1. Canadian indicators for the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) – article 5: equality and non-discrimination
On this page
Alternate formats
A PDF version of the Canadian Indicators for the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is available on the index page.
1.1 Discrimination of any type
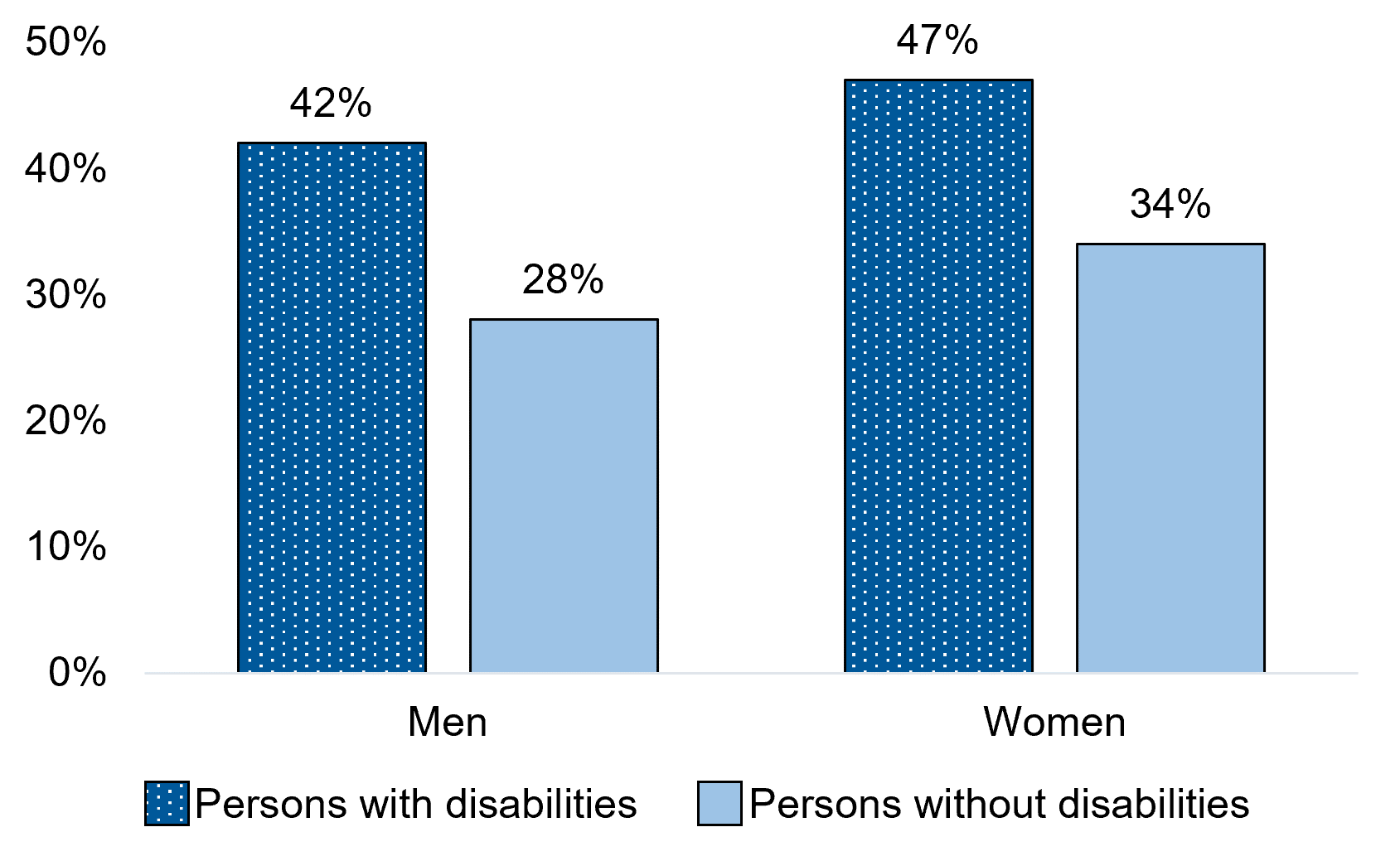
Figure 1.1 - Text description
| Gender | Persons with disabilities | Persons without disabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Men+ | 42% | 28%* |
| Women+ | 47% | 34%* |
* significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Notes: "Discrimination of any type" refers to respondents being treated differently, negatively, or adversely because of their race, age, religion, sex, etc.
- To protect the confidentiality of non-binary persons, a two-category gender variable was used, given the relatively small size of this population in Canada. Non-binary respondents were redistributed into the men and women categories, denoted as "men+" and "women+" in charts and tables.
- * significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Differences between men and women are statistically significant for both persons with and without disabilities (p<0.05).
- Source: Statistics Canada, General Social Survey - Social Identity, 2020 (Social Research Division calculations).
In the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, men with disabilities were 1.5 times as likely as those without disabilities to face discrimination of any type (42% versus 28%). Similarly, women with disabilities were more likely than those without disabilities to experience discrimination of any type in the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic (47% versus 34%).
Generally, women were more likely than men to experience discrimination regardless of disability status.
1.2 Discrimination based on a physical or mental disability
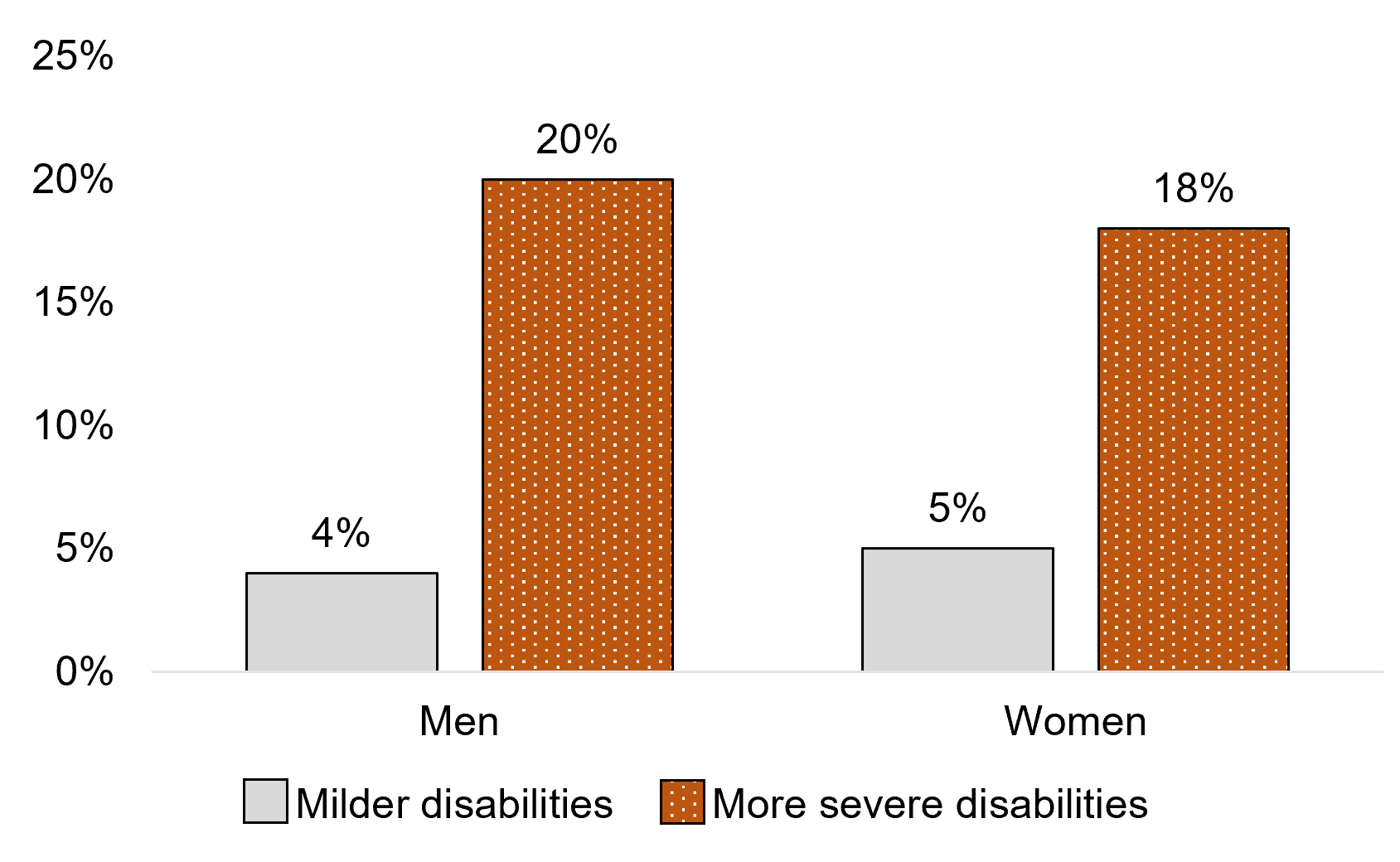
Figure 1.2 - Text description
| Gender | Milder disabilities | More severe disabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Men+ | 4% | 20%* |
| Women+ | 5% | 18%* |
* significantly different from estimate for persons with milder disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Notes: Respondents were asked if, in the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, they had experienced discrimination or had been treated unfairly by others because of a physical or mental disability.
- To protect the confidentiality of non-binary persons, a two-category gender variable was used, given the relatively small size of this population in Canada. Non-binary respondents were redistributed into the men and women categories, denoted as "men+" and "women+" in charts and tables.
- "Milder" disabilities combines those with "mild" and "moderate" disabilities. "More severe" disabilities combines those with "severe" and "very severe" disabilities.
- * significantly different from estimate for persons with milder disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- For both levels of severity, differences between men and women are not statistically significant (p<0.05).
- Source: Statistics Canada, General Social Survey - Social Identity, 2020 (Social Research Division calculations).
In the 5 years before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, men with more severe disabilities were 5 times as likely as those with milder disabilities to experience discrimination based on a physical or mental disability (20% versus 4%). Similarly, women with more severe disabilities were over 3 times as likely as those with milder disabilities to experience discrimination based on a physical or mental disability (18% versus 5%).
1.3 Discrimination based on physical appearance
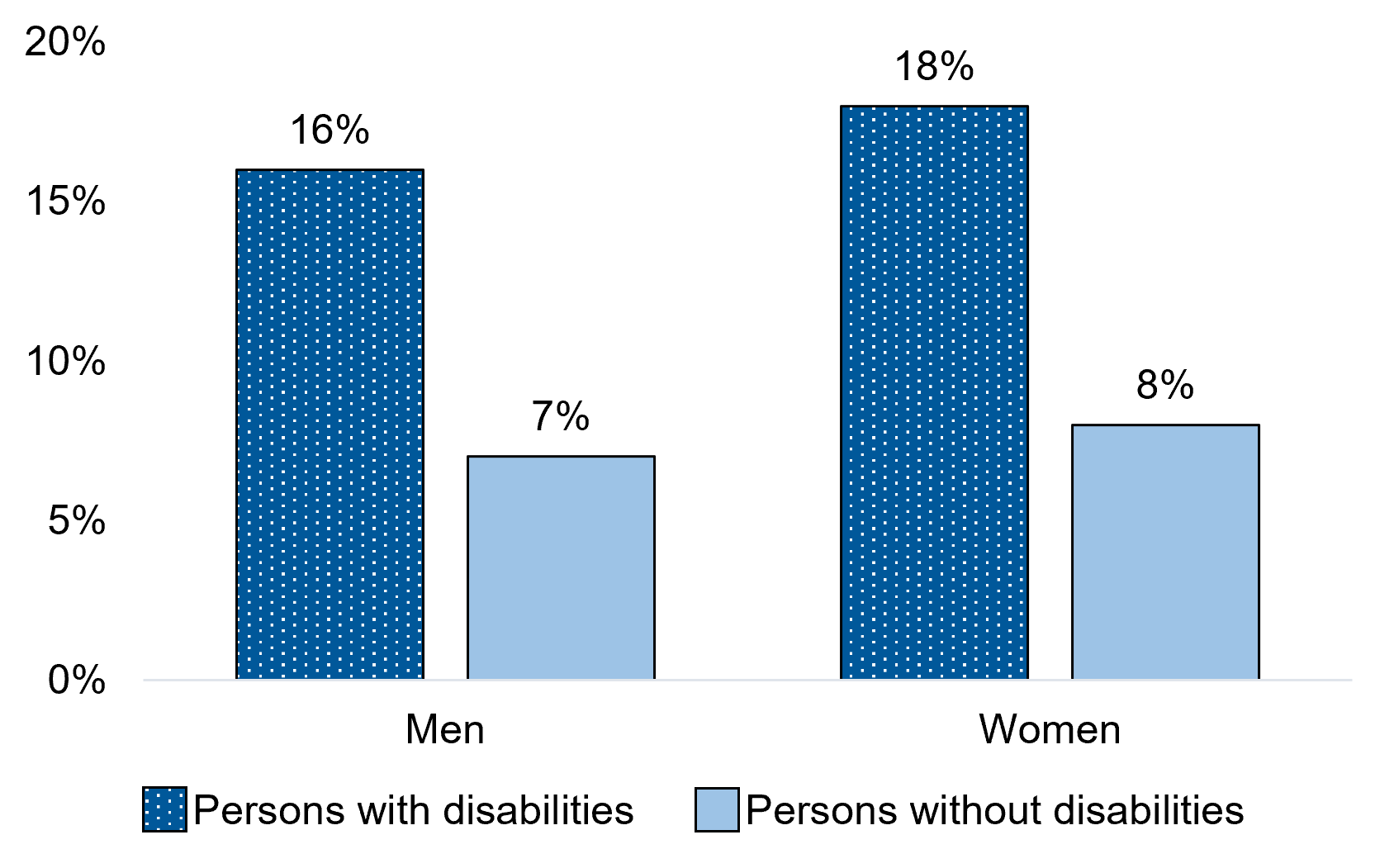
Figure 1.3 - Text description
| Gender | Persons with disabilities | Persons without disabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Men+ | 16% | 7%* |
| Women+ | 18% | 8%* |
* significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Notes: Respondents were asked if, in the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, they had experienced discrimination or had been treated unfairly by others because of their physical appearance.
- To protect the confidentiality of non-binary persons, a two-category gender variable was used, given the relatively small size of this population in Canada. Non-binary respondents were redistributed into the men and women categories, denoted as "men+" and "women+" in charts and tables.
- * significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Differences between men and women are not statistically significant for both persons with and without disabilities (p<0.05).
- Source: Statistics Canada, General Social Survey - Social Identity, 2020 (Social Research Division calculations).
In the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, persons with disabilities aged 15 years and over were more than twice as likely as persons without disabilities to be discriminated against based on their physical appearance. Among men, 16% of those with disabilities and 7% of those without disabilities reported experiencing this type of discrimination. Similarly, 18% of women with disabilities and 8% of women without disabilities reported this type of discrimination.
1.4 Age-based discrimination
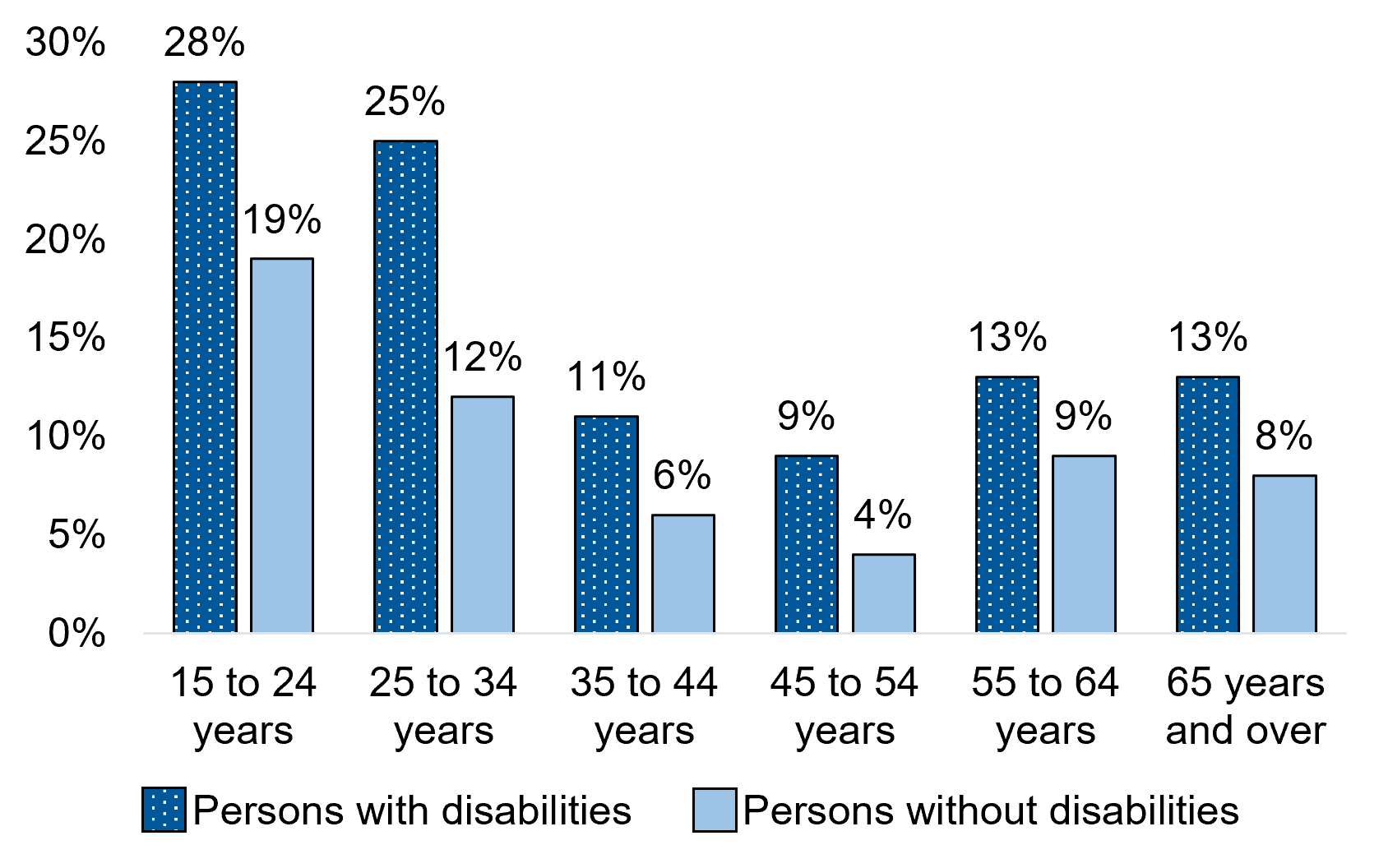
Figure 1.4 - Text description
| Age group | Persons with disabilities | Persons without disabilities |
|---|---|---|
| 15 to 24 years | 28% | 19%* |
| 25 to 34 years | 25% | 12%* |
| 35 to 44 years | 11% | 6%* |
| 45 to 54 years | 9% | 4%* |
| 55 to 64 years | 13% | 9%* |
| 65 years and over | 13% | 8%* |
* significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same age group (p<0.05)
- Notes: Respondents were asked if, in the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, they had experienced discrimination or had been treated unfairly by others because of their age.
- * significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same age group (p<0.05)
- Among persons with disabilities, except for those aged 25 to 34 years, estimates for all other age groups are significantly different from estimates for persons aged 15 to 24 years (p<0.05).
- Among persons without disabilities, differences between those aged 15 to 24 years and all other age groups are statistically significant (p<0.05).
- Source: Statistics Canada, General Social Survey - Social Identity, 2020 (Social Research Division calculations).
Across all 6 age groups, persons with disabilities were more likely than persons without disabilities to face age-based discrimination in the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic. Regardless of disability status, younger respondents were more likely than older respondents to face age-based discrimination. Persons aged 15 to 24 years with and without disabilities (28% and 19% respectively) were more than twice as likely to report experiencing such discrimination as those aged 65 years and over (13% and 8% respectively). Prevalence of age-based discrimination was highest among persons aged 15 to 24 years and gradually decreased with age to reach its lowest value among persons aged 45 to 54 years. It then increased slightly among persons aged 55 to 64 years and 65 years and over.
1.5 Sex-based discrimination
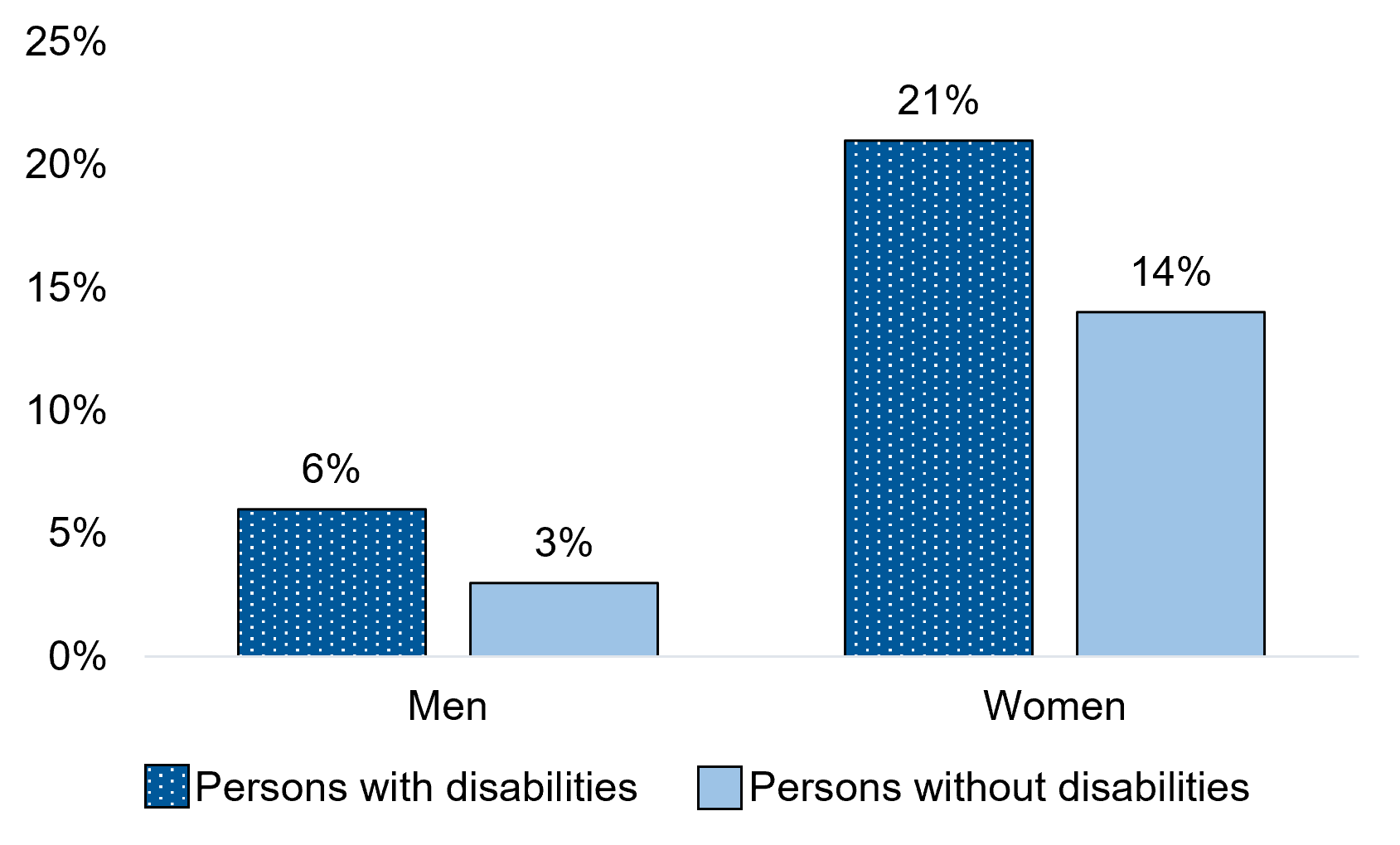
Figure 1.5 - Text description
| Gender | Persons with disabilities | Persons without disabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Men+ | 6% | 3%* |
| Women+ | 21% | 14%* |
* significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Notes: Respondents were asked if, in the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, they had experienced discrimination or had been treated unfairly by others because of their sex.
- To protect the confidentiality of non-binary persons, a two-category gender variable was used, given the relatively small size of this population in Canada. Non-binary respondents were redistributed into the men and women categories, denoted as "men+" and "women+" in charts and tables.
- * significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Differences between men and women are statistically significant for both persons with and without disabilities (p<0.05).
- Source: Statistics Canada, General Social Survey - Social Identity, 2020 (Social Research Division calculations).
In the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, men with disabilities aged 15 years and over were twice as likely as those without disabilities to experience discrimination based on their sex (6% versus 3%). Similarly, women with disabilities aged 15 years and over were 1.5 times as likely as women without disabilities to experience discrimination based on their sex (21% versus 14%) in that time frame. Regardless of disability status, women were more likely than men to report experiencing sex-based discrimination in the 5 years before the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
1.6 Discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity/expression
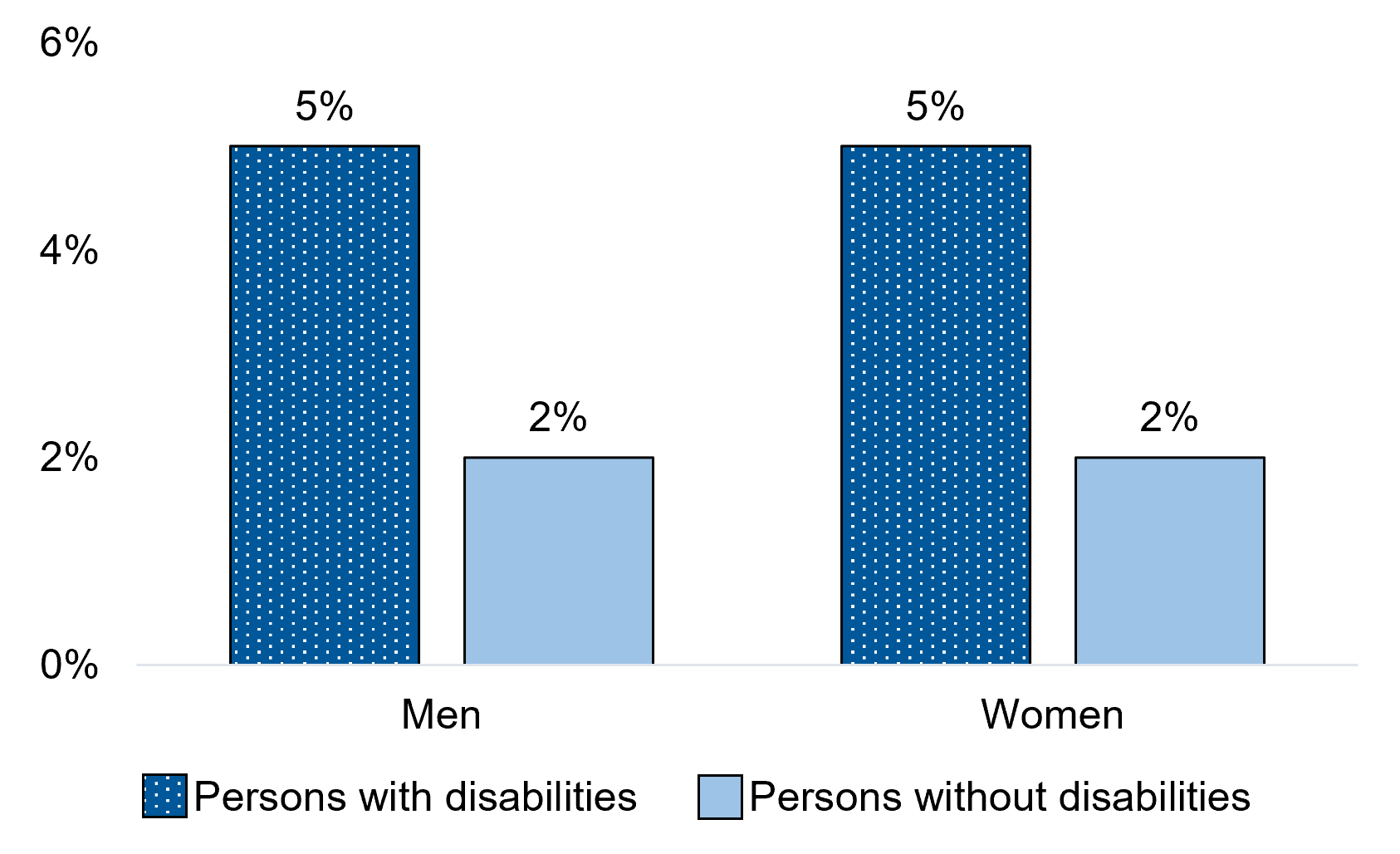
Figure 1.6 - Text description
| Gender | Persons with disabilities | Persons without disabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Men+ | 5% | 2%* |
| Women+ | 5% | 2%* |
* significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Notes: Respondents were asked if, in the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, they had experienced discrimination or had been treated unfairly by others because of their sexual orientation or their gender identity or expression. Gender identity or expression include gender diverse identities such as transgender, two-spirit, non-binary.
- Due to data quality concerns, reported experiences of discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity or expression were combined.
- To protect the confidentiality of non-binary persons, a two-category gender variable was used, given the relatively small size of this population in Canada. Non-binary respondents were redistributed into the men and women categories, denoted as "men+" and "women+" in charts and tables.
- * significantly different from estimate for persons with disabilities in the same gender category (p<0.05)
- Differences between men and women are not statistically significant for both persons with and without disabilities (p<0.05).
- Source: Statistics Canada, General Social Survey - Social Identity, 2020 (Social Research Division calculations).
In the 5 years before the COVID-19 pandemic, persons with disabilities aged 15 years and over were over twice as likely as those without disabilities to experience discrimination based on their sexual orientation or gender identity/expression. Among persons with disabilities, 5% of men and women had experienced this type of discrimination, compared with 2% of men and women without disabilities.