Canada's Anti-Money Laundering and Anti-Terrorist Financing Regime Strategy 2023-2026
Table of Contents
Canada's AML/ATF Regime Strategy
The Three Pillars of Canada's AML/ATF Regime
Improving Canada's AML/ATF Regime
ANNEX A: Supplementary AML/ATF Regime Background
ANNEX B: Key Reports on Canada's AML/ATF Regime
- 2016 Financial Action Task Force Mutual Evaluation & 2021 Follow-Up Report
- 2018 Parliamentary Review of the PCMLTFA
- Anti-Money Laundering Efforts in the Province of British Columbia
ANNEX C: Recent Actions Taken to Strengthen the Regime
ANNEX D: Measuring the Performance of the Canadian AML/ATF Regime
List of Acronyms
AML/ATF - anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing
APG - Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering
ARIN - Asset Recovery Interagency Network
CBSA - Canada Border Services Agency
CFATF - Caribbean Financial Action Task Force
CIFA-BC - Counter Illicit Finance Alliance of British Columbia
CIFG - Counter ISIL Finance Group
COSUN - Co-operating and Supporting Nation
CRA - Canada Revenue Agency
CSIS - Canadian Security Intelligence Service
FATF - Financial Action Task Force
FC3 - Financial Crime Coordination Centre
FINTRAC - Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada
FIU - financial intelligence unit
FLSC - Federation of Law Societies of Canada
FSRB - FATF-style Regional Body
GAC - Global Affairs Canada
IM/IT - information management/information technology
IMLIT - Integrated Money Laundering Investigative Team
ISED - Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada
ISIL - Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
NIRA - National Inherent Risk Assessment
OECD - Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
OSFI - Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions
PCMLTFA - Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Act
PPSC - Public Prosecution Service of Canada
PSPC - Public Services and Procurement Canada
RCMP - Royal Canadian Mounted Police
RPAA - Retail Payment Activities Act
TBML - trade-based money laundering
Executive Summary
Money laundering and terrorist financing compromise the integrity of the financial system and are a threat to global safety and security. The Government of Canada takes these issues very seriously and continually works to enhance its anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing (AML/ATF) Regime (the Regime) in response to emerging money laundering and terrorist financing risks.
Canada's AML/ATF framework consists of a robust and comprehensive set of legislative statutes that set out the responsibilities of Regime partners and that seek to combat money laundering and terrorist financing while respecting the constitutional division of powers, the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, and the privacy rights of Canadians.
Combatting money laundering and terrorist financing is a collaborative effort, requiring coordination across all orders of government, public and private sectors, and international borders. The Regime is operated by 13 federal departments and agencies, each with their own respective mandates and areas of responsibilities, coordinated by the Department of Finance Canada. Provincial and municipal law enforcement agencies, as well as provincial and territorial regulators, are also involved in combatting these illicit activities.
Within the private sector, more than 24,000 Canadian businesses play a critical frontline role in efforts to prevent and detect money laundering and terrorist financing, by complying with obligations set out in the Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Finance Act (PCMLTFA). Many of these businesses take extra steps to combat money laundering and its associated predicate crimesFootnote 1 by collaborating closely with key Regime partners in the form of public-private partnerships.
At the international level, the Government of Canada works with a strong network of international organizations and key allies to effectively address complex and evolving security threats involving money laundering and terrorist financing. This includes working with the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), FATF-Style Regional Bodies (FSRBs), the Egmont Group of Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs), Five Eye Partners (United States, United Kingdom, New Zealand and Australia), and other international bodies to identify emerging trends, share information, and develop international best practices to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
To remain effective, the Regime must continually adapt to changes in its operating environment. For instance, a significant trend towards financial sector digitalization accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic has changed the way people interact with the financial sector – providing opportunities for Canadians, but also challenging existing approaches to regulation and law enforcement. This includes the growing use of virtual currencies and other financial technologies that facilitate international transfer of value, often with enhanced anonymity.
In order to keep pace with evolving money laundering and terrorist financing threats, various Regime partners conduct assessments and publish strategic intelligence reports to provide policy makers with the information needed to address emerging gaps and promote awareness of emerging risks. This includes the Department of Finance Canada's 2023 update of the National Inherent Risk Assessment (NIRA), which assessed the inherent money laundering and terrorist financing risks faced by specific sectors and products in Canada.
Recent reviews of the Regime have found that it is generally effective, with strong national policy and operational coordination. However, areas for improvement have been outlined in various assessments, including Canada's 2016 FATF mutual evaluation report, the 2018 Parliamentary Review of the PCMLTFA, and most recently, in the Regime's Report on Performance Measurement Framework 2019-20. These include weaknesses in information sharing, low levels of money laundering and terrorist financing investigations and prosecutions, as well as legislative gaps, such as the coverage of the legal profession and issues regarding beneficial ownership transparency.
In order to respond to this evolving context and to address identified gaps, the Regime Strategy provides the Government of Canada's plan to combat money laundering and terrorist financing throughout the 2023-2026 period. These priority actions are grouped under four themes: 1) increasing operational effectiveness; 2) addressing legislative and regulatory gaps; 3) improving Regime governance and coordination; and 4) contributing to international community efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. The Strategy is intended to complement the 2023 Parliamentary Review of the PCMLTFA, which will explore in greater depth how Canada's AML/ATF Regime can remain responsive to the evolving ML/TF threat environment and further advance these strategic priorities.
This is the first AML/ATF Regime Strategy published by the Government of Canada and demonstrates the importance of public accountability and transparency to the success of the Regime. As the Regime's operating context continues to evolve, the Regime Strategy will be revisited and updated to reflect future actions.
Canada's AML/ATF Regime Strategy
Money laundering and terrorist financing are serious threats to the safety and security of Canadians, as well as the integrity of Canada's financial system. Canada's AML/ATF Regime helps to protect the integrity of Canada's financial system by deterring individuals from using it to carry out money laundering, terrorist financing, or other criminal financial activity. It also contributes to the safety and security of Canadians by providing financial intelligence to support law enforcement and national security efforts to detect and disrupt criminal and terrorist activities.
The purpose of this document is to set out the Government of Canada's strategy to combat money laundering and terrorist financing over the 2023-2026 planning period. The Regime Strategy takes a holistic view of the Regime and its ever-evolving operating environment to respond to Canada's greatest areas of money laundering and terrorist financing risk and ensure that all federal partners work collaboratively to achieve sustained results.
The Regime Strategy provides an overview of the current money laundering and terrorist financing threat environment and presents the Government of Canada's priority actions to improve Regime performance and outcomes. The actions presented in the Regime Strategy respond to the findings of recent reviews of the Regime, as well as identified long-term trends impacting the effectiveness of the Regime's compliance, intelligence, and enforcement activities. In addition to guiding Regime-wide objectives, the Regime Strategy supports public accountability and transparency by identifying priority actions to combat money laundering and terrorist financing in Canada over the medium-term.
While the Regime Strategy focuses on the role of federal departments and agencies, cooperation between various national and international partners is required to ensure the smooth functioning of the Regime. This includes provincial, territorial, and municipal departments and agencies that have a role in policy and enforcement; private sector reporting entities that are on the front line of preventing and detecting money laundering and terrorist financing; and international partners that work with Canada to combat these crimes on a transnational level.
The Three Pillars of of Canada's AML/ATF Regime
Money laundering is the process used to conceal or disguise the origin of criminal proceeds to make them appear as if they originated from legitimate sources. Money laundering benefits domestic and international criminals and organized crime groups. Terrorist financing is the collection and provision of funds from legitimate or illegitimate sources for terrorist activity. It supports and sustains the activities of domestic and international terrorists that can result in terrorist attacks in Canada or abroad, causing loss of life and destruction.
The Regime operates based on three interdependent pillars:
- Policy and coordination – assessing money laundering and terrorist financing risks, domestic and international policy development, and coordination;
- Prevention and detection – promoting, supervising, and enforcing AML/ATF compliance and collecting, analyzing, and disseminating financial and other intelligence; and
- Investigation and disruption – identifying, investigating, prosecuting, and sanctioning money laundering and terrorist financing offences.
AML/ATF Regime Pillars
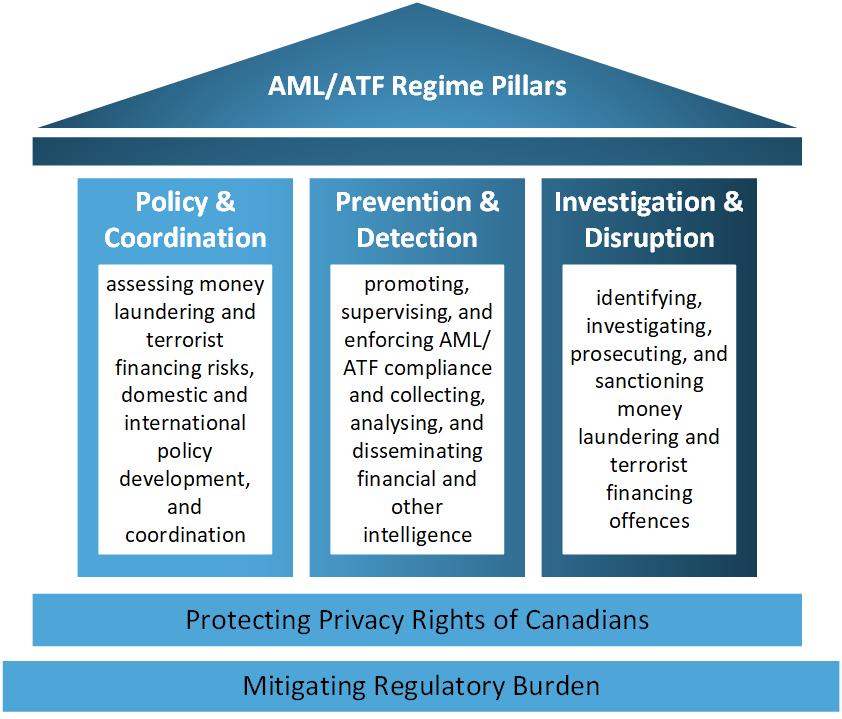
These three pillars work together to support efforts to combat organized crime, terrorism, and other major crimes, such as tax evasion, corruption, cybercrime, drug trafficking, and fraud. The Regime balances the objectives of safeguarding the integrity of Canada's financial system, ensuring the safety and security of Canadians, and respecting Canadian individual rights and freedoms, including privacy rights.
The government recognizes that measures to enhance Canada's AML/ATF legislative framework should strike the appropriate balance among sometimes conflicting objectives at play in the conduct of the Regime. A key consideration is the appropriate level of regulatory burden placed on reporting entities, which are the private sector entities on the front lines of the fight against money laundering and terrorist financing. This includes applying a risk-based approach wherever possible to maximize Regime effectiveness while minimizing burden.
A number of federal statutes, such as the PCMLTFA, establish Canada's AML/ATF framework, set out the roles and responsibilities of Regime partners, and indicate the business sectors subject to AML/ATF regulatory requirements. This legislative framework is also supported by regulations and guidance that clarify expectations, and treaties and conventions that support international efforts to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
One of the keys to the overall effectiveness of the Regime is the effective collection and use of financial intelligence, which includes information sharing across the Regime. In this sense, financial intelligence affects all three pillars of the Regime. Effective policy and legislative coverage, along with diligent private sector compliance with the PCMLTFA, ensures that the right information is submitted to the Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada and that criminals and terrorist financiers are prevented from using the financial system for their purposes. This information can be used to produce actionable financial intelligence, enabling law enforcement and national security agencies to refine the scope of their investigations, to shift their sights to different targets, and to identify assets for seizure and forfeiture. Financial intelligence is also a powerful tool to identify predicate crimes and criminal and terrorist networks, which is a wider strategic objective of the Regime.
An effective Regime must be able to adapt to changes and new threats. This requires coordination among private and public sector entities; law enforcement that has the appropriate resources, tools, and expertise to investigate financial crimes; and a legal system that includes deterrents for money laundering and terrorist financing. Improving these elements will ensure that the Canadian AML/ATF Regime continues to prevent, detect, and disrupt money laundering and terrorist financing. A strong AML/ATF Regime also contributes to a resilient national security framework, helping to keep Canadians safe from threats at home and abroad.
Canada's AML/ATF Regime Partners
The Canadian AML/ATF Regime is a comprehensive horizontal framework that consists of federal partners, contributing provincial, regional, and municipal regulatory and law enforcement bodies, and private sector entities that have obligations under the PCMLTFA and its regulations.
All federal partners share responsibility for the ultimate outcomes of the Regime, which is governed by various inter-departmental committees and a model to guide performance measurement. These committees work together to ensure an efficient Regime with a focus on both policy and operations—anchored in shared intelligence on current money laundering and terrorist financing trends, as well as the wider structure and activities of criminal and terrorist networks operating and transacting within the Canadian financial system.
In addition to official Regime partners, the Regime may also draw on the expertise of other departments and agencies, as appropriate. Coordination with provincial, territorial, and municipal policy makers, law enforcement bodies, and regulators is also important to combat money laundering and terrorist financing effectively. While the Regime as a whole falls under federal jurisdiction, there are many areas with shared provincial and territorial responsibility, including incorporation of companies, regulation of the casino and gaming sector and some financial institutions (e.g., credit unions), responsibility for corporate and land registries, and protection of privacy. From an operational perspective, provincial and municipal law enforcement agencies participate in the investigation of money laundering and terrorist financing cases, including the use of civil forfeiture.
The following 13 official federal partners contribute to Canada's AML/ATF Regime:
- Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA)
- Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
- Canadian Security Intelligence Service (CSIS)
- Department of Finance Canada
- Department of Justice Canada
- Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada (FINTRAC)
- Global Affairs Canada (GAC)
- Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED)
- Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI)
- Public Prosecution Service of Canada (PPSC)
- Public Safety Canada (PS)
- Public Services and Procurement Canada (PSPC)
- Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP)
See ANNEX A for additional background on Canada's AML/ATF Regime, including descriptions of federal Regime partners, the Regime governance framework, and the Canadian AML/ATF legislative context. Additional information on the Regime's Performance Measurement Framework and logic model is available in ANNEX D.
The Important Role of the Private Sector
There are over 24,000Footnote 2 Canadian financial institutions and designated non-financial businesses and professions with reporting obligations under the PCMLTFA.Footnote 3 These businesses play a critical frontline role in efforts to prevent and detect money laundering and terrorist financing.
Feedback from the private sector and other stakeholders supports analysis of the framework's effectiveness. The government seeks feedback from the private sector in various ways, including through the Advisory Committee on Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing and its working groups, as well as through public consultation processes.
FINTRAC has also had success in engaging the private sector through innovative public-private partnerships, such as Project Protect, Project Guardian, and Project Chameleon, which are aimed at more effectively combatting money laundering associated with human trafficking in the sex trade, the trafficking of illicit fentanyl, and romance fraud. Other notable public-private partnerships include Project Shadow, Project Athena, Project Legion, and the recently launched Project Anton, which aimed to combat the laundering of proceeds from online child sexual exploitation, through casino-related underground banking schemes, illicit cannabis and from illegal wildlife trade, respectively.
In British Columbia, the RCMP leads the Counter Illicit Finance Alliance of British Columbia (CIFA-BC), whose vision is to optimize the capacity of the public sector and private industry across Canada to uphold a safe, prosperous, and resilient economy. CIFA-BC will fulfill its mandate through collaboration between the public sector and private industry to lawfully share information in the interest of protecting the economic integrity of British Columbia and to enhance efforts in the prevention, detection, and disruption of illicit financial activity.
By partnering with Canadian businesses, the government has been effective in identifying potential ML/TF threats, uncovering broader financial connections, and providing intelligence to advance national investigations.
International Context
The global nature of money laundering and terrorist financing threats necessitates a coordinated international response. Canada works with a strong network of international organizations and key allies to effectively address complex and evolving security threats involving money laundering and terrorist financing.
Through international cooperation, Canada and its allies and partners can more effectively identify global money laundering and terrorist financing trends, share information to contribute to investigations with transnational elements, and develop international best practices to prevent, detect, and deter money laundering and terrorist financing. In this way, Canada's domestic AML/ATF efforts are reinforced and strengthened by the strong leadership role it plays in global efforts to counter money laundering and terrorist financing.
The following are examples of some of the key international organizations and partnerships for Canada:
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF): The FATF is the global AML/ATF watchdog. This inter-governmental body sets international standards that aim to prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, as well as the harm these illegal activities cause to society. Canada is a founding member of the FATF, which includes 37 member jurisdictions and two regional bodies, representing most major financial centres around the world. Canada will assume the Vice-Presidency of the FATF for a period of two years beginning in July 2023.
FATF-Style Regional Bodies (FSRBs): FSRBs are regional autonomous organizations that form the global AML/ATF network and aim to implement the FATF standards. Participation in FSRBs allows Canada to monitor, influence, and support the AML/ATF activities and efforts of member countries in regions of strategic interest to Canada. Canada works in close cooperation with FSRBs such as the Caribbean Financial Action Task Force (CFATF), where Canada is a Co-operating and Supporting Nation (COSUN) and the Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering (APG), where Canada is a full member. Canada is the co-Chair APG from July 2022 to July 2024.
The Egmont Group of Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs): In June 2002, FINTRAC became a member of the Egmont Group of FIUs, whose purpose is to enhance cooperation and information exchange in support of member countries' AML/ATF regimes. Currently comprised of FIUs from over 160 jurisdictions, the Egmont Group's goals are to foster communication and improve the exchange of information, intelligence, and expertise among the global network of FIUs.
Five Eyes Partnership: The Five Eyes partnership is composed of Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. These countries share a broad range of information with one another and collaborate on national security, defence, and intelligence-related issues.
The Regime also collaborates with other international bodies, including the G7, the G20, and more recently the Global Coalition against Da'esh Counter ISIL Finance Group (CIFG). Commitments from the broader global community also affect the Regime. This includes decisions made by the United Nations Security Council, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), and other international organizations and conferences.
Current Environment
The money laundering and terrorist financing environment is continuously evolving. In order to remain relevant and effective, the Regime must keep pace with emerging trends across sectors of relevance to the Regime, as well as international and domestic developments. At the same time, the Regime must continuously monitor and adapt to money laundering and terrorist financing risks that undermine the integrity of the financial system and pose a threat to national security.
Financial Sector Trends
Technology has advanced rapidly in recent years, with significant trends towards digitalization across the financial sector. This includes developments related to virtual currencies, which offer new ways to move value with a certain degree of anonymity; the development of new financial technologies (fintech), which are changing the ways people interact with the financial system; and digital identity recognition, which can facilitate identity verification and customer due diligence processes. Many of these new technologies cross international borders and often do not require a physical presence to offer services. Coordination on a global level is essential to addressing the money laundering and terrorist financing risks posed by these emerging technologies, as well as capitalizing on the opportunities they present for both AML/ATF compliance and economic growth.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this trend towards digitalization, with more financial consumers adopting digital channels, as well as new financial services and products being made available by emerging technologies. The pandemic has also shown that criminal actors are adapting in the current context by leveraging online schemes and COVID-19 related fraud to generate funds. This shift to digital platforms and financial products may also present new opportunities for criminals and terrorist organizations to move funds. New experiences from the COVID-19 pandemic reinforce the importance of national authorities and the private sector monitoring and understanding evolving risks on an ongoing basis.
National Security Context
Canada's national security framework prioritizes protecting the safety and security of Canadians at home and abroad. Federal departments and agencies with mandates to protect Canadians and Canadian interests coordinate and cooperate to deliver initiatives and programs in key areas. These include addressing hostile activities by state actors; cyber security, space, and emerging technologies; countering violent extremism and terrorism; border security; environmental and health security; and the link between organized crime and national security, among others. Though the threats across these areas are diverse, criminal activity in each area is commonly enabled by money laundering and/or terrorist financing. AML/ATF measures and tools are also relevant to preventing, detecting and countering sanctions evasion.
The transnational nature of modern criminal networks and the techniques they use heightens the complexity of addressing these threats, underscoring the need for cooperation across municipal, provincial, federal, and international jurisdictions. Such operational cooperation can more effectively detect, disrupt, and prevent money laundering and terrorist financing, and combat the crimes and threats they enable. As such, AML/ATF efforts are integrated into Canada's broader national security and public safety framework.
Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing Threats
Canada's money laundering and terrorist financing threat and risk environment changes as new methods to launder money and finance terrorism emerge over time. In order to keep pace with these developments, various Regime partners, including FINTRAC, conduct assessments and publish strategic intelligence reports to promote the awareness of reporting entities and the public regarding emerging risks.
For instance, in July 2020, FINTRAC and the Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre jointly published the Special Bulletin on COVID-19: Trends in Money Laundering and Fraud, which highlights areas that may pose an increased money laundering risk associated with the exploitation of the pandemic. Other strategic intelligence reports cover issues including professional money laundering through trade and money services businesses, as well as indicators for the laundering of proceeds from romance fraud, child sexual exploitation, and human trafficking.Footnote 4
Recent assessments of the money laundering threat in Canada have demonstrated that there is a broad range of profit-oriented crime conducted by a variety of threat actors in Canada. This criminal activity generates billions of dollars of illegal proceeds annually that might be laundered. Assessments have also shown that the terrorism threat landscape in Canada is complex, continuously evolving, diverse, and inherently connected to larger geopolitical developments. Over the past few years, the nature of terrorist attacks has changed, becoming smaller in scale and lower in cost.
National Inherent Risk Assessment
The National Inherent Risk Assessment (NIRA) serves as the Regime's primary tool for understanding ongoing money laundering and terrorist financing trends and methods. This comprehensive, whole-of-government initiative is conducted to assess inherent money laundering and terrorist financing risks faced by key sectors and products within the Canadian economy, inform new policy responses, and provide risk information to industry. The NIRA leverages information from a wide range of sources, including assessments and strategic intelligence reports developed by Regime partners. Canada's first NIRA was published in 2015 and an update published in 2023.
The 2023 NIRA assessed the money laundering threat posed by 22 profit-oriented crimes, as well as the threat posed by third-party money launderers. The assessment found that transnational organized crime groups and professional money launderers remain the key money laundering threat actors in the Canadian context. It is estimated that the largest money laundering risks in Canada come from illicit drug trafficking, various types of fraud, especially mass-marketing fraud, and third-party money laundering.Footnote 5 Illegal gambling, as well as corruption, collusion and bribery, were also assessed as significant concerns. The risk level of certain money laundering threats was adjusted in comparison to the levels observed in the 2015 assessment. For example, the money laundering risk level associated with tax evasion, wildlife trafficking and illegal gambling increased, while the risk level decreased in the case of illegal tobacco smuggling, counterfeiting, and piracy.Footnote 6
The largest terrorist financing threats are from Hizballah and Al-Shabaab. The assessment of terrorist financing is based on a careful review of evidence and intelligence from Canadian security and intelligence agencies on threat actors identified by the United Nations Security Council and listed in Canada as terrorist entities. There is generally a low prevalence of sophisticated and organized terrorist financing networks in Canada. For many of the threat actors assessed, the main activities observed were around individuals making direct financial contributions to a group or joining its ranks abroad.
Another trend being carefully monitored is the financing risks linked to ideologically motivated violent extremist (IMVE) threat actors, including white-supremacist groups recently listed as terrorist organizations in Canada. For instance, in July 2021 FINTRAC published the Special Bulletin on Ideologically Motivated Violent Extremism: A Terrorist Activity Financing Profile, which noted the presence and activities of both lone actors and groups in relation to this threat. It also noted the risk that individuals in Canada may fund international IMVE networks, while not necessarily being members of organized groups themselves. The 2023 NIRA includes a preliminary assessment of IMVE and listed terrorist actors. Understanding of terrorist financing risks linked to IMVE is developing and will be updated in future national risk assessment updates.
In addition to identifying threat actors that pose a risk to the Canadian economy, the NIRA also considers which economic sectors are most vulnerable to exploitation for money laundering and terrorist financing purposes. The 2023 NIRA found that the sectors most at risk for money laundering and terrorist financing activities are domestic banks, corporations and express trusts, as well as certain types of money services businesses. Trade-based money laundering was also identified as an important concern through the assessment of different sectors, including import/export companies and freight forwarders, and the analysis of criminal activities around third-party money laundering and commercial fraud.
Analysis on non-reporting entities that pose money laundering or terrorist financing risks in Canada were also completed, such as for crowdfunding platforms and payment service providers. These sectors were assessed as posing medium and high risks, respectively, and were incorporated into the regulatory framework in April 2022.
The NIRA provides an overview of money laundering and terrorist financing risks posed to various business types and sectors before the application of any mitigation measures. These measures include a range of legislative, regulatory, and operational actions that prevent, detect, and disrupt money laundering and terrorist financing. Sectors confronted with higher inherent money laundering and terrorist financing risks typically also have strong measures in place to mitigate those risks. Risks and risk mitigation practices will vary, and so in practice are to be considered on a case by case basis.
In no instances should this information be used as basis or justification for discriminatory behaviour or action toward specific communities in Canada or abroad.
Improving Canada's AML/ATF Regime
Recent reviews of Canada's AML/ATF Regime found that the Regime is generally effective, with good national coordination at the policy and operational levels. Reporting entities are subject to appropriate risk-sensitive supervision, supervisory actions have positive effects on compliance by reporting entities, and FINTRAC receives a wide range of information used to produce good quality intelligence.
Areas for improvement are outlined in Canada's 2016 FATF mutual evaluation report, the 2018 Parliamentary Review of the PCMLTFA, and other reports. These include weaknesses in information sharing; low levels of convictions for money laundering and terrorist financing; low levels of proceeds of crime recovery; as well as legislative and regulatory gaps, such as the coverage of the legal profession and issues regarding beneficial ownership transparency.
A recent non-profit sector review update, which considered registered charities as well as non-profit organizations in Canada, also noted a possible coverage gap with respect to non-profit organizations. These organizations were identified as being at risk of terrorist financing abuse, as they are not monitored for terrorist financing activities or educated about their terrorist financing risks in the same way that registered charities are by the CRA. This coverage gap is also noted in Canada's fourth follow-up report to its 2016 FATF mutual evaluation.
In addition, the Regime's Report on Performance Measurement Framework 2019-20 highlighted gaps in the Regime's capacity to investigate and prosecute financial crimes, its slow progress in complying with international AML/ATF standards on beneficial ownership transparency and regulation of the legal profession, and a need to implement improved practices to better use financial intelligence and target enforcement actions.
In its effort to continuously adapt to changes in the AML/ATF operating environment and address emerging threats and vulnerabilities, the Regime relies on its comprehensive governance framework to identify measures to respond to identified gaps and weaknesses. This includes advancing priority actions in response to results from Parliamentary reviews, FATF evaluations, evolving international standards, stakeholder feedback, and internal risk and performance assessments.
A list of recent reviews of the Canadian AML/ATF Regime is available in ANNEX B, and additional information on the Regime's Performance Measurement Framework and logic model is available in ANNEX D.
Priority Actions
The Regime will take substantive steps to achieve measurable improvements to the prevention, detection, and disruption of money laundering and terrorist financing in Canada. These priorities for medium-term action aim to address the gaps identified through the Regime's Performance Measurement Framework and in recent Regime reviews, as well as respond to key money laundering and terrorist financing risks in the Canadian context.
These priority actions are being taken in the areas likely to have the most material impact on results and effectiveness. Priority actions are grouped under the following four themes:
- Increasing operational effectiveness;
- Addressing legislative and regulatory gaps;
- Improving Regime governance and coordination; and
- Contributing to international community efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
Increasing Operational Effectiveness
Federal money laundering and terrorist financing charges, convictions, and federal asset forfeitures have decreased over the past decade. To address declining investigations and prosecutions, the Regime will explore ways to improve operational effectiveness, allowing Canada to improve its ability to "follow the money" and help take criminals off the streets through the following actions:
Explore new operational approaches to support investigations, prosecutions, and criminal asset recovery
In Budget 2022 the government announced its intention to establish a new Canada Financial Crimes Agency, which will bolster Canada's ability to quickly respond to complex and fast-moving cases of financial crime as its lead enforcement agency in this area. The Budget provided $2 million to Public Safety Canada in 2022-23 to undertake initial work to develop and design the new agency. A portion of this funding is being used to establish a dedicated project team of policy and operational experts housed within Public Safety Canada's Financial Crime Coordination Centre (FC3) to examine the legislative, operational and jurisdictional landscape in Canada in order to develop recommendations on the agency's mandate, priorities and authorities. The remaining funding is being used to engage financial crime and other experts through professionally contracted services, providing an independent assessment of international best practices to complement the efforts of the dedicated project team throughout the Canada Financial Crimes Agency development and design process.
In December 2020, the RCMP announced the creation of new Integrated Money Laundering Investigative Teams (IMLITs). The IMLITS have been established in British Columbia, Alberta, Ontario, and Quebec. These teams bring together expertise from a variety of agencies to address high-profile cases and advance investigations into money laundering and proceeds of crime nation-wide.
The IMLITs will continue to integrate specialized investigative resources from partners across Canada's AML/ATF Regime to undertake money laundering and proceeds of crime investigations to reduce the capacity of, and increase the costs to, targeted organized criminals and crime groups through the removal of their assets. These money laundering/proceeds of crime dedicated teams and integrated partners will use criminal intelligence to create operational plans that clearly indicate all avenues into the investigation of the accumulation of illicit wealth, including the laundering of money derived from criminal activity.
In parallel, the CBSA will continue its work through the Trade Fraud and Trade-Based Money Laundering Centre of Expertise, which was officially launched on April 1, 2020. The Centre has strengthened the CBSA's ability to identify and investigate complex trade fraud, as well as refer cases of trade-based money laundering (TBML) to federal law enforcement. The Centre has provided an increased volume of tactical, operational, and strategic intelligence on trade fraud and trade-based money laundering. It has begun to refer viable leads for possible investigation by partners and contribute to improving Canada's capacity to disrupt trade fraud and trade-based money laundering through increased regulatory and enforcement actions.
In relation to proceeds of crime recovery, the government will consider options that could provide additional resources to support future investigations and criminal asset recovery efforts, to increase the recovery of the proceeds of crime.
To support investigations and prosecutions, the government will continue to develop specialized training and the necessary expertise to investigate and prosecute money laundering and terrorist financing through initiatives such as the Public Safety Canada Financial Crime Coordination Centre (FC3). These actions will increase training resources available to Canadian AML/ATF practitioners, enhance specialized AML knowledge across the Regime, as well as increase the number of dedicated experts and raise their level of expertise.
Furthermore, in order to support the prosecution of non-compliance charges under the PCMLTFA, FINTRAC will work to increase awareness of non-compliance investigations. FINTRAC will also work with PPSC to enhance awareness regarding investigating and prosecuting non-compliance charges under the PCMLTFA. These actions will further enhance the effectiveness of FINTRAC's enforcement mandate.
Develop options to enhance information sharing
While protecting the privacy of Canadians is paramount, secure and timely information sharing, especially between public and private sector entities, is critical for combatting money laundering and terrorist financing. For that reason, there is a need for both safeguards against the unrestricted flow of information in order to protect Canadians' rights and privacy, as well as having the ability to share the information necessary to protect the financial security of Canadians and Canada's financial system.
The government will continue to analyze real and perceived barriers to information sharing and consider options to enhance public-public, public-private, and private-private information sharing. Regime partners recognize that enhanced information sharing between private sector and government institutions, as well as among themselves, can facilitate more targeted disruption of illicit activities related to money laundering and terrorist financing, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of the AML/ATF Regime.
Enhance promotion, supervision, and enforcement of AML/ATF compliance
Legislative amendments enacted through Budget 2021 will, once in force, require FINTRAC to issue assessments to recover costs for its compliance function from the reporting entities it regulates. To implement these changes, the Department of Finance and FINTRAC consulted with industry on assessment models in 2022. In February 2023, the government released draft regulations which would prescribe the formula for calculating assessment fees.
FINTRAC will also engage industry on plans to strengthen and modernize its compliance program under a cost-recovery framework. This engagement will inform the identification and prioritization of opportunities to strengthen FINTRAC's risk-based approach to supervision and reduce barriers that make it difficult for reporting entities to comply with their requirements under the PCMLTFA.
Modernize FINTRAC's IT infrastructure for compliance and intelligence processes
FINTRAC remains focused on the modernization of its information technology systems in order to keep pace with the rapid technological innovation that is taking place in the financial sector and all sectors around the world.
In March 2021, FINTRAC finalized its Digital Strategy: an enterprise-wide, three-year strategic plan that sets its future technology and infrastructure direction and is focused on ensuring that FINTRAC has the appropriate tools, technology, and systems in place to continue to securely deliver on its critical intelligence and compliance mandates in a digital landscape.
Covering the 2021 through 2024 period, the FINTRAC Digital Strategy aims to use new digital technology to improve business performance, enhance digital services, enrich user experiences, and explore new ways to meet FINTRAC's mandate. This progressive plan maps out how FINTRAC will stabilize and modernize its information management and technology infrastructure, as well as how it will improve value for its financial intelligence and compliance functions.
It is anticipated that through this Digital Strategy, FINTRAC will implement new technologies that enhance and standardize information exchange with FINTRAC systems. This will allow for a smoother modernization of internal systems and will enable more seamless integration with external stakeholder systems. As an example, FINTRAC is renewing its platform for secure document sharing, which is used by businesses that are obligated under the PCMLTFA to report financial transactions. This initiative will enhance FINTRAC's ability to collaborate with these businesses on a variety of activities related to compliance with the PCMLTFA, contributing towards more timely and valuable compliance, intelligence, and strategic products.
Budget 2022 provided additional funding to the FINTRAC to advance this work, including to update its financial management, human resources, intelligence, and disaster recovery systems.
Addressing Legislative and Regulatory Gaps
In order to respond to an ever-evolving operational and threat environment, the Government of Canada seeks to identify opportunities for continual improvements to its AML/ATF legislative and regulatory frameworks. This includes strengthening the Regime through amendments to the PCMLTFA and Criminal Code to address gaps, modernize the Regime, and increase effectiveness. Addressing legislative and regulatory gaps improves the breadth of intelligence available to Regime partners and reduces barriers that make it difficult to investigate complex money laundering operations.
Budget 2022 announced that the government will conduct a comprehensive review of the Regime and develop legislative changes to strengthen the PCMLTFA, the Criminal Code, and other legislation to enhance the ability of authorities to detect, deter, investigate and prosecute financial crimes and ensure the government is well placed to manage current and emerging threats outside of the scope of the current AML/ATF Regime.
Over the planning period, the PCMLTFA will also undergo a Parliamentary review. In accordance with the legislative requirement to review the Act every five years, these regular reviews provide an opportunity to keep Canada's AML/ATF framework current in response to market developments, as well as new and evolving risks. The last Parliamentary review of the PCMLTFA took place in 2018. Regime partners will support the Parliamentary review process, and feedback generated during the review will inform analysis of potential future legislative and regulatory changes to improve the Regime.
Mitigate risks in the legal profession
The legal profession remains vulnerable to exploitation given its specialized knowledge, clients that do not need to be disclosed to regulators or authorities, and its frequent involvement in establishing trusts and corporations. In June 2019, the federal government formed a new working group with the Federation of Law Societies of Canada (FLSC) to address the inherent risks of money laundering and other illicit activity that may arise in the practice of law. Since its creation, the working group has helped deepen the government's and the FLSC's understanding of risks in the legal profession, facilitated the exchange of information and best practices, and served as a forum to discuss emerging risks.
The government and the FLSC will continue to collaborate on ways to ensure that the supervision of the legal profession effectively addresses money laundering and terrorist financing risks.
Improve beneficial ownership transparency for corporations
To counter the misuse of anonymous Canadian shell companies to conceal illegal activities, such as money laundering, corruption, and tax evasion, authorities need access to timely and accurate data on the individuals who own and control these entities. To this end, through Budget 2022, the government committed to amend the Canada Business Corporations Act (CBCA) to implement a public and searchable beneficial ownership registry by the end of 2023. The registry will cover corporations governed under the CBCA and be scalable to allow access to beneficial ownership data held by provinces and territories that agree to participate. The government will also work with provincial and territorial partners to advance a national approach to a beneficial ownership registry of real property.
These initiatives build on past efforts to strengthen beneficial ownership transparency in collaboration with Canada's provinces and territories. In 2018, the government amended the CBCA to require federally incorporated, privately held corporations to create and populate a register of "individuals with significant control". In 2019, further amendments allowed police and tax authorities to make a request to these corporations to provide information from their registers where authorities believe it would be relevant to an investigation. All these changes entered into force at the same time in June 2019. As of January 2023, the majority of provincial governments have passed or are introducing legislation similar to the federal requirements, while Quebec has passed legislation requiring businesses to submit their beneficial ownership information to provincial registry and making this information searchable by name.
In February 2020, the Department of Finance and Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED) initiated public consultations on the proposed creation of a publicly accessible registry (or registries) of corporate beneficial ownership. A report on the outcomes of the consultations titled "Public consultations on strengthening corporate beneficial ownership transparency in Canada: What we heard" was published in April 2021. The government will continue collaborating with provincial and territorial counterparts to advance a national approach to beneficial ownership transparency, while respecting jurisdictional responsibilities for corporations.
Understand and mitigate terrorist financing risks in the non-profit sector
The strategy to understand and mitigate terrorist financing risks is based on threat groups identified by the United Nations Security Council as well as a careful review of intelligence and information from Canadian security and intelligence agencies. In no instances should this strategy be used as basis or justification for discriminatory behavior or action toward specific communities in Canada or abroad. Measures taken by government or private sector entities to mitigate risks related to terrorist financing should be considered on a case-by-case basis and recognize that many Canadians have ties to communities around the world which they maintain, and that while there are risks, these relationships are not, in and of themselves, a vector for terrorist financing and money laundering.
The CRA plays an important role in the fight against terrorist financing and money laundering in Canada. In support of this role, amendments were made to the Income Tax Act in 2021 to address legislative gaps and streamline the revocation process to prevent abuse of the charitable sector. For example, legislative changes were made to:
- allow for the immediate revocation of charitable status for organizations listed as a terrorist entity;
- prevent individuals with a known history of supporting terrorism from becoming a director, trustee, or similar official of a registered charity; and,
- allow for the revocation of charitable status when a charity provides false statements for the purpose of maintaining their registration.
Revocation is reserved for the most egregious cases of non-compliance and charities are provided the opportunity to make representations before the CRA comes to a final decision following an audit. Recourse also remains available to charities that do not agree with a decision by the CRA to impose a sanction or revocation. In the unique circumstance where a charity is listed as a terrorist entity, the amendments enable immediate revocation of charitable status without recourse. By preventing the abuse of charities, these measures will contribute to strengthening Canada's AML/ATF Regime.
In the coming years, the government will maintain its ongoing efforts to mitigate terrorist financing risks in the charitable sector, and may consider whether additional measures are required with respect to the non-profit sector.
Respond to new and emerging risks
The PCMLTFA was modified in 2021 to add armoured car companies as reporting entities due to the nature of their business, their role in facilitating financial transactions, and the money laundering and terrorist financing risks they pose. In February 2023, the government published draft regulations to establish AML/ATF obligations for this sector, such as record-keeping and reporting requirements. FINTRAC will also conduct outreach to educate armoured car companies on their new AML/ATF obligations and provide guidance to assist the implementation of requirements. FINTRAC compliance officers will be trained on this sector's business models and activities so that their compliance with the PCMLTFA and associated regulations can be assessed and enforced.
In recent years, there has been a growth in mortgages issued by lending businesses not regulated under the national anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing rules that apply to other financial institutions, such as banks. As announced in Budget 2022 the government introduced draft regulations in February 2023 to help prevent financial crimes in the real estate sector by extending anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing requirements to all businesses conducting mortgage lending in Canada.
AML/ATF requirements for virtual currency dealers came into force in June 2020, with further measures in June 2021, to respond to the ML/TF risks posed by virtual assets, which continue to be elevated. FINTRAC is responsible for ensuring the compliance of virtual currency dealers and continues to strengthen the assessment and enforcement framework for the supervision of virtual currency dealers, as well as engage the sector to increase respective understanding of their different business models and sector-specific risks. FINTRAC will continue to collaborate with other domestic and foreign regulators to inform its risk-based compliance assessment approach to virtual currency dealers. FINTRAC and the Department of Finance will also continue to assess and mitigate the risks of new technologies associated with virtual assets such as Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and enhanced privacy cryptocurrencies.
In April 2022, the Government of Canada introduced new regulations that extend AML/ATF obligations to crowdfunding platforms and certain payment service providers not previously subject to the PCMLTFA. These requirements cover prescribed transactions in both fiat and virtual currency, and apply to domestic entities, as well as foreign entities when they direct their services to Canadians. These important amendments address money laundering and terrorist financing risks highlighted in early 2022, when illegal blockades took place across Canada that were financed, in part, through crowdfunding platforms and payment service providers. FINTRAC will update its guidance to reflect these regulatory changes and undertake possible outreach activities to ensure that new and current reporting entities are aware of these new requirements.
Relatedly, in June 2021, the Government of Canada's Retail Payment Activities Act (RPAA) received Royal Assent. The RPAA and forthcoming regulations will implement a new retail payments supervision framework. This framework seeks to build confidence in the retail payment sector, to ensure that payment service providers have sound risk management practices and protect user funds against losses. The Bank of Canada will oversee compliance with operational and end user funds safeguarding requirements of the retail payments oversight framework and maintain a public registry of payment service providers. Many payment service providers are also required to register as money services businesses with FINTRAC. Given the overlap, the new payment service provider registration program will consist of multiple data exchanges between FINTRAC and the Bank of Canada. FINTRAC will collaborate with the Bank of Canada and share accurate, timely information to ensure compliance with each organization's respective mandates, and RPAA related obligations. In addition, the RPAA seeks to address risks related to national security that could be posed by payment service providers.
Improving Regime Governance & Coordination
The Regime benefits from continued and enhanced coordination between federal entities to ensure shared accountability, enhanced focus on results-driven policy, and consistent data collection. Through the following actions, federal partners will continue to strengthen their coordination efforts, including through enhanced coordination with the private sector, provinces, and territories.
Expand public-private collaboration to improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the AML/ATF Regime
In recent years, the RCMP and FINTRAC have led a number of successful public-private partnerships that have contributed to improving the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the Regime. Current partnerships aim to effectively combat money laundering, in British Columbia and across Canada, online child sexual exploitation, human trafficking in the sex trade, romance fraud, illegal wildlife trade and the trafficking of illicit fentanyl.
Over the planning period, the RCMP and FINTRAC will continue to build on these partnerships and work with businesses that are subject to the PCMLTFA to improve information-sharing, increase value-added intelligence products, and implement relevant technology to continue to mitigate money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
As part of these efforts, the RCMP successfully leads the Counter Illicit Finance Alliance of British Columbia (CIFA-BC), an initiative that focuses on enhanced collaboration and information exchange between the public and private sectors with the goal of protecting the economic integrity of British Columbia. As the RCMP commitment to public-private partnerships has continued to evolve and grow, the establishment of a law enforcement-led, National-level public-private partnership has resulted in the development of a Concept of Operations (ConOps) for Counter-Illicit Financial (CIF) National. CIF National is led by RCMP Federal Policing Criminal Operations – Financial Crime (FPCO-FC) and aims to address ongoing investigative challenges, explore information-sharing opportunities and assist private sector partners in their risk mitigation activities.
In addition, FINTRAC co-chairs the Public-Private Collaboration Steering Committee with the Bank of Nova Scotia. This committee includes members from Canada's AML/ATF Regime and private sector businesses, and aims to coordinate efforts to improve efficiency and effectiveness within existing AML/ATF legislative authorities. FINTRAC will continue its work with this committee, which includes establishing shared priorities; enhancing information sharing between businesses and between the public and private sectors; and leveraging technology in appropriate situations to increase automation, strengthen analytical capabilities, and enhance the financial intelligence that is disclosed to law enforcement and national security agencies.
Financial Crime Coordination Centre (FC3)
In 2021-22, Public Safety Canada launched an integrated unit of experts from across intelligence and law enforcement agencies known as the Financial Crime Coordination Centre (FC3). Tailored to operate within the Canadian legislative framework, FC3 aims to test a collaborative, integrated, public-to-public model to address significant financial crime threats. The new team is focused on policy development in three key areas: (1) advancing horizontal policy and legislative solutions to enhance Canada's enforcement capacity; (2) developing and designing the Canada Financial Crimes Agency (CFCA); and (3) expanding knowledge and learning for enforcement and prosecutorial partners.
In 2022-23, FC3 launched the FC3 Knowledge Hub Portal, an online, access-restricted collaboration space that serves professionals at all levels of government who deal with money laundering and other financial crimes, particularly those in investigative or enforcement roles. The portal connects members to key resources and subject matter experts and raises awareness of anti-money laundering efforts across Canada. It also provides practical information to help investigators, prosecutors, and other professionals in their work. FC3 continues to maintain and update the Portal with new resources for the eLibrary, Subject Matter Expert Contact List, Event Catalogue, News Links and Training Inventory pages to further support the work of the anti-money laundering community.
From February 27 to March 3, 2023, FC3 hosted the Second Annual "Spin Cycle Conference," a large-scale anti-money laundering (AML) conference open to public sector AML professionals across Canada to discuss aspects of Canada's enforcement environment, prosecutorial developments and priorities, and share lessons learned and best practices from experts both domestically and internationally. Themes included: asset recovery, the implications of the Commission of Inquiry into Money Laundering in British Columbia, information sharing, and Canada's upcoming PCMLTFA Parliamentary Review.
Throughout its operations, FC3 continues to collaborate domestically and internationally, drawing from best practices, to make recommendations for improving Canada's AML framework, such as enhancing asset recovery, and contributing to global AML initiatives.
Guidance and support for implementation of sanctions
Targeted sanctions are an important tool in the fight against financial crime, particularly terrorist and proliferation financing, and corruption. Sanctions imposed by Canada on countries, entities, or individuals can prohibit a wide range of activities, including export and import of specified goods, financial transactions, exchanges of information, and other restrictions. Persons in Canada and Canadians abroad, including Canadian financial institutions and businesses, are responsible for complying with sanctions and are obligated to continuously monitor their accounts and transactions for assets linked to listed persons. In instances where those assets are identified, they are to be effectively frozen as a result of the dealings ban prohibitions, and their existence disclosed to the RCMP or CSIS, and/or a designated regulatory body. Further, new authorities introduced in Budget 2022 made Canada the first country in the G7 to also subject these assets to forfeiture and disposal, where appropriate.
The government will seek to better support the private sector in meeting obligations related to sanctions by strengthening coordination between federal departments to provide clearer guidance on sanctions obligations and related risks, and better monitor the implementation of targeted sanctions. For example, in March 2022, FINTRAC published a Special Bulletin on Russia-linked money laundering related to sanctions evasion (canada.ca). This will also include developing a national proliferation financing risk assessment to improve understanding within the public and private sectors of domestic risks of non-implementation or evasion of counter-proliferation financing sanctions, and this will support Canada's compliance with newly strengthened international standards on counter-proliferation financing.
More effective implementation of sanctions will also support Canada's efforts to hold Russia to account for its unjustified invasion of Ukraine as well as designated individuals in Iran for their engagement in terrorism and systemic and gross human rights violations. This commitment is reflected in the announcement made by the Prime Minister on October 7, 2022, to invest $76 million to strengthen Canada's capacity to implement sanctions and identifying and addressing sanctions evasion linked to money laundering and terrorist financing. This investment positions Canada to provide guidance and support to the private sector to effectively implement Canada's sanctions, as well as move more quickly to investigate and identify assets and gather evidence as well as freeze and seize sanctioned individuals' assets.
Contributing to International Community Efforts to Combat ML/TF
Given the transnational nature of money laundering and terrorist financing activities, international cooperation and support for effective AML/ATF regimes globally are critical. No single country can combat money laundering and terrorist financing risks effectively on its own. Moreover, Canada's strong leadership role in global efforts to counter terrorist financing and money laundering reinforces and strengthens the domestic Regime by ensuring it stays current with the most up-to-date international best practices. Over the next three years, the following actions will help ensure that the Regime continues to contribute to and keep pace with international efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing:
Contributions to the FATF and support to the global network
Canada's commitment to AML/ATF is clearly visible in the leadership role Canada plays internationally. As a founding member of the FATF, Canada is committed to a strong implementation of the FATF standards and participates actively on FATF working groups and projects. Throughout the planning period, Canada will strengthen its domestic AML/ATF Regime to meet the FATF standards. During its Vice-Presidency of the FATF from July 2023 to July 2025, Canada's priorities will include strengthening the FATF's relationship with the G7 and G20, as well as the IMF and World Bank, and deepening partnerships in the Americas region.
The Regime will also continue to make significant contributions to the FATF global network by participating in FSRBs of strategic interest to Canada. Most notably, from July 2022 to July 2024, Canada will have the opportunity to exercise global leadership and influence in combatting money laundering and terrorist financing as the APG Co-Chair. Priorities Canada is advancing in the region are beneficial ownership transparency, combatting grand corruption, countering terrorist financing and digital transformation.
Additionally, Canada is committed to providing training, expertise, and funding to support FSRBs in assessing and supporting the implementation of the FATF standards around the world. This will include supporting FSRBs by providing assessors and reviewers for FSRB mutual evaluations and follow-up reports.
Bilateral cooperation
Recognizing the transnational nature of money laundering and terrorist financing, AML/ATF Regime partners will continue to cooperate actively with their international counterparts. For instance, FINTRAC cooperates with foreign FIUs to protect Canadians and the integrity of Canada's financial system. Through over 110 bilateral agreements, FINTRAC is able to disclose financial intelligence to FIUs worldwide when appropriate conditions are met. At the same time, FIUs are able to share information with FINTRAC, which broadens its analyses of international financial transactions.
The RCMP works with law enforcement agencies around the world through formal and informal cooperative mechanisms. For example, the RCMP is the Canadian law enforcement point of contact for both the Camden Assets Recovery Interagency Network (CARIN) and the Asset Recovery Interagency Network for the Caribbean (ARIN CARIB), which both aim to facilitate and promote the informal sharing of information related to the cross-border identification, freezing, seizure, and confiscation of the proceeds of crime. Through the ARINs, the RCMP has established a group of contacts concerned with all aspects of confiscating the proceeds of crime and a mechanism for the international tracing of assets.
The Department of Justice Canada administers the Mutual Legal Assistance in Criminal Matters Act and the Extradition Act, which are the two main statutes in relation to Canada's ability to provide international cooperation to Regime partners as well as to Canada's international treaty partners. Justice Canada also negotiates and administers Canada's treaties for mutual legal assistance and extradition. These support Canadian investigations and prosecutions involving evidence and/or individuals located abroad, and fulfill international AML/ATF commitments. Budget 2019 committed to modernize and expand extradition and mutual legal assistance treaty relationships in order to better support Canadian money laundering and terrorist financing investigations and prosecutions involving evidence and individuals located abroad, as well as foreign money laundering and terrorist financing investigations and prosecutions. To advance this commitment, Justice Canada will continue ongoing outreach to new and existing partners.
The government will also continue to help build global capacity to counter money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit financial flows through the ongoing delivery of targeted technical assistance. This work is primarily supported by the government's two main capacity-building programs managed by Global Affairs Canada, the Anti-Crime Capacity Building Program and the Counter-Terrorism Capacity Building Program, which fund the majority of Canada's AML/ATF technical assistance.
Various Regime partners, including FINTRAC, the RCMP, Justice Canada, PSPC, and the CRA, also provide technical assistance directly, helping to enhance global knowledge of money laundering and terrorist financing issues and to strengthen international legal and operational capacities.
Over the planning period, Canada will continue to deliver technical assistance in a targeted and prioritized manner to address gaps internationally, and ensure the safety and security of Canada's financial system.
Next Steps
The Government of Canada takes the issues of money laundering and terrorist financing very seriously. Over the 2023-2026 planning period, Regime partners will work to implement the medium-term priority actions identified in this Strategy. Implementation progress will be monitored on an ongoing basis through the Regime's robust governance framework and publicly reported on through the Regime's Performance Management Framework and subsequent updates to the Strategy. At the same time, the government will continue to assess the Regime's operating environment, including financial sector trends, emerging money laundering and terrorist financing risks, and the changing national security context, and take action to continually enhance the Regime where needed.
ANNEX A: Supplementary AML/ATF Regime Background
Canada's Regime is comprised of federal departments and agencies, including regulators and supervisors; law enforcement agencies; and reporting entities. Canada's AML/ATF legal framework is comprised of a number of federal statutes, including the PCMLTFA and its regulations, which are an essential component of Canada's broader AML/ATF Regime.
The Regime involves 13 federal departments and agencies with authorities provided by the PCMLTFA or other legislation. In addition to federal organizations, provincial and municipal law enforcement bodies and provincial regulators (including those with a role in the oversight of the financial sector) are also involved in combatting money laundering and terrorist financing.
Within the private sector, there are over 24,000Footnote 7 Canadian financial institutions and designated non-financial businesses and professions with reporting obligations under the PCMLTFA. This includes accountants and accounting firms; agents of the Crown; British Columbia notaries; casinos; dealers in precious metals and stones; financial entities; life insurance companies, brokers, and agents; money services businesses, including, for example, virtual currency dealers, crowdfunding platforms, payment service providers, and armoured car companies;Footnote 8 real estate brokers, sales representatives, and developers; and securities dealers. These entities, known as reporting entities, play a critical frontline role in efforts to prevent and detect money laundering and terrorist financing.
Federal Regime Partners
The Canadian AML/ATF Regime is composed of 13 official federal partners. The roles and responsibilities of these organizations, as they pertain to the Regime, are outlined below:
Canada Border Services AgencyThe CBSA is responsible for the administration and enforcement of Part 2 of the PCMLTFA, which requires reporting on the cross-border movement of currency or monetary instruments valued at $10,000 or more and any associated seizures. The CBSA transmits information from reports and seizures to FINTRAC and is a disclosure recipient of information from FINTRAC.
The CBSA also has the mandate and the authorities to detect, identify, and investigate the commercial trade fraud that underlies many TBML schemes. Trade fraud is characterized by the intentional misrepresentation of the price, quantity, quality, origin, classification and/or description of goods on commercial customs declarations and related shipping documentation. TBML, on the other hand describes the process of disguising proceeds of crime (from predicate crimes such as human trafficking, human smuggling, tobacco smuggling, firearms trafficking, and illicit drug trafficking) or terrorist financing activities as legitimate trade transactions.
Canada Revenue Agency
The CRA's role in the context of the Regime is twofold: to minimize the impact money laundering and terrorist financing have on the Government of Canada's ability to collect and protect taxes and duties; and to protect the integrity of Canada's charitable registration system from the risk of terrorist financing abuse.
Since 2010, the CRA can use the powers available under the Regime to investigate money laundering offences when the designated offence is tax evasion under the Income Tax Act and the Excise Tax Act. Following investigations, the CRA refers cases to the PPSC for prosecution.
The CRA receives information from Regime partners that is relevant to investigating a money laundering offence, when that information is also related to investigations of the evasion of tax or duty obligations under the Income Tax Act and the Excise Tax Act. The CRA also receives information from Regime partners relevant to terrorist financing activity when that information relates to a registered charity or applicant.
The CRA may disclose relevant information to assist police organizations or Regime partners in carrying out their money laundering or terrorist financing investigations. The CRA can only disclose information related to money laundering to a national security agency when the designated offence is one of the terrorism offences under Section 83 of the Criminal Code. The CRA also provides Voluntary Information Records to FINTRAC, and is a disclosure recipient of information from FINTRAC in cases where the information is expected to be relevant to tax evasion or the registration of a charity.
The CRA reviews applications for charitable registration, potentially denying registration where a risk of terrorist abuse is identified. It regularly audits charities to ensure they continue to meet their registration obligations under the Income Tax Act and common law, taking administrative actions (ranging from education to a revocation of charitable status) in cases of non-compliance, including those related to terrorist financing.
More recently, the CRA played a role in policy discussions that relate to tax evasion, such as work to improve the transparency of beneficial ownership information and the reporting requirements for trust companies.
Canadian Security Intelligence Service
CSIS has a mandate to collect, analyze, and report to the Government of Canada information and intelligence concerning threats to Canada's national security, and to take measures to reduce those threats. CSIS is a designated recipient from FINTRAC of financial intelligence relevant to threats to the security of Canada. In the course of its investigations of individuals suspected to be engaged in activities constituting threats to the security of Canada, CSIS may identify individuals engaged in the financing of terrorist activities.
Department of Finance Canada
The Department of Finance is responsible for developing AML/ATF policy for the PCMLTFA and its regulations and advising the Minister of Finance on policy issues, Regime-related activities, the Minister's responsibility for oversight of FINTRAC, and developments related to combatting money laundering and terrorist financing. As the policy lead for the federal Regime, the Department of Finance is the secretariat for approval, management, and reporting on Regime initiatives. The Department of Finance has overall responsibility for coordinating the collection of financial and non-financial performance information and public reporting via the Departmental Plan and Departmental Results Report.
Department of Justice Canada
The Department of Justice provides legal advice on money laundering and terrorist financing offences to Regime partners and aids policy development by providing legal opinions with respect to legal challenges. The Department of Justice is responsible for the Criminal Code of Canada, as well as the Mutual Legal Assistance in Criminal Matters Act and the Extradition Act, the two main statutes in relation to Canada's ability to provide international cooperation to Regime partners as well as to Canada's international treaty partners.
The Department of Justice also negotiates and administers Canada's treaties for mutual legal assistance and extradition. These support Canadian investigations and prosecutions involving evidence and/or individuals located abroad, and fulfill international AML/ATF commitments.
Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada
FINTRAC is Canada's financial intelligence unit and AML/ATF regulator. As such, FINTRAC has a dual operational mandate:
- Compliance: ensuring that reporting entities comply with their obligations under the PCMLTFA and its regulations, including obligations related to customer identification, reporting, and record keeping.
- Financial intelligence: analyzing and assessing reports and information from a variety of sources in order to assist in the detection, prevention, and deterrence of money laundering and terrorist activity financing.
FINTRAC is an independent agency, operating at arm's length from law enforcement and other government departments and agencies to which it is authorized to provide financial intelligence. Its mandate and powers were designed to safeguard individual privacy and respect the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. It reports to the Minister of Finance, who is accountable to Parliament for FINTRAC's activities.
Global Affairs Canada
GAC implements elements of Canada's efforts to combat terrorist financing, proliferation financing, and the laundering of proceeds of certain crimes. GAC is responsible for the administration of Canada's sanctions regime with respect to the Justice for Victims of Corrupt Foreign Officials Act, the Special Economic Measures Act,and the United Nations Act. GAC is also the lead department for the United Nations crime conventions that Canada has ratified, such as the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime and the United Nations Convention against Corruption, some of which contain legal obligations relating to money laundering, terrorist financing, and other related public safety issues.
In addition, GAC's Counter-Terrorism Capacity Building Program and Anti-Crime Capacity Building Program provide technical assistance for capacity building to address the needs of countries with regard to laws, policies, plans, training, or operational expertise to prevent and mitigate acts of terrorism and combat organized crime and corruption.
Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada
ISED is responsible for the regulation and oversight of many aspects of Canada's marketplace framework, which includes corporate governance of federally incorporated corporations regulated under the Canada Business Corporations Act.
ISED plays an important part within the Regime as part of the government's commitment to work with the provinces and territories towards amending relevant corporate statutes to ensure that corporations hold information on beneficial owners. The concealment of information on the ultimate ownership or control of corporations (also called "beneficial ownership") can be part of international webs used to facilitate tax evasion, money laundering, corruption, financing of terrorist activities, and the proliferation of dangerous goods.
ISED is also responsible for the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act and the related guidance and regulations. This is particularly important in discussions surrounding enhanced information sharing (both between public and private sector and amongst private sector entities).
ISED also administers the Investment Canada Act, which applies broadly across the economy except with respect to cultural businesses, which are administered by the Minister of Canadian Heritage. The Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry is supported by the department in administering the Act in a manner that encourages investment, economic growth, and employment opportunities in Canada while ensuring that Canada's national security is protected.
Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions
OSFI supports the Regime through its prudential oversight of money laundering and terrorist financing risks that could affect the financial soundness of federally regulated financial institutions. This complements FINTRAC's responsibility for supervising compliance with the PCMLTFA.
Public Prosecution Service of Canada
The PPSC operates on behalf of the Attorney General of Canada, under the direction of an independent Director of Public Prosecutions. PPSC prosecutors are responsible for initiating and conducting federal prosecutions, including those that involve money laundering and terrorist financing offences. They may prosecute a money laundering offence where the predicate crime is a contravention of a federal law other than the Criminal Code of Canada, or where authority to prosecute the predicate crime is shared between federal and provincial prosecution services on behalf of their respective Attorneys General. The PPSC also provides legal advice to law enforcement agencies over the course of their investigations. When charges are laid following an investigation, full responsibility for the proceedings shifts to PPSC.
Public Safety Canada
Public Safety has an important leadership role within the Regime as the lead policy department responsible for combatting transnational organized crime, terrorism, and other threats to the security of Canada. Public Safety is responsible for the implementation of Canada's Counter-Terrorism Strategy and provides support to AML/ATF operational partners through the Financial Crime Coordination Centre (FC3). The FC3 is an integrated unit of experts from across intelligence and law enforcement agencies that regroups knowledge and expertise for investigators and prosecutors to increase the effectiveness of money laundering investigations, prosecutions, and asset forfeiture.
Additionally, the department supports the Minister of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness as the lead Minister for overall counter-terrorism planning, preparedness, and response within the Government of Canada, and for national leadership and coordination on matters relevant to national security. This includes supporting the Minister's statutory responsibilities to recommend terrorist entities for listing under Section 83.05 of the Criminal Code. The RCMP, CSIS, and CBSA are part of the Public Safety portfolio, and work collectively on issues of mutual interest.
Public Services and Procurement Canada
PSPC is responsible for managing assets seized or restrained by law enforcement in connection with criminal offences and for disposing of and sharing the proceeds of crime upon court declared forfeitures under specific sections of the Criminal Code of Canada, the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act, and the PCMLTFA,through the Seized Property Management Directorate.
PSPC, through the Forensic Accounting Management Group, also participates in and supports investigations and prosecutions related to money laundering, proceeds of crime and/or terrorist criminal activity.
Royal Canadian Mounted Police
As the national police force, and as the provincial or local police force in many jurisdictions across Canada, the RCMP plays a fundamental role in the Regime. The RCMP investigates money laundering and terrorist financing cases, makes arrests, lays charges, and seizes funds or assets suspected of being proceeds of crime or used in support of terrorist criminal activity. The RCMP acts as a liaison for exchanging criminal intelligence with international police forces, and liaison officers assist in pursuing AML/ATF cases. Following investigations, the RCMP also refers cases to the PPSC for prosecution.
Regime Governance Framework
Federal Regime partners coordinate AML/ATF efforts through work on various interdepartmental governance committees, as described below.
Canada's AML/ATF Regime Governance Structure
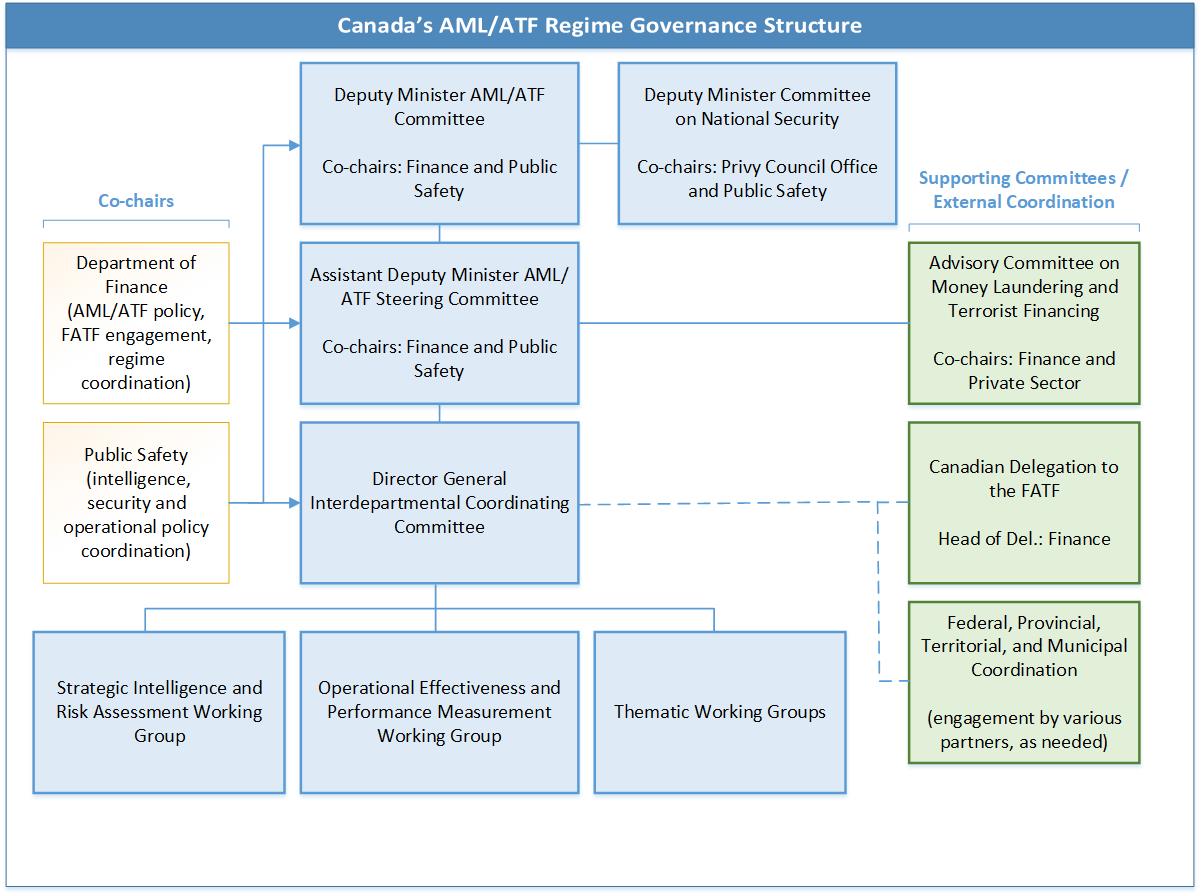
Deputy Minister Committee on National Security : Considers a wide range of current and emerging issues affecting Canada's national security.
Deputy Minister AML/ATF Committee : Strengthens accountability for policy and operational outcomes and ensures alignment and integration with government strategy on national security and economic prosperity.
Assistant Deputy Minister AML/ATF Steering Committee : Strengthens alignment of policy and operational priorities, sustains attention to enforcement outcomes, and addresses gaps and challenges within the Regime.
Director General Interdepartmental Coordinating Committee : Bridges strategy and operations by developing coordinated approaches to addressing any gaps to ensure the smooth functioning of the Regime. Key to this role is the prioritization and triage of issues raised by the working groups.
Strategic Intelligence and Risk Assessment Working Group : Performs individual threat and sector risk analyses, develops the National Inherent Risk Assessment, and identifies gaps and vulnerabilities that may require further consideration by the Regime.
Operational Effectiveness and Performance Measurement Working Group : Maintains key performance indicators that work in a Canadian context, ensures comprehensive and regular reporting on results, and identifies and elevates operational issues to ensure a sustained Regime focus on operational results.
Thematic Working Groups : Deepen the understanding of specific topics or provide recommendations to address gaps in the Regime, as required.
In addition, external coordination supports the Regime:
Advisory Committee on Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing – A public-private advisory committee, and associated working groups, with the role of encouraging collaboration and transparency with the private sector. This group is responsible for facilitating information sharing and consultation, and providing a high-level discussion forum to address emerging issues.
Canadian Delegation to the Financial Action Task Force : Leverages expertise of all Regime partners to ensure that Canada has a coordinated view that reflects this country's operational and policy positions on AML/ATF when contributing to setting global standards at the FATF.
Legislative Context
The Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Act (PCMLTFA), as well as a number of other federal statutes and regulations, establish Canada's AML/ATF framework and set out the roles and responsibilities of the Regime partners. This legislative framework is also supported by guidance that clarifies expectations, and treaties and conventions that support international efforts to combat money laundering, terrorist financing, and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.
Proceeds of Crime (Money Laundering) and Terrorist Financing Act and Regulations
The PCMLTFA is the primary legislation that establishes Canada's AML/ATF framework. The overarching objectives of the PCMLTFA are to implement specific measures to detect, prevent, and deter money laundering and the financing of terrorist activities, while facilitating the investigation and prosecution of these crimes. These objectives place equal emphasis on preventing the proceeds of crime from entering or moving through Canada's financial system and creating a paper trail to assist law enforcement in detecting and prosecuting these crimes.
The PCMLTFA requires persons and entities with obligations under the Act and regulations (referred to as reporting entities) to identify their clients, keep records, and have an internal compliance program in place, and establishes a regime for the registration of money services businesses. The Act also outlines mandatory reporting for prescribed transactions, such as electronic funds transfers, large cash transactions, as well as for suspicious financial transactions.
The PCMLTFA also establishes FINTRAC as Canada's financial intelligence unit and authorizes it to receive, analyze, and assess financial transaction reports and to disclose designated information to law enforcement, intelligence agencies, and other disclosure recipients when specific legislated thresholds are met. As part of its mandate, FINTRAC also ensures the compliance of reporting entities with their obligations under the PCMLTFA.
Other pieces of federal legislation with a bearing on the Regime's effectiveness and its federal partners include:
Access to Information Act : Subject to certain exemptions, provides the public with access to information under the control of a government institution, including information relating to money laundering and terrorist financing.
Canada Business Corporations Act : Provides the basic corporate governance framework for federally incorporated corporations, including the requirement to keep records with respect to shareholders, creditors, directors and individuals with significant control over the corporation (the latter of which is vital for determining beneficial ownership of a corporation), and to disclose this information to the Director of Corporations Canada (once legislative provisions are brought into force).
Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms : A fundamental Canadian law that provides constitutional protection of human rights. This includes the right to life, liberty, and security of the person under Section 7, the right to be free from unreasonable searches and seizures under Section 8, and equality before and under the law under Section 15. As a part of Canada's Constitution, the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms takes precedence over other laws and sets limits on government action; therefore all laws and government actions at both the federal and provincial levels must take into account these fundamental rights.
Canadian Security Intelligence Service Act : Establishes CSIS and its authority to collect, investigate, analyze, and retain information and intelligence on activities suspected of constituting threats to the security of Canada; to advise the Government of Canada; and to take measures to reduce those threats.
Charities Registration (Security Information) Act : Provides the legislative framework for the CRA to use security and intelligence information that may reveal an organization's ties to terrorist groups. It also provides a means by which sensitive security information can be used in determining an organization's eligibility or continued eligibility for registration under the Income Tax Act, and yet be protected from disclosure.
Criminal Code : The federal government's jurisdiction in the area of combatting money laundering and terrorist financing stems from the criminal law power. While a number of possible predicate crimes may result in money laundering, possession of the proceeds of crime and money laundering are in and of themselves criminal acts under the Criminal Code. The Criminal Code also includes various offences related to terrorist financing. For example, it is a crime for anyone, directly or indirectly, to make available or provide financial or other related services to a listed terrorist entity.
Customs Act : Provides legislative authority to administer and enforce the collection of duties and taxes imposed under separate taxing legislation; controls the movement of people and goods into and out of Canada; protects Canadian industry from real or potential injury caused by dumped or subsidized goods and other forms of unfair competition; and establishes recourse provisions for recovering seized currency.
Excise Tax Act : Establishes the authority to disclose taxpayer information to law enforcement for the purpose of investigating whether a money laundering offence has been committed. When the designated offence is tax evasion, the CRA can then investigate for money laundering.
Extradition Act : Provides that both nationals and non-nationals can be extradited for an offence relating to money laundering and terrorist financing, subject to an extradition agreement on the request of an extradition partner.
Freezing Assets of Corrupt Foreign Officials Act : Enables the Governor in Council to make regulations freezing the Canadian assets of allegedly corrupt politically exposed foreign persons, at the request of a foreign country undergoing political turmoil or uncertainty.
Immigration and Refugee Protection Act – Stipulates that a permanent resident or a foreign national cannot be admitted to the country for engaging in criminal activities such as money laundering across national borders.
Income Tax Act : Establishes the authority to disclose taxpayer information to law enforcement or national security partners for the purpose of investigating whether a money laundering or terrorist financing offence has been committed, or whether the activity of any person may constitute threats to national security. When the designated offence is tax evasion, the CRA can then investigate for money laundering. In addition, the Act also governs the registration of Canadian charities.
Investment Canada Act : Provides for the review of significant investments in Canada by non-Canadians in a manner that encourages investment, economic growth, and employment opportunities in Canada, as well as for the review of investments in Canada by non-Canadians that could be injurious to national security.
Justice for Victims of Corrupt Foreign Officials Act : Enables Canada to impose dealings ban prohibitions against foreign nationals who, in the opinion of the Governor in Council, are responsible for or complicit in gross violations of internationally-recognized human rights or are foreign public officials, or their associates, who are responsible for or complicit in acts of significant corruption.
Library and Archives of Canada Act : Establishes the Library and Archives of Canada and includes provisions relating to the destruction of records. This Act is referenced in s. 54(1) of the PCMLTFA, which requires FINTRAC to destroy records after 15 years.
Mutual Legal Assistance in Criminal Matters Act : Establishes the legal authority to obtain court orders on behalf of countries that are parties to mutual legal assistance agreements with Canada. These include bilateral treaties and multilateral conventions containing provisions for mutual legal assistance.
National Defence Act : Establishes the Department of National Defence, the Canadian Armed Forces, and the Communications Security Establishment.
National Security and Intelligence Committee of Parliamentarians Act : Establishes the authorities of the Committee of Parliamentarians to review the national security activities of any department or agency of the Government of Canada.
Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act : Sets the legal requirements for the protection of personal information in Canada and sets limits on the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information by organizations. It also sets out limited and specific conditions under which organizations can disclose personal information to government institutions and law enforcement.
Privacy Act : Provides the basic legal framework for the collection, retention, use, and disclosure of personal information by government institutions.
Retail Payment Activities Act – Legislation under which the Bank of Canada will be responsible for supervising payment service providers with the aim of building confidence in the safety and reliability of their services, while protecting users from certain risks.
Security of Canada Information Disclosure Act : Establishes an explicit authority for Government of Canada institutions to disclose national security-related information, either proactively or in response to a request, to designated Government of Canada recipient institutions with jurisdictions or responsibilities in respect of activities that undermine the security of Canada.
Seized Property Management Act : Authorizes the Minister of Public Works and Government Services to provide consultative and managerial services to law enforcement in relation to property seized or restrained in connection with designated criminal offences; dispose of this property when the Courts declare forfeiture; and share the proceeds of disposition.
Special Economic Measures Act : Enables the Governor in Council to make regulations to impose sanctions against a foreign state, as well as individuals and entities related to that foreign state, if any of the following circumstances has occurred: an international organization or association of states has called on its members to take measures, a grave breach of international peace and security has resulted in or is likely to result in a serious international crisis, gross and systematic human rights violations have been committed, or for acts of significant corruption.
State Immunity Act : Assists individuals who have obtained a judgement against a foreign state on terrorism-related matters to request assistance in locating financial assets in Canadian jurisdiction belonging to foreign states that support terrorism.
United Nations Act : Enables the Governor in Council to make regulations to implement sanctions decisions of the United Nations Security Council into Canadian domestic law.
ANNEX B: Key Reports on Canada's AML/ATF Regime
Key reports assessing Canada's AML/ATF Regime produced in recent years include the following:
2016 Financial Action Task Force Mutual Evaluation & 2021 Follow-Up Report
2018 Parliamentary Review of the PCMLTFA
Anti-Money Laundering Efforts in the Province of British Columbia
In addition to the national reviews above, the province of British Columbia has also been actively reviewing the AML Regime.
Peter M. German, QC (March 31, 2018), Dirty Money: An Independent Review of Money Laundering in Lower Mainland Casinos conducted for the Attorney General of British Columbia.
Peter M. German, QC (March 31, 2019), Dirty Money – Part 2: Turing the Tide – An Independent Review of Money Laundering in B.C. Real Estate, Luxury Vehicle Sales & Horse Racing.
Expert Panel on Money Laundering in BC Real Estate (2019), Combatting Money Laundering in BC Real Estate.
Austin F. Cullen, Commissioner (June 2022), Commission of Inquiry into Money Laundering in British Columbia: Final Report. https://cullencommission.ca/files/reports/CullenCommission-FinalReport-Full.pdf
| Actions Taken | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Governance | |
| Introduced a dedicated Deputy Minister-level Steering Committee and Public Safety Canada as a Regime co-Chair with Finance | Stronger senior level coordination to set and oversee Regime priorities and increase the Regime's contribution to combatting organized crime and terrorism |
| Development of a Regime Charter and Regime Strategy | Clearer roles, responsibilities, and accountabilities across federal organizations for joint Regime outcomes |
| Development of a Performance Measurement Framework | Improved data on effectiveness and impact to promote transparency and accountability for Regime results |
| Updated national inherent ML/TF risk assessment | Current understanding of the highest ML/TF threats and vulnerabilities to inform risk-based policy and actions |
| Legislative & Regulatory Measures | |
| Amendments to the PCMLTFA regulations to broaden the scope of the Regime | Address regulatory gaps related to new technologies, including virtual currency, crowdfunding and payment service providers, beneficial ownership and politically exposed persons identification requirements, armoured car companies, mortgage lenders and correspondent banking relationships. |
| Amendments to the PCMLTFA to allow FINTRAC to go back to reporting entities for clarifying information, add new financial intelligence disclosure recipients, increase transparency of administrative monetary penalties, strengthen criminal penalties, and implement levies on reporting entities to recover costs (forthcoming) | Improve compliance with international standards for financial intelligence units (access to information) Improve dissemination and use of financial intelligence Improve transparency and effectiveness of penalties for non-compliance with AML/ATF obligations Increased, sustainable funding for AML/ATF supervision |
| Criminal Code amendments to add an alternative requirement of recklessness to the offence of money laundering | Improve the ability to investigate and prosecute professional money launderers |
| Amendments to the Canada Business Corporations Act to require federal private corporations to maintain beneficial ownership records and eliminate bearer shares | Prevent establishment of anonymous corporations, make beneficial ownership information (individuals who own, control, and profit from corporations) more readily available to law enforcement and establish model requirements for provinces and territories to implement |
| Amendments to the Seized Property Management Act to broaden access to PSPC asset management services | Reduce need for duplication of these services nationwide |
| Amendments to the Income Tax Act to address legislative gaps and streamline the revocation process to prevent abuse of the charitable sector (in force as of 2021) | Prevent individuals with a known history of supporting terrorism from becoming a director, trustee, or similar official of a registered charity, and allow for the revocation of charitable status when a charity provides false statements for the purpose of maintaining their registration, and for the immediate revocation of charitable status for organizations listed as a terrorist entity |
| Recent Funding Initiatives | |
| AML Action, Coordination and Enforcement Team Pilot Initiative (renamed to Financial Crime Coordination Centre (FC3)) (Public Safety) $24M over five years (Budget 2019) |
Brings together experts from across intelligence and law enforcement agencies to pilot a collaborative, public-to-public model to address AML/ATF, through enhanced support to operational partners |
|
Canada Financial Crimes Agency (Public Safety) $2M in 2022-23 (Budget 2022) |
Undertake initial work to develop and design the new Canada Financial Crimes Agency, which will become Canada's lead enforcement agency in this area |
| Additional Funding to FINTRAC to strengthen their oversight functions (FINTRAC) $89.9M over five years, $8.8 ongoing (Budget 2022) |
Enables FINTRAC to implement new anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing requirements for crowdfunding platforms and payment service providers; support the supervision of federally regulated financial institutions; continue to build expertise related to virtual currency; modernize its compliance functions; and update its financial management, human resources, intelligence, and disaster recovery systems |
| Trade Fraud and Trade-Based Money Laundering Centre of Expertise (CBSA, FINTRAC) $27.4M over five years, $10M ongoing (Budget 2019) |
Strengthen the CBSA's ability to identify and investigate trade fraud and identify and refer trade-based money laundering cases to the RCMP |
| Funding to strengthen FINTRAC compliance and financial intelligence functions and address program pressures (FINTRAC) $66.9M over five years, $5.3M ongoing (Budget 2019) |
Increase outreach and examinations in the high-risk sectors (e.g., real estate and casino sectors), timely guidance to support implementation of new regulations, expand public-private partnerships, strengthen FINTRAC capacity to supervise financial institutions, enhance financial intelligence, stabilize critical IM/IT infrastructure, and improve public communications |
| Increasing RCMP federal policing capacity, including establishment of Integrated Money Laundering Investigative Teams (IMLITs) in British Columbia, Alberta, Ontario, and Quebec and investments in information management and technology (RCMP) $98M over four years, $20M ongoing (Budget 2019) |
Increase resources dedicated to investigating money laundering in key jurisdictions and modernize analytic systems and resources to process growing volumes of increasingly complex data and digital evidence information more rapidly to support money laundering and proceeds of crime investigations |
| Dedicated forensic accounting expertise for financial crime investigations (PSPC) $14.6M over five years, $3.6M ongoing (2020 Economic and Fiscal Snapshot) |
Increase the number of forensic accounting resources dedicated to supporting federal, provincial, and municipal money laundering and terrorist financing investigations |
| Modernization of Canada's international agreements and mutual legal assistance treaties (Justice) $17.6M over five years, $5M ongoing (Budget 2019) |
Better support Canadian money laundering investigations and prosecutions involving evidence and individuals located abroad, as well as foreign money laundering investigations |
| Funding to strengthen Finance policy capacity and co-chairing the Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering (Finance) $6M over five years, $0.8M ongoing (July 2020 Economic and Fiscal Snapshot) |
Address capacity pressures for coordinating policy responses to growing money laundering and terrorist financing threats and take on leadership roles in international efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing |
| Funding to enhance Canada's sanctions regime, including through increasing capacity to implement and administer sanctions measures (GAC, CBSA) $22.2M over five years and $4.3M ongoing (Budget 2018) | Strengthen Canada's sanctions regime, including the development of sanctions policy, coordination with international partners, and provision of guidance to Canadians on sanctions obligations |
| Monitoring of real estate purchases and federal data needs assessment (Statistics Canada) $1M over two years (Budget 2019) |
Facilitate streamlining of data sharing between federal and provincial governments relating to AML, tax compliance, and mortgage fraud |
| Automation of cross-border currency reporting (CBSA) $6.9M over five years, $0.4M ongoing (July 2020 Economic and Fiscal Snapshot) |
Enhanced information transmission between federal partners to improve financial intelligence on cross-border movements of currency and monetary instruments |
| Funding for action against money laundering and terrorist financing (FINTRAC) $4.6M over four years, $0.6M ongoing (Budget 2021) |
Enable FINTRAC to build its expertise related to virtual currency; supervise the armoured car sector; and develop and administer a cost recovery scheme for its compliance activities |
| Beneficial ownership transparency (ISED) $2.1M over two years (Budget 2021, and 2022) |
Support the implementation of a publicly accessible corporate beneficial ownership registry by end of 2023 |
| Other Policy and Coordination Initiatives | |
| Working group with Federation of Law Societies of Canada (FLSC) | Better understand and help address risks in the legal profession, as well as facilitate the exchange of information and best practices |
| British Columbia-Canada Ad-Hoc Working Group on Money Laundering in Real Estate | Understand and address money laundering risks in British Columbia's real estate sector |
| Federal-Provincial-Territorial Working Group on Beneficial Ownership Transparency | Coordinate measures across jurisdictions for consistent and stronger corporate transparency measures |
| Public-Private Collaboration Steering Committee | Coordinate efforts to improve efficiency and effectiveness within existing legislative authorities through enhancements in private-private and private-public information sharing and by leveraging technology |
| Counter Illicit Finance Initiative | Establish a permanent, national public-private partnership model to achieve better enforcement outcomes |
| Illicit Income Audit Program (CRA) | Disrupt the financial flows related to organized crime and other illicit activity, through powers to obtain non-conviction based forfeitures for tax liabilities stemming from illicit enterprise |
ANNEX D: Measuring the Performance of the Canadian AML/ATF Regime
Regular measurement of the Regime's outputs, using key performance indicators, is crucial for understanding whether it is meeting its expected outcomes, while supporting accountability and strategic decision-making.
In 2023, the Department of Finance published a report to present the latest results for key performance indicators captured under the Regime's new Performance Measurement Framework up to the 2019-20 fiscal year. The 2019-20 Performance Measurement Framework Report also identifies significant long-term trends, while discussing contributing factors and their relationship to expected results.
The focus on key performance information and trends reflects a decision by Deputy Ministers to target the core compliance, intelligence, and enforcement activities most central to the Regime. For all indicators, up to ten years of data are used where available. Results are grouped based on the core "pillars" of the Regime: i) policy and coordination, ii) prevention and detection, and iii) investigation and disruption.
The logic model, shown below, visually articulates how the inputs contributed by each partner to their respective activities and outputs contribute to Regime-wide outcomes (short and longer-term).
Canada's Anti-Money Laundering and Anti-Terrorist Financing Regime Logic Model
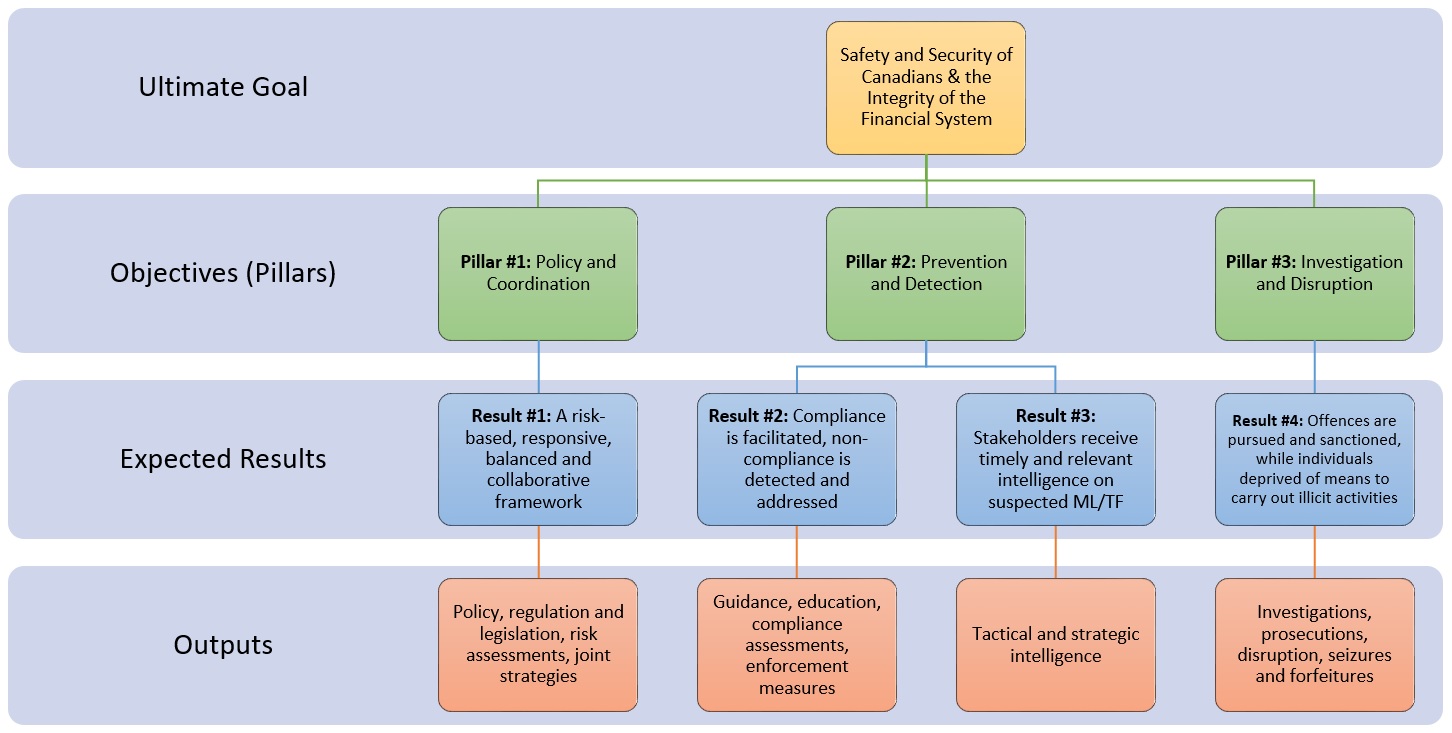
Hyperlink References
Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering. (n.d.). About APG.
Caribbean Financial Action Task Force. (n.d.). CFATF Overview.
Financial Action Task Force. (n.d.). Who we are.
Government of Canada. (n.d.). Security capacity-building programs.
