Personal Importation of certain drugs for food-producing animals
We are restricting personal importation (also known as own use importation) of veterinary drugs for food-producing animals or animals intended to be consumed as food (including horses). These restrictions are put in place to help protect public health and the safety of our food supply.
On this page
- Changes to the rules
- Who these rules apply to
- Criteria for adding a drug to List B
- How to request a drug be added to List B
- How to import a drug for food-producing animals
- Food safety and comparable Canadian drugs
Changes to the rules
The restrictions on importation for personal use began when the regulations came into effect on November 13, 2017.
Under these rules no person can import a drug for use in food-producing animals or animals intended to be consumed as food (including horses) unless authorized by Health Canada.
This means that the drug that is not authorized for sale in Canada can only be imported for personal use if it is on List B: List of Certain Veterinary Drugs Which May Be Imported But Not Sold. Health Canada considers that drugs on List B do not compromise public health or food safety.
As with the personal importation of any health product, drugs on List B may be imported in quantities that are less than a 90-day supply for use in food-producing animals (including horses), based on the directions for use.
Once they are imported into Canada, the drugs cannot be sold, given to someone else or distributed for free.
Who these rules apply to
These rules apply to anyone importing drugs for food-producing animals or for animals intended to be consumed as food (including horses).
Criteria for adding a drug to List B
Health Canada considers specific criteria before adding a drug to List B:
-
The drug cannot be prescription status for veterinary use in Canada
Drugs requiring a prescription for veterinary use in Canada are not eligible to be included on List B.
Pesticides and vaccines are not drugs. For more information on the importation of pesticides and vaccines, please visit:
- For pesticides: The Grower Requested Own Use Program
- For vaccines: Importation of Veterinary Biologics - Overview
-
The drug is in final dosage form and within commercial packaging
Drugs on List B are in their finished form. Active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) are not eligible to be included on List B.
-
The drug is not a medicated premix
Drugs that are intended to be mixed in animal feed are not eligible to be included on List B.
-
The drug is not a medically important antimicrobial on List A
Drugs on List B are those that do not contain a medically important antimicrobial found on List A: List of Certain Antimicrobial Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients.
-
The drug is approved by a recognized foreign regulator
Drugs on List B are approved for sale in another country by a regulatory authority that we have experience working with. The foreign regulator also:
- Has a similar veterinary drug regulatory regime, evaluation and approval requirements and procedures as Canada
- Participates in and actively contributes to international standard-setting activities such as the United States Food and Drug Administration, Centre for Veterinary Medicine (FDA-CVM)
-
The drug has established Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs) in Canada
Drugs on List B have established MRLs in Canada for the drug ingredients and the species in which it will be used, or we have determined that no MRL is required. Refer to the List of MRLs for Veterinary Drugs in Foods.
-
There is a comparable drug approved in Canada with a Drug Identification Number (DIN)
Drugs on List B have similar directions for use to a drug approved in Canada.
-
There are no unresolved safety issues with the drug or the comparable Canadian drug
Drugs on List B or their comparable Canadian drugs do not have issues regarding safety or quality. For more information about recalls and alerts of health products, visit the Recalls and safety alerts web page.
How to request a drug be added to List B
If you want to import a drug that is not already on List B, a request must be submitted to Health Canada.
To help you submit a request to add a drug to List B we recommend that you contact:
- your producer association to make a request on your behalf or
- us to get a copy of the Request Form to add a drug to List B:
- telephone: 613-941-8845
- email: hc.vdd.HSD-DIH.dmv.sc@canada.ca
How to import a drug for food-producing animals
To import a drug for your food-producing animal(s), look for the drug as described on List B: List of Certain Veterinary Drugs Which May be Imported but Not Sold.
To make sure you meet the rules, at the border we check to see if the drug is on List B and that it is being brought in for treating the appropriate species.
The drug also has to be less than a 90-day supply based on the number of animals to be treated under your care and the drug's directions for use.
A lack of information can result in refusal of your shipment entering Canada.
Food safety and comparable Canadian drugs
Canada's food safety standards are the same for imported and domestic food products. We:
- conduct comprehensive scientific reviews of veterinary drugs before they are approved for sale in Canada
- set standards such as maximum residue limits (MRLs) in the tissues and food products derived from such food-producing animals
That is why it is important that you follow the label of the comparable Canadian drug including:
- all Directions for Use
- all Warnings, including the Withdrawal and Withholding Periods
For imported drugs on List B, the MRLs established by Health Canada for the comparable Canadian drug apply.
To find the comparable Canadian drug, go to the Drug Product Database and follow these tips:
-
Under Status, click on Select All
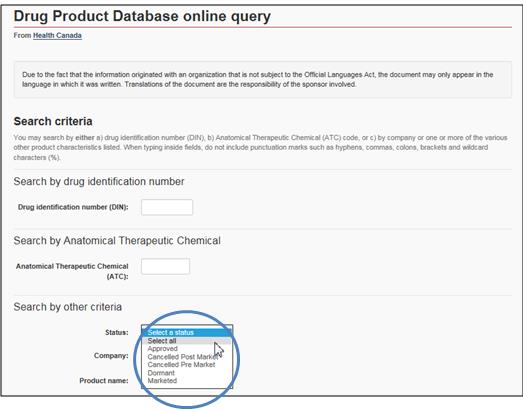
Text Equivalent
The figure presents a screen shot of the Drug Product Database online query with the 3 areas of search criteria by identification number, anatomical therapeutic chemical, and other criteria. The Status field is circled in blue.
-
Enter the same active or medicinal ingredient as the one indicated on the label of the drug you imported
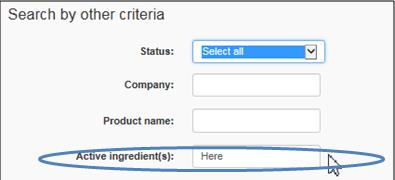
Text Equivalent
The figure presents a screen shot of 1 of the 3 areas of search criteria, i.e.,search by other criteria. In the field Status, Select All is highlighted in blue. The Active ingredient(s) field is circled in blue.
-
Under Class(es), click on Veterinary
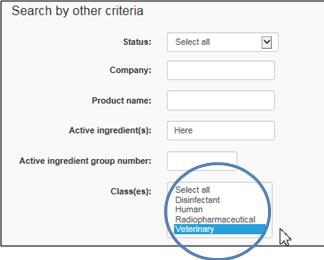
Text Equivalent
The figure presents a screen shot of 1 of the 3 areas of search criteria, i.e.,search by other criteria. The Class(es) field is circled in blue.
-
Under Route(s) of administration, select the same route of administration as indicated on the label of the drug you imported, such as oral
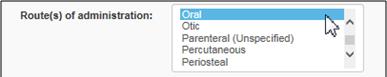
Text Equivalent
The figure presents a screen shot of the field: Route(s) of administration. The selection Oral is highlighted in blue.
-
Under Dosage form(s), select the same dosage form as indicated for the drug you imported, such as bolus, and hit the Search button
Text Equivalent
The figure presents a screen shot of the field: Dosage form(s). The selection Bolus is highlighted in blue.
-
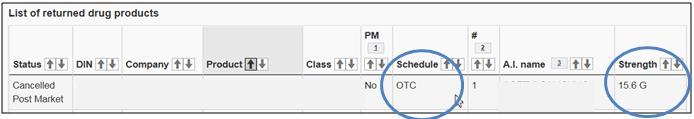
Select a comparable Canadian product for which the schedule is "OTC" (non-prescription) and that has the same strength.
Text Equivalent
The figure presents a screen shot of 1 entry of the List of returned drug products. The Schedule, i.e., OTC, and the Strength, i.e., 15.6 G, are circled in blue.
If you have any difficulties finding the comparable Canadian drug, you can contact us by
- telephone: 613-941-8845
- email: hc.vdd.HSD-DIH.dmv.sc@canada.ca