Demographic Snapshot of Canada’s Public Service, 2022
Preamble
This snapshot provides key demographics for Canada’s federal public service and supplements the Clerk of the Privy Council’s Thirtieth Annual Report to the Prime Minister on the Public Service of Canada.
The Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer (OCHRO) works in partnership with departments and agencies to access, analyze, and share federal public service workforce data to identify current workforce trends. In the coming year, the public service will aim to recruit and equip the next generation of federal public servants to carry out the Government of Canada’s priorities. In the process, there will be an increased focus on ensuring that the public service is diverse and inclusive and reflects the population it serves.
On this page
Introduction
This snapshot compares the current workforce with that of the baseline year of 2010. The data in this snapshot is current as of March 31, 2022, unless indicated otherwise.
Part 1 of this document covers all employees of the entire federal public service (the core public administration and separate agencies), and Part 2 focuses on executives. Part 3 provides highlights from the 2022/2023 Public Service Employee Survey and the 2022 Student Exit Survey.
Canada’s federal public service consists of two population segments:
- the core public administration; and
- separate agencies.
The term “core public administration” refers to approximately 70 departments and agencies for which the Treasury Board is the employer. These organizations are listed in Schedules I and IV of the Financial Administration Act. More information on this segment of the population is available in the Interactive data visualization tool.
The term “separate agencies” refers to agencies listed in Schedule V of the Financial Administration Act. Separate agencies conduct their own negotiations and may set their own classification system and compensation levels for their employees.
The principal separate agencies are:
- Canada Revenue Agency;
- Parks Canada;
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency; and
- National Research Council Canada.
Population counts for the following separate agencies are not included because their employee information is not available in the pay system:
- Canadian Security Intelligence Service;
- National Capital Commission;
- Canada Investment and Savings; and
- Canadian Forces Non‑Public Funds.
The data does not include:
- ministers’ exempt staff;
- employees locally engaged outside Canada;
- Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) regular force members;
- RCMP civilian force members; and
- Canadian Armed Forces members.
Highlights from 2022
-
In this section
Number of employees
- 335,957 active employees (282,980 in 2010)
- Represents 0.86% of the Canadian population (0.84% in 2010)
Location of work
- 57.8% of employees are in the regionsFootnote 1 (59.4% in 2010)
- 42.2% of employees are in the National Capital Region (40.6% in 2010)
Employment type
- 80.8% are indeterminate employees (86.2% in 2010)
- 13.7% are term employees (9.1% in 2010)
- 5.5% are casuals and students (4.7% in 2010)
WomenFootnote 2
- 56.3% of employees are women (55.2% in 2010)
- 52.5% of executives are women (43.8% in 2010)
Official languagesFootnote 3
- 71.7% of employees indicated English as their first official language (71.0% in 2010)
- 28.3% of employees indicated French as their first official language (29.0% in 2010)
AgeFootnote 4
- The average age of employees is 43.5 years (43.9 years in 2010)
- The average age of executives is 50.0 years (50.1 years in 2010)
Part 1: Federal public service
Relative size and spending
Between 2010 and 2022:
- the population of Canada grew from approximately 33.9 million to 39.3 million (an increase of 15.9%)Footnote 5; and
- the number of federal public servants increased from 282,980 to 335,957 (an increase of 18.7%).Footnote 6
The federal public service comprised 0.86% of the Canadian population in 2022. Over the last 10 years, the size of the federal public service in relation to the Canadian population fluctuated but it now represents a greater proportion of the Canadian population than in 2010 when it represented 0.84%.
Between 2009 to 2010 fiscal year and 2021 to 2022 fiscal year:
- Canada’s real gross domestic product (GDP) increased by 28.8%Footnote 7; and
- real federal program expenses increased by 46.0% (in constant dollars)Footnote 8.
Most recently, from the 2020 to 2021 fiscal year to the 2021 to 2022 fiscal year, there was:
- an increase of 4.0% in real gross domestic product; and
- a decrease of 28.1% in real federal program expenses.
Since the 2010 to 2015 period, where the workforce decreased in response to budget reductions, there has been an increase in the federal public service workforce. In the last year the workforce increased by 5.1%.
Figure 1 shows trends in the economy, the Canadian population, real federal program expenses and the size of the federal public service, from 2010 to 2022.

Figure 1 - Text version
| Year | Canadian Population Indextable 1 note 1 | Federal Public Service Workforce Indextable 1 note 2 | Real GDP Index, in chained dollars (2012)table 1 note 3 | Real Program Expenses Indextable 1 note 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2011 | 101 | 100 | 103 | 96 |
| 2012 | 102 | 98 | 106 | 94 |
| 2013 | 103 | 93 | 108 | 93 |
| 2014 | 104 | 91 | 111 | 93 |
| 2015 | 105 | 91 | 114 | 93 |
| 2016 | 106 | 92 | 115 | 98 |
| 2017 | 107 | 93 | 116 | 102 |
| 2018 | 109 | 97 | 122 | 106 |
| 2019 | 110 | 102 | 124 | 109 |
| 2020 | 112 | 106 | 118 | 117 |
| 2021 | 113 | 113 | 124 | 203 |
| 2022 | 116 | 119 | 129 | 146 |
Sources: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat; Statistics Canada; and Department of Finance Canada (Fiscal Reference Tables).
Table 1 Notes
- Table 1 Note 1
-
Based on data as of April 1 for each year.
- Table 1 Note 2
-
Based on active employees only and data as of March 31 for each year.
- Table 1 Note 3
-
Based on calendar year data.
- Table 1 Note 4
-
Based on fiscal year data. Real program expenses include transfers and were deflated using the Consumer Price Index.
Diversity in the federal public service
Sex
As shown in Figure 2, in 2022, women made up 56.3% of the federal public service, a 1.1 percentage point increase from 2010.
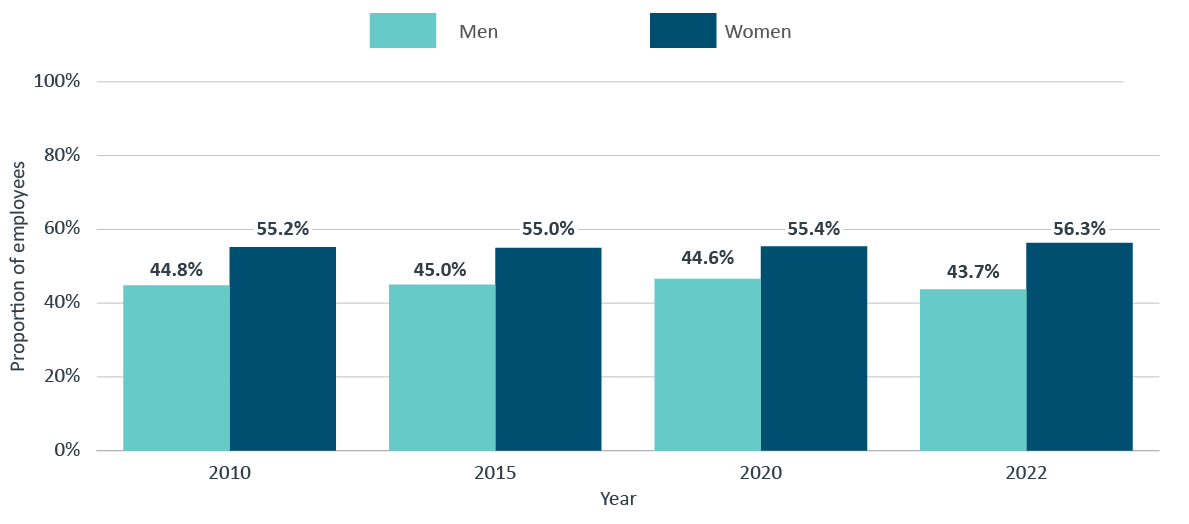
Figure 2 - Text version
| Sex | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 44.8% | 45.0% | 44.6% | 43.7% |
| Women | 55.2% | 55.0% | 55.4% | 56.3% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes all employment tenures and active employees only (employees on leave without pay are excluded).
The information provided excludes employees of unknown sex and is based on data as of March 31.
Employment equity designated groups
Representation
Figure 3 shows that there have been increases in the representation levels of all four employment equity designated groups in the core public administration since 2018.
The representation rate for women was slightly higher than the previous year while the representation rate of persons with disabilities increased from 5.6% in 2021 to 6.2% in 2022. As well, representation rates for members of visible minorities showed an increase for the last five consecutive years. However, the representation rate of Indigenous peoples in the core public administration remained relatively stable over the last five years.
Overall, representation of the employment equity groups (women, Indigenous peoples and members of visible minorities) continue to exceed their respective workforce availabilityFootnote 9 with the exception of persons with disabilities.
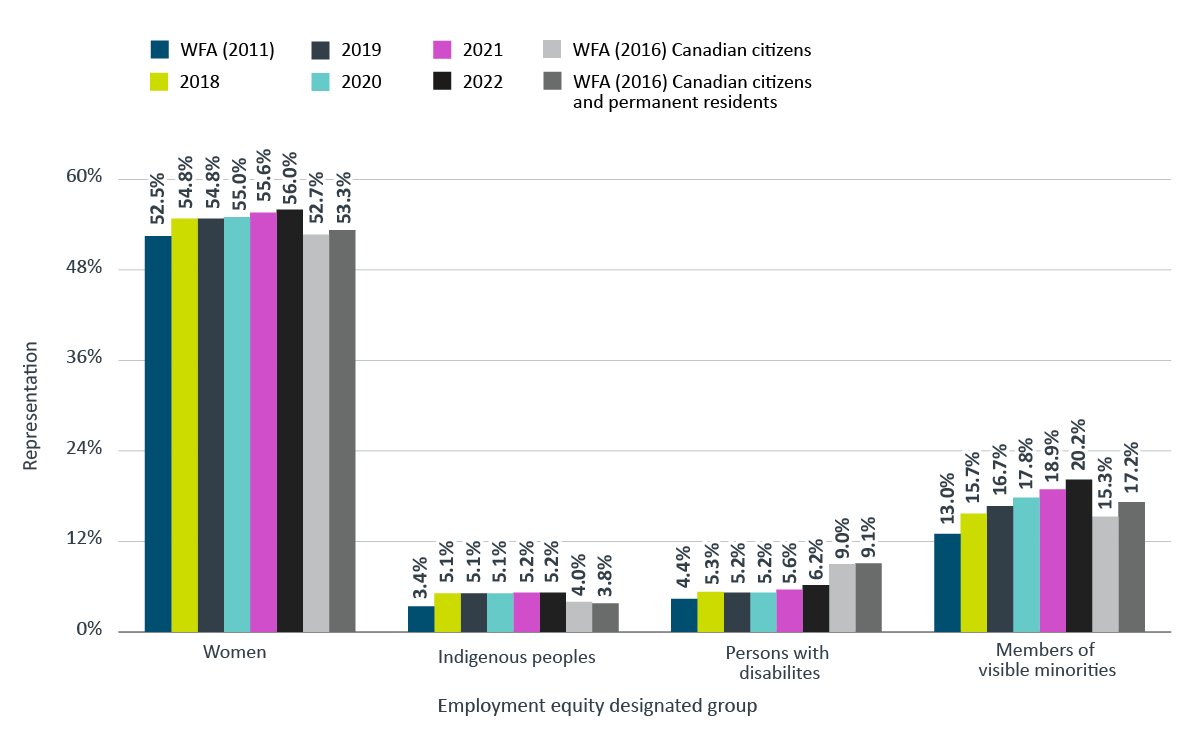
Figure 3 - Text version
| Employment equity designated group | WFA (2011) | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | WFA (2016) Canadian citizens | WFA (2016) Canadian citizens and permanent residents |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | 52.5% | 54.8% | 54.8% | 55.0% | 55.6% | 56.0% | 52.7% | 53.3% |
| Indigenous peoples | 3.4% | 5.1% | 5.1% | 5.1% | 5.2% | 5.2% | 4.0% | 3.8% |
| Persons with disabilities | 4.4% | 5.3% | 5.2% | 5.2% | 5.6% | 6.2% | 9.0% | 9.1% |
| Members of visible minorities | 13.0% | 15.7% | 16.7% | 17.8% | 18.9% | 20.2% | 15.3% | 17.2% |
Source: Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat Pay System as of March 31st of each year and Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat Employment Equity Data Bank (EEDB).
Population: The information includes indeterminates, terms of three months or more, and seasonal employees of organizations captured under the Financial Administration Act, Schedules I and IV (core public administration). Excluded from this information are employees on leave without pay, terms less than 3 months, students and casual workers, Governor in Council appointees, Ministers’ exempt staff, federal judges and deputy ministers.
The data in this table covers employees identified for the purpose of employment equity in the regulations to the Employment Equity Act.
Technical Notes:
Internal representation for Indigenous peoples, persons with disabilities and members of visible minorities is based on those who have voluntarily chosen to self-identify in one of the respective employment equity groups, while sex information is taken from the pay system.
The 2016 workforce availability estimates (WFA) are based on information from the 2016 Census of Canada and the 2017 Canadian Survey on Disability.
The 2011 workforce availability estimates are based on information from the 2011 National Household Survey and the 2012 Canadian Survey on Disability.
The 2011 WFA is the relevant comparison for 2018 representation data. The 2016 WFA based on Canadian citizens only is the relevant comparison for 2019, 2020 and 2021, while the 2016 WFA based on Canadian citizens and permanent residents is the relevant comparison for 2022.
Workforce availability estimates include Canadian citizens and starting in 2022, permanent residents, in those occupations in the Canadian workforce that correspond to occupations in the core public administration.
Hiring
Figure 4 shows that the share of new hires for indeterminate and term positions of three months or more remains above the current workforce availability of all employment equity designated groups except for persons with disabilities, which remains below the group’s current workforce availability.

Figure 4 - Text version
| Employment equity designated group | WFA (2011) | 2017 to 2018 | 2018 to 2019 | 2019 to 2020 | 2020 to 2021 | 2021 to 2022 | WFA (2016) Canadian citizens | WFA (2016) Canadian citizens and permanent residents |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | 52.5% | 58.7% | 56.5% | 58.3% | 60.2% | 60.1% | 52.7% | 53.3% |
| Indigenous peoples | 3.4% | 4.0% | 4.1% | 4.0% | 3.8% | 4.2% | 4.0% | 3.8% |
| Persons with disabilities | 4.4% | 3.6% | 3.7% | 3.9% | 4.3% | 5.5% | 9.0% | 9.1% |
| Members of visible minorities | 13.0% | 17.7% | 19.3% | 21.3% | 21.2% | 23.2% | 15.3% | 17.2% |
Source: Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat Pay System, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat Employment Equity Data Bank (EEDB) and the Public Service Commission of Canada’s files on hiring and staffing activities.
Population: The information includes indeterminates, terms of three months or more, and seasonal employees of organizations captured under the Financial Administration Act, Schedules I and IV (core public administration).
Technical Notes:
Internal representation for Indigenous peoples, persons with disabilities and members of visible minorities is based on those who have voluntarily chosen to self-identify in one of the respective employment equity groups, while sex information is taken from the pay system.
“Employees hired” refers to employees who were added to the public service of Canada payroll between April 1 and March 31 of each given fiscal year.
Percentages are that designated group’s share of all hirings.
The 2016 workforce availability estimates (WFA) are based on information from the 2016 Census of Canada and the 2017 Canadian Survey on Disability.
The 2011 workforce availability estimates are based on information from the 2011 National Household Survey and the 2012 Canadian Survey on Disability.
The 2011 WFA is the relevant comparison for 2017-2018 representation data. The 2016 WFA based on Canadian citizens only is the relevant comparison for 2018-2019, 2019-2020 and 2020-2021, while the 2016 WFA based on Canadian citizens and permanent residents is the relevant comparison for 2021-2022.
Workforce availability estimates include only Canadian citizens and starting in 2022, permanent residents, in those occupations in the Canadian workforce that correspond to occupations in the core public administration.
First official language
As shown in Figure 5, the breakdown of federal public servants by first official language in 2022 is almost the same as it was in 2010, 2015 and in 2020.
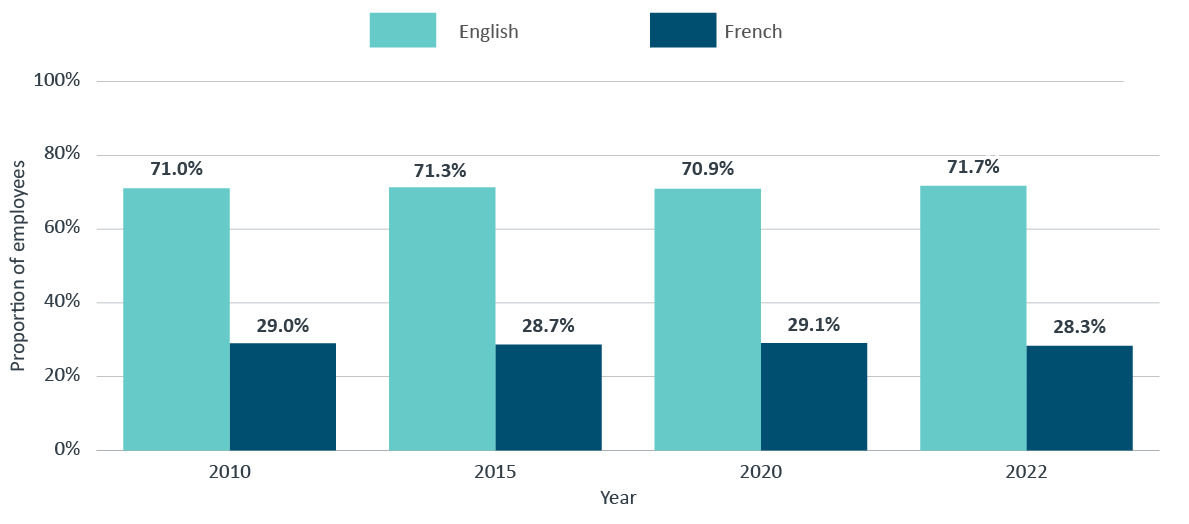
Figure 5 - Text version
| First official language | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | 71.0% | 71.3% | 70.9% | 71.7% |
| French | 29.0% | 28.7% | 29.1% | 28.3% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes all employment tenures and active employees only (employees on leave without pay are excluded).
The information provided excludes employees with an unknown first official language and is based on data as of March 31.
Age of federal public servants
Figure 6 compares the breakdown of federal public servants in 2010, 2015, 2020 and 2022 by age. From 2010 to 2022, the age breakdown changed slightly, with:
- a decrease in the proportion of employees aged 30 to 34 years and those aged 45 to 59 years; and
- an increase in the proportion of employees aged 20 to 29 years, 35 to 44 years and those above the age of 60 years.
The average age of federal public servants increased slightly between 2010 and 2015 (from 43.9 years in 2010, to 45.0 years in 2015) and then decreased between 2015 and 2022 from 45.0 years in 2015 to 43.5 years in 2022.
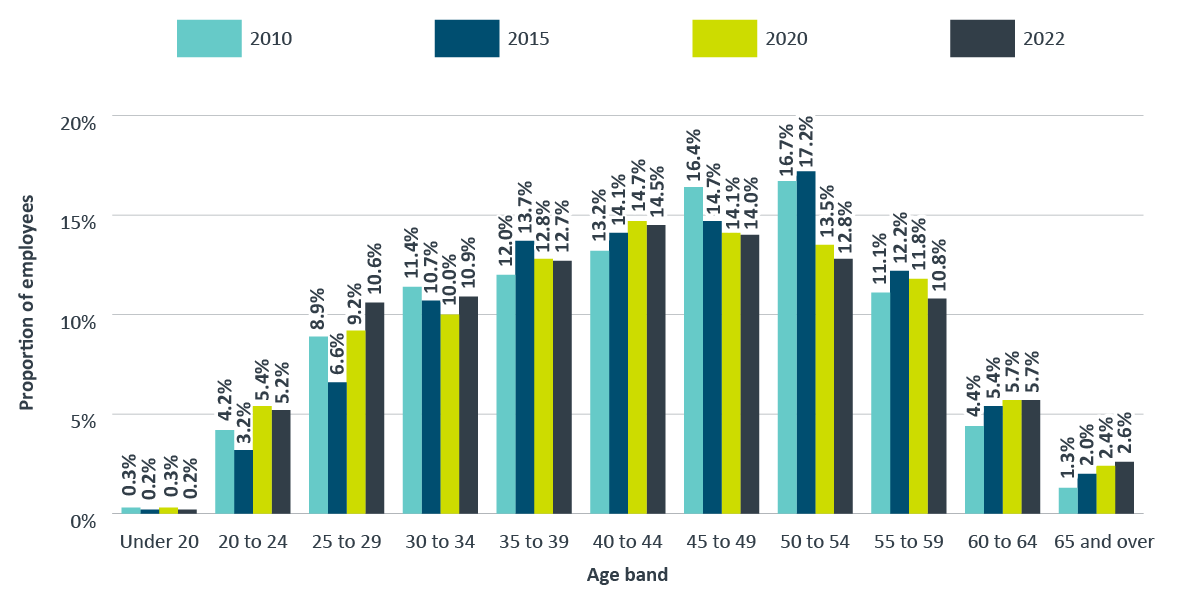
Figure 6 - Text version
| Age band | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 20 | 0.3% | 0.2% | 0.3% | 0.2% |
| 20 to 24 | 4.2% | 3.2% | 5.4% | 5.2% |
| 25 to 29 | 8.9% | 6.6% | 9.2% | 10.6% |
| 30 to 34 | 11.4% | 10.7% | 10.0% | 10.9% |
| 35 to 39 | 12.0% | 13.7% | 12.8% | 12.7% |
| 40 to 44 | 13.2% | 14.1% | 14.7% | 14.5% |
| 45 to 49 | 16.4% | 14.7% | 14.1% | 14.0% |
| 50 to 54 | 16.7% | 17.2% | 13.5% | 12.8% |
| 55 to 59 | 11.1% | 12.2% | 11.8% | 10.8% |
| 60 to 64 | 4.4% | 5.4% | 5.7% | 5.7% |
| 65 and over | 1.3% | 2.0% | 2.4% | 2.6% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes all employment tenures and active employees only (employees on leave without pay are excluded).
The information provided excludes employees with an unknown age and is based on data as of March 31.
Figure 7 shows the distribution of federal public servants by generation for 2010, 2015, 2020 and 2022. Up until 2015, baby boomers (people born between 1946 and 1966) made up the largest group of federal public servants. However, they are being replaced by Generation Xers (people born between 1967 and 1979) and millennials (people born between 1980 and 2000). Millennials now represent the largest group of public servants (45.3%) followed by Generation Xers (35.4%).

Figure 7 - Text version
| Generation | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baby Boomers | 53.2% | 41.8% | 24.6% | 18.4% |
| Generation X | 31.2% | 36.5% | 36.8% | 35.4% |
| Millennials | 13.9% | 21.2% | 38.4% | 45.3% |
| Other | 1.7% | 0.5% | 0.2% | 0.9% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes all employment tenures and active employees only (employees on leave without pay are excluded).
The information provided excludes employees of unknown age and is based on data as of March 31.
Other includes employees who were born in other generations (i.e., the Greatest generation, Traditionalists and Generation Z).
Hiring into the core public administration
Figure 8 shows new indeterminate hiring into the core public administration over time. Indeterminate hiring has been on the rise since the 2012 to 2013 fiscal year. There was a decline in indeterminate hires between the 2019 to 2020 fiscal year and the 2020 to 2021 fiscal year, however it has since risen. New indeterminate hiring in the core public administration increased by 32.7%, from 16,528 in the 2020 to 2021 fiscal year to 21,925 in the 2021 to 2022 fiscal year.

Figure 8 - Text version
| Generation | 2011 to 2012 | 2012 to 2013 | 2013 to 2014 | 2014 to 2015 | 2015 to 2016 | 2016 to 2017 | 2017 to 2018 | 2018 to 2019 | 2019 to 2020 | 2020 to 2021 | 2021 to 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Millennials | 3,775 | 1,284 | 2,060 | 3,274 | 4,168 | 6,712 | 9,169 | 12,381 | 13,127 | 11,247 | 15,532 |
| Other | 4,867 | 1,581 | 2,255 | 2,819 | 3,530 | 4,373 | 5,580 | 6,864 | 6,206 | 5,281 | 6,393 |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes new indeterminate core public administration hires only.
Generation information is based on an employee's age at the time they were hired.
“Other” includes employees who were born in all generations (i.e., the Greatest generation, Traditionalists, baby boomers, Generation X and Generation Z) except for millennials. Other also includes employees with an unknown age.
The proportion of new indeterminate hires who are millennials increased from 68.0% in the 2020 to 2021 fiscal year to 70.8% in the 2021 to 2022 fiscal year. During this same period:
- the proportion of new indeterminate hires from the baby boomer generation decreased from 8.1% to 6.2%; and
- the proportion of hires who are Generation Xers decreased from 23.5% to 22.5%.Footnote 10
Figure 9 shows the entire age distribution of new indeterminate hires in the core public administration. The median age was 34.4 years.
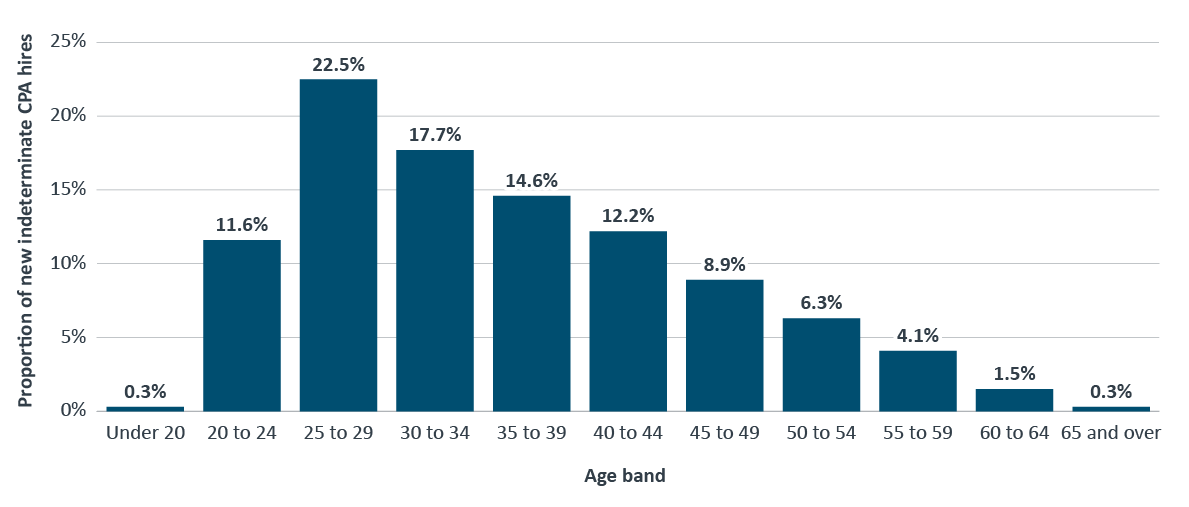
Figure 9 - Text version
| Age band | Proportion of new indeterminate CPA hires |
|---|---|
| Under 20 | 0.3% |
| 20 to 24 | 11.6% |
| 25 to 29 | 22.5% |
| 30 to 34 | 17.7% |
| 35 to 39 | 14.6% |
| 40 to 44 | 12.2% |
| 45 to 49 | 8.9% |
| 50 to 54 | 6.3% |
| 55 to 59 | 4.1% |
| 60 to 64 | 1.5% |
| 65 and over | 0.3% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes new indeterminate core public administration hires only.
The information provided excludes employees with an unknown age.
Departures from the federal public service
Retirements accounted for 71.3% of departures while resignations accounted for 15.2% in the 2021 to 2022 fiscal year. Additionally, as shown in Figure 10, in the 2021 to 2022 fiscal year, the federal public service departure rates for retirements, resignations and all other specified reasons were 3.2%, 0.7%, and 0.6%, respectively.
Since the 2012 to 2013 and the 2013 to 2014 period, where the number of departures from the federal public service increased in response to budget reductions, there has been a steady decrease of departures from the federal public service workforce up until the 2020 to 2021 fiscal year. Between the 2020 to 2021 fiscal year and the 2021 to 2022 fiscal year, the number of departures increased by 30.6%. This jump is mostly likely due to employees delaying their retirement until after the pandemic.

Figure 10 - Text version
| Departure Type | 2011 to 2012 | 2012 to 2013 | 2013 to 2014 | 2014 to 2015 | 2015 to 2016 | 2016 to 2017 | 2017 to 2018 | 2018 to 2019 | 2019 to 2020 | 2020 to 2021 | 2021 to 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retirements | 3.2% | 2.9% | 3.1% | 3.2% | 3.6% | 3.3% | 3.4% | 3.3% | 3.0% | 2.6% | 3.2% |
| Resignations | 0.8% | 0.9% | 0.9% | 0.9% | 1.0% | 0.8% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.5% | 0.7% |
| All other specified reasons | 0.3% | 2.4% | 2.0% | 1.0% | 0.7% | 0.8% | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.6% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Indeterminate federal public servants, including employees who departed (retired, resigned or left for other specified reasons) while on leave without pay.
Departure rates have not been provided for employees without a specified departure reason.
Departure figures/rates from fiscal year 2016 to 2017 onwards are subject to change.
Knowledge-intensive workforce in the core public administration
In 1990, the public service workforce was composed mainly of clerical and operational workers. Since then, employees undertaking more knowledge-intensive work comprise an ever-increasing share of employees in the core public administration. The cadre of knowledge workers is highly skilled, with significant expertise gained through a combination of education, training and experience. The transformation in work has been in response to:
- an increasingly demanding environment;
- new challenges; and
- technological advances since 2000.
As shown in Figure 11, the five largest knowledge-intensive classification groups in the core public administration are:
- Administrative Services (AS);
- Program Administration (PM);
- Economics and Social Science Services (EC);
- Information Technology (IT)Footnote 11; and
- Engineering and Scientific Support (EG).
In 2022, these classification groups represented 50.0% of the core public administration workforce and in 2010, they represented only 40.7%.

Figure 11 - Text version
| Classification Group | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | 13.8% | 14.5% | 16.0% | 16.5% |
| PM | 11.3% | 10.8% | 12.3% | 14.6% |
| EC | 5.9% | 6.6% | 8.2% | 9.2% |
| IT | 6.4% | 7.0% | 7.2% | 7.3% |
| EG | 3.2% | 3.2% | 2.8% | 2.6% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes all employment tenures and active employees only (employees on leave without pay are excluded), based on effective employment classification (acting appointments are included).
The information provided is based on data as of March 31.
On June 22, 2009, the Economics, Sociology and Statistics (ES) and the Social Science Support (SI) classification groups were combined to form the Economics and Social Science Services (EC) classification group.
The Computer Systems (CS) group changed to a new classification group called Information Technology (IT).
Part 2: Executives
-
In this section
This section provides demographic information about the federal public service’s Executive groupFootnote 12.
Typically, assistant deputy ministers (classified as EX-04 and EX-05) fulfill senior leadership functions, providing strategic direction and oversight. Directors, executive directors and director generals (classified from EX-01 to EX-03) fulfill executive functions and are responsible for managing employees.
Population size of the executive group
As of March 31, 2022, there were 8,506 executives in the federal public service:
- about half of them (50.6%) were EX-01s; and
- only 5.9% were EX-04s and EX-05s.
As of March 31, 2022, executives accounted for 2.5% of the federal public service.
Between 2010 and 2022, the federal public service workforce grew by 18.7%, while the executive population grew by 25.6% over this same period.
Executive diversity
Employment equity designated groups among core public administration executives
Figure 12 illustrates the levels of executive representation in the core public administration for all four employment equity groups from 2018 to 2022.
In 2022, the core public administration representation levels for women, persons with disabilities and members of visible minorities in the executive category exceeded their respective workforce availability, while representation of Indigenous peoples fell short of their workforce availability.
Compared with 2021, the representation levels of all four designated groups at the executive level increased.
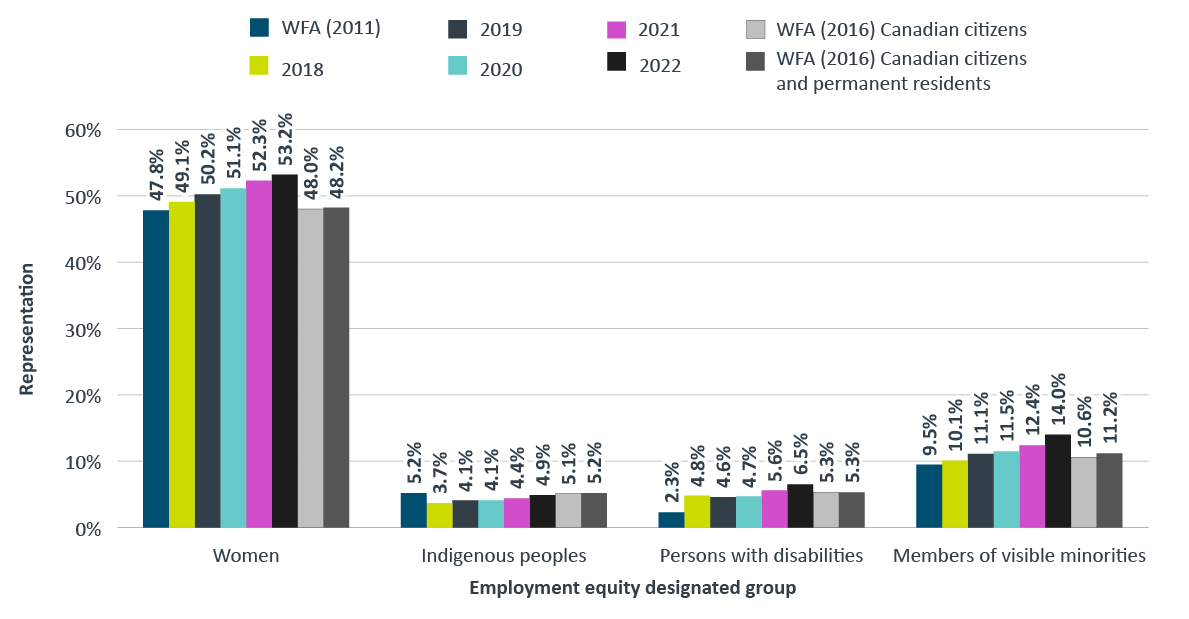
Figure 12 - Text version
| Employment equity designated group | WFA (2011) | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | WFA (2016) Canadian citizens | WFA (2016) Canadian citizens and permanent residents |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | 47.8% | 49.1% | 50.2% | 51.1% | 52.3% | 53.2% | 48.0% | 48.2% |
| Indigenous peoples | 5.2% | 3.7% | 4.1% | 4.1% | 4.4% | 4.9% | 5.1% | 5.2% |
| Persons with disabilities | 2.3% | 4.8% | 4.6% | 4.7% | 5.6% | 6.5% | 5.3% | 5.3% |
| Members of visible minorities | 9.5% | 10.1% | 11.1% | 11.5% | 12.4% | 14.0% | 10.6% | 11.2% |
Source: Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat Pay System as of March 31st of each year and Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat Employment Equity Data Bank (EEDB).
Population: The information includes indeterminates, terms of three months or more, and seasonal employees of organizations captured under the Financial Administration Act, Schedules I and IV (core public administration). Excluded from this information are employees on leave without pay, terms less than 3 months, students and casual workers, Governor in Council appointees, Ministers’ exempt staff, federal judges and deputy ministers.
The data in this table covers employees identified for the purpose of employment equity in the regulations to the Employment Equity Act.
Technical Notes:
Internal representation for Indigenous peoples, persons with disabilities and members of visible minorities is based on those who have voluntarily chosen to self-identify in one of the respective employment equity groups, while sex information is taken from the pay system.
The Law Management (LC) group has been included as part of the executive workforce since 2011 to 2012 fiscal year.
The 2016 workforce availability estimates (WFA) are based on information from the 2016 Census of Canada and the 2017 Canadian Survey on Disability.
The 2011 workforce availability estimates are based on information from the 2011 National Household Survey and the 2012 Canadian Survey on Disability.
The 2011 WFA is the relevant comparison for 2018 representation data. The 2016 WFA based on Canadian citizens only is the relevant comparison for 2019, 2020 and 2021, while the 2016 WFA based on Canadian citizens and permanent residents is the relevant comparison for 2022.
Workforce availability estimates include Canadian citizens and starting in 2022, permanent residents, in those occupations in the Canadian workforce that correspond to occupations in the core public administration.
First official language of executives
As shown in Figure 13, between 2010 and 2022 the proportion of executives in the federal public service who indicated that French was their first official language increased from 30.1% to 32.5%. This trend was not seen for the overall federal public service for the same period of time. The proportion of federal public servants who indicated that French was their first official language decreased slightly from 29.0% in 2010 to 28.3% in 2022.

Figure 13 - Text version
| First official language | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | 69.9% | 68.9% | 67.1% | 67.5% |
| French | 30.1% | 31.1% | 32.9% | 32.5% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes all federal public service executives, specifically, core public administration executives and their equivalents in separate agencies (such as Executive group (EX) and Management group (MG) classifications) in all tenures (indeterminate, term and casual). It does not include executives on leave without pay or those whose data on first official language is missing.
The information provided is based on data as of March 31.
Age of executives in federal public service
Figure 14 shows the age breakdown of federal public service executives for 2010, 2015 and 2022. The proportion of executives between 40 and 49 years of age and 65 years and older has increased between 2010 and 2022, while the proportion of executives aged 39 and under and between 50 and 64 years of age has decreased.
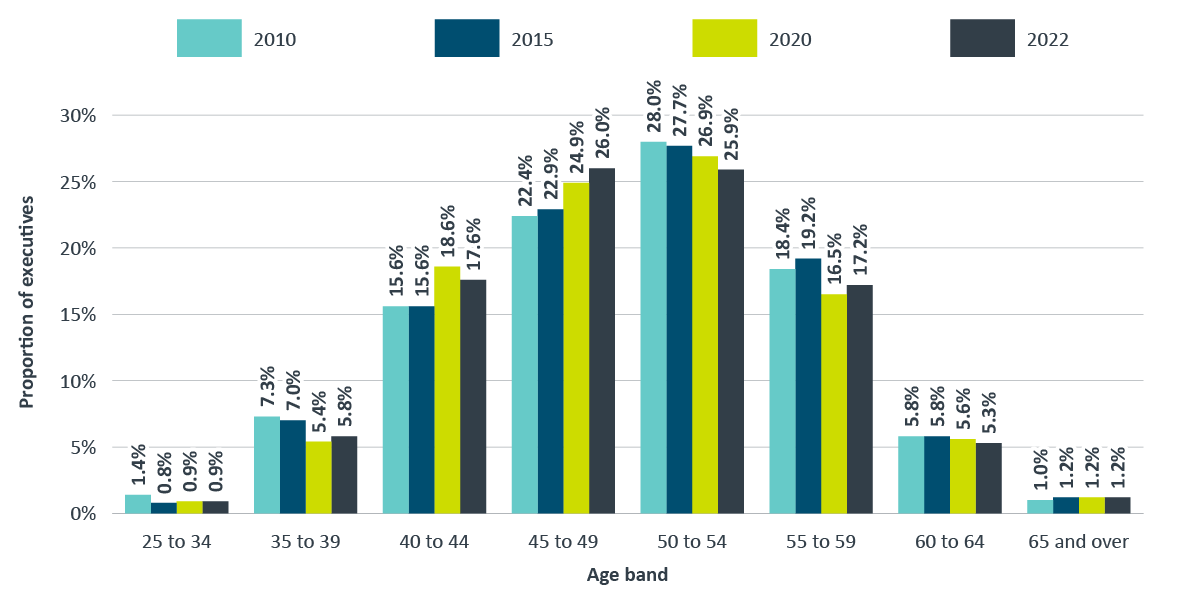
Figure 14 - Text version
| Age band | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 to 34 | 1.4% | 0.8% | 0.9% | 0.9% |
| 35 to 39 | 7.3% | 7.0% | 5.4% | 5.8% |
| 40 to 44 | 15.6% | 15.6% | 18.6% | 17.6% |
| 45 to 49 | 22.4% | 22.9% | 24.9% | 26.0% |
| 50 to 54 | 28.0% | 27.7% | 26.9% | 25.9% |
| 55 to 59 | 18.4% | 19.2% | 16.5% | 17.2% |
| 60 to 64 | 5.8% | 5.8% | 5.6% | 5.3% |
| 65 and over | 1.0% | 1.2% | 1.2% | 1.2% |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes all federal public service executives, specifically, core public administration executives and their equivalents in separate agencies (such as Executive group (EX) and Management group (MG) classifications) in all tenures (indeterminate, term and casual). It does not include executives on leave without pay.
The information provided excludes employees with an unknown age and is based on data as of March 31.
Figure 15 shows that between 2010 and 2022:
- the average age of junior executives at the EX-01 to EX-03 levels in the federal public service remained stable at approximately 50 years of age;
- the average age of senior executives at the EX-04 to EX-05 levels hovered between 53 and 54 years of age; and
- the average age of non-executives varied slightly between 43 and 45 years of age.
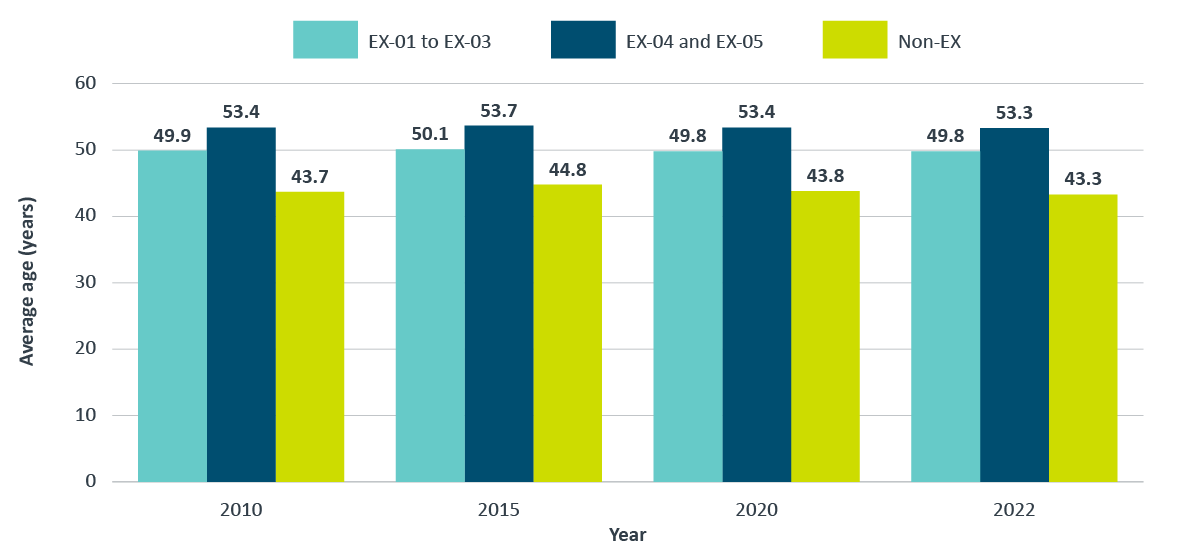
Figure 15 - Text version
| Executive level | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EX-01 to EX-03 | 49.9 | 50.1 | 49.8 | 49.8 |
| EX-04 and EX-05 | 53.4 | 53.7 | 53.4 | 53.3 |
| Non-EX | 43.7 | 44.8 | 43.8 | 43.3 |
Source: Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer, Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat.
Technical Notes:
Population: Includes all federal public service executives, specifically, core public administration executives and their equivalents in separate agencies (such as Executive group (EX) and Management group (MG) classifications) in all tenures (indeterminate, term and casual). The population does not include executives on leave without pay.
The information provided excludes employees with an unknown age and is based on data as of March 31.
Part 3: Highlights from employee surveys
-
In this section
2022/2023 Public Service Employee Survey
The 2022/2023 Public Service Employee Survey (PSES) was administered by Statistics Canada in partnership with Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat. It took place from November 21, 2022 to February 5, 2023. This comprehensive survey measures the federal government employees’ opinions about their engagement, leadership, workforce, workplace, workplace well-being and compensation.
A total of 189,584 employees in 90 federal departments and agencies responded to the 2022/2023 PSES, for a response rate of 53%.
The results from the 2022/2023 PSES indicate that more than four in five (81%) public servants like their job, and 78% of employees report having support in balancing their work and personal life. The results show that employees felt more positive regarding their career development than they did in 2020. 79% indicated that they feel that their immediate supervisor supports their career goals, up from 77% in 2020/2021.
Most employees indicated that they believe that their workplace is respectful, and the results relating to many aspects of respect in the workplace were more positive than they were in 2020/2021. 87% of employees indicated that in their work unit, individuals behave in a respectful manner, slightly higher than 2020/2021 (85%).
Overall, results related to harassment and discrimination have improved year over year.
- Harassment numbers have been steadily declining over the years. There was a decrease from 14% in 2019/2020 to 11% in 2020/2021. These levels have remained at 11% in 2022/2023. Discrimination also remained around the 7-8% mark from 2019/2020 to 2022/2023.
- 72% of employees indicated their department or agency works hard to create a workplace that prevents harassment, up from 71% in 2020/2021, and 74% of employees indicated their department or agency works hard to create a workplace that prevents discrimination (73% in 2020/2021).
Most employees (83%) indicated that their immediate supervisor supports their mental health and well-being, up from 79% in 2020/2021, and 83% of employees indicated that they would feel comfortable sharing concerns with their immediate supervisor about their physical health and safety.
For more information, consult the results of the 2022/2023 Public Service Employee Survey.
2022 Student Exit Survey
The Student Exit Survey (SES) is led by the Office of the Chief Human Resources Officer (OCHRO) and has been conducted annually since 2017. The SES was developed to:
- inform recruitment and onboarding strategies;
- contribute to improvements to the student application process; and
- lead to enhancements of student work assignments.
It is important that students are provided with a meaningful work experience, not only to showcase the federal public service as an employer of choice, but also to train and recruit strong candidates who will help shape the future of the public service.
The 2022 SES was conducted from August 2, 2022 to September 16, 2022 and included questions related to different stages of the student work term, such as:
- the application process;
- recruitment;
- onboarding and orientation;
- work experience;
- accommodations;
- work environment;
- workplace well-being; and
- pay and compensation issues relating to the Phoenix pay system.
74 organizations participated in the survey, yielding 6,324 submitted surveys.
For the most part, the positive gains in the SES results that were seen from 2020 to 2021 were maintained in 2022.
Overall, students were positive about the recruitment process: 84% of students felt that the application process was clear and easy to understand.
- 67% of students were satisfied with the amount of information they were provided about the job prior to accepting the position, unchanged from 2021.
The vast majority of students were positive about their onboarding experience:
- More than nine in ten students were satisfied with the welcome they received from their supervisor (95%) and from their colleagues (94%), similar to 2021 SES results (95% and 93%, respectively); and
- 84% of students were satisfied with the overall orientation they received about their organization, up from 82% in 2021.
As in 2021, there were widespread positive perceptions of the student work experience in 2022:
- 94% of students agreed that overall, they had a positive work experience, up from 93% in 2021;
- 94% of students felt that they were generally made to feel part of the team, up from 92% in 2021;
- 86% of students felt that they were given meaningful work, slightly higher than 2021 (85%); and
- 87% of students believed that their job was a good fit with their skills, slightly higher than 2021 (86%).
Similar to 2021, students in 2022 overwhelmingly endorsed a future career in the public service:
- 88% would recommend to other students that they seek a career in the federal public service, the same as in 2021 and 2020;
- 83% of students would seek a career in the federal public service, the same as in 2021 and slightly higher than 2020 (82%); and
- 92% of students felt that their current job provided them with valuable skills needed for future employment, slightly higher than 2021 (91%) and 2020 (90%).
Students identified the following factors as most important in choosing their future employment after completing their education: gaining work experience in their field of study; salary; and innovative and exciting opportunities and experiences.
For more information, consult the results of the 2022 Student Exit Survey.