Human emerging respiratory pathogens bulletin: Issue 46, October 2020

Download the alternative format
(PDF format, 1.0 MB, 2 pages)
Organization: Public Health Agency of Canada
Date published: 2020-11-10
Monthly situational analysis of emerging respiratory diseases affecting humans (data to October 31, 2020)
In this bulletin
- COVID-2019 update
- Avian influenza updates
- Swine influenza updates
- Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) update
| Novel influenzaTable 1 Footnote 1 | Cumulative Case CountTable 1 Footnote 2 | Deaths | Case Fatality Rate %Table 1 Footnote 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A(H7N9) | 1,568 | 615 | 39% |
| A(H5N1) | 879 | 461 | 52% |
| A(H9N2) | 59 | 1 | 2% |
| A(H5N6) | 24 | 7 | 29% |
| A(H7N4) | 1 | 0 | 0% |
| A(H1N2) | 2 | 0 | 0% |
| A(H3N2)v | 436 | 1 | <1% |
| A(H1N2)v | 27 | 0 | 0% |
| A(H1N1)v | 26 | 0 | 0% |
| MERS-CoVTable 1 Footnote 1 | Cumulative Case CountTable 1 Footnote 2 | Deaths | Case Fatality Rate %Table 1 Footnote 3 |
| Global Case Count | 2,553 | 872 | 34% |
| Saudi Arabia | 2,157 | 794 | 37% |
|
|||
COVID-19 update
On December 31, 2019, cases of a pneumonia of unknown etiology were reported in Wuhan, China. These cases have since been determined to be due to a novel coronavirus called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC).
As of October 31, 2020, 234,511 COVID-19 cases and 10,136 deaths have been reported in Canada.
The Public Health Agency of Canada is monitoring the situation closely.
Avian influenza updates
Avian influenza A(H7N9)
No new H7N9 cases were reported to the WHO in October 2020. The last case was reported by China in April 2019. Two travel-related cases were reported in Canada in January 2015. A total of 1,568 human cases of avian influenza A(H7N9), including at least 615 deaths, have been reported globally since 2013 (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Temporal distribution of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9), globally, by month and year, January 1, 2013 to October 31, 2020 (n=1568).
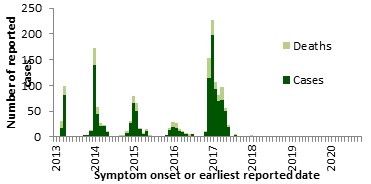
Note: Graph was prepared by the Centre for Immunization and Respiratory Infectious Diseases (CIRID) using data from the latest WHO Monthly Influenza at the Human-Animal Interface Risk Assessment. This graph reflects data available through these risk assessments as of October 31, 2020.
Figure 1 - Text Equivalent
The temporal distribution of avian influenza A(H7N9), globally, January 1st, 2013 – October 31, 2020, has been displayed in Figure 1. The highest number of reports occurred in 2017, with a peak in January. Three cases were reported in 2018 and one case was reported in 2019.
| Dates | Cases | Deaths | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Jun | 2 | 0 |
| Jul | 4 | 0 | |
| Aug | 0 | 0 | |
| Sep | 0 | 0 | |
| Oct | 2 | 0 | |
| Nov | 10 | 2 | |
| Dec | 114 | 39 | |
| 2017 | Jan | 197 | 29 |
| Feb | 93 | 13 | |
| Mar | 70 | 12 | |
| Apr | 72 | 24 | |
| May | 50 | 6 | |
| Jun | 19 | 4 | |
| Jul | 2 | 0 | |
| Aug | 3 | 2 | |
| Sep | 1 | 0 | |
| Oct | 0 | 0 | |
| Nov | 0 | 0 | |
| Dec | 1 | 0 | |
| 2018 | Jan | 1 | 1 |
| Feb | 1 | 0 | |
| Mar | 0 | 0 | |
| Apr | 0 | 0 | |
| May | 0 | 0 | |
| June | 0 | 0 | |
| July | 0 | 0 | |
| Aug | 0 | 0 | |
| Sep | 0 | 0 | |
| Oct | 0 | 0 | |
| Nov | 0 | 0 | |
| Dec | 0 | 0 | |
| 2019 | Jan | 0 | 0 |
| Feb | 0 | 0 | |
| Mar | 0 | 0 | |
| Apr | 1 | 0 | |
| May | 0 | 0 | |
| June | 0 | 0 | |
| July | 0 | 0 | |
| Aug | 0 | 0 | |
| Sept | 0 | 0 | |
| Oct | 0 | 0 | |
| Nov | 0 | 0 | |
| Dec | 0 | 0 | |
| 2020 | Jan | 0 | 0 |
| Feb | 0 | 0 | |
| Mar | 0 | 0 | |
| Apr | 0 | 0 | |
| May | 0 | 0 | |
| June | 0 | 0 | |
| July | 0 | 0 | |
| Aug | 0 | 0 | |
| Sep | 0 | 0 | |
| Oct | 0 | 0 | |
Avian influenza A(H9N2)
No new H9N2 cases were reported to WHO in October 2020. The most recent case was reported on August 28, 2020 in China. Globally, 59 human cases, including one death, have been reported since 1998.
Swine influenza updates
Swine origin influenza A(H3N2)v
The most recent case of swine origin influenza H3N2v was reported in July 2020 in the United States and this case was the first human case of A(H3N2)v reported out of the United States since 2018. A total of 436 cases, including one death, have been reported globally since 2011. One locally acquired case of H3N2v was reported in Canada in December 2016.
Swine origin influenza A(H1N2)v
On October 29, 2020, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) was notified of a confirmed human case of influenza A(H1N2) variant virus, marking the 27th influenza A(H1N2)v case reported to the WHO since 2005 and the first from Canada. The individual developed mild respiratory infection symptoms and presented to an emergency department on October 7, 2020, at which time specimen collection took place. The case was not hospitalized. Testing at the provincial laboratory identified an influenza A(H1N2)v virus of swine origin and the specimen was sent to the National Microbiology Laboratory (NML) for confirmation, viral culture, and additional genetic, antigenic, and antiviral susceptibility testing. The case was isolated at home for 10 days following onset of illness and has since recovered. One household contact had mild symptoms shortly after the case but was not tested, was isolated, and has recovered. No other household contacts reported illness prior to or following the case's illness. Most H1N2v infections result in mild illness. Based on a preliminary investigation, the case has had no known animal or sick human exposure. Epidemiologic, animal health and virological investigations are ongoing and PHAC continues to monitor the situation and provide assistance where needed.
Swine origin influenza A(H1N1)v
The most recent case of swine origin influenza A(H1N1) infection was detected in Germany in June 2020. This case presented with influenza-like illness after contact with pigs during a farm visit. To date, reported H1N1v infections have been associated with mild illness.
Figure 2. Spatial distribution of human cases of avian and swine influenza reported globally in October 2020 (n=1).
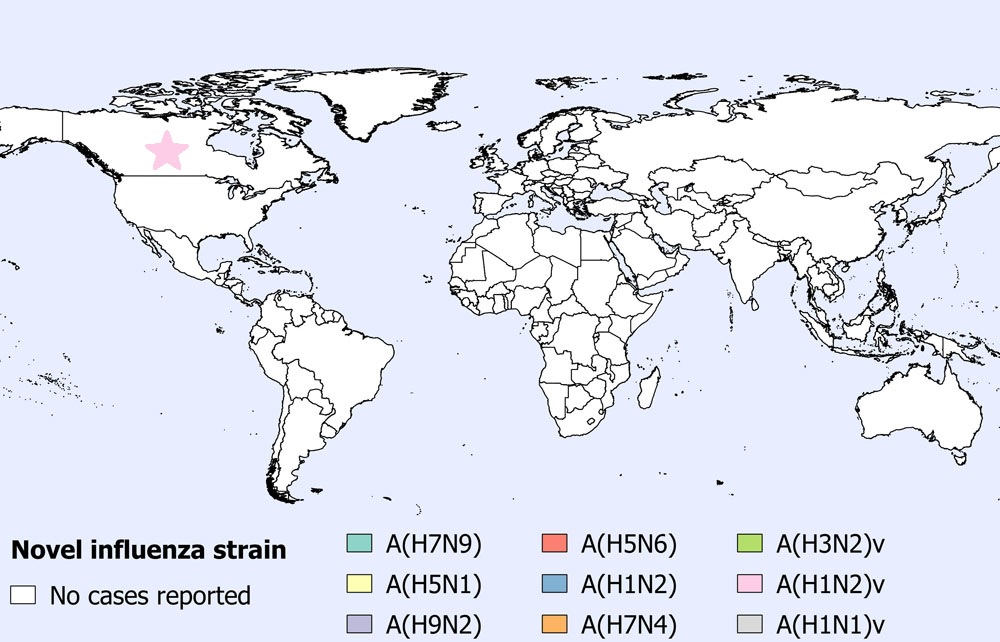
Note: Map was prepared by the Centre for Immunization and Respiratory Infectious Diseases (CIRID) using data from the latest WHO Monthly Influenza at the Human-Animal Interface Risk Assessment. This map reflects data available through these risk assessments as of October 31, 2020.
Figure 2 - Text Equivalent
The spatial distribution of avian and swine influenza human cases in October 2020 has been displayed in Figure 2.
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) update
No new cases of MERS-CoV were reported in October 2020. A total of 2,553 laboratory-confirmed cases of MERS-CoV, including 872 deaths, have been reported globally since 2012 by the WHO. No cases have been reported in Canada.
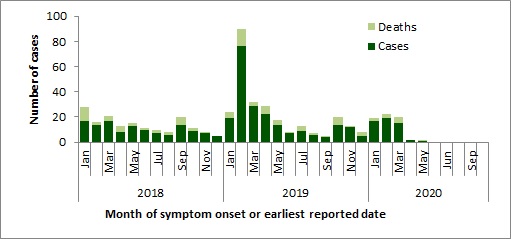
Note: Graph was prepared by the Centre for Immunization and Respiratory Infectious Diseases (CIRID) using data from the WHO Disease Outbreak News and Saudi Arabia's Ministry of Health. This graph reflects data available as of October 31, 2020.
Figure 3 - Text Equivalent
The temporal distribution of MERS-CoV, globally, January 1st, 2018–October 31, 2020, has been displayed in Figure 3.
| Dates | Cases | Deaths | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | Jan | 17 | 11 |
| Feb | 14 | 2 | |
| Mar | 17 | 4 | |
| Apr | 8 | 5 | |
| May | 13 | 2 | |
| June | 10 | 1 | |
| July | 7 | 3 | |
| Aug | 6 | 2 | |
| Sep | 14 | 6 | |
| Oct | 9 | 2 | |
| Nov | 7 | 1 | |
| Dec | 5 | 0 | |
| 2019 | Jan | 19 | 5 |
| Feb | 76 | 14 | |
| Mar | 29 | 3 | |
| Apr | 22 | 7 | |
| May | 14 | 4 | |
| June | 7 | 1 | |
| July | 9 | 4 | |
| Aug | 6 | 1 | |
| Sep | 4 | 1 | |
| Oct | 14 | 6 | |
| Nov | 15 | 2 | |
| Dec | 4 | 2 | |
| 2020 | Jan | 17 | 2 |
| Feb | 19 | 3 | |
| Mar | 15 | 5 | |
| Apr | 2 | 0 | |
| May | 1 | 1 | |
| June | 0 | 0 | |
| July | 0 | 0 | |
| Aug | 0 | 0 | |
| Sep | 0 | 0 | |
| Oct | 0 | 0 | |