GAIM. There was an increase in spending as a result of the application of risk indicator criteria in processing citizenship, temporary resident, and permanent resident applications. Actual spending also increased for the Permanent Resident Status Documents Program due to an increase in permanent resident status documents issued. Actual spending for the Visitor Status Program was lower than planned spending primarily due to lower referrals to partners for security screening. Surpluses from some other programs were used to fund the overall shortage in Program 4.2.
Performance Results – Program 4.2 and Sub-Programs
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| A managed migration of people to Canada that facilitates the movement of legitimate travellers, while denying entry to Canada at the earliest point possible to those who pose a safety or security risk, or are otherwise inadmissible under IRPA | Number of refused electronic travel authorizations (eTA) | TBD | N/A |
| Percentage of TRV applicants enrolled biometrically | 20% | 12% | |
| Immigration violation rate (based on a three-year average) following a visa policy decision on a country (violations as a percentage of all travellers from that country) | ≤ 3% | N/A |
Performance data for the first indicator will become available in 2016, following the August 1, 2015 launch of the Electronic Travel Authorization (eTA) entry requirements.
In 2014–2015, a total of 176,827 or 12%, of 1,407,258 TRV applicants were enrolled biometrically. These results suggest that CIC is well on its way to meeting the 2017 target of having 20% of all visa-required temporary resident applicants provide a digital photograph and fingerprints in support of their application. It is expected that the actual result will gradually increase by 2017 as application intake increases in certain biometric-required countries.
For the third indicator, the immigration violation rate is one of many data sets that the Department uses to assess potential risk posed by a given country with respect to irregular migration when analyzing their potential eligibility for visa-free status. For example, in 2012, the immigration violation rate for Botswana, which was visa-exempt until September of that year, was 26.5%. Following the visa imposition, the violation rate dropped to 3.8% in 2013, then 1.9% in 2014; demonstrating that visa screening was a needed tool to deter and detect non-genuine travellers from that country.
On the other hand, Taiwan is an example of a country/territory where a visa exemption was appropriate when the decision to lift was made, and continues to be appropriate today. Before being granted a visa exemption in 2010, its immigration violation rate was 0.6%, an indication that Taiwanese travellers are low risk. Since then, Taiwan has maintained a low violation rate, with 0.4% in 2014.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent residents have required documentation to re-enter Canada | Number of phase one (new) permanent resident (PR) cards issued | ≥ 240,000 Footnote xliv | 266,270 |
| Number of phase two (existing) PR cards issued | ≥ 140,000Footnote xxxvi | 193,849 | |
| Number of PR travel documents issued | 10,000-20,000Footnote xxxvi | 14,741 |
In 2014–2015, CIC issued 266,270 new PR cards. This represents a decrease from the 269,813 new PR cards issued in 2013–2014.
CIC also issued 193,849 replacement or renewal PR cards. This represents a decrease from the 270,380 replacement or renewal cards issued in 2013–2014. This was the result of both fewer resources allocated to processing renewal PR cards, and lower than anticipated demand for the cards in late 2014–2015.
In the same period, CIC issued 14,741 PR travel documents, which is 586 more than the amount issued in 2013–2014. PR travel documents are used by PRs who are travelling abroad and have either lost or not yet received their PR card.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visitors have been screened to ensure they do not pose a risk to the health, safety and security of Canadians | Percentage of applicants (overseas and in-Canada) referred to CIC partners for security screening | Overseas: 3.5–4.5%; In Canada: 0.5–2.5%Footnote xlv |
Overseas: 2.4%; In Canada: Not available |
| Percentage of applicants (overseas and in-Canada) refused for being found not to be legitimate visitors or ineligible for approval | Overseas: 16 - 19%; In Canada: 8–11% Footnote xl |
Overseas: 18.5%; In Canada: Not available |
|
| Percentage of applicants (overseas and in-Canada) refused for inadmissibility or non-compliance | Overseas: 1–4%; In Canada: 1–4%Footnote xl |
Overseas: 1.6%; In Canada: Not available |
In 2014, CIC referred 32,787 overseas applications to visit Canada to its partners for security screening. This represents 2.4% of all such applications, and is slightly below the historical target planning range. In all, 18.5% of overseas applicants were refused because they were not legitimate travellers or otherwise ineligible for visitors status. Additionally, 1.6% of overseas applicants were refused because they were inadmissible for entry into Canada, or were otherwise non-compliant with entry requirements.
Overall, these indicators demonstrate that, while the majority of applicants for visitors’ status are accepted and allowed to visit Canada, CIC nevertheless has a rigorous screening process in place to protect the integrity of the Visitors Status Program.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| People seeking to enter or remain in Canada who would otherwise be inadmissible are granted a TRPFootnote xlvi | Percentage of TRPs issued for security, organized crime, war crimes and/or crimes against humanity | 0.75%–1.0% | 0.1% Footnote xlvii |
| Percentage of TRPs issued for criminality and/or serious criminality | 57.5%–62.5%Footnote xlii | 61.2% | |
| Percentage of TRPs issued for other inadmissibilities or non-compliance | 38%–42%Footnote xlii | 38.7% |
In 2014, less than one percent of TRPs were issued for security, organized crime, war crimes or crimes against humanity.
CIC issued 6,523 TRPs for criminality or serious criminality, or 61.2% of all TRPs in 2014. Most TRPs in this category were issued to U.S. citizens with offences such as impaired driving that render them inadmissible. Additionally, CIC issued 4,124 TRPs for other inadmissibilities or non-compliance, accounting for approximately 38.7% of all TRPs in 2014.
TRPs are issued only when reasons to allow entry are compelling and sufficient to outweigh any potential risk.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| The integrity of Canada’s citizenship and immigration programs is assured | Percentage of applications processed for which risk indicator criteria have been applied in processing (citizenship, permanent resident, and temporary resident applications) over total number of applications processed in these lines of business | 50% | Citizenship: 83% Permanent Resident: 40% Temporary Resident: 0% |
| Percentage of refused cases over the total number of applications processed for Family Class spouses | 8% | 11% | |
| Percentage of refused cases over the total number of applications processed for TRVs | 16% | 18.4% |
In 2014, CIC applied risk criteria to 83% of citizenship applications and 40% of PR applications. Risk criteria for temporary resident applications are still in development and will be in place by fiscal year 2017–2018. Risk criteria are a series of characteristics present in cases that serve to differentiate non-complex cases from those that are more complex and require greater scrutiny. By applying risk criteria to triage applications, limited processing resources can be focused on those complex cases that have the highest risk of fraud or other inadmissibility concerns.
CIC processed 45,585 applications for spouses in 2014. Of those, 5,016, or 11%, were refused. This is consistent with the 2013 refusal rate of 11%. Of the 1,372,836 TRV applications received by CIC, 252,406, or 18.4%, were refused, which is consistent with the 2013 refusal rate of 17%.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Migrants who are determined not to be refugees reintegrate in their countries of origin | Percentage of migrants who received assistance to establish a business and who are “very satisfied,” “satisfied” or “moderately satisfied” with the performance of their business | 90% | 97% |
| Percentage of migrants surveyed who received reintegration assistance who are “positive” about their future in their home country | 80% | 93% |
In 2014, the GAIM Program provided assisted voluntary returns and reintegration assistance, including business establishment, to 26 stranded migrants. In addition, the program, through its service provider, has also undertaken many activities to raise awareness of the risks of irregular migration and to provide information on safe migration through numerous information and awareness sessions given in both countries of origin and transit states.
It was determined through the recent program evaluation that there is an ongoing need for a global voluntary return and reintegration program in order to support the objectives of Canada’s Migrant Smuggling Prevention Strategy. The GAIM Program had been an integral component in meeting these objectives and is well aligned with both Government of Canada and CIC priorities.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on the Migration Control and Security Management Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Improvement of Processing Times with the Expansion of Business Express and CAN+ (4.2.2)
- In October 2014, CIC expanded Business Express to Bulgaria and Romania, opening visa application centres in the capitals of each country. This adds to the Business Express services already offered in India, China and Mexico. Business Express facilitates timely business travel to and from participating countries by processing most visas within three days for the employees of reliable companies who frequently travel to Canada. By fast-tracking low-risk visa applications, CIC facilitates trade with Canada and frees up processing resources to concentrate on areas requiring higher scrutiny.
- In May 2014, CIC launched CAN+ services to Mexico, and later in July further expanded CAN+ to India. CAN+ provides timely processing of visas between two and six business days for foreign nationals who have travelled to the United States or Canada within the last 10 years. As with Business Express, by fast-tracking low-risk visitor applications, visa officer resources are freed up to work on other cases, improving overall processing time for travelers.
Continued deployment of Visa Application Centres
- In 2014–2015, CIC continued with the deployment of its Visa Application Centre network. As of March 31, 2015, the network consisted of 132 Visa Application Centre in 94 countries, including recent openings in Erbil, Iraq and Doha, Qatar. Visa Application Centre are an example of the Government of Canada’s commitment to improve service to applicants and processing efficiency.
Completion of the Temporary Resident Biometrics Project
- In 2014, the Government of Canada completed the Temporary Resident Biometrics Project, which enabled the capacity to collect, store and process biometric data (digital photographs and fingerprints) for affected temporary resident applicants. This biometric information has been integrated into the border verification process, improving the integrity of the Temporary Economic Residents Program by facilitating the early identification and refusal of visas and permits for known criminals, terrorists and other inadmissible persons.
Program 4.3: Canadian Influence in International Migration and Integration Agenda
As part of its mandate, CIC aims to influence the international migration and integration policy agenda. This is done by developing and promoting, together with other public policy sectors, Canada’s position on international migration, integration and refugee protection issues, and through participation in multilateral, regional and bilateral forums.
CIC works closely with partner countries to ensure the effective administration of immigration laws through the exchange of information, including biometric data. This international migration policy development helps Canada advance its interests in the context of international migration as well as meet its international obligations and commitments.
CIC supports international engagement and partnerships through membership in and contributions to such organizations as the International Organization for Migration, Regional Conference on Migration, the UNHCR, the Global Forum on Migration and Development, and Intergovernmental Consultations on Migration, Asylum and Refugees. The program uses transfer payment funding from the following programs: grant for Migration Policy Development; International Organization for Migration; and International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 57 | 29 | -28 | ||
| Spending | 8,156,032 | 8,156,032 | 5,898,735 | 5,896,698 | -2,259,334 |
Actual spending in 2014–2015 for Program 4.3 was lower than planned spending by $2.3 million and authorities were subsequently adjusted to fund other programs.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canadian positions on managed migration, integration, and international protection are advanced in international fora | Percentage of decisions/reports from international meetings and fora identified as importantFootnote xlviii that reflect the delivered CIC migration-related position | 60% | 92% |
In 2014–2015, CIC attended 38 meetings identified as important; of those meetings, 35, or 92%, resulted in outcomes that were favourable to the Canadian position on migration. This result represents an 8% decrease from 2013–2014, and is 32% above the target range for this indicator.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on this program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Advancing Canada’s Migration Interests in 2014–2015
- In 2014–2015 CIC advanced its engagement and dialogue with Europe in international migration issues, and supported a constructive joint Canada-EU consultation on migration and asylum that resulted in a commitment to closer collaboration in a number of areas.
- CIC worked with the Canada Border Services Agency to successfully chair the Five Country Conference in April 2014 in Quebec City. For its year as Chair, Canada focused on traveller facilitation issues, with the long-term objective of sharing best practices and lessons learned to improve the flow of legitimate travellers throughout the five countries.
- CIC implemented a systematic query-based biographic information-sharing capability with the United States to reduce identity fraud, enhance screening decisions, and support other administrative and enforcement actions. Additionally, Canada and the United States continue work to implement systematic query-based biometric information-sharing capability.
Program 4.4: Passport
CIC is accountable for the Passport Program and collaborates with Service Canada and Foreign Affairs, Trade and Development Canada for the delivery of passport services. The program is managed through a revolving fundFootnote xlix. The program enables the issuance of secure Canadian travel documents through authentication of identity and entitlement, facilitates travel, and contributes to international and domestic security.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15Footnote l |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 802 | 585 | -217 | ||
| Gross Expenditures | 419,548,572 | 419,548,572 | 357,760,911 | -61,787,661 | |
| Respendable Revenue | -673,740,810 | -673,740,810 | -645,148,140 | 28,592,670 | |
| Net Revenue | -254,192,238 | -254,192,238 | -287,387,229 | -33,194,991 |
The decrease in revenue in the Passport Program is due to a reduction in the projected volume of 5.5 million passports to an actual volume of 5.1 million. This decline in revenue was partly offset by reduced costs associated with volume as well as less spending than anticipated on capital and modernization initiatives.
| Expected Result | Performance Indicators | Targets | Actual Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canadians have access to secure travel documents | Percentage compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization Annex 9 standards and recommended practicesFootnote li | 100% | 100% |
| Percentage of Canadians having access to a passport point of service within 100 kilometres in Canada | 90% | 95% | |
| Canadians are satisfied with passport services | Percentage of clients who report they have been satisfied with services they have received | 90% | 96% |
The Passport Program’s 100% compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization Annex 9 standards and practices is an indication that the program is being delivered in accordance with international duties and obligations, which, in turn, facilitates the travel of Canadians.
The Passport Program continues to meet all performance targets in fulfilling its service delivery commitments to Canadians. In addition, some 95% of Canadians continue to have access to passport services within a 100-km range in Canada, while 96% of Canadians continue to be satisfied with the services they receive from the program.
Additional Performance Information
In addition to the above performance results on the Passport Program, the following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015:
Enhanced Passport Services
- In 2014–2015, CIC continued with the modernization of its Passport Program. This included preparations to leverage CIC’s case processing and payment systems—the Global Case Management System (GCMS) and the Integrated Payment Revenue Management System—as a means of accepting payment, processing applications and issuing passports to Canadians. The efficiencies of using an integrated application management and payments system across the Department will also further streamline the application process.
- In 2014–2015, the Passport Program issued over 5.1 million travel documents, with 99.5% processed within service standards. This was an increase of 4% over the previous year. This included applications processed by CIC to issue refugee travel documents, certificates of identity and official passports where volumes increased by 18%.
Improved Security and Integrity of the Passport Program
- In 2014–2015, CIC strengthened program security and integrity by:
- making updates to its facial recognition software to increase effectiveness;
- developing an evolving strategy for automated information sharing with provinces and territories to better validate identities prior to issuing passports;
- continuing to work closely with security and intelligence partners to improve information sharing and operational processes on passport cases involving high-risk individuals; and
- amending the Canadian Passport Order to minimize the risk that the Canadian passport will be used to commit certain crimes, including terrorism offences and transnational sex offences against children.
Adoption of Common Government of Canada Processes and Synergies with CIC Practices and Systems
- Following the Passport Program’s transition from the Department of Foreign Affairs, Trade and Development in 2013, in 2014–2015 CIC finalized the integration of all Passport financial systems and electronic HR files into departmental systems. It also aligned all Passport Program business, financial and investment planning to CIC processes and procedures. By further integrating the Passport Program’s business processes, CIC is improving the efficiency of its overall operations.
Program 5.1: Internal Services
Internal services are groups of related activities and resources that are administered to support the needs of programs and other corporate obligations of an organization. These groups are: management and oversight, services; communications services; legal services; human resources management services; financial management services; information management services; information technology services; real property services; materiel services; acquisition services; and travel and other administrative services. Internal services include only those activities and resources that apply across an organization and not those provided specifically to a program.
| Resource | Total Budgetary Expenditures (Main Estimates) 2014–15 |
Planned 2014–15 |
Total Authorities (available for use) 2014–15 |
Actual 2014–15 |
Difference 2014–15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTEs | 1,487 | 1,530 | 43 | ||
| Spending | 164,414,885 | 164,414,885 | 235,789,928 | 226,988,706 | 62,573,821 |
Actual spending for Internal Services in 2014–2015 was $62.6 million higher than planned, primarily due to a number of improvements to CIC information management and technology systems, strengthened governance practices for management and oversight, and the realignment of internal services expenditures to reflect government policy and guidance on internal services.
Additional Performance Information
The following highlights some of the specific achievements and progress made over the course of 2014–2015 in Internal Services:
Improvements to Information Management and Technology Systems
- In 2014–2015, CIC undertook a number of improvements to its IM/IT systems to improve the management of its programs.
- In autumn 2014, CIC transitioned from its previous records management system to the Government of Canada’s standard electronic document and records management solution, GCDOCS. This secure system is more streamlined, facilitates collaboration across the Department and allows officials to share and manage the Department’s information assets easier than ever.
- In January 2015, CIC began roll-out of its Grants and Contributions System, which improves the management of CIC’s Grants and Contributions programs by providing a single, end-to-end database management solution for information on agreements, spending, correspondence and budget allocations for Grants and Contributions (Vote 5) funding.
- In 2014–2015, CIC replaced four older IM/IT systems with GCMS, a single, integrated and worldwide system used internally to process applications for citizenship and immigration services. By decommissioning these older systems and integrating immigration and citizenship information into a single system, CIC can better manage case files and improve the efficiency of its application processing.
- The Department also implemented a new departmental fee collection system. The new system replaces three older fee management systems and provides a single location for recording and managing all fees collected by CIC in Canada and overseas. The system is fully integrated with GCMS and with the Department’s overarching financial system. It also improves ease of use for clients by increasing the Department’s ability to accept online payments.
- In 2014–2015, CIC enhanced its data collection and multi-user reporting system, which provides high quality performance measurement information. For the first time, CIC is now able to consistently measure Settlement Program and client outcomes across the country.
Enhancements to Project Management Capacity
- In 2014–2015, CIC launched a new three-tiered project management certification program, provided in-house for CIC staff. By offering project management training to its employees, CIC is building a more capable workforce to achieve its long-term goals.
- This certification program also anticipated the March 2015 recommendations of the 9th Annual Report of the Prime Minister’s Advisory Committee on the Public Service to introduce modern project management techniques into the Public Service to better deliver on results for Canadians.
Promotion of Human Resources and Management Excellence
- In 2014–2015, CIC made improvements to its human resources and management capacity. These are highlighted in the Organizational Priorities found in Section I of this report.
Section III: Supplementary Information
Financial Statements Highlights
The financial highlights presented within this Departmental Performance Report are intended to serve as a general overview of CIC’s Consolidated Statement of Operations and Consolidated Statement of Financial Position as presented in CIC’s unaudited financial statements. These are prepared in accordance with accrual accounting principles and, therefore, are different from the information published in the Public Accounts of Canada, which are prepared on appropriation-based reporting. The complete unaudited financial statements can be found on CIC’s Web site.
Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations
| Financial Information | 2014–15 Planned Results |
2014–15 Actual |
2013–14 Actual |
Difference (2014–15 actual minus 2014–15 planned) | Difference (2014–15 actual minus 2013–14 actual) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total expenses | 2,362,742,403 | 2,270,305,130 | 2,093,073,971 | (92,437,273) | 177,231,159 |
| Total revenues | 683,689,622 | 650,195,750 | 468,923,208 | (33,493,872) | 181,272,542 |
| Net cost of operations before government funding and transfers | 1,679,052,781 | 1,620,109,380 | 1,624,150,763 | (58,943,401) | (4,041,383) |
Total departmental expenses have increased by $177 million or 8%, from $2.1 billion in 2013–2014 to $2.3 billion in the current year. This increase is mostly attributable to the Passport Program since 2013–2014 financial results represented nine months of operations while 2014–2015 represents the full year of operations. This increase can also be explained by additional funding and spending associated with the Canada-Quebec Accord as well as a higher number of citizenship grant and proof decisions made in the year as a result of the backlog reduction initiative.
Total expenses for 2014–2015 are $92 million or four percent lower than the planned results reported in CIC’s 2014–2015 Consolidated Future-Oriented Statement of Operations. The variance is mainly attributable to the lapse of operating and grants and contributions resources and variances between the estimates used in the preparation of the Future-Oriented Statement of Operations and the subsequent actual results.
Transfer payments comprise a significant portion of the Department’s expenses (43%, or $984 million) followed by employee costs, which include salaries and benefits (33%, or $753 million).
Most of the Department’s spending was under the Newcomer Settlement and Integration Program, comprising 44% or $1 billion, of the Department’s expenses, of which $974 million are transfer payments.
The charts below outline CIC’s expenses by program and CIC’s net cost of operations before government funding and transfers:
Text version: Expenses by Program
The pie chart above shows a percentage breakdown of Expenses by Program. The table below provides the percentages as indicated in the pie chart.
| Expenses by Program | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Newcomer Settlement and Integration | 44% |
| Passport Canada | 16% |
| Migration Control and Security Management | 9% |
| Citizenship for Newcomers and All Canadians | 5% |
| Permanent Economic Residents | 5% |
| Family and Discretionary Immigration | 3% |
| Temporary Economic Residents | 3% |
| Internal Services | 11% |
| OtherFootnote lii | 4% |


Text version: Net Cost of Operations before Government Funding and Transfers (in millions of dollars
| Operations Before Government Funding and Transfers | $ millions |
|---|---|
| Planned 2014–2015 | 1,679 |
| Actual 2014–2015 | 1,620 |
| Actual 2013–2014 | 1,624 |
Departmental total revenues amounted to $1,232 million in 2014–2015.
Departmental revenues earned on behalf of the government (47% of total revenues, or $582 million) increased by 17% or $86 million compared with the previous year’s revenues. Most revenues earned on behalf of the government are from fees for immigration service (33%, or $405 million).
Departmental respendable revenues (53%, or $650 million) increased by 39% or $181 million compared with the previous year’s revenues. The $34-million variation between the 2014–2015 planned results and actual revenues is mostly due to a lower demand for passports than forecasted. International Experience Canada planned results were also overestimated by $5 million.
The charts below outline all of CIC’s revenues:

Text version: Revenues by Type
| Revenues by Type | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Passport respendable revenues | 52% |
| Immigration service fees | 33% |
| Right of permanent residence | 6.6% |
| Citizenship service fees | 6% |
| IEC respendable revenues | 0.4% |
| Other revenuesNote liii | 2% |

Text version: Revenues including respendable revenues (in millions of dollars)
| Revenues including respendable revenues | $ millions |
|---|---|
| Planned 2014–2015 | 1,240 |
| Actual 2014–2015 | 1,232 |
| Actual 2013–2014 | 966 |
Condensed Consolidated Statement of Financial Position
| Financial Information | 2014–15 | 2013–14 | Difference (2014–15 minus 2013–14) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total net liabilities | 402,280,049 | 422,802,167 | (20,522,118) |
| Total net financial assets | 332,904,241 | 322,758,011 | 10,146,230 |
| Departmental net debt | 69,375,808 | 100,044,156 | (30,668,348) |
| Total non-financial assets | 165,674,900 | 174,878,460 | (9,203,560) |
| Departmental net financial position | 96,299,092 | 74,834,304 | 21,464,788 |
Total net liabilities have decreased by $21 million due to a decrease of $51 million in Immigrant Investor Program liabilities partially offset by an increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
The decrease in the Immigrant Investor Program is attributable to the reduction in moneys held from the Northwest Territories as a result of their early withdrawal from the program.
The increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities is mostly attributable to the implementation of salary payments in arrears.
The chart below outlines CIC’s net liabilities:

Text version: Total Net Liabilities
| Total Net Liabilities | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 73% |
| Immigrant Investor Program | 15% |
| Vacation pay and compensatory leave | 5% |
| Employee future benefits | 7% |
Total net financial assets have increased by $10 million due to a $42-million increase in the amount due from the Consolidated Revenue Fund, an increase of $6 million in inventory held for resale, and a decrease of $39 million in accounts receivable and advances, mostly associated with the timing of fee collection from Service Canada.
The chart below outlines CIC’s net financial assets:

Text version: Total Net Financial Assets
The pie chart above shows a percentage breakdown of Total Net Financial Assets. The table below provides the percentages as indicated in the pie chart.
| Total Net Financial Assets | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Due from Consolidated Revenue Fund | 72% |
| Accounts receivable and advances | 12% |
| Loans receivable | 11% |
| Inventory held for resale | 5% |
Supplementary Information Tables
The
supplementary information tableslisted in this report can be found on the CIC Web site.
- Departmental Sustainable Development Strategy;
- Details on Transfer Payment Programs;
- Internal Audits and Evaluations;
- Response to Parliamentary Committees and External Audits;
- Status Report on Transformational and Major Crown Projects;
- Status Report on Projects Operating With Specific Treasury Board Approval;
- Up-Front Multi-Year Funding; and
- User Fees Reporting.
Tax Expenditures and Evaluations
The tax system can be used to achieve public policy objectives through the application of special measures such as low tax rates, exemptions, deductions, deferrals and credits. The Department of Finance Canada publishes cost estimates and projections for these measures annually in the Tax Expenditures and Evaluations publication. The tax measures presented in the Tax Expenditures and Evaluations publication are the sole responsibility of the Minister of Finance.
Section IV: Organizational Contact Information
For any additional information on this report or other parliamentary reports, please contact ParliamentaryReports-RapportsParlementaires@cic.gc.ca.
Appendix: Definitions
- appropriation ( crédit):
- Any authority of Parliament to pay money out of the Consolidated Revenue Fund.
- budgetary expenditures ( dépenses budgétaires):
- Includes operating and capital expenditures; transfer payments to other levels of government, organizations or individuals; and payments to Crown corporations.
- Departmental Performance Report ( rapport ministériel sur le rendement):
- Reports on an appropriated organization’s actual accomplishments against the plans, priorities and expected results set out in the corresponding Report on Plans and Priorities. These reports are tabled in Parliament in the fall.
- full-time equivalent ( équivalent temps plein):
- Is a measure of the extent to which an employee represents a full person-year charge against a departmental budget. Full-time equivalents are calculated as a ratio of assigned hours of work to scheduled hours of work. Scheduled hours of work are set out in collective agreements.
- Government of Canada outcomes ( résultats du gouvernement du Canada):
- A set of 16 high level objectives defined for the government as a whole, grouped in four spending areas: economic affairs, social affairs, international affairs and government affairs.
- Management, Resources and Results Structure ( Structure de la gestion, des ressources et des résultats):
- A comprehensive framework that consists of an organization’s inventory of programs, resources, results, performance indicators and governance information. Programs and results are depicted in their hierarchical relationship to each other and to the Strategic Outcome(s) to which they contribute. The Management, Resources and Results Structure is developed from the Program Alignment Architecture.
- non-budgetary expenditures ( dépenses non budgétaires):
- Includes net outlays and receipts related to loans, investments and advances, which change the composition of the financial assets of the Government of Canada.
- performance ( rendement):
- What an organization did with its resources to achieve its results, how well those results compare to what the organization intended to achieve and how well lessons learned have been identified.
- performance indicator ( indicateur de rendement):
- A qualitative or quantitative means of measuring an output or outcome, with the intention of gauging the performance of an organization, program, policy or initiative respecting expected results.
- performance reporting ( production de rapports sur le rendement):
- The process of communicating evidence-based performance information. Performance reporting supports decision making, accountability and transparency.
- planned spending ( dépenses prévues):
-
For Reports on Plans and Priorities and Departmental Performance Reports (DPRs), planned spending refers to those amounts that receive Treasury Board approval by February 1. Therefore, planned spending may include amounts incremental to planned expenditures presented in the Main Estimates.
A department is expected to be aware of the authorities that it has sought and received. The determination of planned spending is a departmental responsibility, and departments must be able to defend the expenditure and accrual numbers presented in their Reports on Plans and Priorities and DPRs.
- plan ( plan):
- The articulation of strategic choices, which provides information on how an organization intends to achieve its priorities and associated results. Generally a plan will explain the logic behind the strategies chosen and tend to focus on actions that lead up to the expected result.
- priorities ( priorité):
- Plans or projects that an organization has chosen to focus and report on during the planning period. Priorities represent the things that are most important or what must be done first to support the achievement of the desired Strategic Outcome(s).
- program ( programme):
- A group of related resource inputs and activities that are managed to meet specific needs and to achieve intended results and that are treated as a budgetary unit.
- Program Alignment Architecture ( architecture d’alignement des programmes):
- A structured inventory of an organization’s programs depicting the hierarchical relationship between programs and the Strategic Outcome(s) to which they contribute.
- Report on Plans and Priorities ( rapport sur les plans et les priorités):
- Provides information on the plans and expected performance of appropriated organizations over a three-year period. These reports are tabled in Parliament each spring.
- result ( résultat):
- An external consequence attributed, in part, to an organization, policy, program or initiative. Results are not within the control of a single organization, policy, program or initiative; instead they are within the area of the organization’s influence.
- statutory expenditures ( dépenses législatives):
- Expenditures that Parliament has approved through legislation other than appropriation acts. The legislation sets out the purpose of the expenditures and the terms and conditions under which they may be made.
- Strategic Outcome ( résultat stratégique):
- A long-term and enduring benefit to Canadians that is linked to the organization’s mandate, vision and core functions.
- sunset program ( programme temporisé):
- A time-limited program that does not have an ongoing funding and policy authority. When the program is set to expire, a decision must be made whether to continue the program. In the case of a renewal, the decision specifies the scope, funding level and duration.
- target ( cible):
- A measurable performance or success level that an organization, program or initiative plans to achieve within a specified time period. Targets can be either quantitative or qualitative.
- voted expenditures ( dépenses votées):
- Expenditures that Parliament approves annually through an Appropriation Act. The Vote wording becomes the governing conditions under which these expenditures may be made
- whole-of-government framework ( cadre pangouvernemental):
- Maps the financial contributions of federal organizations receiving appropriations by aligning their programs to a set of 16 government-wide, high-level outcome areas, grouped under four spending areas.
Page details
- Date modified: