Quarterly Financial Report - Statement outlining results, risks and significant changes in operations, personnel and programs - For the quarter ended September 30, 2024
Introduction
This quarterly report has been prepared as required by section 65.1 of the Financial Administration Act and in the form and manner prescribed by the Directive on Accounting Standards, GC 4400 Departmental Quarterly Financial Report. This quarterly financial report should be read in conjunction with the Main Estimates and previous Quarterly Financial Reports. For more information on PCO, please visit PCO's website.
This quarterly report has not been subject to an external audit or review but has been shared with and reviewed by the PCO Departmental Audit Committee.
Mandate
PCO supports the development and implementation of the Government of Canada's policy and legislative agendas, coordinates responses to issues facing the Government and the country and supports the effective operation of Cabinet. PCO is led by the Clerk of the Privy Council, who also serves as Secretary to the Cabinet and the Head of the Public Service.
PCO serves Canada and Canadians by providing advice and support to the Prime Minister, portfolio ministers, and Cabinet.
PCO has three main roles:
- Provide professional non-partisan advice to the Prime Minister, portfolio ministers, Cabinet and Cabinet committees on matters of national and international importance.
- Support the smooth functioning of the Cabinet decision-making process and facilitate the implementation of the Government’s agenda.
- Foster a high-performing and accountable Public Service.
Basis of presentation
This quarterly report has been prepared using an expenditure basis of accounting. The accompanying Statement of Authorities includes PCO’s spending authorities granted by Parliament and those used by the department, consistent with the 2024-25 Main Estimates and Supplementary Estimates (A). This quarterly report has been prepared using a special purpose financial reporting framework (expenditure basis) designed to meet financial information needs with respect to the use of spending authorities.
The authority of Parliament is required before money can be spent by the Government. Approvals are given in the form of annually approved limits through appropriation acts or through legislation in the form of statutory spending authority for specific purposes.
PCO uses the full accrual method of accounting to prepare and present its annual departmental financial statements1 that are part of the departmental performance reporting process. The spending authorities voted by Parliament remain on an expenditure basis.
Highlights of fiscal quarter and fiscal year to date results
This section highlights the significant items that contributed to the net increase or decrease in authorities available for the year and actual expenditures for the quarter ended September 30, 2024.
PCO spent approximately 47% of its authorities available for use by the end of the second quarter, which is comparable to the same quarter of 2023-24 (see graph 1 below).
Graph 1: Comparison of total authorities available for use and total net budgetary expenditures as of Q2 2024-25 and 2023-24
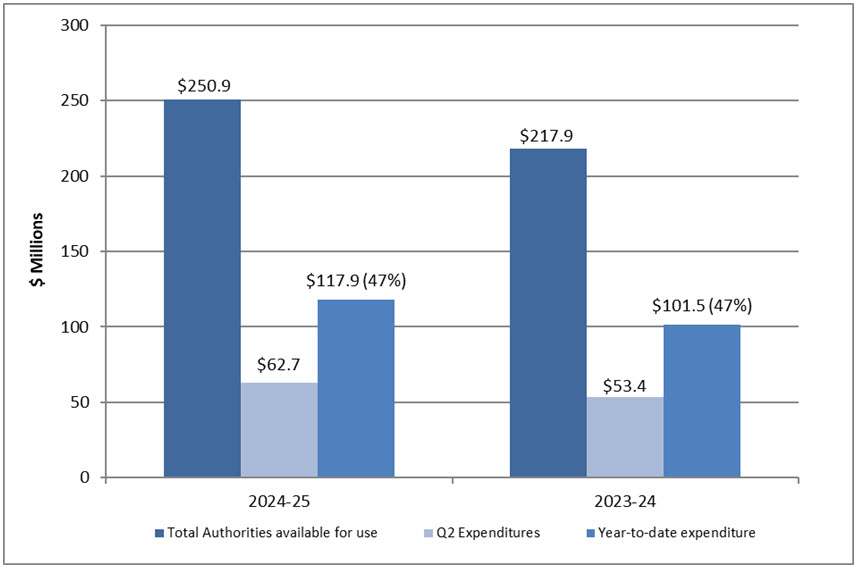
Text version - Graph 1
| 2024-25 | 2023-24 | |
|---|---|---|
| Total authorities available for use | 250.9 | 217.9 |
| Q2 expenditures | 62.7 | 53.4 |
| Year-to-date | 117.9 | 101.5 |
Significant changes to authorities
Further to graph 2 below and Annex A, presented at the end of this document, as at September 30, 2024 PCO has authorities available for use of $250.9 million in 2024-25 compared to $217.9 million as of September 30, 2023, for a net increase of $33.0 million or 15%. The net increase in authorities of $33.0 million is mainly explained by funding related to the Public Inquiry into Foreign Interference in Federal Electoral Processes and Democratic Institutions and an increase in funding for compensation adjustments. This is partially offset by the sunset funding for the Public Order Emergency Commission and the reduction of funding announced in Budget 2023. Commissions of Inquiry are independent organizations but are reported under PCO’s financial statements.
Graph 2: Variance in authorities as at September 30, 2024
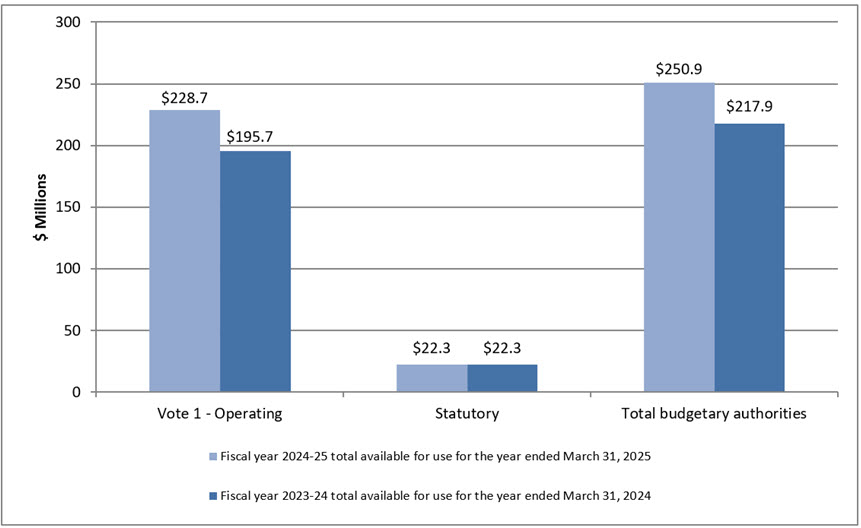
Text version - Graph 2
| Vote 1 - Operating | Statutory | Total budgetary authorities | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiscal year 2024-25 total available for use for the year ended March 31, 2025 | 228.7 | 22.3 | 250.9 |
| Fiscal year 2023-24 total available for use for the year ended March 31, 2024 | 195.7 | 22.3 | 217.9 |
Significant changes to quarter expenditures
The second quarter expenditures totaled $62.7 million for a net increase of $9.3 million (17%) when compared to $53.4 million spent during the same period in 2023-24. Table 1 below presents budgetary expenditures by standard object.
Table 1
| Material Variances to Expenditures by Standard Object | Fiscal year 2024-25 Expended during the quarter ended September 30, 2024 |
Fiscal year 2023-24 Expended during the quarter ended September 30, 2023 |
Variance $ | Variance % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personnel | 47,544 | 45,564 | 1,980 | 4% |
| Transportation and communications | 1,869 | 1,518 | 351 | 23% |
| Information | 811 | 832 | (21) | (3%) |
| Professional and special services | 10,319 | 5,363 | 4,956 | 92% |
| Rentals | 2,133 | 636 | 1,497 | 235% |
| Repair and maintenance | 232 | 203 | 29 | 14% |
| Utilities, materials and supplies | 162 | 374 | (212) | (57%) |
| Acquisition of machinery and equipment | 1,358 | 766 | 592 | 77% |
| Transfer payments | 110 | - | 110 | - |
| Other subsidies and payments | 467 | 201 | 266 | 132% |
| Total gross budgetary expenditures | 65,006 | 55,457 | 9,548 | 17% |
| Less revenues netted against expenditures | (2,313) | (2,046) | (267) | 13% |
| Total net budgetary expenditures * | 62,692 | 53,411 | 9,281 | 17% |
| * Details may not add to totals due to rounding | ||||
Personnel
The increase of $2.0 million in personnel spending is mainly due to compensation adjustments related to pay rate increases, the establishment of the Public Inquiry into Foreign Interference in Federal Electoral Processes and Democratic Institutions on September 7, 2023, and expenditures to support the Clean Growth Office and Public Lands Action Council Secretariat.
Transportation and communications
Transportation and communications increased by $0.4 million primarily due to the establishment of the Public Inquiry into Foreign Interference in Federal Electoral Processes and Democratic Institutions on September 7, 2023.
Professional and special services
The increase of $5.0 million in professional and special services is due to legal expenses incurred for the Public Inquiry into Foreign Interference in Federal Electoral Processes and Democratic Institutions established on September 7, 2023, as well as the timing of invoicing for other legal and information technology services. This was partially offset by a decrease in legal services for the Independent Special Rapporteur.
Rentals
The increase of $1.5 million in rentals is mainly due to the timing of invoicing for software licensing.
Significant changes to year-to-date expenditures
The year-to-date expenditures totaled $117.9 million for a net increase of $16.5 million (16%) when compared to $101.5 million spent during the same period in 2023-24. Table 2 below presents budgetary expenditures by standard object.
Table 2
| Material Variances to Expenditures by Standard Object | Fiscal Year 2024-25 YTD Expenditures as of September 30, 2024 |
Fiscal Year 2023-24 YTD Expenditures as of September 30, 2023 |
Variance $ | Variance % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personnel | 93,703 | 85,740 | 7,963 | 9% |
| Transportation and communications | 3,581 | 2,635 | 946 | 36% |
| Information | 1,973 | 1,891 | 82 | 4% |
| Professional and special services | 16,046 | 10,451 | 5,595 | 54% |
| Rentals | 4,083 | 2,232 | 1,851 | 83% |
| Repair and maintenance | 319 | 282 | 37 | 13% |
| Utilities, materials and supplies | 241 | 447 | (206) | (46%) |
| Acquisition of machinery and equipment | 2,301 | 1,574 | 727 | 46% |
| Transfer payments | 389 | 42 | 347 | 826% |
| Other subsidies and payments | 768 | 543 | 225 | 41% |
| Total gross budgetary expenditures | 123,403 | 105,837 | 17,566 | 17% |
| Less revenues netted against expenditures | (5,464) | (4,377) | (1,088) | 25% |
| Total net budgetary expenditures * | 117,938 | 101,460 | 16,478 | 16% |
| * Details may not add to totals due to rounding | ||||
Personnel
The overall increase of $8.0 million in personnel spending is due to compensation adjustments related to pay rate increases, the establishment of the Public Inquiry into Foreign Interference in Federal Electoral Processes and Democratic Institutions on September 7, 2023 and expenditures to support the Clean Growth Office and Public Lands Action Council Secretariat.
Transportation and communications
Transportation and communications increased by $0.9 million primarily due to the establishment of the Public Inquiry into Foreign Interference in Federal Electoral Processes and Democratic Institutions on September 7, 2023.
Professional services and special services
The increase of $5.6 million in professional and special services is due to legal expenses incurred for the Public Inquiry into Foreign Interference in Federal Electoral Processes and Democratic Institutions established on September 7, 2023, as well as the timing and increases of invoicing for other legal services. This was partially offset by a decrease in legal services for the Independent Special Rapporteur.
Rentals
The increase of $1.9 million is mainly due to conference space for public hearings required for the Public Inquiry into Foreign Interference in Federal Electoral Processes and Democratic Institutions established on September 7, 2023 and the timing of invoicing for software licensing.
Revenues netted against expenditures
The increase of $1.1 million for vote netted revenue is mainly due to more recoveries in 2024-25 for the Secure Communications for National Leadership initiative and for internal services provided to other departments.
Risks and uncertainties
The principal financial risks to PCO lie in the need to reallocate departmental resources to deal with issues that may emerge unexpectedly. As part of its coordinating role, PCO must be able to address emerging issues on short notice, and either manage the necessary expenditures within its own spending authorities, or cash manage until increased spending authorities are approved.
PCO has identified other key risks that could have an impact on the achievement of its mandate and its financial situation. These risks revolve around areas such as threats to security (cybersecurity/insider/physical), information management, increasing horizontality, complexity and scope of work, and the recruitment and retention of employees.
The department will continue to effectively manage its existing and emerging risks through cooperation, engagement and sharing of expertise and best practices with other federal departments and agencies, provincial and territorial governments, as well as community partners, the private sector, international counterparts, and its Department Audit Committee.
Significant changes in relation to operations, personnel and programs
Mark Schaan, previously Senior Assistant Deputy Minister, Strategy and Innovation Policy Sector, Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada, was appointed Deputy Secretary to the Cabinet (Artificial Intelligence) effective July 29, 2024.
There have not been any significant changes in relation to operations and programs during the quarter.
Approval by senior officials:
John Hannaford
Clerk of the Privy Council and
Secretary to the Cabinet
Matthew Shea
Assistant Secretary to the Cabinet,
Ministerial Services and Corporate
Affairs and Chief Financial Officer
Ottawa, Canada
Friday November 29, 2024
Annexes A & B
Annex A
Privy Council Office
Quarterly Financial Report
For the quarter ended September 30, 2024
Statement of authorities (unaudited) (note 2)
| Expenditures/Authorities | Fiscal year 2024-2025 | Fiscal year 2023-2024 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total available for use for the year ending March 31, 2025 (note 1) |
Used during the quarter ended September 30, 2024 |
Year-to-date used at quarter–end | Total available for use for the year ending March 31, 2024 (note 1) |
Used during the quarter ended September 30, 2023 |
Year-to-date used at quarter–end | |
| Vote 1 - Net operating expenditures | 228,654 | 57,119 | 106,767 | 195,654 | 47,885 | 90,338 |
| Budgetary statutory authorities | ||||||
| Contributions to employee benefits plans | 21,891 | 5,473 | 10,946 | 21,906 | 5,477 | 10,953 |
| Prime Minister - Salary and motor car allowance | 205 | 51 | 103 | 194 | 49 | 98 |
| Leader of the Government in the House of Commons - Salary and motor car allowance | 99 | 25 | 74 | 95 | 16 | 40 |
| President of the King's Privy Council for Canada and the Minister of Emergency Preparedness - Salary and motor car allowance | - | - | - | - | 8 | 32 |
| President of the King's Privy Council for Canada and the Minister of Emergency Preparedness and Minister responsible for the Pacific Economic Development Agency of Canada - Salary and motor car allowance | 99 | 25 | 49 | 95 | - | - |
| Minister of Intergovernmental Affairs, Infrastructure and Communities - Salary and motor car allowance | - | - | - | - | (24) | - |
| Total budgetary authorities | 250,947 | 62,692 | 117,938 | 217,944 | 53,411 | 101,460 |
| Total authorities | 250,947 | 62,692 | 117,938 | 217,944 | 53,411 | 101,460 |
| Note 1: Includes authorities available for use and granted by Parliament at quarter-end for each respective fiscal year (Including Frozen Allotments). Note 2: Details may not add to totals due to rounding. |
||||||
Annex B
Privy Council Office
Quarterly Financial Report
For the quarter ended September 30, 2024
Departmental budgetary expenditures by Standard Object (unaudited) (note 2)
| Departmental budgetary expenditures | Fiscal year 2024-2025 | Fiscal year 2023-2024 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planned expenditures for the year ending March 31, 2025 (note 1) |
Expended during the quarter ended September 30, 2024 |
Year-to-date used at quarter–end | Planned expenditures for the year ending March 31, 2024 (note 1) |
Expended during the quarter ended September 30, 2023 |
Year-to-date used at quarter–end | |
| Budgetary expenditures | ||||||
| Personnel | 188,408 | 47,544 | 93,703 | 173,226 | 45,564 | 85,740 |
| Transportation and communications | 5,294 | 1,869 | 3,581 | 5,029 | 1,518 | 2,635 |
| Information | 5,226 | 811 | 1,973 | 4,159 | 832 | 1,891 |
| Professional and special services | 41,262 | 10,319 | 16,046 | 23,687 | 5,363 | 10,451 |
| Rentals | 5,731 | 2,133 | 4,083 | 6,143 | 636 | 2,232 |
| Repair and maintenance | 1,790 | 232 | 319 | 2,042 | 203 | 282 |
| Utilities, materials and supplies | 570 | 162 | 241 | 447 | 374 | 447 |
| Acquisition of machinery and equipment | 9,012 | 1,358 | 2,301 | 11,712 | 766 | 1,574 |
| Transfer payments | 2,248 | 110 | 389 | - | - | 42 |
| Other subsidies and payments | 34 | 467 | 768 | - | 201 | 543 |
| Total gross budgetary expenditures | 259,576 | 65,006 | 123,403 | 226,446 | 55,457 | 105,837 |
| Less revenues netted against expenditures Revenues (note 3) |
(8,628) | (2,313) | (5,464) | (8,502) | (2,046) | (4,377) |
| Total revenues netted against expenditures | (8,628) | (2,313) | (5,464) | (8,502) | (2,046) | (4,377) |
| Total net budgetary expenditures | 250,947 | 62,692 | 117,938 | 217,944 | 53,411 | 101,460 |
| Note 1: Includes authorities available for use and granted by Parliament at quarter-end for each respective fiscal year (Including Frozen Allotments). Note 2: Details may not add to totals due to rounding. Note 3: PCO’s revenues are sourced from the provision of intelligence analysis training and the provision of internal support services to other departments. |
||||||
