Lingua franca – Chapter 5: Technical studies
On this page

Technical Studies
Microfade testing
Microfade testing measures the accelerated fading of photographs and related materials. It is a highly precise and minimally destructive technique used mainly to identify colourants and materials that have a high sensitivity to light.


Polarizing viewer
This non-destructive test can be used to determine if a negative is either cellulose acetate or cellulose nitrate rather than polyester. This test cannot differentiate between cellulose acetate and nitrate bases.
It is important to identify if a negative is polyester, since polyester is more stable than acetate.
Place the negative in question in a polarizing viewer or between two polarizing filters/films. Make sure that you observe the thinnest possible density of the negative through the polarizing viewer. The clear outer edge is a good choice. With the viewer polarized (the film looks black), hold the viewer up to a light source, while tilting to observe any colour change. If no rainbow colours are visible, the negative is on an acetate support. If a pattern of pink, blue, green rainbow effect becomes visible, then the negative support is polyester. This occurs because polyester film is highly birefringent and easily identified by interference patterns (i.e. rainbow colours) that are produced when the film is viewed through polarizing filters.
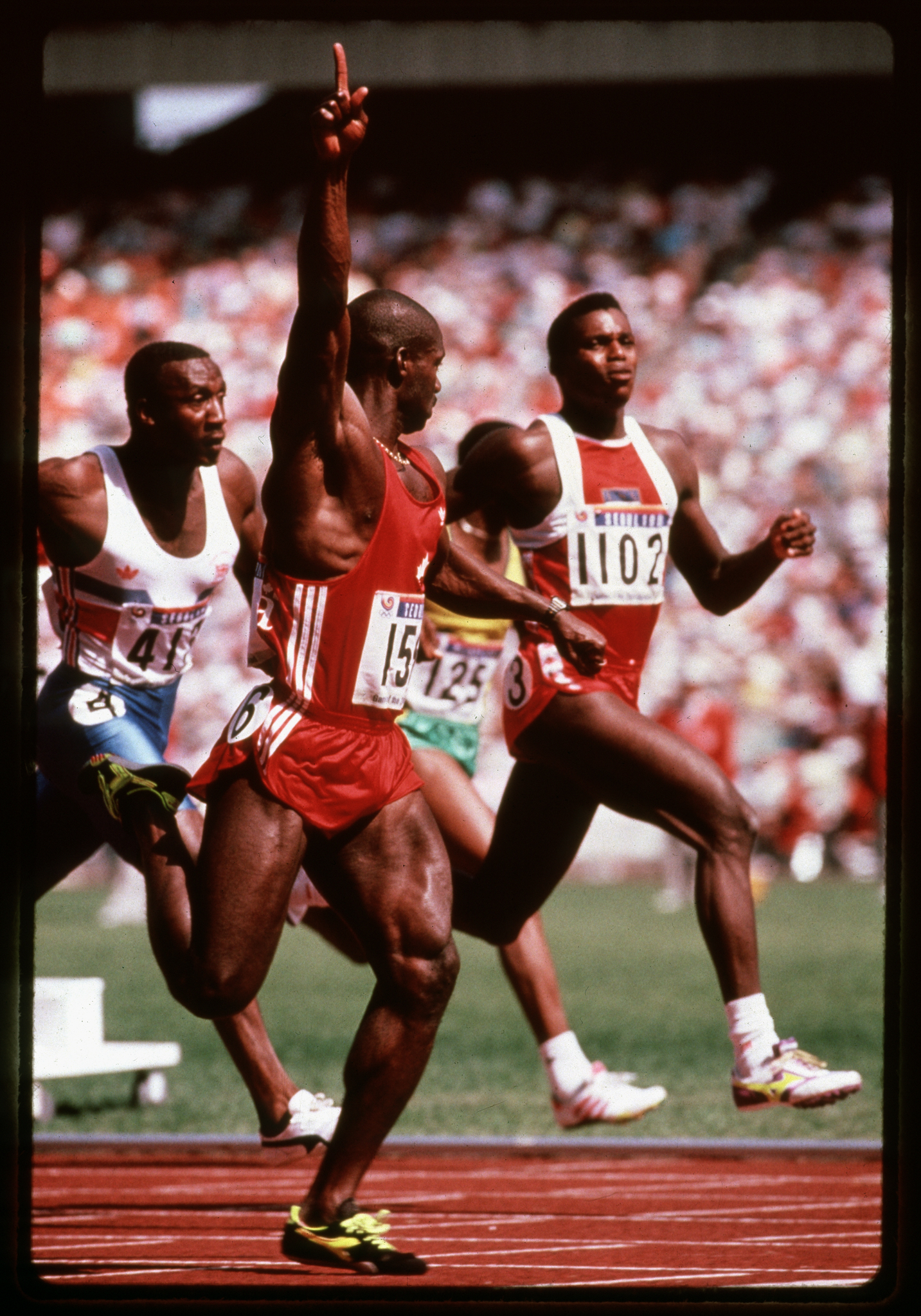
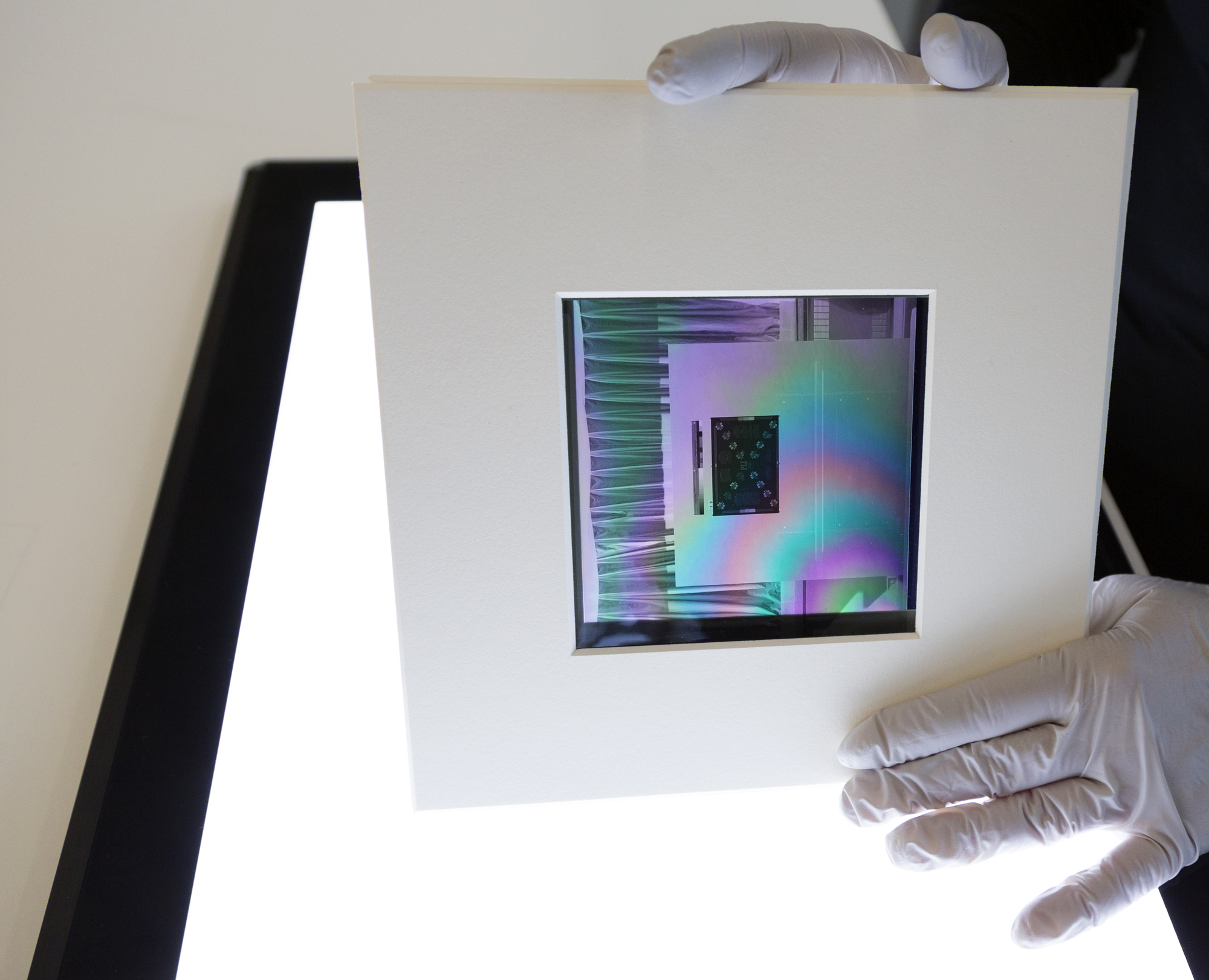

Credit: Ted Grant
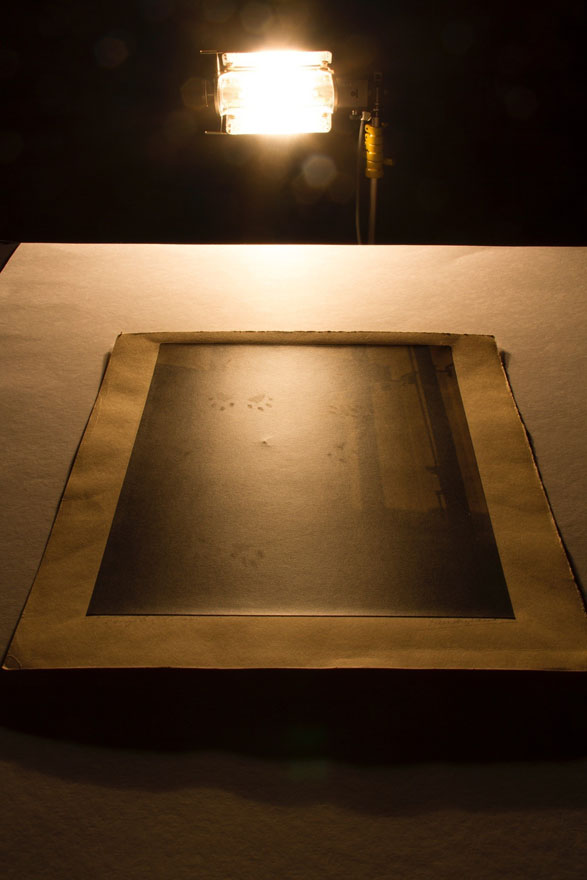
Raking light
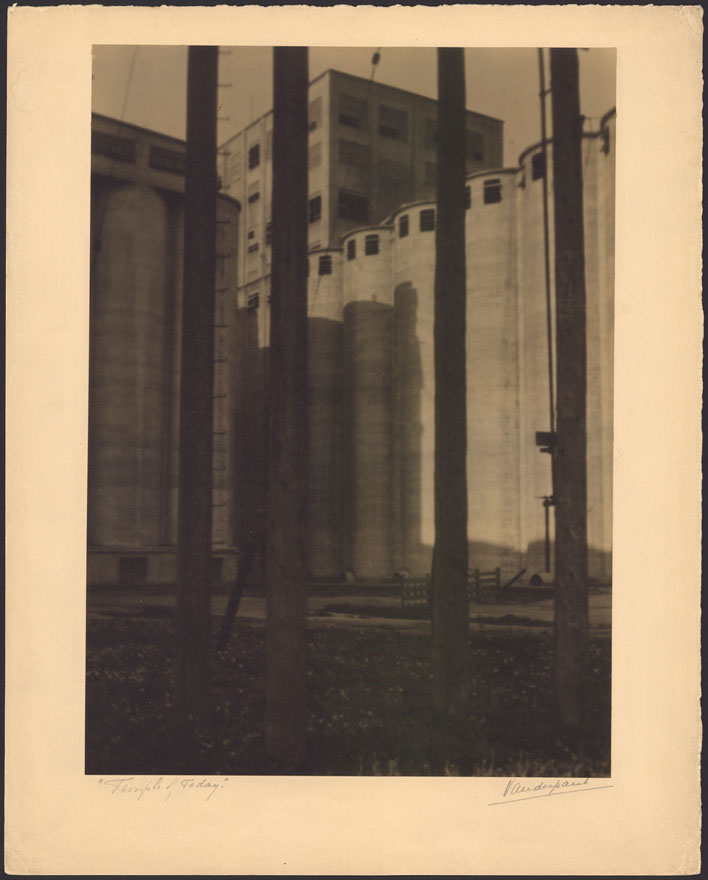
Raking light is a light source that is positioned on one side of the photograph so that the light falls or rakes across the surface. This lighting technique accentuates textures and planar deformations of the photograph.
Here you can see that a cat has walked across the surface of this photograph, leaving its paw prints on the emulsion.

Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light during an exposure of radiation of a different wavelength, such as an ultraviolet light or black light. In conservation examinations it is often used to identify coatings, optical brightening agents, tarnish on daguerreotypes, re-touching materials, mould, foxing, tape and adhesive stains, protein glues and oils, varnishes and certain pigments and dyes.

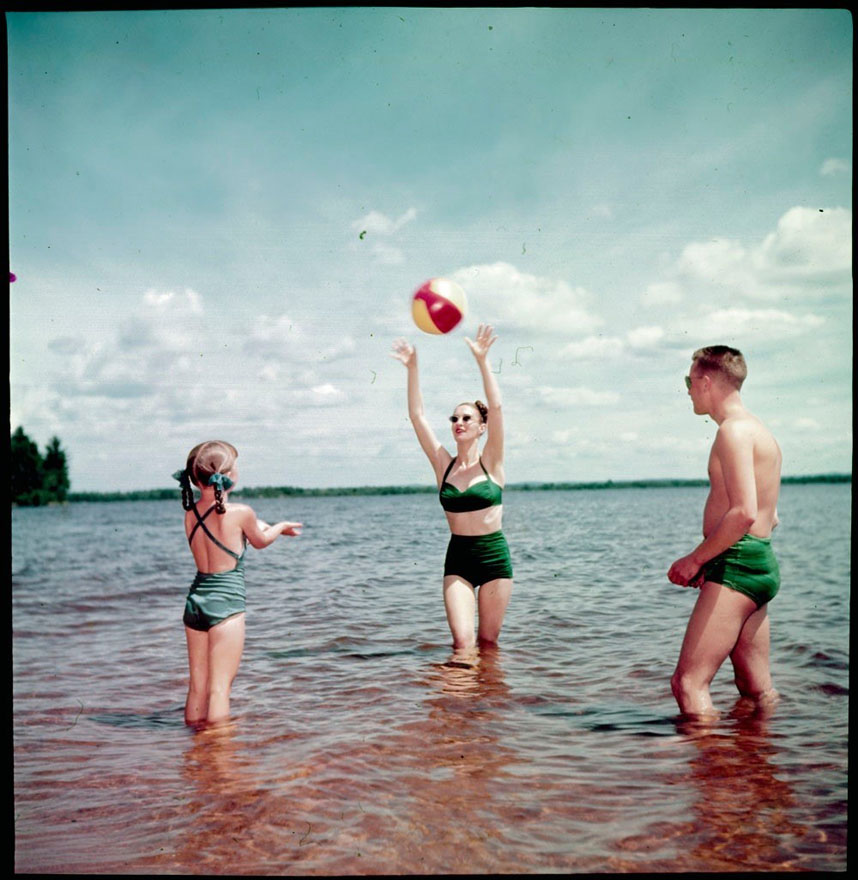
Transmitted light
Transmitted light is a light source that is positioned beneath or behind the support so that the light shines through the fibre matrix and media, watermarks, chain lines, etc.



Plastic testing
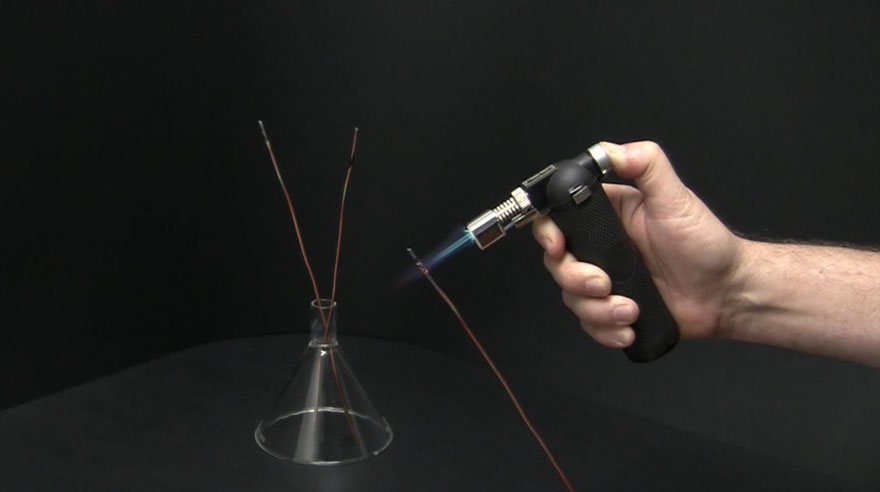
Testing different types of plastic is essential to determine if the plastic is harmful for the photograph. This is the Beilstein test method.
When heating a copper wire, melt the plastic in question onto the copper wire. Then place the copper wire with the melted plastic into a flame. If the flame burns blue, the plastic contains bromide and is therefore safe for photographs. If the flame burns green, the plastic contains chlorine and should not be in contact with photographs.

Visual inspection under binocular microscope
A visual examination under a binocular microscope provides a more accurate means of examining photographic materials than is possible with the unaided eye. In some cases this technique is essential for identification purposes and can aid in the conservation assessment.
