DRDC demonstrates satellite capabilities during Op NANOOK
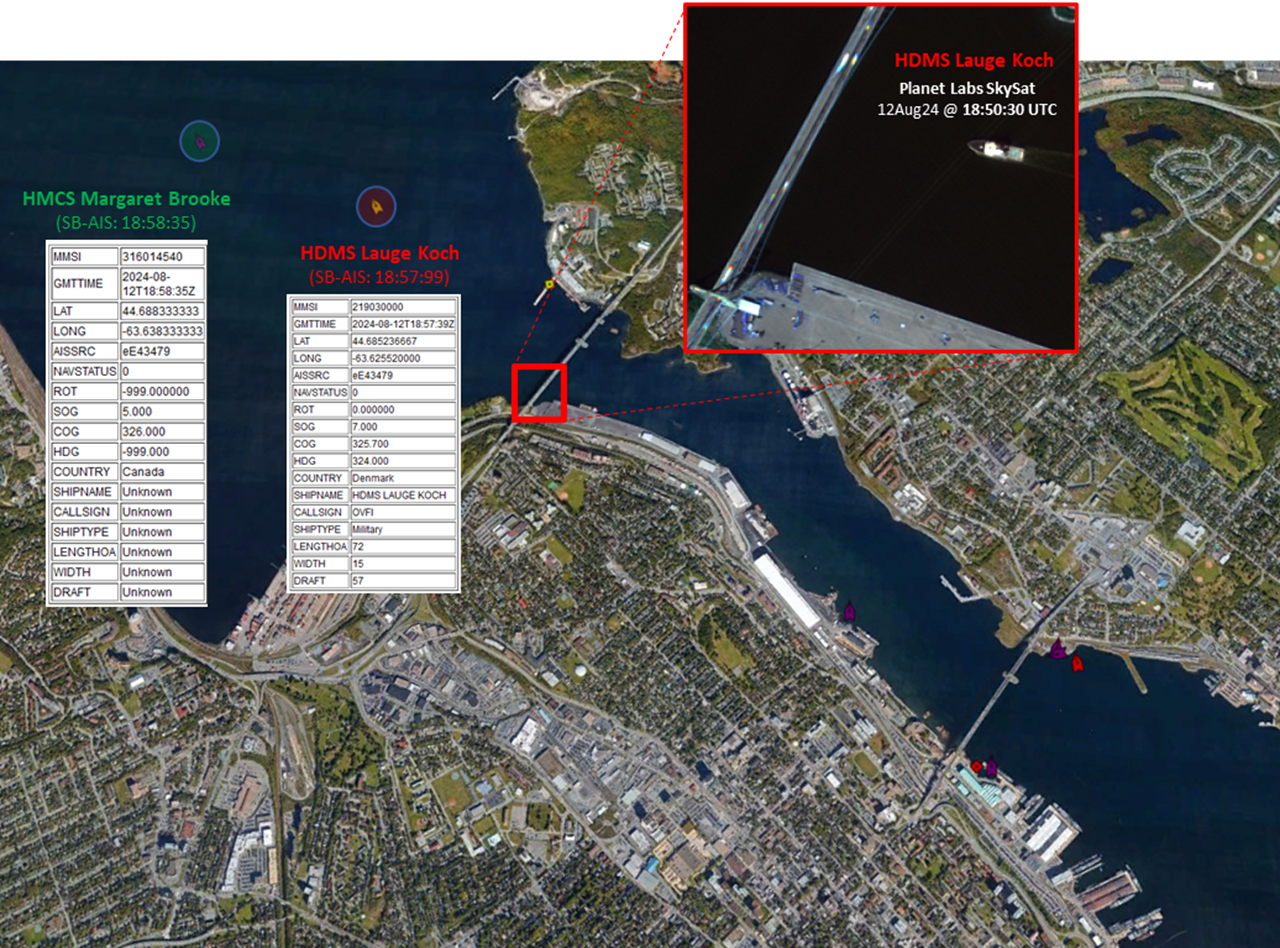
Caption
EN: Figure 1: AIS reported positions of two of the four Commander’s Task Group (CTG) 300.10 vessels departing assembly area HMC Dockyard Halifax as part of OP NANOOK 2024. In the main image, AIS data overlaid on Google Maps shows the HDMS Lauge Koch sailing behind HMCS Margaret Brooke and around the Bedford Basin. The upper right inset image shows the HDMS Lauge Koch captured in the Planet Labs SkySat image acquired on 12 August 2024 at 18:50:30 UTC whilst its position was reported 7 minutes later by AIS.
Imagery intelligence product © DRDC (2024). Background image reproduced with permission from Google.
December 12, 2024 - Defence Stories
Estimated read time - 3:00
For the second year in a row, Defence Research and Development Canada (DRDC), supported by the Canadian Forces Intelligence Group, planned and completed a Space-Based Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (SB ISR) scientific experiment during Operation NANOOK – TUUGAALIK (NA-TU) and NANOOK - NUNAKPUT (NA-NK) 2024.
This annual activity aims at enhancing Canadian Armed Forces (CAF) joint capabilities in Arctic surveillance and mobility along Canada’s Northwest Passage.
From August 4th to August 31st, 2024, with support from several Department of National Defence (DND) organizations, Canadian industry and US industry partners, the space-based ISR experiment brought together representatives from the Ottawa Research Centre (ORC), the Valcartier Research Centre (VRC) and the Canadian Forces Joint Imagery Centre (CFJIC) and Mapping and Charting Establishment (MCE).
The main aim of the DRDC SB ISR Experiment 2024 was to demonstrate and assess how the DND/CAF could use commercial satellites for space-based ISR, by using commercial data and research technologies that compress parts of the Tasking, Collection, Processing, Exploitation and Dissemination (TCPED) cycle.
DRDC accessed a hybrid constellation of more than 250 commercial Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites to collect on participating vessels and aircraft in six different military scenarios. These commercial constellations and satellites included instruments for electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) data (including panchromatic, multispectral, and hyperspectral imagery), synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery (both C-band and X-band images), and ground and space-based automatic identification system (AIS) message data.
These constellations and satellites were used to test ORC’s collection planning tool Commercial Satellite Imagery Acquisition Planning System (CSIAPS) and four semi-automated EO/IR, SAR and AIS data processing and exploitation software prototype systems.
Seven spot reports (SPOTREPs) containing analysis from the semi-automated toolsets were produced during the exercise for different elements of the Royal Canadian Navy (RCN) and CJOC’s Joint Task Force North (JTFN), and as a method to gather feedback for the experiment.
This experimental work supported a program of Arctic warfare-related experimentation and Canada’s commitment to improving the CAF’s expertise, readiness, and interoperability in the Arctic region.
Glossary
- A hybrid constellation refers to a group of satellites, which can be a combination of commercial, military and government satellites of different sizes and capabilities, being used together to complete a task.
- Panchromatic imagery combines information from the visible, red, green and blue (RGB) bands.
- Multispectral imagery captures image data of the scene within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Hyperspectral imagery captures the spectrum of each pixel, providing the detection and identification of materials and targets of the scene using their spectral signatures.
- Synthetic aperture radar is a remote-sensing technology that emits a pulse of energy and measures the reflected energy from the Earth’s surface.
- X-band and C-band are common airborne radar systems. (Source: Radar Basics)
- The Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a maritime digital positional awareness system. (Source: Automatic Identification System (AIS) on Ships)
Related links:
Contributor:
Pierre Lamontagne
Space & ISR Section,
DRDC Ottawa Research Centre
In collaboration with DRDC Internal and Corporate Communications Services