Construction, Renovation & Demolition (CRD) Wood Supply and Demand in Canada- Stakeholders
Download the alternative format
(PDF format, 1081 KB, 1 page)
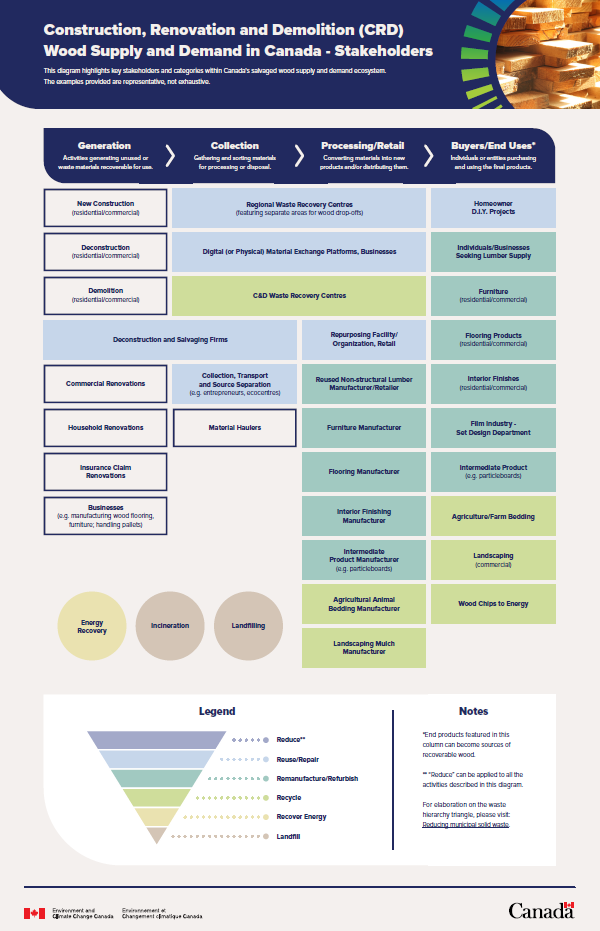
Wood salvaging begins with various activities that generate reclaimable wood materials, including construction, deconstruction, renovations, demolition projects in both residential and commercial settings, and pre-consumer materials generated by businesses that manufacture wood products (e.g. flooring, furniture, etc). The information below highlights key stakeholders and categories within Canada's salvaged wood supply and demand ecosystem. The examples provided are representative, not exhaustive.
- Generation refers to the activities that generate unused (pre-consumer) or waste (post-consumer) wood materials. This can happen through:
- New construction (residential/commercial): This involves the creation of new buildings where excess or leftover wood is generated.
- Deconstruction (residential/commercial): This involves specialized companies that are involved in systematically dismantling buildings to salvage reusable materials.
- Commercial renovations: Large-scale renovations in commercial buildings can result in excess wood material.
- Household renovations: Smaller-scale renovations in homes also generate recoverable wood.
- Insurance claim renovations: Renovations due to insurance claims, such as repairing damage from disasters, generate usable wood waste.
- Demolition (residential/commercial): The process of demolishing buildings, whether residential or commercial, creates waste materials, including wood waste.
- Businesses: Companies involved in the manufacturing of wood products, such as flooring, furniture, and pallets, also generate wood waste during production processes.
- Collection involves gathering and sorting wood materials for further processing or disposal. This process can involve:
- Deconstruction and salvaging firms: This includes companies that focus on recovering wood during deconstruction projects in a way that preserves wood for reuse, playing a critical role in salvaging wood at this stage.
- Collection, transport & source separation: Companies as well as entrepreneurs and ecocentres (recycling centers) handle the collection, transportation of materials and play a role in source separation.
- Material haulers: Businesses and organizations that specialize in transporting materials from generation sites to processing or disposal centers.
Following collection, the wood is processed and prepared for new applications. Various companies repurpose the collected wood into usable products.
- Processing/retail is the stage where material is converted into new products and/or retailed, distributed. Examples of stakeholders and their activities include:
- Regional waste and C&D Waste recovery centers: Regional and private facilities play a role in collection, processing/retail and handling these materials. These include facilities that have a separate area for wood drop-offs.
- Material exchange platforms/businesses: Material exchange platforms facilitate transactions between businesses and individuals, offering a marketplace for salvaged wood and helping to enable its continued circulation in the economy.
- Repurposing facility/organization, retail: These feature facilities that take salvaged wood and transform it into items that can be sold for new purposes.
- Reused non-structural lumber manufacturer/retailer: These manufacturers and retailers convert non-structural wood into products for resale.
- Furniture manufacturer: Manufacturers also process material to build custom and/or generic furniture.
- Flooring manufacturer: This also includes companies that repurpose wood into flooring materials.
- Interior finishing manufacturer: This features companies that specialize in transforming recovered wood into interior finishes.
- Intermediate product manufacturer: Companies that manufacture intermediate wood products, such as particleboards, which are subsequently used as inputs to other products (e.g. cabinets).
- Agricultural animal bedding manufacturer: Manufacturers that convert wood for farm bedding.
- Landscaping mulch manufacturer: This features businesses that convert wood into mulch for landscaping.
- On the buyer/end user side, different types of end users purchase and use these processed wood products (note these can also become future sources of recoverable wood). These end users include:
- Homeowner D.I.Y. projects: Customers repurpose salvaged wood for DIY projects, such as making bookshelves.
- Lumber supply: Customers also purchase lumber made from recovered wood for various purposes.
- Furniture (residential/commercial): Both residential and commercial buyers use salvaged wood to create furniture, or buy furniture already made from salvaged wood.
- Flooring products (residential/commercial): Customers may purchase reclaimed wood for flooring in both residential and commercial settings.
- Interior finishes (residential/commercial): Customers have the option to use repurposed wood for interior finishing in homes and commercial properties, or purchase prefabricated interior finishes made from repurposed wood.
- Film industry (set design): The film industry, specifically the set design departments of studios, purchases salvaged wood for use in film sets.
- Intermediate products: Purchasers of intermediate products (ex. particleboards) which are subsequently used as inputs to other products (e.g. cabinets).
- Agriculture/farm bedding: Farmers and agricultural customers use repurposed wood for animal bedding.
- Landscaping (commercial): Customers have the option to use reclaimed wood products for commercial landscaping projects.
- Wood chips to energy: Collected wood may be converted into wood chips for energy generation.
The process of wood salvaging is aligned with sustainable practices, which prioritize reducing, reusing, and recycling materials before resorting to energy recovery, incineration or landfilling. It is noted that reduce as defined by the waste hierarchy triangle can be applied to all the activities described in this diagram. For elaboration on the waste hierarchy triangle, please visit: Reducing municipal solid waste-Environment and Climate Change Canada.