Substance Identity
This report assesses the long-chain (C9-C20) perfluorocarboxylic acids (PFCAs), their salts and their precursors. The long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs were grouped and assessed due to greater concerns over the bioaccumulation potential and concentrations of long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs in the environment and in non-human biota. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA or C8) has been assessed separately.
“Perfluorinated” refers to fluorochemicals in which the hydrogen atoms directly attached to the carbon atoms are all replaced with fluorine atoms. Perfluorocarboxylic acids and their salts are a homologous series of substances with the molecular formula of CnF2n+1CO2H (where 8=n=20).
Long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs are not on the Domestic Substances List (DSL) and were not subject to the categorization provisions of Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (Canada 1999). However, some of the 90 identified precursors are present on the DSL and were subject to categorization. This assessment considers any precursor to long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs which could transform or degrade to a C9–C20 PFCA given similar use applications and similarties in their physical-chemical properties and structures. This assessment defines precursors as any substance where the perfluorinated alkyl moiety has the formula CnF2n+1 (where 8=n=20) and is directly bonded to any chemical moiety other than a fluorine, chlorine or bromine atom.While the assessment did not consider the potential additive effects of long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs and their precursors and their salts, it is recognized that the precursors and salts may contribute to the total presence of long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs in the environment The expression, C#, is used to define the carbon chain length of the perfluorocarboxylic acid in question, e.g., C9 is a nine carbon PFCA.
Environment Canada considered some 90 perfuoroalkyl compounds as being long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs, their salts and their precursors (Appendix II: Long-chain PFCA Precursor Identification). The long-chain (C9-C20) PFCA grouping was defined using expert judgment, chemical structures and the biodegradation estimation modelling, CATABOL (Mekenyan et al. 2002). Using these approaches, structures were analyzed for their potential to degrade to long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs. CATABOL was trained on the basis of MITI (Ministry of International Trade and Industry, Japan) biodegradation test results and predicts biodegradation over a period of 28 days. It is acknowledged that due to the very limited perfluorinated degradation data in the training set, some degradation products generated by CATABOL may be of limited reliability or relevance in the environment. It should be noted that, for perfluorinated chemistry, the degradation process will be longer but it is difficult to estimate how much longer, especially for high-molecular-weight substances such as oligomers and polymers. The list in Appendix I provides examples of substances in this group and is not considered exhaustive.
In 2000, an industry survey by Environment Canada under the authority of section 71 of Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (Canada 1999) identified a total of 256 perfluorinated alkyl compounds in commerce in Canada for the calendar years 1997, 1998, 1999 and 2000 (Environment Canada 2001). The long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs were not reported to be manufactured or imported in Canada; however, of the approximately 90 identified precursors, several were imported into Canada. The 2004 industry survey of perfluoroalkyl and fluoroalkyl substances (Environment Canada 2005) also found that no long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs were reported to be manufactured in, or imported into, Canada. However, a number of precursors to long-chain (C9-C20) PFCAs were reported to be imported into Canada.
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has prepared a document entitled, Preliminary Lists of PFOS, PFAS, PFOA and Related Compounds that may Degrade to PFCA (OECD2007), which combined information from various member countries, including Canada, to assist the OECD in its risk management activities for perfluorinated compounds. The OECD has gathered a preliminary list of approximately 850 known perfluorinated substances. The majority of the substances on the list can potentially break down to PFCAs. Fluoropolymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene were considered stable and thus not included as a PFCA precursor in the OECD list. Certain PFCAs are used as processing aids in the production of fluoropolymers, and very low concentrations of PFCAs may be present in the finished products, but PFCA is not incorporated into the polymer structure. The long-chain PFCA precursors identified in this assessment can also be found on this OECD list.
Table 1. Substance Identity of C9-C20 Long-chain Perfluorocarboxylic Acids
| Chemical Abstracts Index name | Acronym | Molecular formula | Structural formula | Chemical Abstracts Service Registry Number | Synonyms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonanoic acid, hepta-decafluoro- (C9 PFCA) | PFNA | C9 H F17 O2 |  |
375-95-1 (NDSL) | C 1800; Hepta-deca-fluoro-nonanoic acid; Perfluo-rono-nanoic acid; Perflu-oropelar-gonic acid |
| Decanoic acid, nona-decafluoro- (C10 PFCA) | PFDA | C10 H F19 O2 | 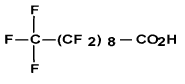 |
335-76-2 (NDSL) | Nona-deca-fluoro-n-decanoic acid; Nona-deca-fluoro-decanoic acid; Perfluoro-n-decanoic acid; Perflu-oroca-pric acid; Perfluo-rodeca-noic acid |
| Undecanoic acid, henei-cosafluoro- (C11 PFCA) | PFUnDA | C11 H F21 O2 | 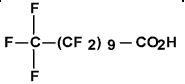 |
2058-94-8 (not listed onNDSL orDSL) | Henei-cosafluoro-undeca-noic acid; Perfluo-rounde-canoic acid; Perfluo-rounde-cylic acid |
| Dodeca-noic acid, trico-safluoro- (C12 PFCA) | PFDoDA | C12 H F23 O2 | 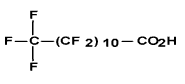 |
307-55-1 (NDSL1) | Perfluo-rodo-decanoic acid; Perfluo-rolauric acid |
| Trideca-noic acid, penta-cosafluoro- (C13 PFCA) | PFTrDA | C13 H F25 O2 | 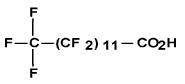 |
72629-94-8 (not listed onNDSL orDSL) | Perfluo-rotri-decanoic acid |
| Tetra-decanoic acid, hepta-cosafluoro- (C14 PFCA) | PFTDA | C14 H F27 O2 | 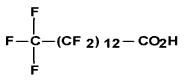 |
376-06-7 (NDSL) | Perfluo-romy-ristic acid; Perfluo-rotetra-decanoic acid |
| Pentadecanoic acid, nonacosafluoro- (C15 PFCA) | PFPeDA | C15H F29O2 | 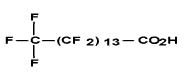 |
141074-63-7 (not listed on NDSL orDSL) | Perfluo-ropenta-decanoic acid |
| Hexa-decanoic acid, hentria-contafluoro- (C16 PFCA) | PFHxDA | C16HF31O2 | 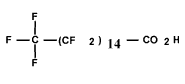 |
67905-19-5 (NDSL) | Perfluo-ropal-mitic acid, perfluo-rohexa-decanoic acid Hexa-decanoic acid |
| Perfluoro-hepta-decanoic acid (C17 PFCA) | PFHpDA | C17HF33O2 | 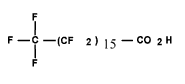 |
57475-95-3 (not listed on the NDSL orDSL) | _ |
| Octa-decanoic acid, penta-triaconta-fluoro- (C18 PFCA) | PFODA | C18HF35O2 | 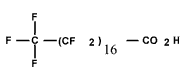 |
16517-11-6 (NDSL) | Perfluo-rostearic acid Perfluo-roocta-decanoic acid Octa-decanoic acid |
| Perfluoro-nona-decanoic acid (C19 PFCA) | PFNDA | C19HF37O2 | 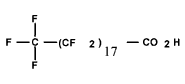 |
133921-38-7 (not listed on NDSL orDSL) | _ |
| Perfluoro-eico-sanoic acid (C20 PFCA) | C20HF39O2 | 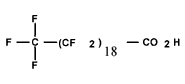 |
68310-12-3 (NDSL) | Eico-sanoic acid, nona-triacon-tafluoro- (9CI); Nona-triacon-tafluoro-eicos-anoic acid |