Prepare your information for a cannabis licence application: Cultivation, processing and sale for medical purposes with possession of cannabis licence
On this page
This page describes what you need to prepare before you can submit it in the Cannabis Tracking and Licensing System (CTLS) and in the site evidence package. This page only applies to these licences:
- micro-cultivation, nursery and standard cultivation
- micro-processing and standard processing
- sale for medical purposes with possession of cannabis
For information on applying for sale for medical purposes without possession of cannabis licences, refer to Prepare your information: Sale for medical purposes without possession of cannabis licences.
Note: Health Canada recommends using a document naming convention for all the information you have to submit. Following the document naming convention will help us process your application more efficiently.
1.0 CTLS submission information
Generally, the information you need to submit in the CTLS is the same for these licences. It will be clearly indicated if the section doesn't apply to a licence.
1.1 For corporations, cooperatives or partnerships
You'll have to create a corporate profile in the CTLS, if you don't already have one, if you're applying for the licence as:
- a corporation
- a cooperative
- a partnership
This section provides the information you need to prepare when you're creating a new corporate profile.
1.1.1 Parent (owning) corporation
Any controlling corporation is required to create a corporate profile, and directors and officers of that corporation need to apply for security clearances. Refer to Who needs a security clearance for more information.
You need to gather the CTLS Account IDs of any controlling corporation, if applicable.
1.1.2 Certificate of incorporation or business registration document
You need to prepare the following document depending on your organization.
- If you're a corporation: copy of your certificate of incorporation, amalgamation or amendment
- If you're a cooperative or a partnership: copy of your business registration or partnership agreement
- If you want to use another name besides your legal business name, you can request that the other name appear on the licence. For example, Legal corporation name d.b.a. Other name. Some provinces and territories may require that this other name be registered. It is your responsibility to consult the registry of the jurisdiction where you plan to do business on the requirements for registration
1.1.3 Directors, officers, partners
You need to gather the CTLS Account IDs of all your directors, officers and partners.
Important: If you'll be conducting Health Canada-regulated cannabis activities in First Nations, Inuit or Métis communities, contact the Navigator Service at navigator-navigateur@hc-sc.gc.ca.
1.2 Site details
This section provides information on what you need to prepare about your site.
Important: If you'll be conducting Health Canada-regulated cannabis activities in First Nations, Inuit or Métis communities, contact the Navigator Service at navigator-navigateur@hc-sc.gc.ca.
1.2.1 Health Canada licences, registrations and authorizations
You need to prepare information about licences, registrations and authorizations issued to the applicant from Health Canada for the same site. This can include information about any:
- cannabis licences, such as:
- research licence
- cannabis drug licence
- industrial hemp licence
- analytical testing licence
- personal or designated production of cannabis for medical purposes
- other specialized licences, such as a site licence for natural health products
For each licence, registration or authorization, submit:
- the name of the licence holder, holder of the authorization or applicant
- the site address
- your licence or registration number, if applicable
- the issuance and expiry date, if applicable
- a description of your activities under that licence or authorization
If the applicant doesn't have any licences, registrations and authorizations issued by Health Canada, indicate this in the document.
1.2.2 Aerial view
You need to prepare a clear and legible aerial view of the proposed site and surrounding area.
- The aerial view needs to show a 500 meter radius around the site. It needs to be accurate and up-to-date when you submit
- The photos can't have blind spots. You can avoid this by taking the photos straight down at the site
Note: A web mapping service, such as Google Maps, is enough for an aerial view. It needs to show an accurate and up to date proposed site and surrounding 500 metre radius.
1.2.3 For a site with multiple addresses
If your site has multiple addresses, such as an area that's exclusively used by the applicant with several buildings, prepare a document listing all addresses.
1.3 Identified people
This section provides information you need to prepare about the identified people that you'll need to submit.
1.3.1 Key site personnel
You need to gather the CTLS Account IDs of all your key site personnel. Include the following personnel.
- Head of security and alternate
- Master grower and alternate, if applicable
- Quality assurance person (QAP) and alternates, if applicable
1.3.2 Associated individuals
You need to prepare information for the associated individuals, if applicable.
1.3.2.1 Consent to communicate, reporter and responsible for finance
You need to gather the CTLS Account IDs of the people who will:
- be authorized to communicate with Health Canada about your application (consent to communicate)
- be submitting monthly reports to Health Canada about your activities once you are licensed (reporter)
- be submitting statements of cannabis revenue for the licence holder in the CTLS (responsible for finance)
For reporters and people responsible for finance, you'll need to include them in the list of all associated individuals requiring security clearances.
1.3.2.2 Associated individuals requiring security clearances, if applicable
You need to prepare a document containing a list of all associated individuals requiring security clearances (including reporters and people responsible for finance), if applicable. Include the following for each person:
- full name
- CTLS account ID
- security clearance application ID
- rationale explaining why they require a security clearance
1.3.3 For processing licences: Quality assurance person
This section only applies to micro-processing and standard processing licences. For each of your identified quality assurance person (QAP) and up to 2 alternates (AQAP), if applicable:
- fill out a Qualifications of the proposed QAP or alternate form
- gather their resume or curriculum vitae (CV), copies of their degrees or diplomas, and other supporting documents
Important: If you're a processor who is only conducting activities with reference standards and test kits, you do not need to have a QAP.
For the Qualifications of the proposed QAP or alternate form:
There are many ways to show how the QAP is qualified for the role. The QAP doesn't need a specific degree or diploma, or previous experience in the cannabis industry. You can show how your QAP is qualified by providing information about their quality assurance training or experience, or a combination of both in other similar fields, such as:
- food
- natural health products
- pharmaceutical manufacturing
In the Qualifications of the proposed QAP or alternate QAP section of the form, you need to provide information about your QAP's knowledge of, experience with, and training in all the sections. This is not required if the QAP has been previously approved by Health Canada. Refer to the following examples of principles and practices you can use to show how the QAP is qualified for the role:
- Development and approval of SOPs (standard operating procedures)
- Preparing SOPs, such as document creation
- Implementing SOPs, such as:
- training
- document control
- compliance and following procedures
- Maintaining SOPs, such as updating and revising SOPs
- Managing of a SOP program
- Good production practices (GPP) relating to facilities, equipment, sanitation, and employee hygiene
- Facilities, such as:
- air filtration and ventilation
- lighting
- water supply
- temperature and humidity control
- waste disposal
- Equipment and conveyances, such as pruning shears and forklifts
- Design and construction of facilities and equipment allow for production under sanitary conditions
- Sanitation programs
- Employee hygiene SOPs
- Facilities, such as:
- Investigations and risk mitigation
- Identifying and investigating cannabis or ingredients which pose a risk of injury to human health, for example:
- identifying hazards and source
- determining affected lots or batches
- determining seriousness of issue considering the exposure and toxicity, or the severity of adverse health consequences
- Implementing and evaluating risk mitigation measures relating to cannabis or ingredients that pose a risk of injury to human health, for example:
- increasing the monitoring of quality indicators
- quarantining affected lots or batches
- conducting a recall
- performing an effectiveness study
- Ensuring compliance with Part 5 of the Cannabis Regulations and Part 6 of the Cannabis Regulations, relating to:
- identifying non-compliances, such as:
- reviewing of out-of-specification test results
- assessing personnel regularly
- performing random verification of quality processes. For example, making sure protocols or procedures, and documentation practices are followed
- investigating non-compliances, such as performing root cause analyses
- implementing and evaluating risk mitigation measures relating to non-compliances, such as:
- quarantining lots or batches
- implementing process controls
- performing regular training programs
- complying with limits on microbial contaminations
- complying with limits on use of caffeine
- complying with restrictions on ingredients in extracts
- identifying non-compliances, such as:
- Identifying and investigating cannabis or ingredients which pose a risk of injury to human health, for example:
- Complaint management or investigation
- Determining if a complaint is quality related, such as:
- interviewing the person who filed the complaint
- reassessing lot or batch production records
- re-testing retention samples
- Performing root cause analyses
- Implementing and evaluating corrective and preventative actions to address the immediate situation and to prevent similar future occurrences
- Determining if a complaint is quality related, such as:
- Approving product quality prior to release for sale
- Following procedures for releasing products for sale, such as:
- quarantining a lot or batch temporarily
- reviewing lot or batch production records
- performing visual inspection
- tracking and releasing the lot or batch
- Determining at what stage in production to test products. For example, testing the products before or after packaging
- Assessing documents and information when approving a product lot or batch, for example:
- assessing test results or the Certificate of Analysis against defined specifications
- assessing lot or batch production records, such as historical information about:
- storage or operating conditions
- areas used
- name of operator or technicians
- date of operations
- documented sanitation records
- Determining the criteria for approving a product lot or batch
- Following procedures for releasing products for sale, such as:
- Testing
- Understanding analytical testing and validation of testing methods, which may include assessing the following elements:
- specificity
- linearity
- accuracy
- precision
- range
- limit of quantification
- limit of detection
- Interpreting test results, relating to:
- trending and statistical analysis, such as:
- tracking quality indicators or attributes
- determining outliers and significance
- products, such as:
- microbial and chemical contamination
- disintegration and dissolution of cannabis capsules, if applicable, as set out in a publication referred to Schedule B of the Food and Drugs Act
- cannabinoid content
- trending and statistical analysis, such as:
- Collecting samples in a representative manner
- Retaining samples for potential lot or batch investigation
- Understanding analytical testing and validation of testing methods, which may include assessing the following elements:
- Recall and adverse reaction reporting
- Performing recalls, such as:
- product tracking
- analysis of distribution records
- recall simulations
- product reconciliation
- effectiveness checks
- risk based decision making
- required notifications for stakeholders and authorities
- recall evaluation or audit
- plan of action
- initiation time
- Reporting and assessing adverse reactions, such as:
- identifying adverse reactions and assessing whether they are product related
- following reporting requirements
- Performing recalls, such as:
1.4 Site ownership
You need to prepare 1 of the 2 options depending on the site ownership.
- If the applicant owns the site, (you as an individual, or an organization such as a corporation, cooperative, or partnership), submit either your own CTLS Account ID or the CTLS corporate profile's Account ID in the CTLS
- If other individuals or organizations own the site, each site owner needs to fill out a Site owner consent form
Important: If you'll be conducting Health Canada-regulated cannabis activities in First Nations, Inuit or Métis communities, contact the Navigator Service at navigator-navigateur@hc-sc.gc.ca.
1.5 Organizational security plan
You need to prepare a copy of your organizational security plan (OSP). Refer to Cannabis organizational security plan for information on what to include in the OSP.
Important: The information submitted in the OSP and the CTLS needs to be consistent. Discrepancies or inconsistencies can cause a delay in processing your application.
1.6 Good production practices
This section provides information you need to prepare about your good production practices (GPP) that will need to be submitted.
Refer to the Good production practices guide for cannabis for how to meet good production practices requirements. It gives examples of principles and practices you can use to show your compliance.
Important: If you're a processor who is only conducting activities with reference standards and test kits, they do not need to meet GPP.
1.6.1 Good production practices report
You need to prepare a GPP report that addresses all the information described in each of the following sections. The GPP report can be in a document with each of the sections outlined, or in separate documents.
1.6.1.1 Storage
Include the following information in your GPP report.
A description of your storage procedures. Include:
- how you'll store cannabis and its ingredients
- where you'll store cannabis and its ingredients
- the conditions (such as presence of temperature control, humidity control) that will maintain its quality
Consider where you store:
- viable cannabis seeds
- in-process cannabis
- bulk cannabis
- industrial hemp
- immediate containers for packaging (with or without cannabis inside)
- samples
- cannabis in quarantine
- products approved for sale
- rejected products
- returned or recalled products
- cannabis materials awaiting destruction
1.6.1.2 Building or part of building
Include the following information in your GPP report.
- A description of the construction of the surfaces showing how you meet section 84 of the Cannabis Regulations, such as:
- walls
- ceilings (non-porous panels, sealant)
- floors (polished concrete, epoxy sealant)
- seams (caulking, joints between floors, walls and ceiling)
Note: Refer to Before you start applying for a licence for information about good production practices for building construction materials.
- Process flow diagram or a "step-by-step" description of the movement of cannabis including cannabis products, and ingredients used through the building. You can show your process flow in 1 diagram or in multiple diagrams. Include the movement between:
- operations areas (including grow areas)
- storage areas
- non-cannabis areas
Figures 1 to 4 show an example of a process flow diagram. Do not copy this example, it's a fictional setting. These process flows can include:
- receiving cannabis into the building
- growing and transferring cannabis within the building
- processing and storing cannabis within the building
- shipping cannabis out of the building
Figure 1 shows how cannabis is received into the building from the Shipping / Receiving Area. Flow arrow 1 represents cannabis plants and seeds received from the Shipping / Receiving Area It goes through Corridor 2 into 3 possible areas:
- the plants and seeds are transferred into the Grow Room 1 or Grow Room 2 for growing
- the seeds are transferred to the Storage Area for storage
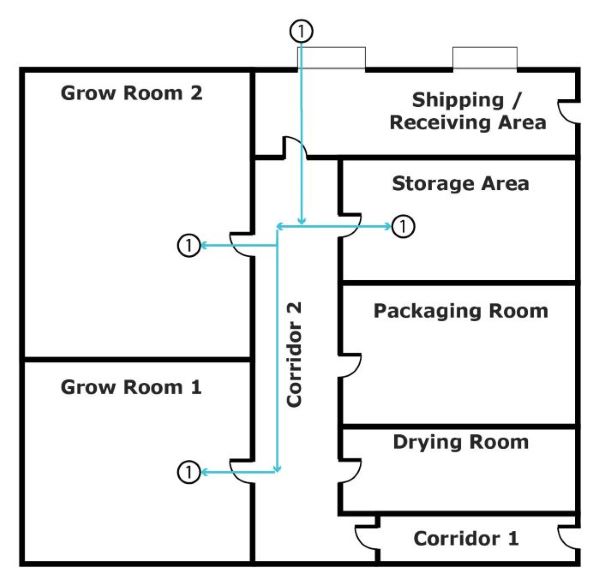
Figure 1 - Text version
Figure 1 shows how cannabis is received into the building from the Shipping / Receiving Area. It goes through Corridor 2 into 3 possible areas:
- they're transferred into the Grow room 1
- they're transferred into the Grow room 2
- they're transferred to the Storage area
Figure 2 shows the transfer of cannabis plants and seeds within the building.
- Flow arrow 2 shows the transfer of seeds from the Storage Area, going through Corridor 2, into Grow Room 1 or Grow Room 2
- Flow arrow 3 shows the transfer of plants between Grow Room 1 and Grow Room 2, going through Corridor 2

Figure 2 - Text version
Figure 2 shows the transfer of cannabis within the building.
- Flow arrow 2 shows the transfer from the Storage area, going through Corridor 2, into Grow room 1 or Grow room 2
- Flow arrow 3 shows the transfer from Grow room 1, going through Corridor 2, into Grow room 2
Figure 3 shows the transfer of harvested cannabis into the operations areas and storage area in the building.
- Flow arrow 4 shows the transfer of harvested fresh cannabis from Grow Room 1 or Grow Room 2, going through Corridor 2, into the Drying Room for drying activities
- Flow arrow 5 shows the transfer of bulk dried cannabis from the Drying Room, going through Corridor 2, into 2 possible areas:
- the Packaging Room for trimming, packaging or labelling activities (processed into packaged and labelled cannabis)
- the Storage Area for storage
- Flow arrow 6 shows the transfer of bulk dried cannabis from the Storage Area, going through Corridor 2, into the Packaging Room for trimming, packaging or labelling activities (processed into packaged and labelled cannabis)
- Flow arrow 7 shows the transfer of packaged and labelled cannabis from the Packaging Room, going through Corridor 2, into the Storage Area for storage

Figure 3 - Text version
Figure 3 shows the transfer of cannabis into the operations areas and storage area in the building.
- Flow arrow 4 shows the transfer of cannabis from Grow room 1 or Grow room 2, going through Corridor 2, into the Drying room
- Flow arrow 5 shows the transfer of cannabis from the Drying room, going through Corridor 2, into 2 possible areas:
- the Packaging room
- the Storage area
- Flow arrow 6 shows the transfer of cannabis from the Storage area, going through Corridor 2, into the Packaging room
- Flow arrow 7 shows the transfer of cannabis from the Packaging room, going through Corridor 2, into the Storage area
Figure 4 shows the transfer of packaged and labelled cannabis and cannabis waste out of the building.
- Flow arrow 8 shows the transfer of packaged and labelled cannabis from the Storage Area, going through Corridor 2 and the Shipping / Receiving Area, out of the building
- Flow arrow 9 shows the transfer of cannabis waste from all the operations areas and storage area, going through Corridor 2 and the Shipping / Receiving Area, out of the building for proper destruction

Figure 4 - Text version
Figure 4 shows the transfer of cannabis out of the building.
- Flow arrow 8 shows the transfer of cannabis from the Storage area, going through Corridor 2 and the Shipping/Receiving area, out of the building
- Flow arrow 9 shows the transfer of cannabis from all the operations areas and storage area, going through Corridor 2 and the Shipping/Receiving area, out of the building
1.6.1.3 Filtration and ventilation system
Include the following information in your GPP report.
- A diagram or floor plan with the filtration and ventilation system. You can show it in 1 diagram or in multiple diagrams. Include:
- filter locations
- air intake and exhaust locations
- direction of air flow within the building
Figure 5 shows an example of a filtration and ventilation diagram. Do not copy this example, it's a fictional setting.

Figure 5 - Text version
The air is drawn into the building through a HEPA (high-efficiency particulate air) filter, before circulating through the duct openings and duct vents into the Storage area, Packaging room, Drying room, Grow room 1 and Grow room 2. There are also portable carbon filters in these areas. The air is drawn out from these areas through the duct openings, duct vents, and a carbon filter before it's exhausted outside of the building.
- A description of the filtration and ventilation system. Include:
- all types of filters that will be used (such as HEPA [high-efficiency particulate air], carbon, charcoal, combination, portable filters)
- how it will filter air to prevent odours associated with cannabis from getting outside
- how it will create sufficient air exchanges to prevent contaminating cannabis and ingredients used. Don't include areas where cannabis and ingredient are only cultivated, propagated or harvested. For example, cultivating cannabis or blueberries that will be used as an ingredient in the cannabis product
- how it will be accessible for cleaning, maintenance or inspection, and is capable of withstanding repeated cleaning and how it works within its intended use. Don't include areas where ingredients are only cultivated, propagated or harvested. For example, cultivating blueberries that will be used as an ingredient in the cannabis product
For more information about cannabis odours, odour control technologies and Health Canada's role in regulating cannabis odours in commercial production sites, refer to Cannabis odours and odour control.
1.6.1.4 Supply of water
Include the following information in your GPP report.
- Description of the water supply source
- If it isn't municipal water, prove that it's appropriate for the intended activities, such as for irrigation, sanitation and processing
- Description of any non-potable water sources
- Include how you'll eliminate cross connection with potable water, or the measures you'll use to remove any risk of contaminating cannabis or ingredients used (for example, backflow valves)
Note: Refer to Before you start applying for a licence for information about good production practices for water sources when processing cannabis extracts, edibles and topicals.
1.6.1.5 Lighting
Include the following information in your GPP report.
- A description of lighting in operation areas, including grow areas, and storage areas. Include:
- how the cannabis and ingredients used won't be contaminated if the lighting breaks, for example:
- using shatter resistant materials
- using fixtures with safety covers
- having lighting breakage procedures on how you'll inspect and fix the issue (including impact on cannabis, ingredients and equipment)
- how it can be repeatedly cleaned and sanitized to prevent contamination. For example, lighting made with materials that can be cleaned and sanitized regularly
- how the cannabis and ingredients used won't be contaminated if the lighting breaks, for example:
1.6.1.6 Sanitation program
Include the following information in your GPP report.
- A description of your sanitation program for:
- all operation areas (including grow areas)
- storage areas
- transitory areas (such as hallways)
- non-cannabis areas (such as washrooms and office space)
- Include this for each of the areas:
- cleaning schedule or frequency
- how you'll make sure cleaning of the building is effective (such as visual quality checks)
1.6.1.7 Hand cleaning and hand sanitizing stations and lavatories
Include the following information in your GPP report.
- Floorplans with the location of all hand cleaning, sanitizing stations and washrooms
- For outdoor cultivation: Indicate if there are any hand cleaning, sanitizing stations and washrooms on-site in your site plan. If there is none on-site, explain how you'll maintain sanitary practices
1.6.2 For processing licences: Good production practices attestation
You need to fill out the Good production practices attestation.
1.7 Record keeping
This section provides information you need to prepare about record keeping that will need to be submitted.
1.7.1 Record keeping attestation
You need to fill out the Record keeping attestation.
1.7.2 For sale for medical purposes licences: Proposed record keeping methods
You need to prepare the following.
- Record keeping methods
- A description of your record keeping methods, such as storing the records electronically in a cloud system or physically in an office
- Medical document verification process
- A description of the medical document verification process, including verification of the information
- Example of registration document
- An example of the registration document that you'll give to clients
- An example of documents used to fill a client's order and refuse to fill a client's order
- Process to limit quantities of 150 g of dried cannabis (or its equivalent amount) per order
- A description of how you'll ensure that the quantity of cannabis, other than plants or seeds, distributed or sold won't exceed 150 g of dried cannabis (or its equivalent amount) per order
1.8 Key investor reports
You need to prepare either a report or an attestation about key investors. Refer to Cannabis key investors for more information about the requirements for applicants:
- not listed on a published market
- listed on a published market
1.9 For cultivation licences: Source of starting material
This section only applies to micro-cultivation, nursery and standard cultivation licences.
You can receive starting materials (cannabis plants and seeds) that were obtained:
- in accordance with:
- the former Access to Cannabis for Medical Purposes Regulations
- the former or current Industrial Hemp Regulations, or
- the Cannabis Regulations (for example, from a federal licence holder)
- from a person authorized to sell cannabis under a provincial Act
You can also receive starting materials from a source that is not listed above, on an exceptional basis. You'll need to submit a declaration under subsection 10(2) of the Cannabis Regulations for your licence application. It needs to:
- contain the quantity of cannabis plants and seeds (individual quantity per type of cannabis) that you'll possess on the effective date of your licence
- be signed and dated by the responsible person
Before Health Canada and the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) issue your licence:
- you may:
- update the declaration at any time before your licence is issued
- you may not:
- bring to your site a number of cannabis plants and seeds that exceeds the quantity identified on the declaration
- do any activities with cannabis until you have a licence, such as cultivating, propagating and harvesting cannabis
Important: If you possess more cannabis starting material than what you've declared, or do any activities other than the ones you're allowed, it may result in enforcement actions from Health Canada and the CRA, such as financial penalties or seizure of material.
Once Health Canada and the CRA issue your licence:
- you need to have possession of all the starting material obtained through the declaration at your site (on the licence's effective date)
- you can't bring in more starting materials under a new or changed declaration
- you can only obtain additional cannabis plants or seeds from the following authorized sources:
- other cannabis licence holders, including nurseries
- your own plant breeding program to produce new varieties
- licensed cannabis researchers, under certain circumstances
- from an import permit for starting materials, only if it's for medical or scientific purposes
All cannabis produced under the licence, regardless of its original source need to meet Part 5 of the Cannabis Regulations and Part 6 of the Cannabis Regulations.
2.0 Site evidence package
Note: Health Canada recommends that you develop your site evidence package at the same time as completing your application in the CTLS.
The site evidence package needs to show that your site is fully built and meets the physical security measures and the good production practices of the Cannabis Regulations. This includes submitting evidence to show that you have an operational and functional site. For example, a building equipped with all permanent fixtures, such as:
- facility lighting
- security features
- ventilation and air filtration systems
For examples of principles and practices that you can use to show compliance for your fully built site, use:
The requirements for an operational and functional site only apply to the areas of your site where you plan to conduct activities with cannabis when you first get your licence. For example, if you'll only use some areas of the building, then you're only required to submit site evidence for the areas you'll use and would like to be approved, instead of the entire building.
You aren't required to submit any information on your cultivation and processing equipment or have it present during the site evidence video walkthrough. This includes your:
- scales
- trimmers
- grow lights
- cultivation tables
- extraction equipment
2.1 How to format
You need to prepare the site evidence package using the following format.
- All video and images need to:
- have sufficient resolution to clearly visualize the area (not a pixelated video or image)
- capture the entirety of the areas identified (no blind spots or obstructed views)
- Photographs need to be in a common file format, such as JPEG, PNG, PDF
- Video evidence needs to be in any of these supported formats
- MP4 Video file (.mp4,.m4v,.mp4v,.3g2,.3gp2,.3gp,.3gpp)
- QuickTime Movie file (.mov)
- Audio Visual Interleave (.avi)
- Microsoft Digital Video Recording (.dvr-ms)
- Moving Pictures Experts Group (.mpg,.mpeg,.m1v,.mp2,.mp3,.mpa,.mpe,.m3u)
- Documents should be in PDF format
You don't have to use any professional or special equipment to produce your footage. You can use a smart phone or a camera. Just make sure you have good lighting, so that the features in the video recording are clearly visible.
2.2 What to prepare
The site evidence package you have to submit for micro-cultivation, nursery and micro-processing licences are different from that for standard cultivation, standard processing and sale for medical purposes with possession of cannabis licences. The main difference is the different physical security requirements you have to meet.
Important: If you're applying for a micro-cultivation, nursery or micro-processing licence together with:
- a sale for medical purposes with possession of cannabis licence, you need to meet the physical security requirements for both licences, and will have to submit your physical security information in your site evidence package to show this
- a sale for medical purposes without possession of cannabis licence, you don't need to meet the extra physical security measures
2.2.1 For micro-cultivation, nursery, and micro-processing licences
This section provides information about what you need to prepare for your site evidence package for micro-cultivation, nursery and micro-processing licences.
2.2.1.1 Site plan (includes storage areas)
You need to include the following information in your site plan.
- Site perimeter
- Perimeter clearly identified (for example, highlight the fence or building envelope)
- Label what the perimeter is (for example, a fence or a building envelope)
- Buildings
- Footprint of any buildings clearly identified and uniquely labelled
- If the site perimeter is the building envelope, indicate the doors and windows along the site perimeter
- Indicate if the building is a multi-unit building or a stand-alone site (only the applicant uses this building)
- If it's a multi-unit building, you need to identify the site perimeter and label all units with their current use (such as the occupant's company name)
- Storage areas (also capture them on the floor plan)
- Location clearly identified within each building
- Outdoor grow areas, if applicable
- Footprint of any outdoor grow area clearly identified and uniquely labelled.
- Latitude and longitude coordinates for all four outer most points or corners for each grow area
2.2.1.2 Floor plans
Important: Your floor plans need to include all areas and rooms, even if there are no activities with cannabis occurring inside. For example, lavatories and transitory areas such as hallways.
You need to prepare floor plans for each building on your site where cannabis activities will take place. You can submit multiple floor plans to show different information. For example, a floor plan showing only the grow surface areas information or the cannabis flow information only. In each building's floor plan, include the following.
- Clear delineation of areas where operations, grow and storage activities will take place
- Storage areas (also capture them on the site plan)
- Locations clearly identified within each building and uniquely labelled
- Locations and names of your access control or restriction devices
- Flow of cannabis between the areas (for example, arrows drawn between areas [dirty to clean])
- For micro-cultivation and nursery licences: grow surface areas
- Clearly identify grow surface areas on the site plan and floor plans
- Include all indoor and outdoor grow areas
- Include dimensions in square meters (m2)
- Indicate if the grow surface areas have multiple surfaces (levels)
- For example, vertically arranged where surfaces are above one another (such as multiple layers of shelves)
- Submit a sample calculation of the total grow surface area to show that it doesn't exceed the limit
- You need to account for each grow surface area, including any vertically arranged surfaces
- If you're planning to use only certain grow areas at specific time periods (for example, on a rotational basis because of weather), explain how you'll not exceed the applicable size limit at any given time
- Clearly identify grow surface areas on the site plan and floor plans
2.2.1.3 Physical barrier and site design
You need to prepare the following information.
- A description of the site and how you'll prevent unauthorized access. Include any access controls at entry or exit points of the site, such as:
- doors
- windows
- fence gates
- vent openings
- A description of materials used as physical barriers to prevent unauthorized access to the site perimeter and for all storage areas. This includes:
- floors
- walls
- doors
- fences
- ceilings
- windows
- vent openings
2.2.1.4 Restricted access
You need to prepare the following information.
- A description of how the access to storage areas is restricted to only people whose presence is required
- Details on the types and specifications of access control or restriction devices for the storage areas. For example:
- padlock
- combination lock
- door lock and key
- proximity card readers or keypads with electric door strikes or electromagnetic locks
- Information on employees' access levels and method (such as issued cards, fobs, PINs, keys) for storage areas
2.2.1.5 Photographs
You need to prepare photographs in separate files for each side of the defined site perimeter (for example, east, west, south and north).
2.2.1.6 Guided video tour
You need to include the following information in the guided video tour of the entire site.
- Site perimeter
- Physical barrier (for example, fence or building envelope)
- Outdoor grow areas
- For each building, the entire building envelope (for example, east, west, south and north sides)
- Physical barrier (for example, the building envelope)
- Indoor areas
- Production process flow
- Have someone moving through the different areas describing the intended production process flow of the cannabis through the facility
- Operations areas, including grow areas
- Good production practices features
- Storage areas
- Physical barriers and access control or restriction devices
- Good production practices features
- Production process flow
2.2.2 For standard cultivation, standard processing and sale for medical purposes with possession of cannabis licences
This section provides information about what you need to prepare for your site evidence package for a standard cultivation, standard processing and a sale for medical purposes with possession of cannabis licences.
2.2.2.1 Site plan (includes storage areas)
You need to include the following information in your site plan.
- Site perimeter
- Perimeter clearly identified (for example, highlight the fence or building envelope)
- Label what the perimeter is (for example, a fence or a building envelope)
- Locations of the security devices and visual monitoring devices. Identify and uniquely label each device
- Direction or area covered by the security devices and visual monitoring devices (for example, arrows drawn or area highlighted)
- Buildings
- Footprint of any buildings clearly identified and uniquely labelled
- If the site perimeter is the building envelope, indicate the doors and windows along the site perimeter
- Indicate if the building is a multi-unit building or a stand-alone site (only the applicant uses this building)
- If it's a multi-unit building, you need to identify the site perimeter and label all units with their current use (such as the occupant's company name)
- Storage areas (also capture them on the floor plan)
- Location clearly identified within each building
- Locations of the security devices and visual monitoring devices for the storage areas. Identify and uniquely label each device
- Direction or area covered by the security devices and visual monitoring devices (for example, arrows drawn or area highlighted)
- Outdoor grow areas, if applicable
- Footprint of any outdoor grow area clearly identified and uniquely labelled
- Latitude and longitude coordinates for all four outer most points or corners for each grow area
2.2.2.2 For outdoor areas (security and visual monitoring devices)
You need to include the following information (can be on the site plan).
- Locations of the security devices and visual monitoring devices. Identify and uniquely label each device
- Direction or area covered by the security devices and visual monitoring devices (for example, arrows drawn or area highlighted)
2.2.2.3 Floor plans
Important: Your floor plan needs to include all areas and rooms, even if there are no activities with cannabis occurring inside. For example, lavatories and transitory areas such as hallways.
You need to prepare floor plans for each building on your site where cannabis activities will take place. You can submit multiple floor plans to show different information. For example, a floor plan showing only the security device information or the cannabis flow information only. In each building's floor plan, include the following.
- Clear delineation of areas where operations, grow and storage activities will take place
- Storage areas (also capture them on the site plan)
- Locations clearly identified within each building and uniquely labelled
- Locations of the security devices and visual monitoring devices clearly identified and uniquely labelled
- Direction or area covered by the security devices and visual monitoring devices (for example, arrows drawn or area highlighted)
- Locations and names of your access control or restriction devices
- Areas that storage areas are in
- Locations of the security devices and visual monitoring devices clearly identified and uniquely labelled
- Direction or area covered by the security devices and visual monitoring devices (for example, arrows drawn or area highlighted)
- Any operations area (including indoor grow areas)
- Locations of the security devices and visual monitoring devices clearly identified and uniquely labelled
- Direction or area covered by the security devices and visual monitoring devices (for example, arrows drawn or area highlighted)
- Locations and names of your access control or restriction devices
- Flow of cannabis between the areas (for example, arrows drawn between areas [dirty to clean])
2.2.2.4 Physical barrier and site design
You need to prepare the following information.
- A description of the site and how you'll prevent unauthorized access. Include any access controls at entry or exit points of the site, such as:
- doors
- windows
- fence gates
- vent openings
- A description of materials used as physical barriers to prevent intrusion for the site perimeter, all the operations areas (including all grow areas), and storage areas and the areas they're in. This includes:
- floors
- walls
- doors
- fences
- ceilings
- windows
- vent openings
2.2.2.5 Visual monitoring devices
This section provides information you need to prepare about your visual monitoring devices that will need to be submitted.
2.2.2.5.1 Visual monitoring devices detail
You need to prepare the following information.
- A description of each device type and specifications, including:
- operating temperature range
- any special features (such as infrared or night vision, weatherproofing for outdoor use)
- A description of how the devices work at all times (for example, during a power outage). This can include having:
- a back-up generator
- an uninterruptible power supply
2.2.2.5.2 Still shots and footage from visual recording devices
You need to prepare still shots from all visual recording devices (daytime and nighttime shots for each device) covering:
- the site perimeter (for example, east, west, south and north)
- all operations areas, including the entry and exit points of all grow areas
- all storage areas and the areas they're in
Important: You need to submit a daytime and nighttime shot for each device in separate files.
- Footage from visual recording devices covering:
- the site perimeter (for example, east, west, south and north)
- show complete coverage by displaying multiple visual recording device feeds that shows a person walking around the perimeter
- all operations areas, including the entry and exit points of the grow areas
- the site perimeter (for example, east, west, south and north)
- all storage areas and the areas they're in
2.2.2.6 Intrusion detection devices
This section provides information you need to prepare about your intrusion detection devices that will need to be submitted.
2.2.2.6.1 Intrusion detection devices detail
You need to prepare the following information.
- Details on your intrusion devices and systems
- Each device type and specifications, including:
- intended use
- operating temperature range
- motion detection range, if applicable
- any special features (such as weatherproofing for outdoor use, tamper-resistance)
- A description of how the systems work at all times (for example, during operating hours and a power outage). This can include having:
- a back-up generator
- an uninterruptible power supply
- A description of how the systems detect tampering at all times (such as back up telephone line, double relay)
- A description of how the systems are continuously monitored (365 days a year, 7 days a week and 24 hours a day), either on-site or off-site (for example, use of a ULC-certified monitoring company)
- Each device type and specifications, including:
- A description of the procedure when an alarm is triggered and your response. Include creating and retaining records of detected occurrences:
- date and time of the occurrence
- date and time of response including measures taken
2.2.2.6.2 Alarm security reports
You need to prepare the following information.
- Test reports for intrusion detection devices
- In these areas:
- site perimeter
- all outdoor and indoor operating areas
- storage areas and the areas they're in
- For each area:
- date and time of the test for each device
- name of the device (same names as on site and floor plans)
- name of area where the device is (same names as on site and floor plans)
- For each area:
- Alarm zone assigned to each intrusion detection device
- Access (entry and exit) log reports for all doors leading to and from storage areas. These reports need to contain, for each access:
- date and time
- name of the device (same as on site and floor plans)
- name of area where the device is
- name of the person (entering and exiting)
- In these areas:
2.2.2.7 Restricted access
You need to prepare the following information.
- A description of how the access to operations areas (including grow areas), and storage areas is restricted to only people whose presence is required
- Details on the types and specifications of access control or restriction devices. For example:
- padlock
- combination lock
- door lock and key
- proximity card readers or keypads with electric door strikes or electromagnetic locks
- Information on employees' access levels and method (such as issued cards, fobs, PINs, keys) for the operation areas including grow areas, storage areas and the areas they're in
2.2.2.8 Access log
You need to prepare the access (entry and exit) logs for all doors leading to and from storage areas. Include the following:
- a description of how you'll log access to storage areas for employees, as well as visitors and contractors
- the method used to record the identities of every entry or exit of a storage area
- the information that will be recorded, for example:
- date and time of entry and exit
- name of the area being accessed
- identifier for the access point used such as door or gate
- name of person accessing the storage areas
2.2.2.9 Photographs
You need to prepare photographs in separate files for each side of the defined site perimeter (for example, east, west, south and north).
2.2.2.10 Guided video tour
You need to include the following information in the guided video tour of the entire site.
- Site perimeter
- Physical barrier (for example, fence or building envelope)
- All security features
- Outdoor grow areas
- All security features
- For each building, the entire building envelope (for example, east, west, south and north sides)
- Physical barrier (for example, building envelope)
- Indoor areas
- Production process flow
- Have someone moving through the different areas describing the intended production process flow of the cannabis through the facility
- Operation areas, including all grow areas
- All security features
- Good production practices features
- Production process flow
- Storage areas and the areas they're in
- All security features
- Good production practices features
3.0 Forms and template
Attestations required in completing your licence application:
- For all licence types:
- Record keeping attestation
- For site ownership, if other individuals or organizations own the site, each site owner needs to fill out a Site owner consent form for your licence application.
- For micro-processing and standard processing licences
Page details
- Date modified: