Determination of volatile acidity of wine, cider and champagne cider

Download the alternative format
(PDF format, 91.8 KB, 5 pages)
Organization: Health Canada
Published: 1981-10-15
Official method FO-2
October 15, 1981
Health Protection Branch
Ottawa
1. Application
This method shall be used for the determination of the per cent weight by volume of volatile acidity, calculated as acetic acid, in wine under Section B.02.101 of the Food and Drug Regulations and in cider or champagne cider under Section B.02.123 of the Food and Drug Regulations.
2. Principle
The volatile acids are distilled and determined by titration.
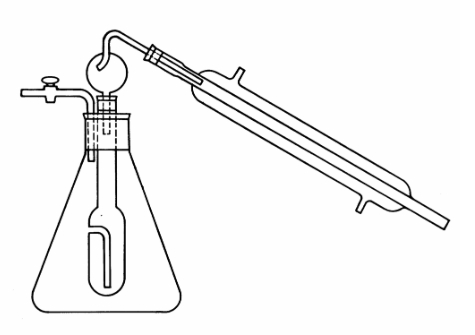
3. Apparatus
- Modified Hortvet distillation apparatus. See Figure 1 Footnote 1.
- Buret, 10 mL size, graduated in 0.02 mL.
- Erlenmeyer flask, 300 mL size, marked at approximately 80 mL.
- Water aspirator.
- Magnetic stirrer.
4. Reagents
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) 0.1 N.
- standardize as described in a recognized text such as that given in reference 2.
- Ethanol, 95%.
- Phenolphthalein solution, 1% w/v in 95% ethanol.
5. Procedure
The test shall be carried out in accordance with the following instructions:
1. Preparation of sample (2)
- place approximately 50 mL of sample under low vacuum (water aspirator) and continuously stir for 2 min to remove dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2) Footnote 2.
2. Distillation
- place 10 mL aliquot of CO2 free sample in inner tube of distillation apparatus;
- add 150 mL of recently boiled distilled water (H2O) in outer flask;
- assemble apparatus as shown in figure 1;
- start flow of cold H2O through condenser;
- heat outer flask and collect 80 mL of distillate in the Erlenmeyer flask Footnote 3.
3. Determination of acid content
- add a few drops of phenolphthalein solution to the distillate;
- titrate with 0.1 N NaOH until pink colour persists for fifteen seconds;
- record mL of 0.1N NaOH used for titration;
6. Calculations
- Calculate g of acetic acid in the aliquot using the factor that one mL of 0.1 N NaOH equals 0.0060 g of acetic acid.
- Report as per cent weight by volume of acetic acid per 100 mL of sample.
7. Notes
- Footnote 1
-
Use approximately 1 ½ x 8" inner Sellier tube and a large distillation trap.
- Footnote 2
-
Alternately place approximately 50 mL of sample in an Erlenmeyer flask, heat to incipient boiling under an air condenser and cool immediately.
- Footnote 3
-
Distill at such a rate as to obtain the 80 mL in approximately 10 minutes.
8. Reference
- Footnote 1
-
Official Methods of Analysis, Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, D.C. Ninth Edition, P. 143, 1960.
- Footnote 2
-
Official Methods of Analysis, Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, D.C. Thirteenth Edition, P. 188, 1980.
The method described above, being comprised of four pages, Figure 1 being comprised of one page, and identified as FO-2, Determination of volatile acidity of wine, cider and champagne cider and dated October 15, 1981, is hereby designated the "Official Method" for the purposes of Sections B.02.101 and B.02.123 of the Food and Drug Regulations.