National surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae annual summary 2018
Executive summary
- This report consists of laboratory surveillance data for Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates submitted by provincial microbiology laboratories to the National Microbiology Laboratory (NML) from 2014 – 2018 as part of the Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (GASP – Canada).
- The Canadian reported rate of gonorrhea is on the rise and has more than doubled from 21.8 per 100,000 in 2001 to 79.5 cases per 100,000 in 2017. Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in Canada with 29,034 cases reported in 2017.
- Over time, N. gonorrhoeae has acquired resistance to many antibiotics such as penicillin, tetracycline, erythromycin and ciprofloxacin. Antimicrobial resistance in N. gonorrhoeae is a serious threat to effective treatment of gonococcal infections. In 2018, 7 extensively drug resistant gonorrhea isolates (XDR-GC; decreased susceptibility to a cephalosporin plus resistance to azithromycin as well as resistance to at least two other antimicrobials) were identified in Canada posing a potential threat to successful treatment.
- In 2017, routine surveillance confirmed the first ceftriaxone resistant N. gonorrhoeae in Canada. In 2018, three ceftriaxone resistant cases were identified in Canada. All were associated with travel to South-East Asia.
- In 2018, a total of 5,607 N. gonorrhoeae isolates were cultured and tested in public health laboratories across Canada; 3,426 of these were submitted to the NML for antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST). AST data for an additional 1,517 N. gonorrhoeae isolates were submitted by provincial public health laboratories and included in the analysis. The total number of isolates cultured in all provinces was used as the denominator to calculate resistance proportions.
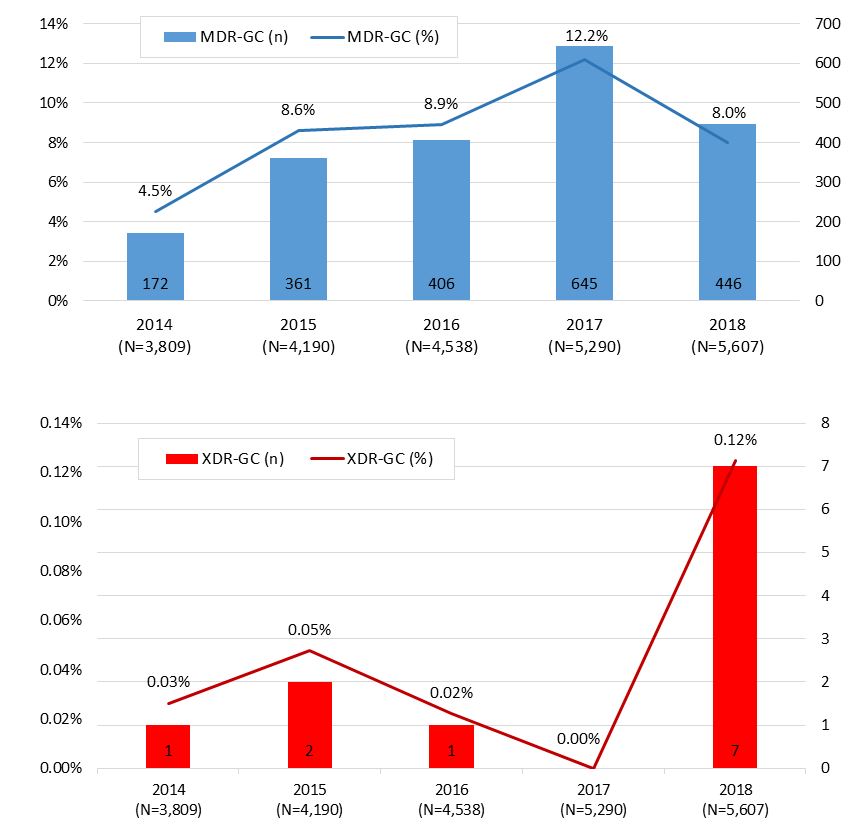
- The proportion of multi-drug resistant (MDR)-GC increased from 4.5% (172/3,809) in 2014 to 12.2% (645/5,290) in 2017 and then decreased to 8.0% (448/5,607) in 2018 (Figure A). These percentages represent the proportion of isolates with decreased susceptibility to the cephalosporins or resistance to azithromycin, along with resistance to at least two other antimicrobials.
- From 2014 to 2016, there were only 4 XDR-GC identified in Canada; none were found in 2017. In 2018, seven [1% (7/5,607)] isolates were classified as XDR-GC (Figure A).
Figure A. Trends of MDR-GC and XDR-GC Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Canada from 2014 to 2018Footnote a - Footnote a
-
Percentage based on total number of isolates tested nationally: 2014=3,809; 2015=4,190; 2016=4,538; 2017=5,290; 2018=5,607
Figure A - Text description
A combination bar and line graph displaying the trending of MDR-GC and XDR-GC in Canada from 2014 to 2018 by percentage based on total number of isolates tested nationally (line graph) and by number (bar graph).
Year (number of cultures tested nationally) MDR (%) XDR (%) MDR (n) XDR (n) 2014 (N=3,809) 5.3% 0.03% 203 1 2015 (N=4,190) 8.6% 0.05% 361 2 2016 (N=4,538) 8.9% 0.02% 406 1 2017 (N=5,290) 12.2% 0% 646 0 2018 (N=5,607) 8.0% 0.12% 446 7 - Isolates with decreased susceptibility to cefixime (MIC ≥ 0.25 mg/L) decreased from 1.0% (38/3,809) in 2014 to 0.5% (27/5,607) in 2018 (Figure B).
- Isolates with decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone (MIC ≥ 0.125 mg/L) decreased from 2.5% (96/3,809) in 2014 to 0.6% (31/5,607) in 2018 (Figure B).
- The proportion of azithromycin resistant (MIC ≥ 2mg/L) N. gonorrhoeae isolates increased from 3.4% (128/3,809) in 2014 to 7.6% (427/5,607) in 2018 (Figure B).
- Three high-level azithromycin resistant (MIC ≥ 256 mg/L) N. gonorrhoeae isolates were identified in 2018 (QC, n=2; BC, n=1).
Figure B. Trends of antimicrobial susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae tested in Canada, 2014-2018Footnote a 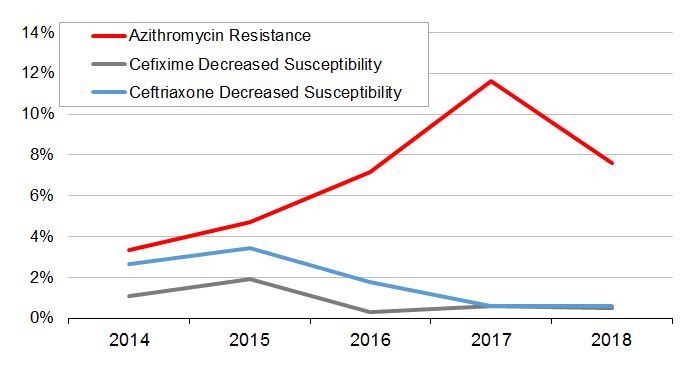
- Footnote a
-
Percentage based on total number of isolates tested nationally: 2014=3,809; 2015=4,190; 2016=4,538; 2017=5,290; 2018=5,607
Figure B - Text description
A line graph with 3 lines representing Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates resistant to azithromycin, decreased susceptibility to cefixime and decreased susceptibility to ceftriaxone in Canada from 2014 to 2018.
Antibiotic 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 Ceftriaxone - (DS) Decreased Susceptibility 96 (2.5%) 144 (3.4%) 80 (1.8%) 30 (0.6%) 31 (0.6%) Cefixime - (DS) Decreased Susceptibility 38 (1%) 79 (1.9%) 14 (0.3%) 32 (0.6%) 27 (0.5%) Azithromycin - (R) Resistant 128 (3.4%) 198 (4.7%) 327 (7.2%) 613 (11.6%) 427 (7.6%) - In 2018, 57.3% (3,214/5,607) of isolates were resistant to ciprofloxacin; 56.0% (1,914/3,417) of the isolates were resistant to erythromycin; 9.2% (356/3,882) were resistant to penicillin; and 47.1% (2,640/5,607) were resistant to tetracycline.
- N. gonorrhoeae isolates submitted to the NML were also analyzed by molecular genotyping using the N. gonorrhoeae multi-antigen sequence type (NG-MAST) method. In 2018, 505 different sequence types (STs) were identified among the 3,375 isolates with STs identified and the most common sequence types were ST-12302 (18.2%), ST-14994 (16.6%), and ST-5985 (5.8%).
- ST-12302 increased from 4.3% of all isolates in 2015 to 24.1% in 2017 and has now decreased to 18.2% in 2018. In 2017, the isolates were primarily identified in central Canada; in 2018, approximately 10% were identified in western provinces (Figure C).
- ST-14994 was newly identified in 2017 (2.1% (60/2,875) and increased dramatically to 16.6% (562/3,379) in 2018 (Figure C). These isolates are resistant to multiple drugs including ciprofloxacin with approximately 5% of them having resistance to azithromycin as well.
Figure C. Trends of prevalent NG-MAST sequence types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates tested by NML, 2014 – 2018 Footnote a 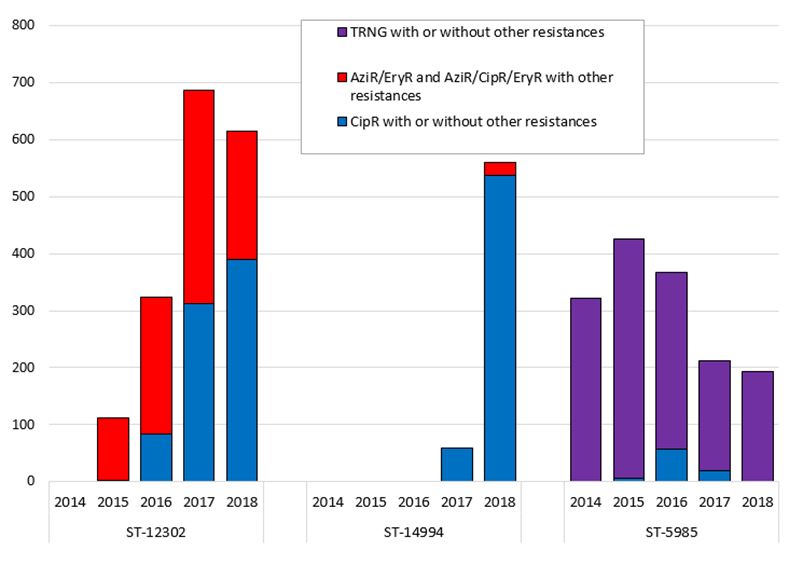
- Footnote a
-
A total of 378 sequence types were identified in 2014, 396 sequence types in 2015, 490 sequence types in 2016, 468 sequence types in 2017 and 503 sequence types in 2018. Only the most prevalent sequence types of 2014 to 2018 are represented in this graph.
Figure C - Text description
A stacked bar graph displaying trending of 3 of the most prevalent NG-MAST sequence types in Canada from 2014 to 2018 and antimicrobial resistance associated with them.
NG-MAST Year CipR with or without other resistances TRNG with or without other resistances AziR/EryR and AziR/CipR/EryR with other resistances ST-12302 2014 N/A N/A N/A N/A 2015 3 N/A 110 N/A 2016 84 N/A 240 N/A 2017 312 N/A 375 N/A 2018 390 N/A 225 ST-14994 2014 N/A N/A N/A N/A 2015 N/A N/A N/A N/A 2016 N/A N/A N/A N/A 2017 60 N/A N/A N/A 2018 537 N/A 23 ST-5985 2014 N/A 322 N/A N/A 2015 6 419 N/A N/A 2016 58 309 N/A N/A 2017 20 193 N/A N/A 2018 N/A 194 N/A
For more details on the report and its key findings, please email: phac.nml.strepsti-lnm.strepits.aspc@canada.ca.