IRCC Anti-Racism Strategy 2.0 (2021-2024) – Governance and accountability
The Strategy, through the activities, pillars and timelines of the Action Plan (Annex B) and the mechanisms of measurement and reporting in the Anti-Racism Accountability and Transparency Framework (Annex C), proposes priorities and milestones, linking up key stakeholders to a multi-year path forward. The inventory of Anti-Racism work outlined in the Strategy has started to generate outputs within the first year of its implementation. More immediate and intermediate outcomes are slated to be completed by the indicated timeframes. The growing momentum of the projects and results thus far are in alignment with government and IRCC senior management priorities that have been emphasizing a renewed sense of urgency since 2020 for proactive Anti-Racism actions. These are supported by the increasing vitality of conversations and grassroots activity that employees are leading. At the same time, to convey a “through line” of the views expressed at the engagement sessions with IRCC employees, there is a clear need to dedicate the requisite resources and formalize more effective governance structures to ensure progress toward transformative change.
Digital Platform Modernization and Anti-Racism Governance
As the Department drives the digital transformation of its core IT infrastructure toward the final implementation phase of Digital Platform Modernization (DPM) in 2021-2026, the vision of DPM for a data-driven and effective integration of policy development, program design and service delivery, brings significant challenges and opportunities for our Anti-Racism Strategy. DPM’s objective to achieve a rapid and responsive managed migration system through greater automation, increased use of advanced analytics and AI solutions will carry the risk of replicating human decisions that are shaped by unconscious bias and racism, and reinforcing existing systemic racism in our policies and programs. At the same time, client-centricity of DPM will allow for accessible client experience, creating opportunities for ‘equity by design’ in policy/program development and safeguards against unintended bias in service delivery by allowing timely and accurate tracking of the application process by the clients.
Closer alignment between the governance processes of DPM and the Anti-Racism Strategy will ensure proactive prevention of racial bias and utilize the benefits of automated decision making. Responsible use of advanced analytics and AI will require formal rules documentation and robust governance that are attuned to fairness, accessibility, transparency and an effective tool-box for ultimately eliminating disparities in client outcomes. In this sense, DPM offers an opportunity to embed equity principles to the redesign of programs and operational processes to reduce racism as we rebuild.
A strategic governance approach that connects the short-term priorities and long-term objectives to the drivers of initiatives will help ensure that the departmental Anti-Racism actions move beyond reactive modes and crystallize into durable results. This will help set the course for transforming workplace practices, policy and program development and service delivery across the sectors and the whole organization. To highlight the key assumptions, rationale and guiding direction of the governance approach, we are aiming for:
- An inclusive and coherent governance structure to clarify the role of key contributors and drivers of Anti-Racism initiatives for long-term stability and effective management of departmental risks and resources;
- Ongoing assessments of best practices and lessons learned, as part of the maturation of Anti-Racism governance, for effective alignment of bottom-up, middle and top-down initiatives, collaboration within IRCC and with other government departments and agencies.
Governance of Anti-Racism Actions at IRCC
The governance of Anti-Racism actions will adopt a whole-of-IRCC approach to encompass decision-making and horizontal collaboration. As the Strategy matures through future iterations, the governance structure will be equipped with more tools and enhanced levers at our disposal for success.
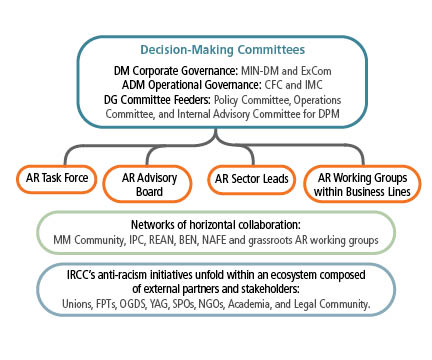
Text version of Figure A: Governance of Anti-Racism Actions at IRCC
- Decision-Making Committees
- DM Corporate Governance: MIN-DM and ExCom
- ADM Operational Governance: CFC and IMC
- DG Committee Feeders: Policy Committee, Operations Committee, and Internal Advisory Committee for DPM
- The Decision-Making Committees feed into the
- AR Task Force
- AR Advisor Board
- AR Sector Leads
- AR Working Groups within business lines
- Networks of horizontal collaboration:
- MM Community
- IPC
- REAN
- BEN
- NAFE
- Grassroots AR working groups
- IRCC’s Anti-Racism initiatives unfold within an ecosystem composed of external partners and stakeholders:
- Unions
- FPTs
- OGDs
- YAG
- SPOs
- NGOs
- Academia
- Legal Community
Figure A presents a visual description of the current approach to Anti-Racism governance within the Department and the ecosystem of external partners and stakeholders to provide an overview of the committees, units, groups and networks according to their location in the governance and the broader ecosystem of Anti-Racism initiatives:
Departmental decision-making
- DM Corporate governance level – Minister-Deputy Minister Committee (MIN-DM) and Executive Committee (ExCom);
- ADM Operational Governance – Issues and Management Committee (IMC) and Corporate and Finance Committee (CFC);
- DG Committee Feeders – Policy Committee and Operations Committee, and Internal Advisory Committee (DG-IAC) for Digital Platform Modernization (DPM).
Director level and working level committees and units
- The Anti-Racism Task Force (ARTF) provides advice, plans and coordinates activities among sectors to strengthen consistency. ARTF is a member of the ExCom, provides regular updates to decision-making committees, and leads the Strategy’s review. The immediate consultation and collaboration partners of the Task Force include the Anti-Racism Advisory Board, Sector Leads, HR, sector and branch teams leading the Anti-Racism initiatives, networks and champions. ARTF also consults with central agencies and the Anti-Racism secretariats or task forces of other government departments, experts in academia and civil society. At the end of a 3-year period, the Task Force will conduct an assessment of the Strategy to inform the way forward in alignment with the vision.
- The Anti-Racism Advisory Board, Sector Leads and the working groups within business lines serve as the primary agents of organization and coordination within the sectors. For Anti-Racism engagements regarding people management matters, Middle Managers Advisory Committee, People Management Governance Committees and joint labour-management and union committees (e.g. National Labour Management Consultation Committee; Inclusion, Diversity and Employment Equity Sub-Committee) are key venues. The ARTF and Sector Leads are supported by the Communications Branch in their broader engagement and promotion activities within the Department and with external partners, stakeholders and the public.
- IRCC sectors, branches and business lines take the lead for their stakeholder engagements and for driving Anti-Racism initiatives within their respective areas of responsibility. Sectors draw support from their respective Anti-Racism and equity expertise to leverage their initiatives. These include but are not limited to
- Settlement and Integration Sector – ADMO (Special Initiatives);
- Operations Sector – ADMO (Operations and Strategic Initiatives and Projects, OSIP); Integrity and Risk Management Branch (Operations Sector Integrity Management Authority, OSIMA); Operational Planning and Performance Branch;
- Strategic and Program Policy Sector – Strategic Policy and Planning Branch (Equity Policy and GBA Plus Unit).
Departmental networks of horizontal collaboration
- Diverse networks have the mandate to build awareness on racism and effect culture change in the Department. These include Middle Managers Community (MM Community), the Indigenous Peoples Circle (IPC), Racialized Employees and Allies Network (REAN), Black Employees Network (BEN), Latin American Employees Network, Jewish Public Servants Network, Network of Asian Federal Employees (NAFE), Muslim Federal Employees Network (MFEN) and grassroots Anti-Racism working groups.
Ecosystem of organizations external to IRCC leading diverse Anti-Racism initiatives
- Engagement with external partners and stakeholders provide key input for the direction of departmental Anti-Racism initiatives. Some of the organizations that help shape departmental actions within this broader context include: Unions; Federal, Provincial and Territorial governments (FPT); other federal government organizations (OGDs); Youth Advisory Group (YAG); Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs), Service Provider Organizations (SPOs); Academia; and Legal community.