Infographic: Mould
Download the alternative format
(PDF format, 246 KB, 2 pages)
Organization: Health Canada
Published: 2017
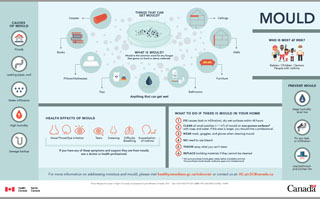
Mould
What is mould?
Mould is the common name for any fungus that grows on food or damp materials
Things that can get mouldy:
- Carpets
- Books
- Pillows/mattresses
- Toys
- Ceilings
- Walls
- Furniture
- Bathrooms
- Anything that can get wet
Who is most at risk?
- Babies
- Children
- Seniors
- People with asthma
Causes of mould
- Floods
- Leaking pipes, roof
- Water infiltration
- High humidity
- Sewage backup
Health Effects of mould
- Nose/throat/eye irritation
- Tears
- Sneezing
- Difficulty breathing
- Exacerbation of asthma
If you have any of these symptoms and suspect they are from mould, see a doctor or health professional.
Prevent mould
- Keep humidity level low
- Fix any leak or infiltration
- Use bathroom and kitchen fan
What if there is mould in your home
- Fix causes (leak or infiltration), dry wet surfaces within 48 hours
- Clean all small patches (< 1m2) of mould on non-porous surfaces with soap and water. If the area is larger, you should hire a professional. Non-porous surfaces include glass, metals, leather and plastics and vinyl. Porous surfaces include drywall, cardboard, paper and untreated wood.
- Wear mask, goggles, and gloves when cleaning mould
- No need to use bleach
- Throw away what you can’t clean
- Replace building materials if they cannot be cleaned
For more information on addressing moisture and mould, please visit healthycanadians.gc.ca/indoorair or contact us at: air@hc-sc.gc.ca