2014-2015 Report on plans and priorities
Correctional Service of Canada
The Honourable Steven Blaney, P.C., M.P.
Minister of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness
2014–15
ESTIMATES
PART III – Departmental Expenditure Plans: Reports on Plans and Priorities
Purpose
Reports on Plans and Priorities (RPP) are individual expenditure plans for each department and agency. These reports provide increased levels of detail over a three-year period on an organization's main priorities by strategic outcome, program and planned / expected results, including links to related resource requirements presented in the Main Estimates. In conjunction with the Main Estimates, Reports on Plans and Priorities serve to inform members of Parliament on planned expenditures of departments and agencies, and support Parliament's consideration of supply bills. The RPPs are typically tabled soon after the Main Estimates by the President of the Treasury Board.
Estimates Documents
The Estimates are comprised of three parts:
Part I - Government Expenditure Plan - provides an overview of the Government's requirements and changes in estimated expenditures from previous fiscal years.
Part II - Main Estimates - supports the appropriation acts with detailed information on the estimated spending and authorities being sought by each federal organization requesting appropriations.
In accordance with Standing Orders of the House of Commons, Parts I and II must be tabled on or before March 1.
Part III - Departmental Expenditure Plans - consists of two components:
- Report on Plans and Priorities (RPP)
- Departmental Performance Report (DPR)
DPRs are individual department and agency accounts of results achieved against planned performance expectations as set out in respective RPPs.
The DPRs for the most recently completed fiscal year are tabled in the fall by the President of the Treasury Board.
Supplementary Estimates support Appropriation Acts presented later in the fiscal year. Supplementary Estimates present information on spending requirements that were either not sufficiently developed in time for inclusion in the Main Estimates or have subsequently been refined to account for developments in particular programs and services. Supplementary Estimates also provide information on changes to expenditure forecasts of major statutory items as well as on such items as: transfers of funds between votes; debt deletion; loan guarantees; and new or increased grants.
For more information on the Estimates, please consult the Treasury Board Secretariat website.Endnote i
Links to the Estimates
As shown above, RPPs make up part of the Part III of the Estimates documents. Whereas Part II emphasizes the financial aspect of the Estimates, Part III focuses on financial and non-financial performance information, both from a planning and priorities standpoint (RPP), and an achievements and results perspective (DPR).
The Management Resources and Results Structure (MRRS) establishes a structure for display of financial information in the Estimates and reporting to Parliament via RPPs and DPRs. When displaying planned spending, RPPs rely on the Estimates as a basic source of financial information.
Main Estimates expenditure figures are based on the Annual Reference Level Update which is prepared in the fall. In comparison, planned spending found in RPPs includes the Estimates as well as any other amounts that have been approved through a Treasury Board submission up to February 1st (See Definitions section, page iv). This readjusting of the financial figures allows for a more up-to-date portrait of planned spending by program.
Changes to the presentation of the Report on Plans and Priorities
Several changes have been made to the presentation of the RPP partially to respond to a number of requests – from the House of Commons Standing Committees on Public Accounts (PAC - Report 15Endnote ii), in 2010; and on Government and Operations Estimates (OGGO - Report 7Endnote iii), in 2012 – to provide more detailed financial and non-financial performance information about programs within RPPs and DPRs, thus improving the ease of their study to support appropriations approval.
- In Section II, financial, human resources and performance information is now presented at the Program, Sub-program and Sub-sub-program levels for more granularity.
- The report’s general format and terminology have been reviewed for clarity and consistency purposes.
- Other efforts aimed at making the report more intuitive and focused on Estimates information were made to strengthen alignment with the Main Estimates.
How to read this document
RPPs are divided into four sections:
Section I: Organizational Expenditure Overview
This Organizational Expenditure Overview allows the reader to get a general glance at the organization. It provides a description of the organization’s purpose, as well as basic financial and human resources information. This section opens with the new Organizational Profile, which displays general information about the department, including the names of the minister and the deputy head, the ministerial portfolio, the year the department was established, and the main legislative authorities. This subsection is followed by a new subsection entitled Organizational Context, which includes the Raison d’être, the Responsibilities, the Strategic Outcomes and Program Alignment Architecture, the Organizational Priorities and the Risk Analysis. This section ends with the Planned Expenditures, the Alignment to Government of Canada Outcomes, the Estimates by Votes and the Contribution to the Federal Sustainable Development Strategy. It should be noted that this section does not display any non-financial performance information related to programs (please see Section II).
Section II: Analysis of Programs by Strategic Outcome
This Section provides detailed financial and non-financial performance information for all strategic outcomes, programs, sub-programs and Sub-sub-programs. This section allows the reader to learn more about programs by reading their respective description and narrative entitled “Planning Highlights”. This narrative speaks to key services or initiatives which support the plans and priorities presented in Section I; it also describes how performance information supports the department’s strategic outcome or parent program.
Section III: Supplementary Information
This section provides supporting information related to departmental plans and priorities. In this section, the reader will find Consolidated Future-Oriented Statement of Operations and a link to supplementary information tables regarding transfer payments, as well as information related to the greening government operations, internal audits and evaluations, horizontal initiatives, user fees, major crown and transformational projects, and up-front multi-year funding, where applicable to individual organizations. The reader will also find a link to the Tax Expenditures and Evaluations Report, produced annually by the Minister of Finance, which provides estimates and projections of the revenue impacts of federal tax measures designed to support the economic and social priorities of the Government of Canada.
Section IV: Organizational Contact Information
In this last section, the reader will have access to organizational contact information.
Definitions
- Appropriation
- Any authority of Parliament to pay money out of the Consolidated Revenue Fund.
- Budgetary Vs. Non-budgetary Expenditures
- Budgetary expenditures - operating and capital expenditures; transfer payments to other levels of government, organizations or individuals; and payments to crown corporations. Non-budgetary expenditures – net outlays and receipts related to loans, investments and advances, which change the composition of the financial assets of the Government of Canada.
- Expected Result
- An outcome that a program is designed to achieve.
- Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)
- A measure of the extent to which an employee represents a full person-year charge against a departmental budget. FTEs are calculated as a ratio of assigned hours of work to scheduled hours of work. Scheduled hours of work are set out in collective agreements.
- Government of Canada Outcomes
- A set of high-level objectives defined for the government as a whole.
- Management Resources and Results Structure (MRRS)
- A common approach and structure to the collection, management and reporting of financial and non-financial performance information.
An MRRS provides detailed information on all departmental programs (e.g.: program costs, program expected results and their associated targets, how they align to the government’s priorities and intended outcomes, etc.) and establishes the same structure for both internal decision making and external accountability. - Planned Spending
- For the purpose of the RPP, planned spending refers to those amounts for which a Treasury Board (TB) submission approval has been received by no later than February 1, 2014. This cut-off date differs from the Main Estimates process. Therefore, planned spending may include amounts incremental to planned expenditure levels presented in the 2014–15 Main Estimates.
- Program
- A group of related resource inputs and activities that are managed to meet specific needs and to achieve intended results, and that are treated as a budgetary unit.
- Program Alignment Architecture
- A structured inventory of a department’s programs, where programs are arranged in a hierarchical manner to depict the logical relationship between each program and the Strategic Outcome(s) to which they contribute.
- Spending Areas
- Government of Canada categories of expenditures. There are four spending areasEndnote iv (social affairs, economic affairs, international affairs and government affairs) each comprised of three to five Government of Canada outcomes.
- Strategic Outcome
- A long-term and enduring benefit to Canadians that is linked to the department's mandate, vision, and core functions.
- Sunset Program
- A time-limited program that does not have on-going funding or policy authority. When the program is set to expire, a decision must be made as to whether to continue the program. (In the case of a renewal, the decision specifies the scope, funding level and duration).
- Whole-of-Government Framework
- A map of the financial and non-financial contributions of federal organizations receiving appropriations that aligns their Programs to a set of high level outcome areas defined for the government as a whole.
Table of Contents
- Minister's Message
- Section I: Organizational Expenditure Overview
- Section II: Analysis of Programs by Strategic Outcome
- Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and in institutions, contribute to public safety.
- Program 1.0: Custody
- Program 2.0: Correctional Interventions
- Program 3.0: Community Supervision
- 4.0: Internal Services
- Section III: Supplementary Information
- Section IV: Organizational Contact Information
- Endnotes
Minister's Message
As Canada's Minister of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness, I am pleased to present to Parliament the Correctional Service of Canada (CSC) Report on Plans and Priorities for the 2014-15 fiscal year.
Our Government remains committed to making sure that Canadians feel safe in their streets and communities. CSC contributes to this important priority by correcting criminal behaviour and strengthening offender accountability through appropriate correctional interventions and services.
We assist offenders to become law-abiding, contributing members of society by providing them with the tools they need, such as job-skills training to help find employment after release, and programs that work to correct those behaviours that lead to crime.
We will also continue to address the specific concerns and challenges faced by some offenders, by enhancing the delivery of Aboriginal corrections and improving resources and support for offenders with mental health needs.

The Honourable Steven Blaney, P.C., M.P. Minister of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness
Most importantly, our Government will continue to put the rights of victims first by maintaining timely and responsive victim services, and ongoing outreach and support for those affected by crime.
This report establishes the way forward for the coming fiscal year, and outlines the important work that CSC does to help enhance public safety.
The Honourable Steven Blaney, P.C., M.P.
Minister of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness
Section I: Organizational Expenditure Overview
Organizational Profile
Minister: The Honourable Steven Blaney, P.C., M.P.
Deputy Head: Don Head
Ministerial portfolio: Department of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness
Year Established: 1979
Main legislative authorities: Corrections and Conditional Release ActEndnote v and Corrections and Conditional Release RegulationsEndnote vi
Organizational Context
Raison d’être
The purpose of the federal correctional system, as defined in law, is to contribute to the maintenance of a just, peaceful and safe society by carrying out sentences imposed by courts through the safe and humane custody and supervision of offenders; and by assisting the rehabilitation of offenders and their reintegration into the community as law-abiding citizens through the provision of programs in penitentiaries and in the community (Corrections and Conditional Release Act, s.3).
Mission
The Correctional Service of Canada, as part of the criminal justice system and respecting the rule of law, contributes to public safety by actively encouraging and assisting offenders to become law-abiding citizens, while exercising reasonable, safe, secure and humane control.
Responsibilities
The Correctional Service of Canada’s (CSC) responsibilities are derived from the Corrections and Conditional Release Act and the Corrections and Conditional Release Regulations. Section 5 of the Act specifically directs CSC to be responsible for:
- the care, custody and supervision of offenders: CSC manages institutions for men and women, mental health treatment centres, Aboriginal healing lodges, community correctional centres, and parole offices where offenders under conditional release are supervised in the community. CSC provides services across the country in large urban centres, in remote Inuit communities across the North, and at all points in between. On a typical day during 2012–13, CSC was responsible for 22,762 offenders, of which 15,056 were in federal custody (including temporary detaineesFootnote 1) and 7,706 were supervised in the community.
- the provision of interventions: CSC encourages offenders to be accountable for their behaviour and rehabilitation by delivering correctional interventions that contribute to successful reintegration into the community. CSC continues to ensure it delivers the most relevant, appropriate and effective interventions to address the risks and needs of the offender population while in custody or under community supervision.
- the preparation of offenders for release: CSC staff work with inmates and partners to establish viable plans to prepare inmates for release. This includes pre-release case preparation, developing release plans, presenting cases to the Parole Board of Canada, and developing community strategies to ensure the safe release of inmates in the community.
- the supervision of offenders on conditional release: CSC provides an integrated continuum of supervision, accommodation, employment and intervention in the effective management of supervised offenders, in line with the Service’s strategic outcome of enhancing public safety.
- public education about the operations of the Service: CSC works to build partnerships with Canadian communities, to foster understanding of correctional programs and processes among Canadians, to boost public support for safe reintegration, and to reinforce the reality that the CSC’s ultimate goal is a safe Canadian population.
The Act also requires CSC to develop, implement and monitor correctional policies, programs and practices that respect gender, ethnic, cultural and linguistic differences and are responsive to the specific needs of women, Aboriginal peoples and other groups. As well, it requires that CSC provide essential health care services and reasonable access to non-essential mental health care that will contribute to the inmate’s rehabilitation and successful reintegration into the community. The Act mandates CSC to provide services to victims of crime, such as information sharing and awareness building to support victims.
CSC constantly assesses and adjusts the allocation of resources to ensure effective and efficient offender rehabilitation. During this planning period, CSC continues to support Canada’s Economic Action Plan 2012 by reducing its operating budget by $295.4 million by April 1, 2014. CSC strives to achieve administrative efficiencies through streamlining of its operations and program delivery. These and other related initiatives will optimize available resources for CSC’s key priorities and core mandate, and ensure that the organization continues to deliver strong public safety results for Canadians.
Strategic Outcome and Program Alignment Architecture (PAA)
Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and in institutions, contribute to public safety.
- 1.0 Program: Custody
- 1.1 Sub-program: Institutional Management and Support
- 1.2 Sub-program: Institutional Security
- 1.2.1 Sub-sub-program: Intelligence and Supervision
- 1.2.2 Sub-sub-program: Drug Interdiction
- 1.3 Sub-program: Institutional Health Services
- 1.3.1 Sub-sub-program: Public Health Services
- 1.3.2 Sub-sub-program: Clinical Health Services
- 1.3.3 Sub-sub-program: Mental Health Services
- 1.4 Sub-program: Institutional Services
- 1.4.1 Sub-sub-program: Food Services
- 1.4.2 Sub-sub-program: Accommodation Services
- 2.0 Program: Correctional Interventions
- 2.1 Sub-program: Offender Case Management
- 2.2 Sub-program: Community Engagement
- 2.3 Sub-program: Spiritual Services
- 2.4 Sub-program: Correctional Reintegration Program
- 2.4.1 Sub-sub-program: Violence Prevention Program
- 2.4.2 Sub-sub-program: Substance Abuse Program
- 2.4.3 Sub-sub-program: Family Violence Prevention Program
- 2.4.4 Sub-sub-program: Sex Offender Program
- 2.4.5 Sub-sub-program: Maintenance Program
- 2.4.6 Sub-sub-program: Social Program
- 2.5 Sub-program: Offender Education
- 2.6 Sub-program: CORCAN Employment and Employability
- 3.0 Program: Community Supervision
- 3.1 Sub-program: Community Management and Security
- 3.2 Sub-program: Community-Based Residential Facilities
- 3.2.1 Sub-sub-program: Community Residential Facilities
- 3.2.2 Sub-sub-program: Community Correctional Centres
- 3.3 Sub-program: Community Health Services
- 4.0: Internal Services
Organizational Priorities
CSC’s priorities stem from its mission and responsibilities and provide specific focus for the organization’s direction, programs and initiatives. They point CSC towards continuously improving its contribution to public safety in Canadian communities by helping offenders to correct their criminal behaviour, rehabilitate their lives and reintegrate as law-abiding citizens into the community.
CSC manages its priorities in an evolving Canadian social context. The organization ensures that its programs, standards and policies are aligned with government directions set through the Speech from the Throne, the passing of new legislation or amendments to existing laws. CSC is an active participant in the development of policies and legislative measures that have an impact on its operations and the offender population it manages. It is through the review, modernization, and alignment of programs and policies that CSC translates its support for the government.
| Priority | TypeFootnote 2 | Strategic Outcome & Programs |
|---|---|---|
Safe transition to and management of eligible offenders in the community | Ongoing | Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and institutions, contribute to public safety Programs:
|
| Description | ||
Why is this a priority? The majority of offenders will be released into Canadian communities. CSC must continue to focus its efforts on safe release and minimize re-offending by offenders. Safe transition of offenders to the community is a key part of CSC’s contribution to public safety. What are the plans for meeting this priority? CSC will continue to achieve this priority by delivering nationally-recognized correctional programs based on offenders’ assessed risks and needs to correct criminal behaviour and reduce reoffending. The Service will continue to improve the reliability and validity of assessment processes, and provide evidence-based correctional interventions to increase public safety results for Canadians, including expanding the implementation of the Integrated Correctional Program Model. Correctional plans will continue to be developed and regularly updated for all offenders, and will include measures of offender accountability. CSC will begin implementing the Structured Assessment and Intervention Framework to deliver case management assessment, intervention, and supervision in a more efficient and effective way. Health care will be provided to offenders in order to meet their appropriate individual physical and mental health care needs consistent with professional standards and CSC policies. CSC will continue to offer educational, vocational, employment and social programs, as well as other initiatives to assist in the safe transition of offenders into the community. CSC will continue to support community-based initiatives across the country that contribute to the successful transition of offenders in communities and minimize reoffending. Faith-based services continue to support offenders as they transition from institutions back to communities. In addition, CSC will continue to deliver the Parole Officer Induction Training and Parole Officer Continuous Development programs and ensure that its training components are evidence-based and kept up to date. | ||
| Priority | Type | Strategic Outcome & Programs |
|---|---|---|
Safety and security of staff and offenders in our institutions and in the community | Ongoing | Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and institutions, contribute to public safety Programs:
|
| Description | ||
Why is this a priority? Maintaining safe, secure and humane custody is essential to delivering correctional programs that help to change criminal behaviour. CSC is committed to continuing efforts to prevent violent behaviour and maintain a safe working environment, thereby ensuring the safety and security of staff and offenders in its institutions and in the community. What are the plans for meeting this priority? CSC will continue to implement its comprehensive population management approach that includes risk assessments, offender placements and strategies for managing occupancy, including temporary accommodation such as double bunking where necessary. CSC will enhance protocols that increase the safety and security of operational sites, including security intelligence, search plans, dynamic security, and monitoring at principal entrances to prevent entry of contraband in institutions, including drugs. The Service will continue to deliver correctional interventions that respond to identified offender risks and needs in both institutions and communities. CSC will continue to develop and implement a long-term national solution for the safety of staff who work in the community. In alignment with its 2013-2018 Accommodation Plan, CSC will continue to maintain, and if possible, improve the condition of its facilities. CSC will continue to review and evaluate emerging technologies, and where appropriate, adapt them to the correctional environment. CSC’s emergency management plans enable the Service to react to emergency situations quickly and effectively, should they arise. | ||
| Priority | Type | Strategic Outcome & Programs |
|---|---|---|
Enhanced capacities to provide effective interventions for First Nations, Métis and Inuit offenders | Ongoing | Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and institutions, contribute to public safety Programs:
|
| Description | ||
Why is this a priority? There is a disproportionate representation of Aboriginal offenders (First Nations, Métis and Inuit) in CSC compared to their overall number in Canadian population. What are the plans for meeting this priority? CSC will continue to strengthen the Aboriginal Corrections Accountability Framework with the ongoing implementation of programs, policies, services and interventions that are culturally appropriate and effective, leading to better results for Aboriginal offenders. CSC will continue to enhance its policy framework to address any systemic barriers to effectively managing Aboriginal offenders. In addition, CSC will continue to improve collaboration with Aboriginal communities and partners to strengthen initiatives that support the safe reintegration of Aboriginal offenders such as the Aboriginal Continuum of Care and Circles of Communication. CSC will strive to improve community capacity, strengthen partnerships and promote the use of Corrections and Conditional Release Act (CCRA) section 84 in the process of releasing Aboriginal offenders who want to return to an Aboriginal community. The Service will streamline the performance measures of the Aboriginal Correctional Accountability Framework to focus on reporting correctional outcomes. | ||
| Priority | Type | Strategic Outcome & Programs |
|---|---|---|
Improved capacities to address mental health needs of offenders | Ongoing | Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and institutions, contribute to public safety Programs:
|
| Description | ||
Why is this a priority? A significant number of offenders admitted to federal custody face mental health issues. Mental illness is, in itself, a barrier to engaging in their correctional plans and participating in programs that address the criminogenic factors that led to criminal behaviour. In order for CSC to engage those offenders in a rehabilitation process, it must address their mental health needs through assessment, diagnosis, and treatment. What are the plans for meeting this priority? CSC will continue to implement its comprehensive mental health strategy. In 2014-15, it will focus on correctional results for offenders with mental health needs. It will strengthen the continuum of mental health care throughout the duration of offenders’ sentences. It will also increase collaboration with other jurisdictions to provide mental health services for offenders on supervision in the community. | ||
| Priority | Type | Strategic Outcome & Programs |
|---|---|---|
Efficient and effective management practices that reflect values-based leadership | Previously committed to | Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and institutions, contribute to public safety Program:
|
| Description | ||
Why is this a priority? CSC employs more than 18,000 staff working in institutions, parole offices and headquarters across the country. As a large and decentralized organization, CSC must effectively and efficiently manage a diverse and segmented operational system and maintain professional standards and operating practices. CSC’s management practices are anchored in the organization’s Values Statement, thus supporting its workforce, workplace and strategic outcome. What are the plans for meeting this priority? CSC will complete the implementation of its strategic plan for human resources that includes recruitment, retention, training, support for linguistic duality and cultural diversity. It will also implement its five-year evaluation plan, its three-year audit plan, its research plan and its Performance Management Framework, all of which enhance knowledge and support more effective decision making. CSC will enhance management practices by advancing the implementation of the Treasury Board Policy on Internal Control and continue to improve its costing and forecasting approaches. It will streamline the procurement and lifecycle of equipment and modernize food service delivery and preparation. CSC’s IM / IT plan will be updated and reviewed to ensure it continues to support CSC’s requirements. Through all these initiatives, CSC management will promote and reinforce with its employees CSC’s Values Statement and the Values and Ethics Code for the Public Sector. It will also analyze and seek to correct any problems that may arise in areas related to gender and diversity. | ||
| Priority | Type | Strategic Outcome & Programs |
|---|---|---|
Productive relationships with increasingly diverse partners, stakeholders, and others involved in public safety | Ongoing | Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and institutions, contribute to public safety Programs:
|
| Description | ||
Why is this a priority? The majority of federal offenders will be released to Canadian communities, and need assistance and support to adjust to living crime-free in society. CSC alone cannot provide everything offenders need during their incarceration and after they are released. Partners, stakeholders and community experts are essential to safe offender reintegration. In the interest of the well-being of offenders and Canadian communities, CSC partners with community-based organizations that reflect the diversity of the offender population in order to facilitate the safe return of offenders to communities. What are the plans for meeting this priority? CSC will continue to work on sustaining existing partnerships and developing new and diverse ones as it implements the Federal Community Corrections Strategy and the Integrated Engagement Strategy. The service will continue to support opportunities to enhance and optimize engagement activities by leveraging local, regional and national partnerships such as Citizen Advisory Committees, Victim Advisory Committees, and the National Ethnocultural Advisory Committee. CSC will also continue to provide information and restorative justice services to victims. | ||
Risk Analysis
CSC continuously examines its internal and external environment to ensure that strategic, organizational, financial, legal and cultural factors are considered in its risk management process. This leads to the identification of risks which are then monitored, managed and mitigated. The risks and response strategies articulated below are captured within CSC’s Corporate Risk Profile.
| Organizational Risk | Risk Response Strategy | Link to Program Alignment Architecture | |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
There is a risk that CSC will not be able to respond to the complex, diverse and evolving profile of the offender population |
|
|
2 |
There is a risk that CSC will not be able to maintain required levels of operational safety and security in institutions and in the community |
|
|
3 |
There is a risk that CSC will not be able to manage significant change related to transformation, legislative changes, and fiscal constraints |
|
|
4 |
There is a risk that CSC will lose support of partners delivering critical services and providing resources for offenders |
|
|
5 |
There is a risk that CSC will not be able to sustain results related to re-offending violently |
|
|
Developing, providing and sustaining correctional services requires organized efforts. Through the administration of court-imposed sentences to offenders, CSC plays a key role in public safety by implementing a comprehensive set of measures, controls and practices that assist offenders to become law-abiding citizens and contributing members of Canadian society upon their return to the community. The accurate identification and effective management of risks lead to the identification of priorities and facilitate the achievement of results. Risk management is a central part of daily business in all areas of CSC’s large, decentralized and multifaceted work environment.
CSC responds to the complex, diverse and evolving profile of the offender population it manages, including:
- offenders with histories of violence and previous youth and / or adult convictions
- offenders with employment, education and substance abuse needs
- offenders affiliated with criminal groups
- offenders with mental health needs
- offenders with Hepatitis C and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection
- an ethnoculturally diverse population
CSC operates in a continuously changing environment that requires a high level of adaptability and transformational skill. As a high reliability organization, CSC implements processes and crisis management methods to ensure the integrity of its operations. These processes and crisis management methods must be current and sustainable 24 hours a day, seven days a week, under all circumstances. The operations of CSC largely depend on its ability to maintain control of its activities as well as manage and anticipate risks at all times. It does so by identifying, developing, and assessing innovative ways to ensure the safety and security of staff, offenders and the public. Information, knowledge and technology are used to minimize the occurrence of incidents and when they occur, to manage and learn from them. Clearly articulated responsibilities and a robust governance structure ensure that risks are managed appropriately at the operational level as well as at the corporate level. Strategies to reduce risks across hazardous systems facilitate the management and sustainability of the correctional environment and the development of organizational resilience. The implementation of measures, systems, and controls increases CSC’s high reliability capacity and benefits the management of corporate risks at CSC.
These risks guide decision making, as well as audit, evaluation and research planning. The risk analysis and management process is ever evolving, mitigates potential risks, and ensures delivery of core business that contributes to public safety.
This integrated approach allows CSC to handle risk-related challenges that may arise, without compromising public safety.
Planned Expenditures
| 2014–15 Main Estimates | 2014–15 Planned Spending | 2015–16 Planned Spending | 2016–17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2,334,682,392 | 2,334,682,392 | 2,323,234,721 | 2,327,584,010 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 18,721 | 18,721 | 18,721 |
| Strategic Outcome, Programs and Internal Services | 2011–12 Expenditure | 2012–13 Expenditure | 2013–14 Forecast Spending | 2014–15 Main Estimates | 2014–15 Planned Spending | 2015–16 Planned Spending | 2016–17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategic Outcome: The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and in institutions, contribute to public safety | |||||||
| Program 1Custody | 1,650,039,924 | 1,739,638,256 | 1,816,176,779 | 1,471,011,448 | 1,471,011,448 | 1,461,224,723 | 1,465,874,636 |
| Program 2 Correctional Interventions | 515,421,682 | 457,038,705 | 568,494,083 | 465,029,970 | 465,029,970 | 464,133,040 | 463,970,700 |
| Program 3 Community Supervision | 112,408,779 | 117,648,594 | 140,099,806 | 93,399,963 | 93,399,963 | 93,219,817 | 93,187,211 |
| Program Sub-Total | 2,277,870,385 | 2,314,325,555 | 2,524,770,668 | 2,029,441,381 | 2,029,441,381 | 2,018,577,580 | 2,023,032,547 |
| Internal Services Sub-Total | 388,983,721 | 328,673,656 | 326,504,201 | 305,241,012 | 305,241,012 | 304,657,141 | 304,551,463 |
| Strategic Outcome Total | 2,666,854,106 | 2,642,999,211 | 2,851,274,869 | 2,334,682,392 | 2,334,682,392 | 2,323,234,721 | 2,327,584,010 |
The increase between 2012-13 Expenditures and 2013-14 Forecast Spending is mainly due to the payment of severance and retroactive pay for signed collective agreements.
The decrease between 2013-14 Forecast Spending and 2014-15 Planned Spending is mostly attributable to additional savings related to the Canada’s Economic Action Plan 2012, and the reduction in capital investment and some expenditures that will not be incurred at the same level in 2014-15 as in 2013-14, such as severance and retroactive pay.
The trend in planned spending remains relatively stable for 2014-15 to 2016-17. Minor changes from year to year are mainly attributable to capital funding, and therefore have no impact on the Planned FTEs.
Alignment to Government of Canada Outcomes
| Strategic Outcome | Program | Spending Area | Government of Canada Outcome | 2014–15 Planning and Spending |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders in communities and in institutions, contribute to public safety. | 1.0 Custody | Social Affairs | A Safe and Secure Canada | 1,471,011,448 |
| 2.0 Correctional Interventions | Social Affairs | A Safe and Secure Canada | 465,029,970 | |
| 3.0Community Supervision | Social Affairs | A Safe and Secure Canada | 93,399,963 |
| Spending Area | Total Planned Spending |
|---|---|
| Social Affairs | 2,029,441,381 |
Departmental Spending Trend
Departmental Spending Trend Graph (dollars)
Departmental Spending Trend Graph (dollars)
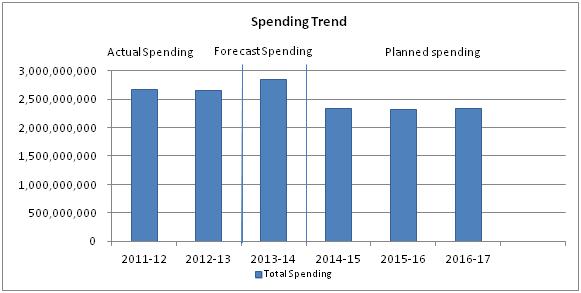
Note: The 2014-15 Forecast Spending is as of the end of November 2014.
The above profile illustrates CSC's Actual Spending for the last two years, Forecasted Spending for 2013-14 and Planned Spending for the next three years.
Estimates by Vote
For information on our organizational appropriations, please see the 2014–15 Main EstimatesEndnote ix publication.
Contribution to the Federal Sustainable Development Strategy (FSDS)
While not bound by the Federal Sustainable Development Act, CSC will contribute to the 2013-16 Federal Sustainable Development Strategy and the Federal Contaminated Sites Action Plan by completing remediation and risk management activities at known high priority federal contaminated sites. Two remediation projects are planned to begin during 2014-15:
- Frontenac Landfill #1 (along Front Road) (Project # 441-L02) - remediation in planning stage, remediation work to start in spring 2014.
- Frontenac Landfill #3 (along Cataraqui Creek) (Project # 441-L03) - remediation in planning stage; remediation work to start in spring 2014
In addition, CSC has its own corporate sustainable development strategy for 2012-15, and will continue to provide details on progress in future Departmental Performance Reports. Further, CSC completes environmental assessments prior to commencing any major infrastructure project such as the construction of new units in its existing facilities.
Section II: Analysis of Programs by Strategic Outcome
Strategic Outcome
The custody, correctional interventions, and supervision of offenders, in communities and institutions, contribute to public safety.
Program 1.0: Custody
Description
This program includes providing for the day-to-day needs of offenders, including health and safety, food, clothing, mental health services, and physical health care. It also includes security measures within institutions such as drug interdiction, and appropriate control practices to prevent incidents.
| 2014-15 Main Estimates | 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,471,011,448 | 1,471,011,448 | 1,461,224,723 | 1,465,874,636 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 10,966 | 10,966 | 10,966 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | RangesFootnote 3 | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSC manages the custody of offenders in institutions in a safe, secure and humane manner. | Rate of non-natural offender deaths in custody | 0.00 – 1.11 | 2014-15 |
| Rate of escapes from federal custody | 0.00 – 1.76 | ||
| Percentage of upheld inmate grievances | 3.88% – 4.39% |
Planning Highlight
- Further develop and implement the population management approach to enhance safety and security results, and to address accountability.
Sub-program 1.1: Institutional Management and Support
Description
The Institutional Management and Support sub-program includes the daily management of operational activities and institutional services for offenders. Key activities include the daily administration, operation and maintenance of institutions, establishing operational processes and procedures, ensuring compliance with national standards and regulations, managing allocated financial and human resources, directing and overseeing the delivery of integrated correctional operations, monitoring the effectiveness of institutional security activities, considering threats, risks, vulnerabilities and physical security requirements and controls, managing the intelligence function of the institution, ensuring coordination across the criminal justice system, ensuring a safe environment for staff and inmates, and making decisions and recommendations relative to offenders within delegated authorities.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 87,479,981 | 87,311,253 | 87,280,714 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 1,002 | 1,002 | 1,002 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Institutional management is compliant with policy and law. | Rate of critical safety incidentsFootnote 4 in federal institutions (suicides, accidental deaths) | 0.00 – 0.56 | 2014-15 |
| Rate of serious safety incidentsFootnote 5 in federal institutions | 0.00 – 3.65 | ||
| Rate of minor/ moderateFootnote 6 safety incidents in federal institutions | 0.00 – 74.90 |
Planning Highlight
- Improve institutional safety and security by focusing on policies and procedures at principal entrances to help prevent contraband and prohibited items from entering institutions.
Sub-program 1.2: Institutional Security
Description
The Institutional Security sub-program includes all activities related to the implementation of and compliance with policies and procedures designed to ensure the safety and security of staff, offenders and the public. Key activities include the implementation and coordination of security measures and related activities to meet the stratified requirements of a diverse inmate population.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 714,163,506 | 712,786,058 | 712,536,746 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 7,092 | 7,092 | 7,092 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Institutions are safe and secure. | Rate of critical security incidentsFootnote 7 in federal institutions (security-related deaths) | 0.00 – 0.22 | 2014-15 |
| Rate of serious security incidentsFootnote 8 in federal institutions | 0.00 – 7.30 | ||
| Rate of minor / moderate security incidentsFootnote 9 in federal institutions | 0.00 – 127.20 |
Planning Highlights
- Ensure effective management of cell assignment to support safe supervision strategies and reduce the number of institutional security incidents.
- Adapt emerging security-related technologies to the correctional environment to ensure program or service delivery IT security safeguards needs are met.
- Maintain, evaluate, update and implement, as required, emergency management plans (security, strategic emergency, and contingency), to enhance CSC’s ability to react to emergency situations quickly and in a manner that will mitigate the potential for security incidents arising out of emergency situations.
Sub-sub-program 1.2.1: Intelligence and Supervision
Description
The Intelligence and Supervision sub-sub-program encompasses all activities related to security and intelligence when dealing with offenders in institutions, and in the community in conjunction and cooperation with external partner agencies. Key activities include ongoing assessment of threats and risks to identify and mitigate both internal and external threats to the safety of individuals, (inmates, staff and public) and the institution; collaborating, liaising and sharing information with justice partners both domestically and internationally; identifying and managing Security Threat Groups; preventing, intercepting and eliminating any illegal or threatening activities in order to enhance our capacity to provide safe and secure institutions and community operations.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 701,246,513 | 699,893,979 | 699,649,176 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 6,994 | 6,994 | 6,994 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activities that threaten the safety and security of institutions are managed. | Rate of involuntary transfers | 101.60 – 105.90 | 2014-15 |
| Rate of serious security chargesFootnote 10 | 530.70 – 559.90 | ||
| Percentage of involuntary segregation utilization | 4.82% – 5.16% |
Planning Highlights
- Continue to work with key partners to help prevent contraband and prohibited items (e.g., drugs, tobacco, alcohol and cell phones) from entering institutions in order to reduce the supply of and prevent the transfer of illicit drugs, contraband and / or prohibited items in institutions.
- Continue to enhance the capacity of preventive security and intelligence in order to respond to and prevent threats and risks that exist in operational settings (institutional and community).
- Continue CSC’s working relationship with police for intelligence sharing and investigations related to security threat groups.
Sub-sub-program 1.2.2: Drug Interdiction
Description
The Drug Interdiction sub-sub-program encompasses all activities related to the coordination of Correctional Service of Canada’s national drug strategy, including the use of urinalysis and other security services such as drug detector dogs, ion mobility spectrometry, and other similar devices. Key activities include assessing risk related to drug use and trafficking, the detection and deterrence of drug use and / or trafficking of drugs, as well as procedures for reviewing the imposition of administrative measures. Ensuring a safe, drug-free institutional environment is a fundamental condition for the success of the reintegration of offenders into society as law-abiding citizens.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 12,916,993 | 12,892,079 | 12,887,570 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 98 | 98 | 98 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug interdiction activities contribute to successful completion of offenders' correctional plans. | Rate of critical drug-related incidentsFootnote 11 in federal institutions (deaths by overdose) | 0.00 – 0.09 | 2014-15 |
| Rate of serious drug-related incidentsFootnote 12 | 0.00 – 2.94 | ||
| Rate of minor / moderate drug-related incidentsFootnote 13 | 0.00 – 195.60 |
Planning Highlight
- Strengthen operational policies and / or procedures to eliminate the entry of illicit materials to reduce the trafficking and supply of drugs in institutions, thereby reducing drug-related incidents and helping offenders complete their correctional plans.
Sub-program 1.3: Institutional Health Services
Description
The Institutional Health Services sub-program includes provision of essential health care services and reasonable access to non-essential mental health services to inmates, in accordance with professionally accepted standards. Key activities include the delivery of public, clinical and mental health services such as basic primary health care, dental care, psychological counselling and infectious disease detection, treatment and prevention, as well as overall administration, developing, implementing and updating medical directives, policy, quality improvement, accreditation, research and performance measurement for health services.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 189,610,528 | 189,244,816 | 189,178,623 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 1,340 | 1,340 | 1,340 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health services are available to all offenders in institutions in accordance with professionally accepted standards. | Maintain Health Services Accreditation. | Accreditation | 2014-15 |
| Of the offenders identified by the Computerized Mental Health Intake Screening System (COMHISS) as requiring follow-up mental health services, the percentage who received a service | Not less than 72% | ||
| Percentage of offenders who received an institutional mental health service | 32% |
Planning Highlight
- Maintain CSC’s health accreditation status as per Accreditation Canada standards, including the Continuous Quality Improvement program, to ensure that health services are available to all offenders in institutions in accordance with professionally accepted standards.
Sub-sub-program 1.3.1: Public Health Services
Description
The Public Health Services sub-sub-program encompasses all public health activities related to: infectious disease prevention, control and management among offenders; health promotion and health education; surveillance and knowledge sharing; and includes a focus on Aboriginal and women offender health.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 11,305,483 | 11,283,677 | 11,279,731 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 97 | 97 | 97 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public health services are available to all offenders in institutions in accordance with professionally accepted standards. | Percentage of newly admitted offenders who were offered assessments for Blood Borne and Sexually Transmitted Infections (BBSTI) and Tuberculosis (TB) | BBSTI 85% - 90% TB 85% - 90% |
2014-15 |
| Percentage of newly admitted offenders who attended Reception Awareness Program at admission | 65% - 75% |
Planning Highlight
- Continue to deliver public health services to inmates in order to prevent and control disease and promote good health within federal institutions.
Sub-sub-program 1.3.2: Clinical Health Services
Description
The Clinical Health Services sub-sub-program includes the provision of medical and clinical services for inmates in institutions, including nursing, pharmacy services, Opiate Substitution Therapy Program, palliative care, outside hospitalization, dental services and optometry, etc.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 121,167,564 | 120,933,862 | 120,891,562 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 755 | 755 | 755 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical health services are available to all offenders in institutions in accordance with professionally accepted standards. | Percentage of newly admitted offenders receiving intake nursing assessment within 24 hours of initial reception | 90% - 100% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of offenders receiving comprehensive nursing assessment within 14 days of admission to Correctional Service of Canada | 90% - 100% |
Planning Highlight
- Continue monitoring the application of essential services framework and implementation of regional pharmacies to ensure CSC provides offenders with essential health care that conforms to professionally accepted standards, respects gender, cultural and linguistic differences and is responsive to the special and specific needs of women and Aboriginal people.
Sub-sub -program 1.3.3: Mental Health Services
Description
The Mental Health Services sub-sub program includes provision of essential mental health services and reasonable access to non-essential mental health services for inmates. The activities include provision of mental health services in mainstream institutions by interdisciplinary teams of mental health professionals (which may include psychiatrists, psychologists, mental health nurses, social workers, etc.). In addition, CSC operates five Regional Treatment Centres that provide care to offenders with the most serious mental health conditions who require in-patient treatment.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 57,137,481 | 57,027,277 | 57,007,330 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 487 | 487 | 487 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mental health services are available to offenders in institutions in accordance with professionally accepted standards. | Percentage of newly admitted offenders screened by Computerized Mental Health Intake Screening System within prescribed timeframes | 72% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of target staff trained in the fundamentals of mental health | 90% (MarkerFootnote 14) |
Planning Highlights
- Strengthen the continuum and continuity of specialized mental health support throughout the duration of offenders’ sentences to address the mental health needs of the offender population.
- Implement sub-population approaches for offenders with mental health care needs to provide offenders with efficient, effective health services that encourage individual responsibility, promote healthy reintegration and contribute to safe communities.
Sub-program 1.4: Institutional Services
Description
The Institutional Services sub program includes all activities related to the daily operations of institutions for offenders. Key services include accommodation support, engineering services, food services, clothing, institutional maintenance, fleet management, telecommunications, environmental protection and sustainable development, fire safety protection, security electronics.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 479,757,433 | 471,882,596 | 476,878,553 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 1,532 | 1,532 | 1,532 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inmates are provided safe, secure and humane living conditions. | Percentage of upheld grievances related to living conditions | 3.3% – 5.8% | 2014-15 |
Planning Highlight
- Streamline the procurement and lifecycle of equipment and services in order to provide safe, secure and humane living conditions to inmates.
Sub-sub-program 1.4.1: Food Services
Description
The Food Services sub-sub program provides for the provision of nutritious balanced meals to offenders. Key activities include setting the overall policy direction for the delivery of food services, monitoring food services activities to ensure adherence to standards; ensuring meals provided to the inmate population meet the appropriate nutrition standards for Canadians such as Eating Well with Canada’s Food GuideEndnote x and dietary reference intakes; meeting the dietary needs of inmates following a specific diet to meet the requirements of their faith or a therapeutic diet as part of a treatment regimen; ensuring all activities required for ordering, storage, preparation and service of food and disposal of waste meet the food safety standards, and ensuring that the cost of meals provided are within established allotments.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 58,900,224 | 58,790,478 | 58,770,614 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 413 | 413 | 413 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inmates' dietary needs are met in accordance with the Canada Food Guide. | Percentage of positive health inspections by external health inspectors | 91% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of compliance with menus meeting Canada’s Food Guide and Dietary Reference Intakes | 25% (Marker) | ||
| Percentage of upheld grievances related to food services | 5.3% - 7.25% |
Planning Highlight
- Modernize food services preparation and delivery to reduce costs and positively impact the rate of compliant health inspections and the compliance with Canada’s Food Guide and Dietary Reference Intakes.
Sub-sub-program 1.4.2: Accommodation Services
Description
The Accommodation Services sub-sub-program includes all physical resources and support services necessary to meet operational requirements within institutions for offenders. Key activities include the provision of basic necessities to offenders, technical support, housekeeping, laundry services, plant maintenance, engineering services, environmental services, waste management, electrical, water and sewage, heating / co-generation of energy, plumbing, fire protection, motor vehicle maintenance and operations, carpentry, masonry, painting, welding and millwright, general labour, general maintenance, and landscaping.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 420,857,209 | 413,092,118 | 418,107,939 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 1,119 | 1,119 | 1,119 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inmates are provided safe and clean living and working environments. | Percentage of upheld grievances related to accommodation services | 1.71% - 4.63% | 2014-15 |
Planning Highlight
- Implement a revised governance structure for facilities maintenance for the provision of safe and clean living and working environments to inmates.
Program 2.0: Correctional Interventions
Description
The Correctional Interventions program includes assessment activities and program interventions for federal offenders, as well as activities directed toward engaging Canadian citizens as partners in CSC's correctional mandate and outreach to victims of crime. Correctional Interventions are designed to assist the rehabilitation of offenders and facilitate their reintegration into the community as law abiding citizens.
| 2014-15 Main Estimates | 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|---|
| 465,029,970 | 465,029,970 | 464,133,040 | 463,970,700 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 4,615 | 4,615 | 4,615 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offender risks and needs are identified and addressed with targeted correctional interventions. | Percentage of sentence served prior to first release | 63.7% (Marker) | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of offenders with an identified need who complete a nationally recognized correctional program prior to full parole eligibility date | 56.6% – 61.9% | ||
| Percentage of offenders with an identified need who complete a nationally recognized correctional program prior to warrant expiry date | 90.1% – 90.6% |
Planning Highlights
- Strengthen relationships with the Commissioner’s National Aboriginal Advisory Committee through consultations, in order to maximize their contributions to the enhancement of Aboriginal correctional policies, programs and operations in CSC.
- Continue the focus on and use of pathways units as a key culturally – based environment for all security levels.
- Continue to strengthen the case management framework to identify and address offender risks and needs through targeted correctional interventions.
Sub-program 2.1: Offender Case Management
Description
The Offender Case Management sub-program encompasses all activities at the community institutional, regional and national levels related to offender reintegration risks and needs assessment; the development and management of individualized offender correctional plans, institutional and community case supervision, as well as, overall sentence management. Key activities include: sentence management, intake assessment, penitentiary placement, offender personal development, transfers, correctional plan development, institutional and community supervision.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 279,062,126 | 278,523,883 | 278,426,463 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 2,938 | 2,938 | 2,938 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| The accurate assessment of risk and supervision of offenders contributes to a reduction in crime. | Percentage of initial penitentiary placements uninterruptedFootnote 15 | 94.7% – 95.1% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of successful transfers to lower security | 95.5% – 96.3% | ||
| Percentage of Day Parole cases reviewed by Parole Board Canada, based on the total number of cases eligible for a review | 61.9% (Marker) |
Planning Highlights
- Continue implementing the Strategic Plan for Aboriginal Corrections (SPAC) through engaging sectors and regions and working with community partners to improve results in Aboriginal corrections.
- Continue to implement strategies to enhance the successful reintegration of Inuit offenders into society, such as providing culturally-relevant service to Inuit offenders.
- Continue to strengthen the case management framework in providing evidence-based assessment and interventions relative to offender risks and needs.
Sub-program 2.2: Community Engagement
Description
The Community Engagement sub-program includes all activities related to enhancing the engagement of citizens as partners in the fulfillment of the correctional mandate with offenders. Key activities include: raising public awareness and improving confidence in federal corrections; providing victims with information, creating collaborative working relationships with various segments of the community, including citizens, non-governmental agencies, other government departments, and offenders who have successfully reintegrated into the community; and negotiating partnership agreements with various stakeholders.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 8,203,500 | 8,187,677 | 8,184,814 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 73 | 73 | 73 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| The involvement of the public contributes to the offender reintegration process. | Number of Canadians engaged through initiatives funded under the Outreach Fund that address the themes of: Building relationships with new or existing stakeholders; Enhancing the role of Aboriginal communities; Cultural diversity; Mental health; and Current issues / Community safety | 1,500 | 2014-15 |
| Number of operational units which engage citizens to provide advice, promote volunteer involvement, act as impartial observers, provide feedback and liaise with partners and stakeholders | 87 | ||
| Number and percentage of offenders with registered victims | 3,874 and 17% (Markers) |
Planning Highlights
- Strengthen community engagement by sustaining existing partnerships and developing new and diverse ones with partners and stakeholders at local and national levels to share information and provide support and continuum of care for offenders, thereby contributing to the safe reintegration of offenders into Canadian communities.
- Continue to provide services to victims of crime, such as providing notifications, raising awareness, receiving information from victims, and including their concerns in decision making.
- Develop and implement CSC’s Integrated Engagement Strategy to promote, build and maintain strong relationships with community partners to help successful reintegration of offenders in Canadian communities.
- Increase use of technological communications to maintain engagement with citizen advisory groups, victim services, community chaplaincy organizations, and other partners.
Sub-program 2.3: Spiritual Services
Description
The Spiritual Services sub-program includes all activities related to spiritual guidance to offenders. Key activities include directing and coordinating religious services and sacramental ministry for inmates, creating, coordinating, and delivering religious activities, interpreting to the community the needs and concerns of persons affected by the criminal justice system and educating the community concerning their role in reconciliation as well as establishing and maintaining partnerships to assist ex-offenders to live in the community as law-abiding citizens.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 17,287,493 | 17,254,149 | 17,248,114 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offenders have access to spiritual services | Percentage compliance with established standards for spiritual services | 100% | 2014-15 |
| Number of contacts with offenders | Institutional Chaplains: 152,000 contacts with offenders; Faith-community reintegration partners: 15,050 contacts with offenders |
||
| Number of activities and / or hours in which volunteers are engaged | Institutional Chaplains: 23,050 activities Faith-community reintegration partners: 17,075 hours |
Planning Highlights
- Increase volunteer involvement with faith-based organizations to enhance and sustain offender support opportunities. CSC will continue to foster these external partnerships to ensure that the religious and spiritual needs of offenders are identified and addressed with respect to CSC’s legal obligations.
- Maintain relationship with the Interfaith Committee (IFC) on Chaplaincy to ensure that the religious and spiritual needs of offenders are met, and partnerships with individual faith groups are strengthened.
Sub-program 2.4: Correctional Reintegration Program
Description
The Correctional Reintegration Program sub-program encompasses structured interventions that address empirically-validated factors directly linked to federal offenders’ criminal behaviour in order to reduce re-offending. Key activities include the development, implementation, delivery and effective management of national correctional programs designed to prevent criminal behavior.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 110,037,165 | 109,824,931 | 109,786,517 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 937 | 937 | 937 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participation in Correctional Reintegration Programs contributes to the offender reintegration process | Median time to first enrolment in a nationally recognized institutional correctional program | 160 – 187 days | 2014-15 |
| Median time to first enrolment in a nationally recognized community-based correctional program | 42 – 43 days | ||
| Percentage nationally recognized correctional program completions | 80.2% – 83.5% |
Planning Highlights
- Continue the development and implementation of initiatives to improve and enhance reintegration program delivery that target the criminogenic needs of offenders at intensity levels commensurate with the risk levels to reduce recidivism.
- Fully implement the Integrated Correctional Program Model that holistically addresses the multiple individual needs and risks of offenders in order to enhance efficiency and effectiveness of correctional program delivery and thus improve public safety results.
- Ensure all correctional program policies and guidelines are up to date, and address efficient and effective program delivery so that the framework for program delivery continues to be relevant.
Sub-sub-program 2.4.1: Violence Prevention Program
Description
The Violence Prevention Program sub-sub program is a set of structured interventions designed to assist the rehabilitation of offenders convicted of violent crimes. The Violence Prevention Program addresses empirically-validated factors directly linked to offenders’ violent behaviour. Key activities include the development, implementation, delivery and management of national correctional programs designed to protect society by preventing violent behavior.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 9,921,241 | 9,902,106 | 9,898,642 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 95 | 95 | 95 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Completion of correctional program to address violence contributes to reduced crime, including violent crime | Percentage of offenders with an identified need for Violence Prevention programming who complete prior to full parole eligibility date | 32.6% – 47.8% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of offenders with an identified need for Violence Prevention programming who complete prior to warrant expiry date | 75.9% – 80.5% |
Planning Highlight
- Continue to plan, deliver, and monitor nationally-recognized correctional programs to address violence with initiatives that target the criminogenic needs of offenders at intensity levels commensurate with the assessed risk.
Sub-sub-program 2.4.2: Substance Abuse Program
Description
The Substance Abuse Program sub-sub-program is a set of structured interventions designed to assist the rehabilitation of offenders convicted of crimes complicated by substance abuse. The Substance Abuse Program addresses empirically-validated factors directly linked to offenders’ criminal behavior, alcohol and drug use. Key activities include the development, implementation, delivery and management of national correctional programs designed to protect society by preventing substance abuse and crime.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 9,877,952 | 9,858,899 | 9,855,451 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 93 | 93 | 93 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Completion of correctional program to address substance abuse contributes to reduced crime, including violent crime | Percentage of offenders with an identified need for Substance Abuse programming who complete prior to full parole eligibility date | 47.8% – 52.2% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of offenders with an identified need for Substance Abuse programming who complete prior to warrant expiry date | 74.1% – 79.2% |
Planning Highlight
- Continue to plan, deliver, and monitor nationally recognized correctional programs to address substance abuse with initiatives that target the criminogenic needs of offenders at intensity levels commensurate with the assessed risk.
Sub-sub-program 2.4.3: Family Violence Program
Description
The Family Violence Prevention Program sub-sub-program is a set of structured interventions designed to assist the rehabilitation of offenders convicted of violent crimes against intimate partners. The Family Violence Prevention Program addresses empirically-validated factors directly linked to offenders’ violent behaviour. Key activities include the development, implementation, delivery and management of national correctional programs designed to protect society by preventing domestic violence.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 2,111,312 | 2,107,240 | 2,106,503 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Completion of correctional program to address family violence contributes to reduced crime, including violent crime | Percentage of offenders with an identified need for Family Violence programming who complete prior to full parole eligibility date | 23.5% – 42.7% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of offenders with an identified need for Family Violence programming who complete prior to warrant expiry date | 58.9% – 66.5% |
Planning Highlight
- Continue to plan, deliver, and monitor nationally recognized correctional programs to address family violence with initiatives that target the criminogenic needs of offenders at intensity levels commensurate with the assessed risk.
Sub-sub-program 2.4.4: Sex Offender Program
Description
The Sex Offender Program sub-sub-program is a set of structured interventions designed to assist the rehabilitation of offenders who are at risk to commit sexual offences. The Sex Offender Program addresses empirically-validated factors directly linked to offenders’ criminal sexual behaviour. Key activities include the development, implementation, delivery and management of national correctional programs designed to protect society by preventing sexual offences.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 4,903,452 | 4,893,995 | 4,892,283 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 42 | 42 | 42 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Completion of correctional program to address sexual violence contributes to reduced crime, including violent crimes | Percentage of offenders with an identified need for Sex Offender programming who complete prior to full parole eligibility date | 27.3% – 34.1% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of offenders with an identified need for Sex Offender programming who complete prior to warrant expiry date | 82.9% – 83.7% |
Planning Highlight
- Continue to plan, deliver, and monitor nationally recognized correctional programs to address sexual violence with initiatives that target the criminogenic needs of offenders at intensity levels commensurate with the assessed risk.
Sub-sub-program 2.4.5: Maintenance Program
Description
The Correctional Maintenance Program sub-sub-program is a set of structured interventions designed to assist the rehabilitation of offenders who have completed national correctional programs. It addresses empirically-validated factors directly linked to offenders’ criminal behaviour. Key activities include the development, implementation, delivery and management of national correctional programs designed to protect society by preventing crime.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 6,370,412 | 6,358,125 | 6,355,901 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 71 | 71 | 71 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Completion of Community Maintenance Programs contributes to reduced crime, including violent crime | Percentage Community Maintenance program completions | 55.0% – 65.6% | 2014-15 |
Planning Highlight
- Continue to plan, deliver, and monitor maintenance programs that are included as part of nationally recognized correctional programs with initiatives that target the criminogenic needs of offenders at intensity levels commensurate with the assessed risk.
Sub-sub-program 2.4.6: Social Program
Description
The Social Program sub-sub program is a set of activities designed to assist humane custody and the reintegration of all federal offenders through the provision of recreation, self-help, life skills training, and community contact opportunities. Key activities include the development, implementation, delivery and management of social programs designed to assist offender reintegration into the community as law abiding citizens.
NOTE: The delivery of the Integrated Correctional Program Model, first mentioned on page 8, is also largely incorporated into this sub-sub-program, and so the planned financial and FTE numbers recorded below capture more than social programs. It is being implemented gradually across all regions, which will require adjustments to program and financial reporting. The Integrated Correctional Program Model model includes three distinct correctional program streams: a multi-target program, an Aboriginal multi-target program, and a sex offender program, all of which include a maintenance component. This model targets the needs and risks presented by specific offender populations. The multi-target nature of the program streams allows CSC to more holistically address the individual needs and risks of offenders, and it enhances offenders’ understanding of the interplay among their multiple personal risk factors, as well as their understanding of how the same skill sets can be used to effectively manage them.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 76,852,796 | 76,704,566 | 76,677,737 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 612 | 612 | 612 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offenders participate in social programs | Number of Community Integration Programs delivered | 35 (Marker) | 2014-15 |
Planning Highlight
- Provide activities, such as recreation, self-help, life skills training, to offenders to allow them to participate in social programs and gain social skills that help them reintegrate into the community.
Sub-program 2.5: Offender Education
Description
The Offender Education Program sub-program is a set of interventions designed to assist the reintegration of federal offenders by increasing education levels to promote employment and rehabilitation opportunities. Offender Education Programs include academic assessment, delivery of provincially accredited and certified education curricula, and library services. Key activities include: education needs assessment, the implementation, delivery and management of provincial adult basic and secondary education programs and library services.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 24,343,106 | 24,296,154 | 24,287,656 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 170 | 170 | 170 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education programs contribute to the rehabilitation and reintegration of offenders. | Percentage of offenders with an identified education need who upgrade their education prior to full parole eligibility date | 30.5% – 36.4% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of offenders with an identified education need who upgrade their education prior to warrant expiry date | 41.3% – 49.4% |
Planning Highlight
- Continue to develop and monitor the plans and results of education programs in order to provide offenders with the basic literacy, academic, and personal development skills that are needed to succeed in the community.
Sub-program 2.6: CORCAN Employment and Employability
Description
The CORCAN Employment and Employability sub-program is focused on employment skills development to meet the specific demands of the labour market while preparing offenders for release. It includes employment training and career planning programs for inmates and is designed to allow offenders to acquire skills, attitudes and behaviours valued by employers. CORCAN program plays a key role in CSC’s efforts to actively encourage offenders to become law-abiding citizens. Vocational Education, Employment Skills and Career Counselling, and Specific Employment Skills, On-the-job Training and National Employability Skills Program are also included in this program area. CSC provides employment services and job placement to offenders after release.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 26,096,580 | 26,046,246 | 26,037,136 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 475 | 475 | 475 |
NOTE: The Planned Spending does not include CORCAN’s expenditures; however, the planned Human Resources figures include CORCAN’s FTEs that will be funded from the CORCAN Revolving Fund.
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offenders have the employment skills to meet labour markets and obtain employment upon release from institutions. | Percentage of offenders with an identified employment need who complete vocational training prior to first release | 49.5% – 50.84% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of offenders with an identified employment need who secure employment in the community prior to warrant expiry date | 59.6% – 62.8% |
Planning Highlight
- Provide offenders with marketable employment skills through “learning to work” and on-the-job skills development along with certified apprenticeship hours and vocational certificates certified through various partnerships that will assist them to be employment ready upon release.
Program 3.0: Community Supervision
Description
The Community Supervision program includes all program activities that protect society through the administration of community operations, including the provision of accommodation options, establishment of community partnerships and provision of community health services as necessary. Community supervision provides the structure to assist offenders to safely and successfully reintegrate into society.
| 2014-15 Main Estimates | 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|---|
| 93,399,963 | 93,399,963 | 93,219,817 | 93,187,211 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 211 | 211 | 211 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offenders are reintegrated into the community as law-abiding citizens while under supervision. | Percentage of offenders on conditional release successfully reaching warrant expiry date without re-offending (no revocation, charge or conviction) | 47.75% – 53.6% | 2014-15 |
| Percentage of supervision intensity successfully reduced | 83.5% (Marker) | ||
| Percentage of time employed in the community | 58.9% – 61.2 % |
Planning Highlight
- Strengthen management and community capacity by implementing the Federal Community Corrections Strategy to identify and address specific targets to increase community capacity and thus enhance the safe reintegration of offenders under supervision in the community.
Sub-program 3.1: Community Management and Security
Description
The Community Management and Security sub-program includes all activities related to the administration of the supervision and management of offenders in the community in an effort to ensure safe reintegration of offenders thereby contributing to public safety.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 12,671,608 | 12,647,167 | 12,642,744 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 120 | 120 | 120 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community management is compliant with policy and law. | Rate of critical convictions under supervision | 0.00 – 0.84 | 2014-15 |
| Rate of serious convictions under supervision | 0.00 – 53.60 | ||
| Rate of minor/moderate convictions under supervision | 225.20 – 256.80 |
Planning Highlights
- Explore the use of technology and software to enhance the safety of community staff members and the public.
- Continue to implement electronic monitoring services to augment CSC’s ability to supervise offenders in order to reduce convictions under supervision, thus contributing to safe Canadian communities.
Sub-program 3.2: Community-based Residential Facilities
Description
The Community-based Residential Facilities sub-program includes all activities related to the provision of a structured and supportive environment during the gradual reintegration process through the provision of accommodation for offenders on parole, statutory release, temporary absence or Long Term Supervision Order. CSC has federally operated residential facilities and contracts with numerous non-governmental organizations to provide services, support and monitoring of offenders on release.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 73,688,937 | 73,546,809 | 73,521,084 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 17 | 17 | 17 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community-based Residential Facilities provide supervised and supportive accommodation that supports safe reintegration | Percentage of successful residency supervision periods (no revocations, sensational incidents, charges or convictions) - Community-based Residential Facilities | 69.41% – 71.6% | 2014-15 |
| Rate of Community-based Residential Facility incidents | 156.80 (Marker) |
Planning Highlights
- Implement strategies to provide the flexibility required to appropriately respond to future offender population requirements.
- Enhance community accommodation for offenders in conjunction with community partners to establish the most appropriate accommodation options for offenders who are on conditional release, particularly those with special needs and/or with a residency requirement, and to respond to operational needs.
Sub-sub-program 3.2.1: Community Residential Facilities
Description
The Community Residential Facilities sub-sub-program includes all activities related to the provision of accommodation for offenders in what is commonly referred to as halfway houses as well as Hostels, Private Home Placements and Treatment Centres. Community Residential Facilities are operated by non-profit community-based agencies under contract with CSC. Community Residential Facilities promote the successful reintegration of offenders and ensure public safety by providing supervision, intervention, support, monitoring and accommodation for offenders on release.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 65,439,986 | 65,313,768 | 65,290,923 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| Not applicable – contracts with community agencies |
Not applicable – contracts with community agencies |
Not applicable – contracts with community agencies |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Ranges | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offenders with residency conditions have appropriate supervision and housing in the community. | Percentage of successful residency supervision periods (no revocations, sensational incidents, charges or convictions) - Community Residential Facilities | 71.99% – 74.66% | 2014-15 |
| Rate of "fail to returnFootnote 16" among offenders residing in a Community Residential Facility | 0.00 – 442.20 |
Planning Highlight
- Manage Community Residential Facility (CRF) contracts to provide a continuous, integrated continuum of offender accommodation services allowing for improved planning in response to offender needs to support safe supervision strategies that will provide the flexibility required to appropriately respond to future offender population requirements.
Sub-sub-program 3.2.2: Community Correctional Centres
Description
The Community Correctional Centres sub-sub-program encompasses all activities related to the management of federally operated community-based residential facilities that provide a 24-hour, structured living environment for the purpose of safely reintegrating offenders into the community. Community Correctional Centres accommodate offenders under federal jurisdiction who have been released to the community on unescorted temporary absences, day parole, full parole, work releases, statutory release, as well as those subject to long-term supervision orders. Community Correctional Centres are designated as minimum security institutions.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 8,248,951 | 8,233,041 | 8,230,161 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 17 | 17 | 17 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Higher risk offenders have appropriate levels of supervision and housing while on conditional release with a residency condition | Percentage of successful residency supervision periods (no revocations, sensational incidents, charges or convictions) - Community Correctional Centres | 47.77% – 50.65% | 2014-15 |
| Rate of "fail to returnFootnote 17" among offenders residing in a Community Correctional Centre | 0.00 – 769.80 |
Planning Highlight
- Improve community accommodation for offenders by providing a highly-structured living environment for those who require specialized accommodation to successfully and safely reintegrate into the community to ensure higher risk offenders are appropriately supervised while on conditional release with a residency condition, which contributes to community safety.
Sub-program 3.3: Community Health Services
Description
Through the Community Health Services sub-program, CSC pays, on a fee-for-service basis, the costs associated with essential health services for non-insured offenders in the community. In addition, at some community sites, CSC provides mental health services to offenders with significant mental health challenges in order to contribute to their successful reintegration into the community. Key activities include providing specialized psychological support and services to address mental health needs (e.g. crisis intervention and counselling), and linkage with community agencies.
| 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|
| 7,039,418 | 7,025,841 | 7,023,383 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 75 | 75 | 75 |
| Program Expected Results |
Performance Indicators | Expected Performance | Fiscal Year Achieved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mental health services are available to offenders in the community in accordance with professionally accepted standards | Percentage of offenders who received a community mental health service | 22% | 2014-15 |
Planning Highlight
- Collaborate with other jurisdictions on mental health in order to provide continuity of mental health services to offenders in the community.
4.0: Internal Services
Description
Internal Services are groups of related activities and resources that are administered to support the needs of programs and other corporate obligations of an organization. These groups are: Management and Oversight Services; Communications Services; Legal Services; Human Resources Management Services; Financial Management Services; Information Management Services; Information Technology Services; Real Property Services; Materiel Services; Acquisition Services; and Travel and Other Administrative Services. Internal Services include only those activities and resources that apply across an organization and not to those provided specifically to a program.
| 2014-15 Main Estimates | 2014-15 Planned Spending | 2015-16 Planned Spending | 2016-17 Planned Spending |
|---|---|---|---|
| 305,241,011 | 305,241,011 | 304,657,141 | 304,551,463 |
| 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 |
|---|---|---|
| 2,929 | 2,929 | 2,929 |
Planning Highlights
- Promote the Values and Ethics Code for the Public Sector and the CSC Values Statement by updating existing values and ethics training components embedded in various CSC learning programs, as well as maintaining specialized training in Values and Ethics.
- Promulgate and implement a new guideline that focuses on gender and diversity based analysis.
- Continue to collaborate with key stakeholders and increase awareness of Internal Disclosure and services of the Office of Conflict Management among staff and managers to promote the concept of respectful workplaces and engage staff in working together to achieve this goal.
- Continue the implementation of management tools, such as CSC’s Departmental Security Plan, the Five-Year Evaluation Plan (2013–2014 to 2017–2018), the Three-Year Risk-Based Audit Plan, CSC’s Strategic Plan for Human Resource Management 2012-2015, the National Recruitment & Retention Action Plan for health professionals, CSC/Parole Board Canada IM/IT 2014–17 Business Plan to ensure management effectiveness.
- Hold regular and open consultations with provincial/territorial partners at both regional and national levels to ensure that information is shared among the various jurisdictions, thus contributing to effective communications within the Canadian criminal justice system.
- Finalize the implementation of the redesigned Parole Officer Induction Training which provides new parole officers with the necessary skills to complete sound risk assessments.
- Advance CSC’s multi-year action plan to implement the Treasury Board Policy on Internal Control and enhance processes to analyze, monitor and report on the financial situation.
- Develop financial strategies in response to budgetary constraints and continue to implement CSC’s multi-year plan (2012–13 to 2014–15) to enhance the resource allocation model.
- Implement a revised asset management and accounting policy in keeping with the latest Treasury Board Secretariat definitions regarding capital expenditures and ensure capital and operating resources are aligned accordingly.
- Finalize the standardization of chiefs of Materiel Management roles and responsibilities across the organization, and strengthen contracting management by introducing more standardized templates and exploring consolidation of some roles and responsibilities for maximum effectiveness.
Section III: Supplementary Information
Consolidated Future-Oriented Statement of Operations
The Consolidated Future-Oriented Statement of Operations presented in this subsection is intended to serve as a general overview of the Correctional Service of Canada’s operations. The forecasted financial information on expenses and revenues are prepared on an accrual accounting basis to strengthen accountability and to improve transparency and financial management.
Because the Consolidated Future-Oriented Statement of Operations is prepared on an accrual accounting basis and the forecast and planned spending amounts presented in other sections of this report are prepared on an expenditure basis, amounts will differ.
A more detailed Consolidated Future-Oriented Statement of Operations and associated notes, including a reconciliation of the net costs of operations to the requested authorities, can be found on the Correctional Service of Canada website.Endnote xi
| Financial information | Estimated Results 2013−14 | Planned Results 2014–15 |
Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total expenses | 2,669,191,000 | 2,483,566,000 | (185,625,000) |
| Total revenues | 44,568,000 | 47,936,000 | 3,368,000 |
| Net cost of operations | 2,624,623,000 | 2,435,630,000 | 188,993,000 |
CSC's 2014-15 planned expenses are projected to be $2,483,566,000. These expenses include planned spending presented in this Report on Plans and Priorities and also include expenses such as amortization, services provided without charge and accrued employee future benefits. CSC's consolidated future-oriented revenues are projected to be $47,936,000 in 2014-15. Revenues are primarily generated by the CORCAN revolving fund.
The variance in CSC’s net cost of operations is mainly attributable to additional savings related to the Canada’s Economic Action Plan 2012 and some expenditures that will not be incurred at the same level in 2014-15 as in 2013-14, such as the payment of retroactive pay.
List of Supplementary Information Tables
The supplementary information tables listed in the 2014–15 Report on Plans and Priorities can be found on the Correctional Service Canada websiteEndnote xii.
- Disclosure of Transfer Payment Programs (TPPs) under $5 millionEndnote xiii;
- Greening Government OperationsEndnote xiv;
- Upcoming Internal Audits and Evaluations over the next three fiscal yearsEndnote xv; and
- User FeesEndnote xvi
Tax Expenditures and Evaluations
The tax system can be used to achieve public policy objectives through the application of special measures such as low tax rates, exemptions, deductions, deferrals and credits. The Department of Finance publishes cost estimates and projections for these measures annually in the Tax Expenditures and EvaluationsEndnote xvii publication. The tax measures presented in the Tax Expenditures and Evaluations publication are the sole responsibility of the Minister of Finance.
Section IV: Organizational Contact Information
Correctional Service of Canada website: https://www.canada.ca/en/correctional-service/
340 Laurier Avenue West
Ottawa, Ontario
K1A 0P9
Email: Feedback form
Endnotes
Endnotes
- i
-
Estimates on Treasury Board Secretariat website,
http://www.tbs-sct.gc.ca/ems-sgd/esp-pbc/esp-pbc-eng.asp - ii
-
Selected Departmental Performance Reports for 2008-2009 – Department of Industry, Department of Transport. Report of the Standing Committee on Public Accounts, September 2010,
http://www.parl.gc.ca/HousePublications/Publication.aspx?Mode=1&Parl=40&Ses=3&Language=E&DocId=4653561&File=0 - iii
-
Strengthening Parliamentary Scrutiny of Estimates and Supply. Report of the Standing Committee on Government and Operations Estimates, June 2012,
http://www.parl.gc.ca/HousePublications/Publication.aspx?DocId=5690996&Language=E&Mode=1&Parl=41&Ses=1 - iv
-
Whole-of-government framework,
https://www.justice.gc.ca/eng/rp-pr/cp-pm/rpp/2015_2016/rep-rap/p2.html - v
-
Corrections and Conditional Release Act,
http://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/C-44.6/index.html - vi
-
Corrections and Conditional Release Regulations,
http://laws.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-92-620/ - vii
-
Correctional Service of Canada’s Mission,
/en/correctional-service/corporate.html#mandat - viii
-
Treasury Board Secretariat Whole-of-Government Framework:
http://www.tbs-sct.gc.ca/ppg-cpr/frame-cadre-eng.aspx - ix
-
Treasury Board Secretariat 2014–15 Main Estimates:
http://www.tbs-sct.gc.ca/ems-sgd/esp-pbc/me-bpd-eng.asp - x
-
Canada’s Food Guide, http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/fn-an/food-guide-aliment/index-eng.php
- xi
-
Detailed Consolidated Future-Oriented Statement of Operations,
/correctional-service/corporate/transparency/reporting/future-oriented-statement-operations/future-oriented-statement-operations.html - xii
-
Correctional Service of Canada’s website,
/en/correctional-service.html - xiii
-
Disclosure of Transfer Payment Programs (TPPs) under $5 million,
disclosure-transfer-payment-program-under-5-million.html - xiv
-
Greening Government Operations,
greening-government-operations.html - xv
-
Upcoming Internal Audits and Evaluations over the next three fiscal years,
audits-evaluations.html - xvi
-
User Fees,
user-fees.html - xvii
-
Government of Canada Tax Expenditures,
https://www.canada.ca/en/department-finance/services/publications/federal-tax-expenditures/2014.html
Footnotes
- Footnote 1
-
Temporary detainees are held in custody in cases of suspension of a conditional release.
- Footnote 2
-
Type is defined as follows: previously committed to—committed to in the first or second fiscal year prior to the subject year of the report; ongoing—committed to at least three fiscal years prior to the subject year of the report; and new—newly committed to in the reporting year of the RPP or DPR. If another type that is specific to the department is introduced, an explanation of its meaning will be provided.
- Footnote 3
-
“Ranges”/“Expected Performances” are reported as a percentage, or a number, or by a rate per 1,000 offenders.
- Footnote 4
-
Critical safety incidents include all deaths in custody where cause of death is suicide or accident.
- Footnote 5
-
Serious safety incidents comprise any safety incident (that did not result in actual death) including any incident of suicide or attempted suicide (that did not result in actual death) and any incident of: self-inflicted; accident; damage to government property; fire; medical emergency; medical emergency – not attributable to assaultive behavior; damage to property of other person; hunger strike; or protective custody request.
- Footnote 6
-
Minor/moderate safety incidents include the safety incidents not included above and that did not result in actual death; major; or serious bodily harm.
- Footnote 7
-
Critical security incidents comprise all non-natural deaths in custody, including murder, use of force, awaiting coroner’s report, and undetermined.
- Footnote 8
-
Serious security incidents include security incidents that are serious violent, major disturbances, and escapes.
- Footnote 9
-
Minor/Moderate security incidents include any security incident that did not result in actual death, or major or serious bodily harm.
- Footnote 10
-
Serious security charges (which include only those charges that resulted in a “guilty” finding) are laid when an offender commits, attempts or incites acts that are serious breaches of security, are violent, harmful to others, or repetitive violations of rules.
- Footnote 11
-
Critical drug-related incidents are offender deaths in federal institutions due to overdose.
- Footnote 12
-
Serious drug-related incidents include any drug-related incident where there was at least one person involved in the incident who incurred an injury of major or serious bodily harm.
- Footnote 13
-
Minor/moderate drug-related incidents include any drug-related incident where there was at least one identified instigator who committed the incident, or one identified victim and did not have any person involved in the incident who incurred an injury of major; serious bodily harm; or death (that did not result in actual death).
- Footnote 14
-
Markers are used when there is not yet sufficient data to establish a benchmark.
- Footnote 15
-
Initial penitentiary placements uninterrupted represents the percentage of offenders who did not experience any of the following interruptions to their correctional progress within 90 days of initial pen-placement: security level changes; segregation placements >= 30 days; major/serious bodily injuries from incidents; unnatural deaths; or escapes from custody
- Footnote 16
-
The data represent the number of events per 1,000 offenders over a one year period, where a fail to return to a Community Residential Facilities (CRF) is recorded. A fail to return to CRF event occurs when an offender leaves the CRF without authorization, does not return to the CRF or is late returning to the CRF where he/she is residing after having signed out.
- Footnote 17
-
The data represent the number of events per 1,000 offenders over a one year period, where a fail to return to a Community Correctional Centre (CCC) is recorded. A fail to return to CCC event occurs when an offender leaves the CCC without authorization, does not return to the CCC or is late returning to the CCC where he/she is residing after having signed out.
