Archived - The Fiscal Monitor - June 2022
Highlights
June 2022
There was a budgetary surplus of $4.9 billion in June 2022, compared to a deficit of $12.7 billion in June 2021. The budgetary surplus before net actuarial losses was $5.7 billion, compared to a deficit of $11.4 billion in the same period of 2021-22. The budgetary balance before net actuarial losses is intended to supplement the traditional budgetary balance and improve the transparency of the government's financial reporting by isolating the impact of the amortization of net actuarial losses arising from the revaluation of the government's pension and other employee future benefit plans.
As expected, the government's 2022-23 financial results continue to improve compared to the peak of the COVID-19 crisis and the unprecedented level of temporary COVID-19 response measures at the time.
Monthly Budgetary Balance and Budgetary Balance Excluding Net Actuarial Losses
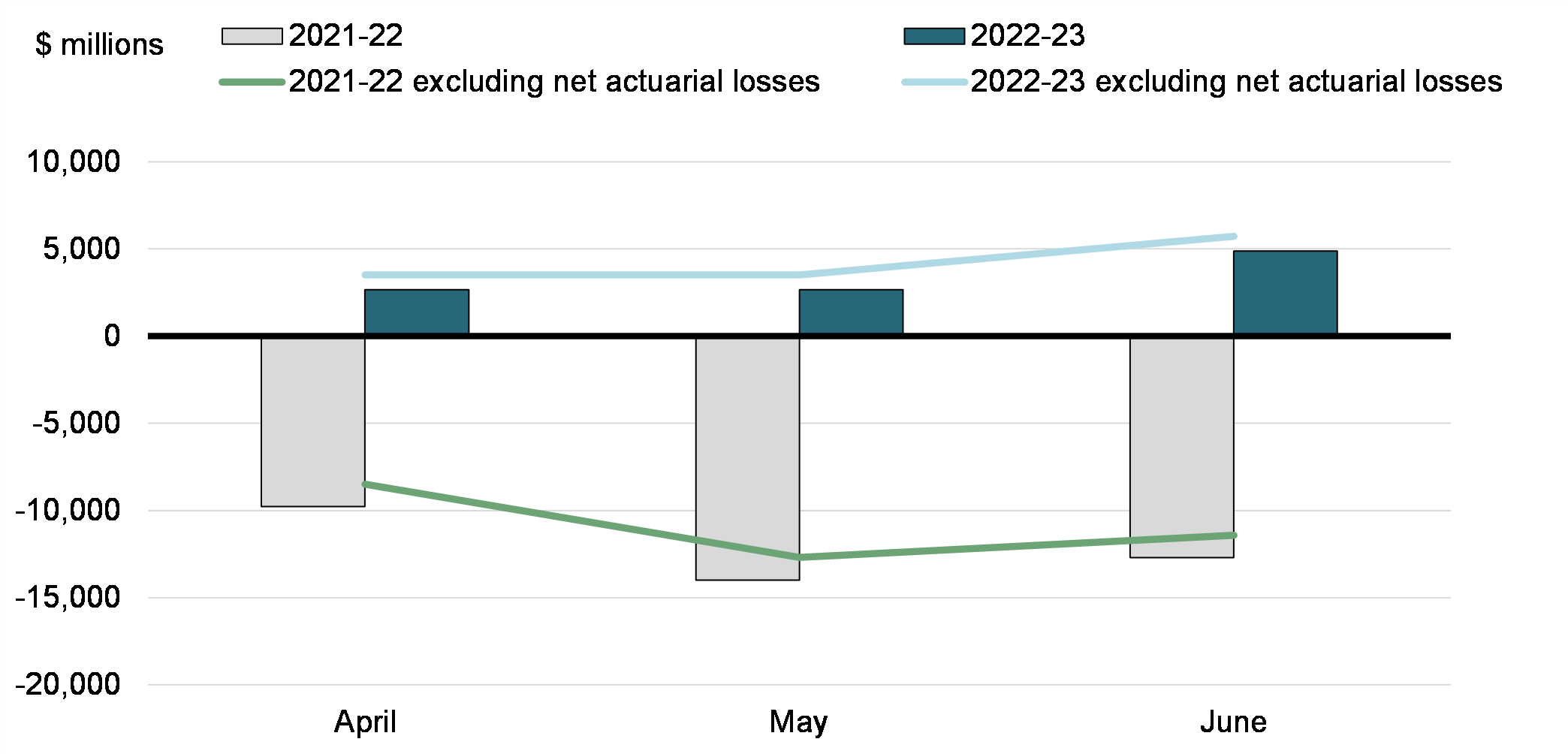
Compared to June 2021:
- Revenues increased by $6.6 billion, or 22.2 per cent, reflecting broad-based improvement across revenue streams.
- Program expenses excluding net actuarial losses were down $11.1 billion, or 28.4 per cent, reflecting lower transfers to individuals and businesses.
- Public debt charges were up $0.5 billion, or 27.9 per cent, largely due to higher interest rates and higher Consumer Price Index adjustments on Real Return Bonds.
- Net actuarial losses were down $0.4 billion, or 33.0 per cent, reflecting the amortization of a decrease in the government's obligations for pensions and other employee future benefits based on actuarial valuations prepared for the Public Accounts of Canada 2021. This decrease is due to a year-over-year increase in year-end interest rates used in valuing these obligations.
April to June 2022
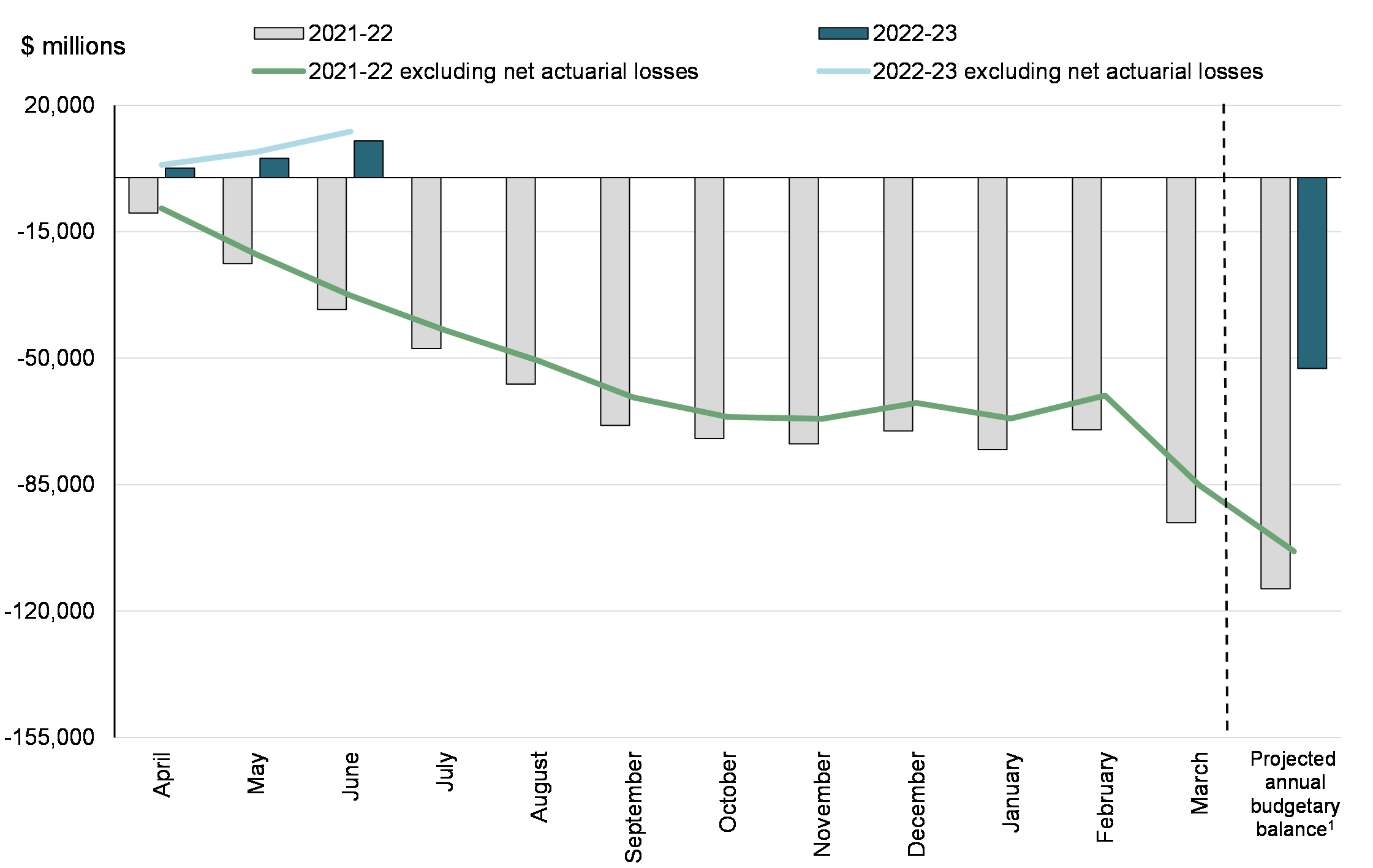
The government posted a budgetary surplus of $10.2 billion for the April to June period of the 2022-23 fiscal year, compared to a deficit of $36.5 billion reported for the same period of 2021-22. The budgetary surplus before net actuarial losses was $12.8 billion, compared to a deficit of $32.6 billion in the April to June period of 2021-22.
Compared to 2021-22:
- Revenues were up $18.7 billion, or 20.9 per cent, reflecting broad-based improvement across revenue streams.
- Program expenses excluding net actuarial losses were down $29.0 billion, or 25.0 per cent, largely reflecting lower transfers to individuals and businesses.
- Public debt charges increased by $2.3 billion, or 38.8 per cent, primarily driven by higher Consumer Price Index adjustments on Real Return Bonds and higher interest rates.
- Net actuarial losses decreased by $1.3 billion, or 33.0 per cent, reflecting a decrease in the measurement of the government's obligations for pensions and other employee future benefits based on the government's latest actuarial valuations. This decrease reflects higher prevailing interest rates at the end of 2020-21 used in valuing these obligations.
Year-to-Date Budgetary Balance and Budgetary Balance Excluding Net Actuarial Losses
| June | April to June | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | |
| Budgetary transactions | ||||
| Revenues | 29,626 | 36,217 | 89,197 | 107,879 |
| Expenses | ||||
Program expenses, excluding net actuarial losses |
-39,143 | -28,038 | -116,007 | -87,030 |
Public debt charges |
-1,909 | -2,442 | -5,812 | -8,069 |
| Budgetary balance, excluding net actuarial losses | -11,426 | 5,737 | -32,622 | 12,780 |
Net actuarial losses |
-1,283 | -860 | -3,849 | -2,580 |
| Budgetary balance (deficit/surplus) | -12,709 | 4,877 | -36,471 | 10,200 |
| Non-budgetary transactions | 286 | -4,589 | -13,600 | -19,531 |
| Financial source/requirement | -12,423 | 288 | -50,071 | -9,331 |
| Net change in financing activities | 15,264 | -7,603 | 53,232 | 13,546 |
| Net change in cash balances | 2,841 | -7,315 | 3,161 | 4,215 |
| Cash balance at end of period | 62,550 | 96,477 | ||
|
Note: Positive numbers indicate net source of funds. Negative numbers indicate net requirement for funds. |
||||
Revenues
Revenues in June 2022 totalled $36.2 billion, up $6.6 billion, or 22.2 per cent, from June 2021, reflecting broad-based improvement in economic activity relative to the greater weight of COVID-19 impacts in the year prior.
- Tax revenues increased by $5.9 billion, or 23.7 per cent, compared to the same period in 2021-22, when COVID-19 restrictions continued to weigh on revenues.
- Employment Insurance (EI) premium revenues were up $0.3 billion, or 14.2 per cent, reflecting better labour market conditions.
- Proceeds from the pollution pricing framework were up $0.1 billion, or 29.2 per cent, reflecting higher carbon pollution pricing in 2022.
- Other revenues, consisting of enterprise Crown corporations' net profits, sales of goods and services, returns on investments and net foreign exchange revenues, were up $0.3 billion, or 11.7 per cent, largely reflecting higher interest and penalty revenue and enterprise Crown corporation profits.
Revenues for the April to June period of 2022-23 totalled $107.9 billion, up $18.7 billion, or 20.9 per cent, from the same period in 2021-22.
- Tax revenues increased by $15.6 billion, or 20.8 per cent, compared to the same period in 2021-22, when COVID-19 restrictions weighed on revenue as well as due to strong economic growth. For its part, the federal portion of assessed cannabis excise duties increased by $13 million to $46 million over the April to June period.
- EI premium revenues were up $0.7 billion, or 10.1 per cent, reflecting better labour market conditions.
- Proceeds from the pollution pricing framework were up $0.7 billion, or 56.5 per cent, reflecting higher carbon pollution pricing in 2022.
- Other revenues were up $1.7 billion, or 27.4 per cent, largely reflecting higher interest and penalty revenue and enterprise Crown corporation profits.
| June | April to June | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | Change | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | Change | |
| ($ millions) | (%) | ($ millions) | (%) | |||
| Tax revenues | ||||||
| Income taxes | ||||||
Personal |
13,352 | 15,105 | 13.1 | 42,744 | 46,203 | 8.1 |
Corporate |
6,158 | 8,565 | 39.1 | 15,729 | 22,649 | 44.0 |
Non-resident |
512 | 1,150 | 124.6 | 1,553 | 3,175 | 104.4 |
Total income tax revenues |
20,022 | 24,820 | 24.0 | 60,026 | 72,027 | 20.0 |
| Other taxes and duties | ||||||
Goods and Services Tax |
3,333 | 4,487 | 34.6 | 10,798 | 14,147 | 31.0 |
Energy taxes |
513 | 445 | -13.3 | 1,194 | 1,210 | 1.3 |
Customs import duties |
390 | 495 | 26.9 | 1,416 | 1,584 | 11.9 |
Other excise taxes and duties |
544 | 445 | -18.2 | 1,370 | 1,391 | 1.5 |
Total excise taxes and duties |
4,780 | 5,872 | 22.8 | 14,778 | 18,332 | 24.0 |
| Total tax revenues | 24,802 | 30,692 | 23.7 | 74,804 | 90,359 | 20.8 |
| Proceeds from the pollution pricing framework | 479 | 619 | 29.2 | 1,264 | 1,978 | 56.5 |
| Employment Insurance premiums | 2,059 | 2,352 | 14.2 | 6,846 | 7,537 | 10.1 |
| Other revenues | 2,286 | 2,554 | 11.7 | 6,283 | 8,005 | 27.4 |
| Total revenues | 29,626 | 36,217 | 22.2 | 89,197 | 107,879 | 20.9 |
|
Note: Totals may not add due to rounding. |
||||||
Expenses
Program expenses excluding net actuarial losses in June 2022 were $28.0 billion, down $11.1 billion, or 28.4 per cent, from June 2021.
- Major transfers to persons, consisting of elderly benefits, EI benefits, COVID-19 income support for workers, and children's benefits, were down $5.8 billion or 38.4 per cent.
- Elderly benefits increased by $0.3 billion, or 5.3 per cent, reflecting changes in consumer prices, to which benefits are fully indexed, and growth in the number of recipients.
- EI benefits decreased by $3.1 billion, or 61.3 per cent, reflecting improved labour market conditions.
- COVID-19 income support for workers decreased $2.9 billion, or 99.0 per cent, reflecting the wind-down of the Canada Recovery Benefit in 2021-22.
- Children's benefits were down $39 million, or 1.9 per cent.
- Major transfers to other levels of government were up $0.3 billion, or 4.0 per cent, largely reflecting legislated growth in the Canada Health Transfer, the Canada Social Transfer, Equalization transfers and transfers to the territories.
- Direct program expenses were down $5.6 billion, or 31.6 per cent. Within direct program expenses:
- Proceeds from the pollution pricing framework returned decreased by $0.2 billion, or 81.7 per cent, reflecting a change in the delivery of the Climate Action Incentive, from annually on personal income tax returns to a quarterly benefit.
- Canada Emergency Wage Subsidy (CEWS) payments decreased by $4.5 billion, reflecting the end of the program and reassessments of previous payments.
- Other transfer payments decreased by $1.2 billion, or 25.1 per cent, largely reflecting timing differences and the wind-down of temporary COVID-19 response measures.
- Operating expenses of the government's departments, agencies, and consolidated Crown corporations and other entities increased by $0.3 billion, or 3.9 per cent, largely reflecting increased expenses of Crown corporations and an increase in personnel costs.
Public debt charges increased $0.5 billion, or 27.9 per cent, largely due to higher interest rates and higher Consumer Price Index adjustments on Real Return Bonds.
Net actuarial losses, which represent the amortization of changes in the value of the government's obligations for pensions and other employee future benefits accrued in previous fiscal years, decreased $0.4 billion, or 33.0 per cent, in large part due to an increase in prevailing interest rates at the end of 2020-21 used in valuing these obligations.
For the April to June period of 2022-23, program expenses excluding net actuarial losses were $87.0 billion, down $29.0 billion, or 25.0 per cent, from the same period the previous year.
- Major transfers to persons were down $14.4 billion or 34.1 per cent.
- Elderly benefits increased by $1.0 billion, or 6.4 per cent, reflecting growth in the number of recipients and changes in consumer prices, to which benefits are fully indexed.
- EI benefits decreased by $7.3 billion, or 56.5 per cent, reflecting improved labour market conditions.
- COVID-19 income support for workers decreased $7.4 billion, or 97.0 per cent, reflecting the wind-down of the Canada Recovery Benefit.
- Children's benefits were down $0.7 billion, or 10.1 per cent, largely reflecting the temporary Canada Child Benefit young child supplement in 2021-22.
- Major transfers to other levels of government were down $2.2 billion, or 9.5 per cent, primarily reflecting a year-over-year difference in the timing of the Canada Community-Building Fund and home care and mental health transfers. This decrease was offset in part by legislated growth in the Canada Health Transfer, the Canada Social Transfer, Equalization transfers and transfers to the territories in the current year.
- Direct program expenses were down $12.3 billion, or 24.4 per cent. Within direct program expenses:
- Proceeds from the pollution pricing framework returned decreased by $3.2 billion, or 96.3 per cent, largely reflecting the change in the delivery of the Climate Action Incentive, from annually on personal income tax returns to a quarterly benefit.
- CEWS payments decreased by $9.0 billion, reflecting the end of the program and reassessments of previous returns.
- Other transfer payments decreased by $1.1 billion, or 7.2 per cent, largely reflecting the wind-down of temporary COVID-19 response measures.
- Operating expenses of the government's departments, agencies, and consolidated Crown corporations and other entities increased by $1.0 billion, or 4.3 per cent, reflecting a number of factors, including increased personnel costs and Crown corporation expenses.
Public debt charges increased by $2.3 billion, or 38.8 per cent, primarily driven by higher Consumer Price Index adjustments on Real Return Bonds and higher interest rates.
Net actuarial losses decreased by $1.3 billion, or 33.0 per cent, reflecting the amortization of a decrease in the government's obligations for pensions and other employee future benefits based on actuarial valuations prepared for the Public Accounts of Canada 2021. This decrease reflects higher prevailing interest rates at the end of 2020–21 used in valuing these obligations.
| June | April to June | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | Change | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | Change | |
| ($ millions) | (%) | ($ millions) | (%) | |||
| Major transfers to persons | ||||||
| Elderly benefits | 5,005 | 5,268 | 5.3 | 14,951 | 15,908 | 6.4 |
| Employment Insurance benefits | 5,084 | 1,965 | -61.3 | 12,873 | 5,599 | -56.5 |
| COVID-19 income support for workers1 | 2,930 | 28 | -99.0 | 7,636 | 229 | -97.0 |
| Children's benefits | 2,074 | 2,035 | -1.9 | 6,872 | 6,176 | -10.1 |
| Total major transfers to persons | 15,093 | 9,296 | -38.4 | 42,332 | 27,912 | -34.1 |
| Major transfers to other levels of government | ||||||
| Canada Health Transfer | 3,594 | 3,767 | 4.8 | 10,781 | 11,302 | 4.8 |
| Canada Social Transfer | 1,289 | 1,328 | 3.0 | 3,868 | 3,985 | 3.0 |
| Equalization | 1,743 | 1,827 | 4.8 | 5,228 | 5,480 | 4.8 |
| Territorial Formula Financing | 298 | 310 | 4.0 | 1,699 | 1,766 | 3.9 |
| Canada-wide early learning and child care | - | - | n/a | - | - | n/a |
| Canada Community-Building Fund | - | - | n/a | 2,269 | - | -100.0 |
| Home care and mental health | - | - | n/a | 750 | 1 | -99.9 |
| Other fiscal arrangements2 | -471 | -521 | -10.6 | -1,433 | -1,582 | -10.4 |
| Total major transfers to other levels of government | 6,453 | 6,711 | 4.0 | 23,162 | 20,952 | -9.5 |
| Direct program expenses | ||||||
| Proceeds from the pollution pricing framework returned | 246 | 45 | -81.7 | 3,344 | 124 | -96.3 |
| Canada Emergency Wage Subsidy | 4,423 | -58 | -101.3 | 8,976 | -58 | -100.6 |
| Other transfer payments | 4,783 | 3,583 | -25.1 | 15,131 | 14,047 | -7.2 |
| Operating expenses | 8,145 | 8,461 | 3.9 | 23,062 | 24,053 | 4.3 |
| Total direct program expenses | 17,597 | 12,031 | -31.6 | 50,513 | 38,166 | -24.4 |
| Total program expenses, excluding net actuarial losses | 39,143 | 28,038 | -28.4 | 116,007 | 87,030 | -25.0 |
| Public debt charges | 1,909 | 2,442 | 27.9 | 5,812 | 8,069 | 38.8 |
| Total expenses, excluding net actuarial losses | 41,052 | 30,480 | -25.8 | 121,819 | 95,099 | -21.9 |
| Net actuarial losses | 1,283 | 860 | -33.0 | 3,849 | 2,580 | -33.0 |
| Total expenses | 42,335 | 31,340 | -26.0 | 125,668 | 97,679 | -22.3 |
|
Note: Totals may not add due to rounding.
|
||||||
The following table presents total expenses by main object of expense.
| June | April to June | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | Change | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | Change | |
| ($ millions) | (%) | ($ millions) | (%) | |||
| Transfer payments | 30,998 | 19,577 | -36.8 | 92,945 | 62,977 | -32.2 |
| Other expenses | ||||||
| Personnel, excluding net actuarial losses | 4,914 | 5,097 | 3.7 | 14,293 | 14,739 | 3.1 |
| Transportation and communications | 185 | 249 | 34.6 | 385 | 501 | 30.1 |
| Information | 27 | 31 | 14.8 | 87 | 64 | -26.4 |
| Professional and special services | 1,084 | 1,312 | 21.0 | 2,229 | 2,598 | 16.6 |
| Rentals | 264 | 292 | 10.6 | 956 | 1,036 | 8.4 |
| Repair and maintenance | 292 | 264 | -9.6 | 523 | 572 | 9.4 |
| Utilities, materials and supplies | 553 | 501 | -9.4 | 1,133 | 1,246 | 10.0 |
| Other subsidies and expenses | 356 | 280 | -21.3 | 2,065 | 1,991 | -3.6 |
| Amortization of tangible capital assets | 462 | 427 | -7.6 | 1,372 | 1,278 | -6.9 |
| Net loss on disposal of assets | 8 | 8 | 0.0 | 19 | 28 | 47.4 |
| Total other expenses | 8,145 | 8,461 | 3.9 | 23,062 | 24,053 | 4.3 |
| Total program expenses, excluding net actuarial losses | 39,143 | 28,038 | -28.4 | 116,007 | 87,030 | -25.0 |
| Public debt charges | 1,909 | 2,442 | 27.9 | 5,812 | 8,069 | 38.8 |
| Total expenses, excluding net actuarial losses | 41,052 | 30,480 | -25.8 | 121,819 | 95,099 | -21.9 |
| Net actuarial losses | 1,283 | 860 | -33.0 | 3,849 | 2,580 | -33.0 |
| Total expenses | 42,335 | 31,340 | -26.0 | 125,668 | 97,679 | -22.3 |
|
Note: Totals may not add due to rounding. |
||||||
Revenues and expenses (April to June 2022)
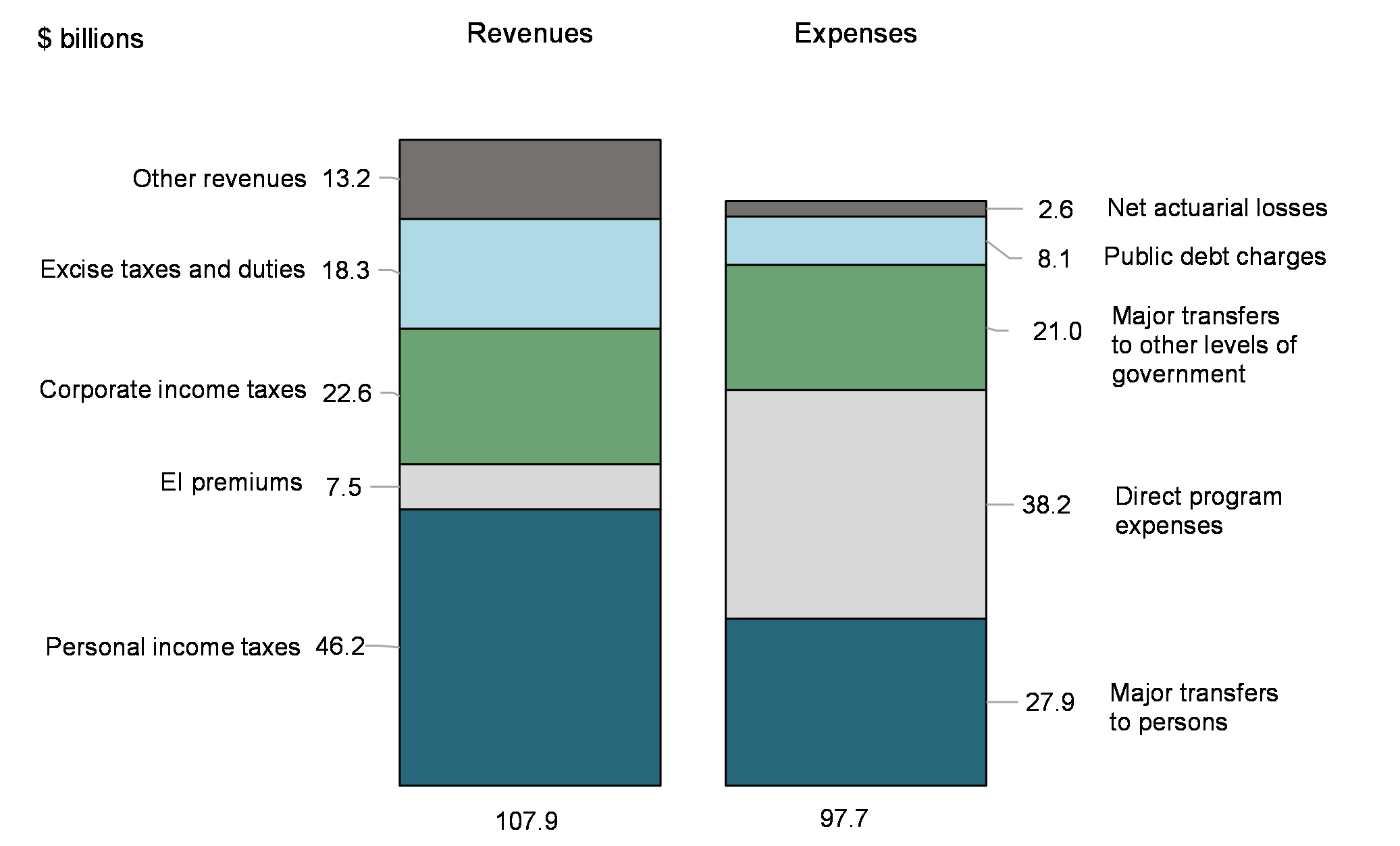
Financial requirement of $9.3 billion for April to June 2022
The budgetary balance is presented on an accrual basis of accounting, recording government revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. In contrast, the financial source/requirement measures the difference between cash coming in to the government and cash going out. This measure is affected not only by changes in the budgetary balance but also by the cash source/requirement resulting from the government's investing activities through its acquisition of capital assets and its loans, financial investments and advances, as well as from other activities, including payment of accounts payable and collection of accounts receivable, foreign exchange activities, and the amortization of its tangible capital assets. The difference between the budgetary balance and financial source/requirement is recorded in non-budgetary transactions.
With a budgetary surplus of $10.2 billion and a requirement of $19.5 billion from non-budgetary transactions, there was a financial requirement of $9.3 billion for the April to June 2022 period, compared to a financial requirement of $50.1 billion for the same period of the previous year.
| June | April to June | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | |
| Budgetary balance (deficit/surplus) | -12,709 | 4,877 | -36,471 | 10,200 |
| Non-budgetary transactions | ||||
| Accounts payable, accrued liabilities and accounts receivable1 | 1,538 | -4,209 | -6,869 | -8,617 |
| Pensions, other future benefits, and other liabilities | 460 | 563 | 3,947 | 1,403 |
| Foreign exchange accounts and derivatives1 | -1,359 | -537 | -6,358 | -9,137 |
| Loans, investments and advances | -55 | -167 | -4,418 | -3,082 |
| Non-financial assets | -298 | -239 | 98 | -98 |
| Total non-budgetary transactions | 286 | -4,589 | -13,600 | -19,531 |
| Financial source/requirement | -12,423 | 288 | -50,071 | -9,331 |
|
Note: Totals may not add due to rounding.
|
||||
Net financing activities up $13.5 billion
The government financed this financial requirement of $9.3 billion and increased cash balances by $4.2 billion by increasing unmatured debt by $13.5 billion. The increase in unmatured debt was achieved primarily through the issuance of marketable bonds.
Cash balances at the end of June 2022 stood at $96.5 billion, up $33.9 billion from their level at the end of June 2021.
| June | April to June | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2022 | 2021-22 | 2022-23 | |
| Financial source/requirement | -12,423 | 288 | -50,071 | -9,331 |
| Net increase (+)/decrease (-) in financing activities | ||||
| Unmatured debt transactions | ||||
Canadian currency borrowings |
||||
Marketable bonds1 |
7,342 | -2,563 | 48,930 | 16,215 |
Treasury bills1 |
7,393 | -4,161 | -1,013 | -7,846 |
Retail debt |
-2 | - | -7 | - |
Total Canadian currency borrowings |
14,733 | -6,724 | 47,910 | 8,369 |
Foreign currency borrowings1 |
397 | -852 | 5,249 | 5,269 |
Total market debt transactions |
15,130 | -7,576 | 53,159 | 13,638 |
Obligations related to capital leases and other unmatured debt |
134 | -27 | 73 | -92 |
| Net change in financing activities | 15,264 | -7,603 | 53,232 | 13,546 |
| Change in cash balance | 2,841 | -7,315 | 3,161 | 4,215 |
| Cash balance at end of period | 62,550 | 96,477 | ||
|
Note: Totals may not add due to rounding.
|
||||
Notes
- The Fiscal Monitor is a report on the consolidated financial results of the Government of Canada, prepared monthly by the Department of Finance Canada. The government is committed to releasing The Fiscal Monitor on a timely basis in accordance with the International Monetary Fund's Special Data Dissemination Standards Plus, which are designed to promote member countries' data transparency and promote the development of sound statistical systems.
- The financial results reported in The Fiscal Monitor are drawn from the accounts of Canada, which are maintained by the Receiver General and used to prepare the annual Public Accounts of Canada.
- The Fiscal Monitor is generally prepared in accordance with the same accounting policies as used to prepare the government's annual consolidated financial statements, which are summarized in Section 2 of Volume I of the Public Accounts of Canada, available through the Public Services and Procurement Canada website.
- The financial results presented in The Fiscal Monitor have not been audited or reviewed by an external auditor.
- There can be substantial volatility in monthly results due to the timing of revenue receipts and expense recognition. For instance, a large share of government spending is typically reported in the March Fiscal Monitor.
- The April to March results reported in The Fiscal Monitor are not the final results for the fiscal year as a whole. The final results are published in the annual Public Accounts of Canada and incorporate post-March end-of-year adjustments made once further information becomes available, including the accrual of tax revenues reflecting assessments of tax returns and valuation adjustments for assets and liabilities. Post‑March adjustments may also include the accrual of measures announced in the budget that are recorded upon receipt of Royal Assent of enabling legislation.
- Table 7, Condensed Statement of Assets and Liabilities, is included in the monthly Fiscal Monitor following the finalization and publication of the government's financial results for the preceding fiscal year, typically in the fall.
- Accounting Changes and Reclassifications:
- Starting in 2022-23, the government has adopted a new standard of the Public Sector Accounting Board regarding asset retirement obligations. Asset retirement obligations represent requirements under an agreement, contract, legislation, or a constructive or equitable obligation to undertake specific actions to retire tangible capital assets at the end of their useful lives. This includes activities such as decommissioning of nuclear reactors and removal of asbestos. The adoption of this standard has not had a material effect on the budgetary balance for the current year. This standard has been applied on a modified retroactive basis and the prior year's results have not been restated for the purposes of The Fiscal Monitor. However, an adjustment to the opening balance of the accumulated deficit for 2022-23 is expected and will be reflected in Table 7, Condensed Statement of Assets and Liabilities, to be included in The Fiscal Monitor following the finalization and publication of the government's financial results for 2021-22 later this year.
- Also starting in 2022-23, the government has adopted a new standard of the Public Sector Accounting Board regarding financial instruments. Financial instruments include receivables, payables, equity instruments, debt, and derivatives, such as forward contracts and cross-currency swaps. Under the new standard, derivatives, which were previously recorded at historical cost, are recognized at fair value. Changes in the fair value of derivatives are not reflected in the budgetary balance, but are instead charged directly to the accumulated deficit as remeasurement gains and losses. The adoption of this standard has also resulted in the reclassification of certain accounts, as follows:
- cross-currency swaps, previously reported as part of unmatured debt, are classified as derivatives and reported outside of unmatured debt;
- forward contracts, previously reported as part of accounts payable and accrued liabilities, are reported as derivatives;
- accrued interest, previously reported as part of accounts payable and accrued liabilities, is now included with the associated category of unmatured debt (i.e., marketable bonds, treasury bills, and foreign currency borrowings); and,
- unamortized discounts and premiums on market debt, previously reported as a separate item within unmatured debt, are now included with the associated category of unmatured debt (i.e., marketable bonds, treasury bills, and foreign currency borrowings).
- This standard has been applied on a prospective basis. The prior year's results have not been restated, but balances in the prior year have been reclassified to reflect the current year's presentation. An adjustment to the opening balance of the accumulated deficit for 2022-23 is expected and will be reflected in Table 7, Condensed Statement of Assets and Liabilities, when published later this year.
Note: Unless otherwise noted, changes in financial results are presented on a year-over-year basis.
For inquiries about this publication, contact Bradley.Recker@fin.gc.ca.
August 2022
© Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada (2022)
All rights reserved
All requests for permission to reproduce this document or any part thereof shall be addressed to the Department of Finance Canada.
Cette publication est également disponible en français.
Cat. No.: F12-4E-PDF
ISSN: 1487-0134
