Compliance and enforcement policy framework
Health Canada's approach to compliance and enforcement, including roles and responsibilities, actions and tools, guiding principles and decision factors.
On this page
- Roles and responsibilities
- Actions and tools
- Guiding principles
- Decision factors
- Visual representation of Health Canada’s general approach to compliance and enforcement
Roles and responsibilities
Health Canada is responsible for helping Canadians maintain and improve their health. Our compliance and enforcement activities help protect you against health and safety risks by:
- supporting the development of acts and regulations for many types of products
- conducting compliance and enforcement actions to help make sure these laws are being followed
This policy framework aims to promote fairness, consistency, transparency and predictability in our compliance and enforcement actions. It overlays and is supported by other established departmental policies, as they relate to specific products, activities and processes regulated by Health Canada.
This compliance and enforcement policy framework will be reviewed every 2 years to ensure it is current and continues to meet the needs of interested parties.
Who has responsibilities under our acts and regulations?
Health Canada, regulated parties and consumers all have responsibilities.
Health Canada
Health Canada helps prevent or reduce risks to your health and safety and the environment. Health Canada is responsible for:
- supporting the development and administration of acts and regulations related to health and safety
- communicating information about health and safety risks to Canadians
- taking actions to help ensure regulated parties meet their legal obligations. The actions that we take fall into three categories:
- compliance promotion: educating and promoting compliance with the law
- compliance monitoring: monitoring and verifying that products, activities and processes comply with the law
- enforcement: taking actions when and if products, activities and processes do not comply with the law
Regulated parties
Regulated parties have mandatory responsibilities under Health Canada's acts and regulations. For regulated products, the key activities that are regulated are:
- importation
- manufacturing
- sale (including distribution)
- advertising
Regulated parties are responsible for:
- understanding the law as it applies to them
- ensuring their products, activities and processes comply with applicable laws
Consumers
Consumers are those who buy and use products in Canada. They are responsible for:
- maintaining and protecting their health and safety and that of others through the appropriate use of products
- making informed decisions about their health and safety
Actions and tools
A wide range of compliance and enforcement actions and tools are available to Health Canada. We can choose the actions, tools and level of intervention that are the most appropriate for the situation.
We use actions and tools that fall under three main categories:
Some actions and tools are designed to help regulated parties understand their responsibilities under the law. Other actions and tools are designed to induce compliance with the law.
Following the premise that the majority of regulated parties will comply with laws if they are aware of them and understand them, Health Canada actively works to promote and monitor compliance. When necessary, enforcement actions are used to address non-compliance with the law.
These actions and tools can be used individually, together or in a graduated manner based on the situation. In some cases, compliance promotion and compliance monitoring are used on an on-going basis.
Compliance promotion
Through compliance promotion we focus on helping regulated parties be aware of, access, understand and comply with the acts and regulations. Actions and tools under this category aim to minimize risks and may include:
- developing and providing education, guidance and information to regulated parties and other stakeholders
- collaborating and consulting with regulated parties and other stakeholders on health and safety requirements
- supporting the development of:
- policies
- guidelines
- standards
- regulations
Compliance monitoring
Through compliance monitoring, we focus on verifying that products and regulated parties comply with the law and we identify risks posed by products or activities. These activities encourage compliance of regulated parties and minimize risks. They may include:
- recording, obtaining or analyzing information on:
- products
- regulated parties
- activities and processes
- carrying out inspections
- sampling and analyzing products to evaluate compliance and identify risks
- following up on complaints, incident reports and adverse reactions
- in appropriate circumstances, sharing information and reports with international, federal, provincial or territorial partners
Enforcement
We take enforcement actions to:
- bring a regulated party, product, activity or process into compliance with the laws
- prevent future non-compliance
Depending on the applicable acts and regulations, we take enforcement actions which may include:
- where appropriate, disclosing information through items such as inspection reports
- publishing alerts, advisories or other risk communications
- pursuing voluntary recalls or other measures, such as labelling changes, to bring a product, activity or process into compliance
- entering into compliance agreements with industry
- issuing warning letters
- adding terms and conditions to licences
- issuing orders for recalls and stop sales of products
Additional enforcement actions may include:
- cancelling or suspending licences or market authorizations
- preventing the sale, import, advertisement or manufacture of non-compliant products
- undertaking activities related to seizure, detention and forfeiture of products
- imposing financial penalties
- applying for injunctions
- conducting criminal investigations
- recommending prosecution
Guiding principles
Health Canada is guided by a number of principles in carrying out our compliance and enforcement activities.
Accountability
Health Canada is accountable to Parliament and to Canadians to help ensure that the compliance and enforcement actions and decisions are consistent with:
- our mandate, values, policies, legal and operational frameworks
- the public interest
- any applicable international requirements
Fairness, consistency and impartiality
Health Canada's acts and regulations are applied in a fair, consistent and impartial manner. Qualified and authorized personnel carry out our compliance and enforcement activities in ways that are reasonable, professional, unbiased and unprejudiced.
Our staff will act with the highest levels of integrity, as set out in the Values and Ethics Code for the Public Sector.
Transparency
Health Canada strives to make its compliance and enforcement actions and decision-making process clear and understandable to everyone. The department provides access to relevant, useful and timely information about compliance and enforcement while respecting privacy rights. One of the ways we do this is by publishing data through our regulatory transparency and openness initiatives.
Targeted and outcomes focused
Health Canada's compliance and enforcement actions are targeted to have the most positive impact on health and safety outcomes based on the effective use of resources. We use the most appropriate actions and tools based on the impact of non-compliance for each situation.
Evidence based
Health Canada's compliance and enforcement actions and decisions are based on the best available evidence, information and science.
Evidence is assessed objectively and is based on Health Canada's Decision Making Framework for Identifying, Assessing and Managing Health Risks and other departmental risk frameworks.
Decision factors
There are several factors that Health Canada uses to identify the most appropriate way to address an issue given the specific situation.
Health and safety risk factors
These factors involve the existing and potential risks posed to the health and safety of Canadians and in some cases the environment. This takes into account the:
- nature of the product
- nature of the regulated activity
- characteristics of any non-compliance
- consequences of non-compliance
These factors range from no or minimal risk to high risk. Our general approach to identifying, assessing and managing risks is detailed under Health Canada's Decision Making Framework for Identifying, Assessing and Managing Health Risks
Health Canada branches and programs establish policies and guidance on risk evaluation for specific products, activities and processes.
Behaviours of the regulated party
These factors include the conduct of the regulated party with respect to issues of compliance and the party's willingness and ability to comply with the law. Behaviours can range from unintended non-compliance to deliberate avoidance of obligations under the law, such as disregarding warnings.
Compliance history of the regulated party
Health Canada takes into account the previous compliance activities of the regulated party, which include:
- any previous efforts to achieve compliance
- previous levels of cooperation with Health Canada and other regulators
The compliance history can range from a one-off issue to repeated non-compliance.
Other considerations
Depending on the issue additional decision factors may include the:
- scope of the issue
- distribution of product
- likelihood that the issue will occur again
- expected impact and success of compliance and enforcement actions
- precedent set by the issue and overall integrity of the regulatory regime
- other unique circumstances
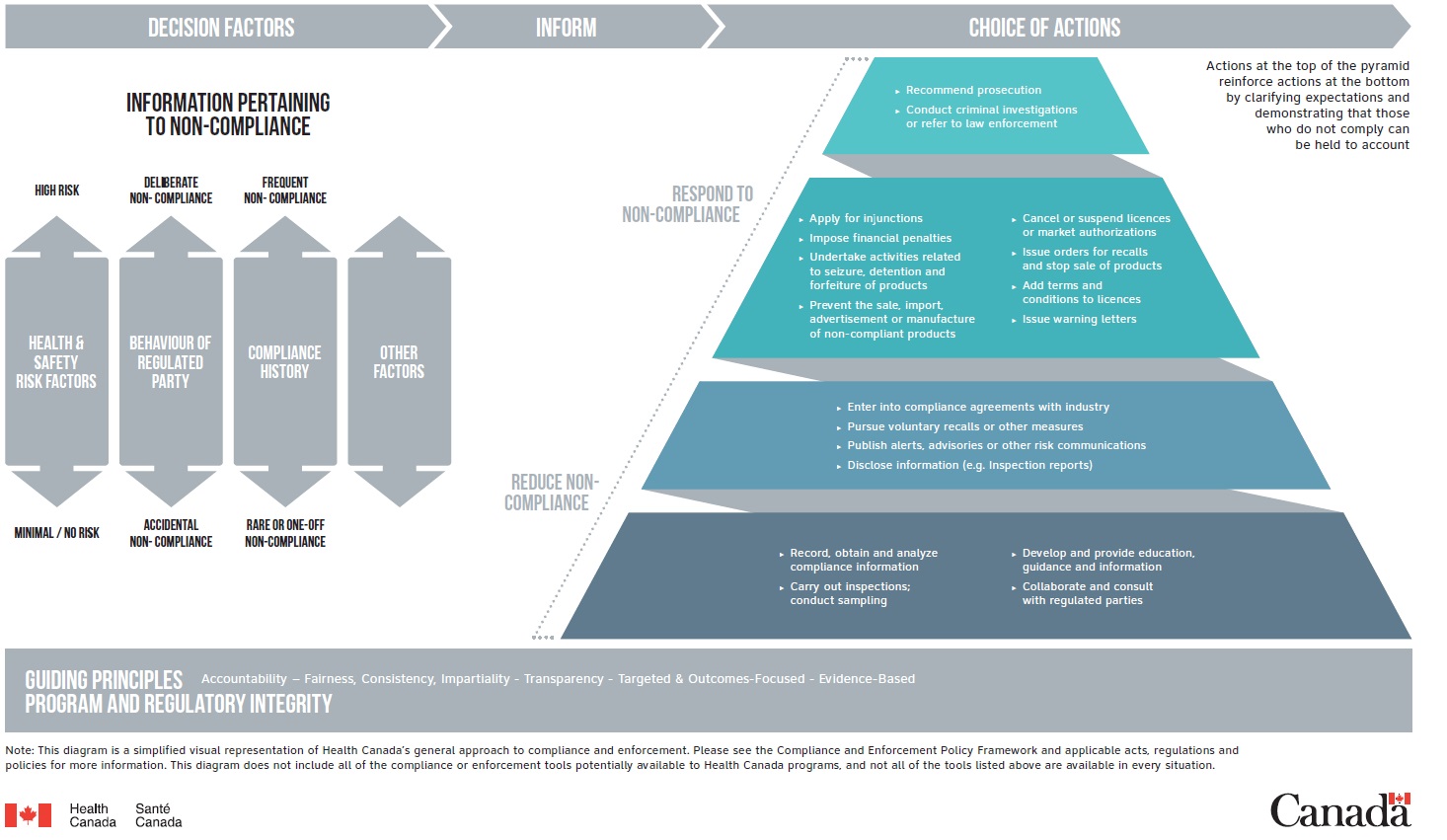
Visual representation of Health Canada’s general approach to compliance and enforcement
This diagram is a simplified visual representation of Health Canada’s general approach to compliance and enforcement.
The decision factors inform the choice of actions.
Decision factors
Information pertaining to non-compliance:
- health and safety risk factors
- behaviour of regulated parties, e.g., including conformance with the conditions of a marketing authorization and post-authorization reporting requirements
- compliance history
- other factors
Choice of actions
A choice of actions intended to reduce non-compliance or respond to non-compliance are presented in a pyramid. Actions at the top of the pyramid reinforce actions at the bottom by clarifying expectations and demonstrating that those who do not comply can be held to account.
Actions:
- record, obtain and analyze compliance information
- carry out inspections; conduct sampling
- develop and provide education guidance and information
- collaborate and consult with regulated parties, regulatory partners and stakeholders
- enter into compliance agreements with industry
- pursue voluntary recalls or other measures
- publish alerts, advisories or other risk communications
- disclose information such as inspection reports
- apply for injunctions
- impose financial penalties
- undertake activities related to seizure, detention and forfeiture of products
- prevent the sale, import, advertisement or manufacture of non-compliant products
- cancel or suspend licences or market authorizations
- issue orders for recalls and stop sale of products
- add terms and conditions to licences
- issue warning letters
- conduct criminal investigations or refer to law enforcement
- recommend prosecution
The decision model is based on a foundation of program and regulatory integrity and guiding principles:
- accountability
- fairness, consistency, impartiality
- transparency
- targeted and outcomes-focused
- evidence-based
Please see the compliance and enforcement policy framework and applicable acts, regulations and policies for more information. This diagram does not include all of the compliance or enforcement tools potentially available to Health Canada programs, and not all of the tools listed above are available in every situation.