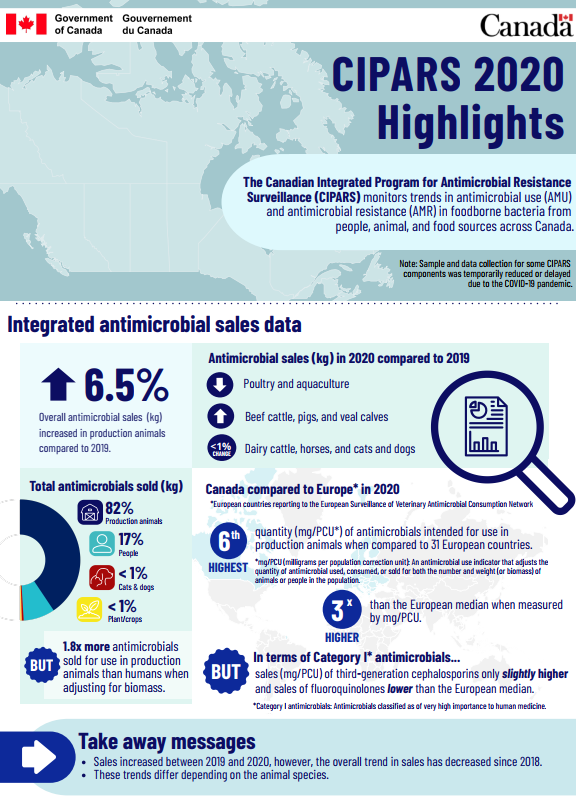
CIPARS 2020 Highlights
Download in PDF format
(825 KB, 1 page)
Organization: Public Health Agency of Canada
Published: 2022-09-06
The Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS) monitors trends in antimicrobial use (AMU) and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in foodborne bacteria from people, animal, and food sources across Canada.Footnote 1
Integrated antimicrobial sales data
The overall antimicrobial sales (kg) increased by 6.5% in production animals compared to 2019.
Antimicrobial sales (kg) in 2020 compared to 2019:
- Has decreased in poultry and aquaculture.
- Has increased in beef cattle, pigs, and veal calves.
- Stayed the same (less than 1% change) in dairy cattle, horses, and cats and dogs.
Total antimicrobials sold (kg):
- 82% for production animals.
- 17% of people.
- Less than 1% for cats and dogs.
- Less than 1% for plant and crops.
But, there was 1.8 times more antimicrobials sold for use in production animals than humans when adjusting for biomass.
Canada compared to EuropeFootnote 2 in 2020:
- Canada was the 6th highest in terms of quantity (mg/PCUFootnote 3) of antimicrobials intended for use in production animals when compared to 31 European countries.
- Canada was 3 times higher than the European median when measured by mg/PCU.
- But, in terms of Category I antimicrobialsFootnote 4, the sales (mg/PCU) of third-generation cephalosporins were only slightly higher and sales of fluoroquinolones were lower than the European median.
Take away messages:
- Sales increased between 2019 and 2020, however, the overall trend in sales has decreased since 2018.
- These trends differ depending on the animal species.
Integrated farm AMU and AMR data from sentinel volunteer farms
Overall reported antimicrobial use decreased in poultry and pigs since 2016 (total nDDDvetCA/1,000 animal-days at riskFootnote 5).
Spotlight on the sentinel farm surveillance of AMU and resistance in E. coli in broiler chickens, grower-finisher pigs, and turkeys from 2016 to 2020:
- There was a decrease in resistance in bacteria from samples from the same sentinel farms (using resistance to 3 classes of antimicrobials or more for E. coli as the indicator).
- There was a decrease in reported antimicrobial use on sentinel farms.
To note:
- These trends coincided with the implementation of veterinary drug regulatory changes and policy interventions by Health Canada in 2017 and in 2018 such as the medically important antimicrobials available by prescription only and the removal of growth promotion claims from all medically important antimicrobials.
- Changes have been made to reduce the use of medically important antimicrobials, including:
- Sector-specific initiatives to eliminate the preventive use of third generation cephalosporins (and other antimicrobial classes in some cases).
- Federal initiatives to update product labelling and improve access to antimicrobial alternatives.
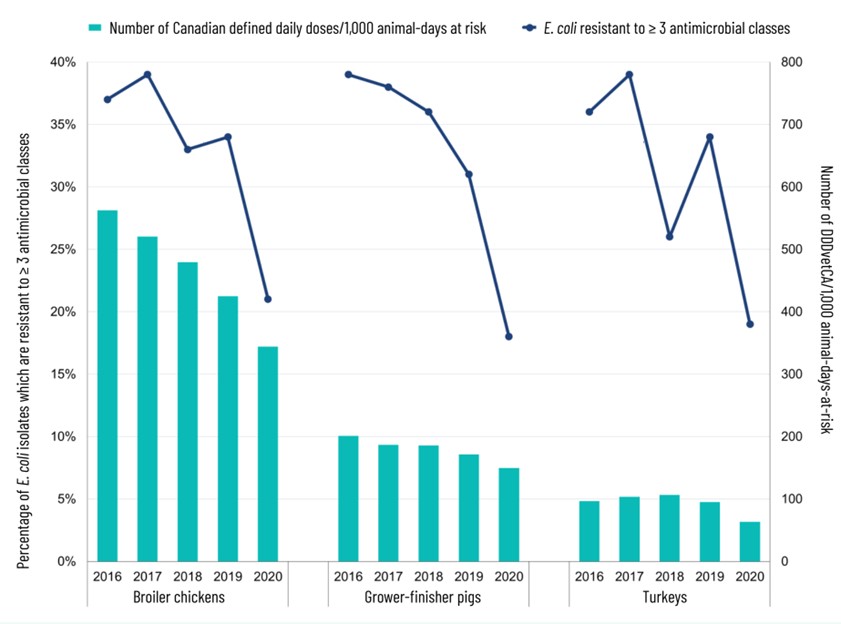
Figure 1 - Text description
| N/A | Broiler chickens | Grower-finisher pigs | Turkeys | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| E. coli resistant to 3 classes of antimicrobials or more | 37.0% | 39.0% | 33.0% | 34.0% | 21.0% | 39.0% | 38.0% | 36.0% | 31.0% | 18.0% | 36.0% | 39.0% | 26.0% | 34.0% | 19.0% |
| Number of Canadian defined daily doses/1,000 animal-days at risk | 562.52 | 520.64 | 479.2 | 424.66 | 343.91 | 200.93 | 186.92 | 185.85 | 171.14 | 149.65 | 96.67 | 103.34 | 106.6 | 95.22 | 63.33 |
Resistance to Category I antimicrobials (2020 compared to 2019):
- Ceftriaxone resistance in Salmonella decreased in pigs and broiler chickens.
- Ceftriaxone resistance in E. coli decreased in broiler chickens.
- Ciprofloxacin resistance in Salmonella decreased in turkeys.
- Nalidixic acid resistance in Salmonella decreased in turkeys but increased in broiler chickens.
- Ciprofloxacin resistance in Campylobacter decreased in turkeys but increased in broiler chickens.
Take away message:
Decreasing trends in antimicrobial use was accompanied by a decrease in multi-class resistance and resistance to Category I antimicrobials in most cases on broiler chickens, grower-finisher pigs, and turkey sentinel farms from 2016 to 2020.
Antimicrobial resistance
Healthy cattle at feedlot and abattoir:
Campylobacter:
- Resistance to ciprofloxacin from healthy feedlot cattle has increased since 2017 to 29%.
- Resistance to ciprofloxacin from healthy cattle at abattoir has increased since 2016.
Salmonella:
- Small number of resistant S. Heidelberg detected for the first time on Alberta feedlots in 2019, but none were found in 2020.
- Salmonella was only recovered from cattle on Ontario feed lots (15 isolates) in 2020, of which resistance was only to Category III antimicrobialsFootnote 6 in:
- 8 isolates of Salmonella Uganda.
- 5 isolates of Salmonella Muenchen.
Colistin resistance:
There is global concern for transmissible colistin resistance, therefore CIPARS conducts routine surveillance in production animals.
Detection of isolates phenotypically resistant to colistin in 2020:
- 1 isolate of both Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Kiambu detected from caecal contents from healthy chickens at slaughter.
- 1 isolate of E. coli detected from a sample collected from a healthy grower-finisher pig on-farm.
- 1 isolate of E. coli detected from ground beef at retail.
But, none of the isolates had transmissible colistin resistance.
Take away messages:
- Given the threat of transmissible colistin resistance, CIPARS will continue to monitor for colistin resistance and contextualize findings when detected.
- Information from CIPARS supports measures to contain the emergence and spread of resistant bacteria between animals, food, and people, with the aim of preserving the effectiveness of antimicrobials.
For more information, visit our surveillance reports webpage.
- Footnote 1
-
Sample and data collection for some CIPARS components was temporarily reduced or delayed due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Footnote 2
-
European countries reporting to the European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption Network.
- Footnote 3
-
mg/PCU (milligrams per population correction unit): An antimicrobial use indicator that adjusts the quantity of antimicrobial used, consumed, or sold for both the number and weight (or biomass) of animals or people in the population.
- Footnote 4
-
Category I antimicrobials: Antimicrobials classified as of very high importance to human medicine.
- Footnote 5
-
nDDDvetCA/1,000 animal-days at risk (number of defined daily doses in per 1,000 animal-days-at-risk): An antimicrobial use indicator that accounts for the average labelled drug dose, the time at risk of exposure to antimicrobials, and the number and weight (or biomass) of animals in the population.
- Footnote 6
-
Category III antimicrobials: antimicrobials classified as of medium importance to human medicine.