Hepatitis C virus (HCV): Screening and testing for health professionals
Download the alternative format
(PDF format, 105 KB, 1 page)
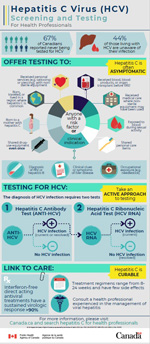
- 67% of Canadians reported never being tested for HCV
- 44% of those living with HCV are unaware of their infection
Hepatitis C is often asymptomatic
Offer testing to anyone with a risk factor or clinical indication.
Risk factors:
- shared drug-use equipment, even once
- received personal services (e.g., tattooing or piercing), with nonsterile equipment
- exposed to blood during sexual activity
- received blood, blood products, or organ transplant before 1992
- received medical care where non-sterile equipment may have been used
- born, travelled, or lived in a region where hepatitis C is common
- born to a mother with hepatitis C
- shared personal care items
Clinical indications:
- diagnosis of HIV or hepatitis B
- clinical clues or symptoms of liver disease
- occupational exposure (e.g., needlestick)
Take an active approach to testing
Testing for HCV: the diagnosis of HCV infection requires 2 tests.
- The first test is the hepatitis C antibody test (anti-HCV):
- a negative anti-HCV test result indicates no HCV infection
- a positive anti-HCV test result indicates current or resolved HCV infection, which requires further testing with a second test called the hepatitis C ribonucleic acid test
- The second test is the hepatitis C ribonucleic acid test (HCV RNA):
- a negative HCV RNA result indicates no HCV infection (resolved HCV infection)
- a positive HCV RNA test result indicates current HCV infection
Hepatitis C is curable
Link to care: interferon-free direct acting antiviral treatments have a sustained virologic response >90%.
- treatment regimens range from 8 to 24 weeks and have few side effects
- consult a health professional experienced in the management of viral hepatitis
For more information, please visit Canada.ca and search 'hepatitis C for health professionals'.