Guide for the preparation of infant formula and human milk fortifier premarket submissions
2021, updated December 2025
Table of contents
- 1.0 Introduction
- 2.0 Regulatory Context
- 3.0 Administrative considerations
- 4.0 Infant formula and human milk fortifier premarket submission requirements
- 4.1 Brand and product name
- 4.2 Name and address
- 4.3 Description of the major change
- 4.4 List of all ingredients
- 4.5 Ingredient specifications
- 4.6 Quality control procedures for testing nutrients
- 4.7 Manufacturing process and quality control procedures
- 4.8 Expiration date and stability data
- 4.9 Nutritional adequacy
- 4.10 Evidence for major changes
- 4.11 Packaging
- 4.12 Directions for preparation, use and storage
- 4.13 Label text
- 4.14 Signed submission
- 4.15 Scientific rationale for new human milk fortifier or major change
- 5.0 Foreign reviews
- 6.0 References to breastmilk
- 7.0 Glossary and abbreviations
- Appendix 1. Examples of minor and major changes, per category
- Appendix 2a. Verification checklist for infant formula submissions – new
- Appendix 2b. Verification checklist for infant formula submissions – major change
- Appendix 3a. Verification checklist for human milk fortifier submissions – new
- Appendix 3b. Verification checklist for human milk fortifier submissions – major change
- Appendix 4. Flow chart for approval of a novel food or new infant food ingredient (NIFI)
- Appendix 5. Nutrient requirement template for preterm infant formula or fortifier with human milk (as fed) per 100 kcal
- Appendix 6. Suggested template for finished product specification data, infant formula
- Appendix 7. Suggested template for stability data, infant formula
1.0 Introduction
Infant formula is a substitute for human milk that is given to infants typically during the first year of life. Infant formula is sold either as a ready-to-serve liquid, a concentrate that must be diluted with water, or as a powder that is to be mixed with water before feeding infants. For some infants, infant formula is the only source of nutrition received from birth to approximately 6 months of life when other foods are typically introduced. The first 6 months are critical for infants as they undergo rapid growth and development during this period. As such, stringent safeguards must be in place to protect this vulnerable population to ensure that infant formulas are well tolerated, safe to use and promote growth and development. The term infant formula includes preterm infant formula as well as specialty infant formula, such as those which are hypoallergenic or are for inborn errors of metabolism.
Human milk fortifiers are foods whose composition includes at least added vitamin, mineral nutrient or amino acid, that are intended to be added to human milk (breast-milk) to increase its nutritional value. Human milk fortifiers are administered to certain preterm infants or other infants (e.g., infants with low birth weight) when they are medically required to meet particular nutritional requirements. Human milk fortifiers are not nutritionally adequate unless they are added to human milk.
In Canada, infant formulas and human milk fortifiers are regulated under the Food and Drugs Act (FDA) and the Food and Drug Regulations (FDR). Specifically under Division 25 of the FDR, manufacturers must submit a premarket submission prior to selling or advertising any new infant formula or human milk fortifier, or an infant formula or human milk fortifier that has undergone a major change. The premarket submission must contain detailed information on the composition and manufacturing of the infant formula or human milk fortifier and its packaging and labelling, as well as evidence to establish that the new or changed infant formula or human milk fortifier is safe and nutritionally adequate to promote acceptable growth and development in infants for whom it is intended. In cases where only minor changes are made to the existing infant formula or human milk fortifier, it is the manufacturer's responsibility to ensure that any minor change does not impact the quality or safety of the product and that a change meets the criteria of a minor change. Health Canada's Food and Nutrition Directorate does not review premarket notifications for minor changes to previously cleared infant formula and human milk fortifiers. Appendix 1 provides examples of minor changes compared to major changes. It is important to note that it is the manufacturer's responsibility to ensure their products continue to comply with all relevant regulatory requirements.
This guide is intended to assist infant formula or human milk fortifier manufacturers in preparing an infant formula or human milk fortifier premarket submission. Sections 4.6, 4.7 and 4.8 of this guide refers to Health Canada's Good Manufacturing Practices for Infant Formula (referred to as "the GMPs" in this document), which also generally apply to human milk fortifiers, which establish the general requirements for effective control of: ingredients, formulations, processes, facilities and equipment used for the production of all infant formulas and human milk fortifiers to be sold, distributed or marketed in Canada. These requirements apply regardless of whether the infant formula or human milk fortifier is manufactured in Canada or in another country whose manufacturing regulations may differ from those of Canada. The GMPs apply to new or changed infant formulas and human milk fortifiers, and to third party facilities subcontracted to manufacture or package these products.
Upon completion of a premarket review of a new infant formula or human milk fortifier submission, and if Health Canada has no further questions or objections, a letter will be issued for the sale of the infant formula or human milk fortifier in Canada.
All infant formula and human milk fortifier manufacturers are required to be licensed under the Safe Food for Canadians Act (SFCA) and Safe Food for Canadians Regulations (SFCR) to conduct activities including manufacturing, labelling, packaging, exporting, importing or sending infant formula or human milk fortifier across provincial or territorial boundaries. After obtaining your letter from Health Canada, please consult MyCFIA and the What to Consider Before Applying for a Safe Food for Canadians licence to apply for the Safe Food Canadians licence.
2.0 Regulatory Context
2.1 Regulatory definitions
The following term is defined under Section 2 of the FDA:
- Sell includes offer for sale, expose for sale, have in possession for sale, and distribute, whether or not the distribution is made for consideration.
The following term is defined under Section A.01.010 of the FDR:
- Manufacturer or distributor is a person, including an association or partnership, who under their own name, or under a trade-, design or word mark, trade name or other name, word or mark controlled by them, sells a food or drug.
The following terms are defined under Section B.25.001 of the FDR:
- Expiration date means, in respect of a human milk substitute (infant formula), the date
- (a) after which the manufacturer does not recommend that it be consumed, and
- (b) up to which it maintains its microbiological and physical stability and the nutrient content declared on the label.
- Infant is a person who is under the age of one year
- Human milk fortifier means 'a food that includes at least one added vitamin, mineral nutrient or amino acid, and is labelled or advertised as intended to be added to human milk to increase its nutritional value in order to meet the particular requirements of an infant in whom a physical or physiological condition exists as a result of a disease, disorder or abnormal physical state'.
- Human milk substitute or infant formula is any food that is represented
- (a) for use as a partial or total replacement for human milk and intended for consumption by infants, or
- (b) for use as an ingredient in a food referred to in paragraph (a).
- Major change means, in respect of an infant formula or human milk fortifier, any change of an ingredient, the amount of an ingredient or the processing or packaging of the infant formula or human milk fortifier where the manufacturer's experience or generally accepted theory would predict an adverse effect on the levels or availability of nutrients in, or the microbiological or chemical safety of, the infant formula or human milk fortifier.
- New human milk substitute is an infant formula that is
- (a) manufactured for the first time,
- (b) sold in Canada for the first time, or
- (c) manufactured by a person who manufactures it for the first time.
The following term is defined under Section B.27.001 of the FDR:
- Low-acid food means a food, other than an alcoholic beverage, where any component of the food has a pH greater than 4.6 and a water activity greater than 0.85.
2.2 Infant formula and human milk fortifier regulations in Canada
Under Sections B.25.046 and B.25.048 (for infant formula) and under Sections B.25.011 and B.25.015 (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, manufacturers are required to send a premarket submission prior to selling or advertising any new infant formula, or one that has undergone a major change. The submission must contain detailed information on:
- The composition and manufacturing of the infant formula or human milk fortifier;
- Its packaging and labelling;
- Evidence to establish that the new or changed infant formula or human milk fortifier is safe and nutritionally adequate to promote acceptable growth and development in infants for whom it is intended.
The specific requirements for a new infant formula are provided under Section B.25.046 (2), subsections (a) to (m) of the FDR, and those for an infant formula having undergone a major change can be found under Section B.25.048 (2), subsections (a) to (g), of the FDR. The specific requirements for a new human milk fortifier are provided under Section B.25.011, subsections (a) to (n), of the FDR, and those for a human milk fortifier having undergone a major change can be found under Section B.25.015 (2), subsections (a) to (g), of the FDR.
2.3 When is a premarket submission required?
A premarket submission is required for 1) any new infant formula or human milk fortifier, 2) any infant formula or human milk fortifier that has undergone a major change.
The regulatory requirements specific to infant formulas are found under Sections B.25.046 and B.25.048 and those specific to human milk fortifiers are under Sections B.25.011 and B.25.015 of the FDR.
Manufacturers are strongly encouraged to use the Verification Checklists provided in this document; Appendix 2 for infant formula submissions, and Appendix 3 for human milk fortifier submissions, to ensure all required information is included in the submission package.
Manufacturers are strongly encouraged to request a pre-submission meeting with Health Canada during preparation of a premarket submission for new infant formula or human milk fortifier or when planning a major change in formulation, packaging or processing. A pre-submission meeting request should be sent to Health Canada's Food and Nutrition Directorate Submission Management and Information Unit (SMIU) at smiu-ugdi@hc-sc.gc.ca.
2.3.1 New infant formula or human milk fortifier
Manufacturers must provide Health Canada with a premarket submission for a new infant formula or human milk fortifier or when it is, for the first time, manufactured, sold in Canada, or manufactured by a person who manufactures it.
Section B.25.046 (2), subsections (a) to (m) of the FDR specify the regulatory requirements for a new infant formula while Section B.25.011, subsections (a) to (n), specify the regulatory requirements for a new human milk fortifier.
2.3.2 Infant formula or human milk fortifier that has undergone a major change
Manufacturers must notify Health Canada prior to the sale of any infant formula or human milk fortifier that has undergone a major change in ingredient(s), packaging or manufacturing process that could be expected to cause an adverse impact on safety, on nutrient levels or nutrient availability. Examples of major changes for which a premarket submission is needed include:
- Any change in processing or packaging;
- A change of or a new manufacturing facility;
- Addition of a new macronutrient source (protein, fat, or carbohydrate);
- A substantial change in the amount of protein, fat, or carbohydrate;
- Addition of a new ingredient or novel food;
- A change in the amount or the sources of vitamins or minerals, which, in the manufacturer's experience or generally accepted theory, would predict an adverse effect on the levels or availability of the nutrients, or the microbiological or chemical safety.
Section B.25.048 (2), subsections (a) to (g) of the FDR specify the regulatory requirements for an infant formula having undergone a major change, while Section B.25.015 (2), subsections (a) to (g), specify the regulatory requirements for a human milk fortifier having undergone a major change.
Manufacturers who are planning on a major change in formulation, packaging or processing should contact Health Canada's Food and Nutrition Directorate SMIU to set up a pre-submission meeting at smiu-ugdi@hc-sc.gc.ca.
2.3.3 New infant food ingredient
A manufacturer of a new ingredient that has never been used in an infant formula or human milk fortifier in Canada should submit either a novel food or new infant food ingredient (NIFI) submission for evaluation. The manufacturer should receive approval of the ingredient as either a novel food or NIFI, before a premarket submission is made for an infant formula or human milk fortifier containing the ingredient. The process is described in Appendix 4, Flow Chart for approval of a novel food or new infant food ingredient.
Novel food
If the ingredient is novel (for example, because it has no history of safe use as a food in Canada), its safety must first be assessed by Health Canada as required under Division 28 of the FDR. The petitioner should consult Health Canada's Guidelines for the Safety Assessment of Novel Foods.
New infant food ingredient (NIFI)
If the new ingredient is not novel for the general population, or if it has been assessed for safety only in the general population, excluding infants, its safety must be evaluated for the infant population. Requirements in support of a NIFI submission are as follows:
- Description of the new ingredient, manufacturing process, and product monograph
- History of use, including regulatory status in other jurisdictions
- Proposed dietary exposure in infants
- Nutritional considerations
- Toxicology
- Bioavailability and function in adults and infants
- Physiological efficacy, gastrointestinal effects and safety considerations in the infant population – This may include clinical studies in term or preterm infants depending on the proposed target population and conducted using the specific new ingredient (or a similar ingredient, provided equivalence is demonstrated with the subject of the NIFI submission)
- Allergenicity
- Chemical considerations, including food additives used, levels of contaminants such as heavy metals
- Microbiology
If the new ingredient is not demonstrated to be safe for infants, it will be rejected.
Premarket submission for infant formula or human milk fortifier
If the NIFI or the Novel Food is assessed as safe for infants, petitioners are welcome to proceed with sending a premarket submission for the infant formula or human milk fortifier with the new ingredient, following the guidelines in this document.
3.0 Administrative considerations
3.1 Administrative information
Submissions to Health Canada should meet the requirements below:
- Pagination must be sequential for each document file submitted;
- The petitioner's identification (for example, company name) should be included at least once on each document file that is submitted;
- Petitioners are responsible for clearly indicating parts of the application that contain proprietary or confidential data (such as, results from an unpublished clinical trial, details on manufacturing);
- Petitioners are responsible for the accuracy of all cited references, published or unpublished. An established style for citing references must be used;
- If a third party is submitting on behalf of the manufacturer/petitioner, the Designated Authorization Party Form must be included in the submission.
Important: All data and information in the submission should be provided in English or French. Material in other languages must be translated into English or French before it can be accepted and considered by Health Canada.
3.2 Cover letter
A cover letter must accompany the petitioner's premarket submission. The letter should be dated and provide complete contact information, including name, title, full address and telephone number for the petitioner and for all parties, including any third parties authorized by the petitioner, to communicate with Health Canada about the submission.
The letter should briefly describe the product and include brand and product name. Reference to any related or previous submission should be mentioned in the cover letter, and should include the submission number, key dates, brand name, etc.
It is common for companies to use the facilities of a separate manufacturer and to assign some of the technical aspects of the submission to qualified personnel at the manufacturing facility. Such arrangements and all relevant contact information should be stated in the cover letter.
3.3 Verification checklists
Verification checklists (Appendices 2 and 3) have been developed to assist petitioners as they assemble their infant formula or human milk fortifier submission. The checklist summarizes administrative and scientific or technical information that is meant to assist both the petitioner in the preparation of a submission as well as the scientific evaluator in verifying that the required information has been submitted. Although not a statutory requirement, it is requested that the completed checklist be sent with the submission and cover letter.
3.4 How to submit
Infant formula, human milk fortifier and NIFI submissions should be sent by email to Health Canada's Food and Nutrition Directorate SMIU at smiu-ugdi@hc-sc.gc.ca.
3.5 Food and Nutrition Directorate's pre-market submission management process for infant formula
Manufacturers are strongly encouraged to refer to the Food and Nutrition Directorate Pre-Market Submission Management Process for Food Additives, Infant Formulas and Novel Foods for information on pre-submission meetings, administrative verification, scientific assessment of submissions and decisions.
3.5.1 Submission timelines
Health Canada is committed to improving the timeliness of application reviews for infant formulas and human milk fortifiers. Once a complete submission package is received, Health Canada will apply a service standard of 90 days of active review time for the vast majority of infant formulas and human milk fortifiers. Active review time refers to the time Health Canada evaluators spend reviewing the submission. If the package is incomplete or the information received is not sufficient to establish the safety of the product, Health Canada will notify the applicant in writing and may request additional information. The time between Health Canada's request for additional information and the receipt of this information is not considered as active review time.
4.0 Infant formula and human milk fortifier premarket submission requirements
This section describes the specific information required as part of an infant formula or human milk fortifier submission under the FDR.
4.1 Brand and product name
As per Sections B.25.046 (2) (a) and B.25.048 (2) (a) (for infant formula) and Sections B.25.011 (a) and B.25.015 (2) (a) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, a premarket submission must specify the Brand and product name under which the infant formula or human milk fortifier will be sold or advertised for sale.
The product name could include characteristics such as:
- The protein source used (e.g., cow milk-based, soy-based);
- The format (e.g., powder, liquid concentrate, or for infant formula only, liquid ready-to-feed);
- The intended infant population for the formula (such as, term, follow-up, preterm, infants with cow's milk protein allergy, etc.);
- The packaging type (e.g., sachet, composite can) and the volume or weight (such as, 120 ml or 120 g).
4.2 Name and address
As per Sections B.25.046 (2) (b), (c) and B.25.048 (2) (b) (for infant formula) and Sections B.25.011 (b), (c) and B.25.015 (2) (b) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, a premarket submission must include the name and address of the principal place of business of the manufacturer and the names and addresses of each establishment in which the infant formula or human milk fortifier is to be manufactured.
If any part of the manufacturing of the new infant formula or human milk fortifier is contracted out to a third party company, the name and address of the contractor should also be submitted. Examples include, but are not limited to, bulk ingredients such as base powder, protein mixtures or carbohydrate powders manufactured by a third party company.
4.3 Description of the major change
As per Section B.25.048 (2) (c) (for infant formula) and Section B.25.015 (2) (c) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, the description of the proposed major change to an existing infant formula or human milk fortifier must be provided. The description of the major change should be accompanied by a description of any other change (such as, ingredients, processing, packaging) which were necessary to accommodate the major change.
In cases where there is a change in formulation, a table comparing the formulation between the current and the proposed formula should be provided.
4.4 List of all ingredients
As per Section B.25.046 (2) (d) (for infant formula) and Section B.25.011 (d) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, the list of all ingredients must be provided with quantitative amounts specified. The bill of materials for a batch of infant formula should be submitted to meet this requirement.
For infant formula, amounts of nutrients should fall within the range provided in Table II in Division 25 of the FDR, where available. For nutrients not listed in Table II, appropriate Codex standards and nutrient ranges from the Life Sciences Research Office Report on the Assessment of Nutrient Requirements for Infant Formulas (LSRO Report, 1998) should be used as guidance.
The nutrient requirements for preterm infants according to the most recent international expert recommendations are summarized in Appendix 5, which is in the form of a template to facilitate manufacturers to compare the nutritional profile of their products against the requirements. The assessment of the preterm infant formula is based on the formula as ready to use, and human milk fortifier is based on the composition of the human milk fortifier when added to preterm human milk (not fortifier alone) according to the directions for use. The levels of nutrients added to a new human milk fortifier or one that has undergone a major change would be reviewed and assessed on a case-by-case basis as part of the pre-market review process.
Any food additives present in the infant formula, human milk fortifier or in the manufacture of an ingredient should be described and their levels of use should be provided as a percentage weight of infant formula or human milk fortifier, as consumed.
4.5 Ingredient specifications
As per Section B.25.046 (2) (e) (for infant formula) and Section B.25.011 (f) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, the specifications for nutrient, microbiological, and physical quality for all ingredients and for the new infant formula or human milk fortifier product must be provided in the premarket submission. They are required to allow Health Canada to determine whether a formula meets the Canadian compositional requirements and for the identification of potential microbial, physical, nutritional and chemical hazards, including allergens. The information required includes, but is not limited to, certificates of analysis and supplier raw material specification sheets.
Finished product specifications with minimums and maximums should also be provided for the infant formula or human milk fortifier product, as prepared according to directions for use, with the amounts expressed as per 100 kcal. The infant formula prepared according to directions for use must comply with the provisions in Sections B.25.054, B.25.055 and B.25.056 of the FDR in addition to all other regulatory requirements in Division 25. Specifically, amounts of nutrients declared in the finished product specifications should fall within the permitted minimum and maximum amounts provided for each nutrient in Table II in Division 25 of the FDR or the appropriate standards (refer to Section 4.4 of this guide). The minimum and maximum amounts of nutrients added to a new human milk fortifier or a human milk fortifier that has undergone a major change would be reviewed and assessed on a case-by-case basis as part of the pre-market review process.
A Finished Product Specification template is available for infant formula in Appendix 6.
4.6 Quality control procedures for testing nutrients
As per Section B.25.046 (2) (f) (for infant formula) and Section B.25.011 (g) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, manufacturers must provide details of quality control procedures regarding the testing of the ingredients and of the new infant formula or human milk fortifier. This would include providing documentation demonstrating that the manufacturer maintains, or has access to, suitably equipped laboratories to control the production and acceptance of raw ingredients, packaging materials, in-process and finished products. Method and process validation and stability capabilities, may also be required. Refer to Section 3.6 of the GMPs.
As articulated in Sections 3.6, 3.9.2 and 3.10 of the GMPs, manufacturers are required to implement a quality control procedure to test each nutrient in each nutrient premix used during manufacturing, and conduct appropriate in-process and finished product testing of nutrients (prior to product release). The results provided should verify that all nutrients required by the regulations and any nutrient added by the manufacturer are present at the appropriate levels in each batch of the infant formula or human milk fortifier.
Each lot of powdered infant formula and human milk fortifier should meet, at a minimum, the microbiological criteria for powdered infant formula adopted by Health Canada as outlined in Table 1 in Section 3.10 of the GMPs. These recommendations are in accordance with the Code of Hygienic Practice for Powdered Formulae for Infants and Young Children (Codex Alimentarius Commission CAC/RCP 66-2008).
For liquid infant formulas and human milk fortifiers, which are considered low-acid foods packaged in hermetically sealed containers (refer to Section 3.9 of the GMPs and Division 27 of the FDR), Part 4 of the SFCR provides the requirements for each application of the scheduled process to low-acid foods. Specifically, each application of the scheduled process to low-acid canned foods requires a record of the incubation results.
General guidelines on incubation testing can be found in Codex CAC/RCP 23-1979 Code of Hygienic Practice for Low and Acidified Low Acid Canned Foods. Section 3.10 of the GMPs for finished product control of liquid and powdered formula.
4.7 Manufacturing process and quality control procedures
As per Section B.25.046 (2) (g) (for infant formula) and Section B.25.011 (h) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, a premarket submission must include details of the manufacturing process and quality control procedures used throughout processing. This means that the information showing effective control of ingredients, formulations, processes, facilities and equipment used in the production of infant formula or human milk fortifier to be sold, distributed or marketed in Canada must be provided. Refer to the GMPs.
The manufacturer must provide the following information for Health Canada's review:
- Formulation, process design, incoming materials (ingredients, food additives, packaging materials, and processing aids), processing equipment, process control, pre- and post-process control, product preparation and blending/mixing/intermediate storage, processing and heat treatment conditions (such as pasteurization or sterilization/commercial sterility requirement), homogenization, packaging and filling, drying, container closure and examination records, storage, in-process, finished product, code or lot number identification, product release and stability testing, and transportation;
- A full Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) Plan or HACCP-based GMP plan to assess the controls that the manufacturer has in place for production of the infant formula or human milk fortifier;
- Manufacturing diagram or a flow diagram (from incoming material to storage and distribution of final product), showing the sequence and interaction of all processing steps in the operation, including where raw materials, ingredients and intermediate products enter the flow and where intermediate products, byproducts and waste are released or removed;
- Detailed text describing the diagram or process flow/procedure for production.
It is the manufacturer's responsibility to notify Health Canada about new manufacturing facilities. Refer to New Manufacturing Facilities for Infant Formula and Human Milk Fortifiers.
4.8 Expiration date and stability data
As per Section B.25.046 (2) (h) (for infant formula) and Section B.25.011 (i) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, Section 3.13 of the GMPs provides general requirements on Stability Program and Expiry Date control, which also apply to human milk fortifiers.
The manufacturer must provide the following information to Health Canada:
- The proposed expiry period for the product;
- Stability data for all the nutrients to support the proposed expiry period for the product;
- Stability data should be of a sufficient number of batches of each product over the labelled shelf-life to support overall conclusions regarding the stability and physical properties of all ingredients, in particular the labile ingredients, as well as at the expiry date;
- Stability data for at least 2 to 3 commercial batches of the proposed product or one that is similar to the proposed product;
- If the submitter chooses to provide stability data for a similar product marketed elsewhere (e.g., U.S.) or provide data from research batches with a different product name, the product name that corresponds to the proposed product should also be provided;
- Stability data for the proposed product in all the applicable packaging formats (such as, glass bottles, metal cans, composite cans);
- Stability data for liquids must be provided up to the proposed shelf life and for powders, it can be provided up to a minimum of half of the proposed shelf life;
- Stability data at more than 2 time points is necessary for new products. The number of batches and frequency of stability testing may be reduced once a sufficient database has been developed by the manufacturer.
Appendix 7 provides a template for infant formula stability data. In addition, Section 3.13 of the GMPs provides general requirements on Stability Program and Expiry Date control, which also apply to human milk fortifiers.
4.9 Nutritional adequacy
As per Sections B.25.046 (2) (i) and B.25.048 (2) (d) (for infant formula) and Sections B.25.011 (j) and B.25.015 (2) (d) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, the evidence relied on to establish that an infant formula or human milk fortifier is nutritionally adequate to promote acceptable growth and development in infants must be submitted to Health Canada for review, as per paragraph B.25.046 (2) (i), B.25.048 (2) (d), and B.25.011(j), B.25.015 (2) (d) of the FDR respectively.
Refer to the following guidance documents to assist with preparation of studies to support nutritional adequacy:
- Scientific Evidence Requirements for Nutritional Adequacy - Term Infant Formula
- Scientific Evidence Requirements for Nutritional Adequacy - Preterm Infant Formulas and Human Milk Fortifiers
- Growth and Tolerance Clinical Trial Protocol - Healthy Term Newborn Infants
- Growth and Tolerance Clinical Trial Protocol - Preterm Infants
4.10 Evidence for major changes
As per Section B.25.048 (2) (e) (for infant formula) and Section B.25.015 (2) (e) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, a clinical growth and tolerance trial and a Protein Efficiency Ratio (PER) study may be required for infant formula or human milk fortifier that has undergone a major change.
Health Canada encourages petitioners to have a pre-submission meeting with Health Canada on the required regulations, since these vary on a case-by-case basis.
4.11 Packaging
As per Section B.25.046 (2) (j) (for infant formula) and Section B.25.011 (k) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, the packaging material used for infant formulas or human milk fortifiers must be approved as food grade, and must comply with Division 23 of the FDR. The manufacturer must provide an issued letter of no objection from the Bureau of Chemical Safety of Health Canada for confirmation of acceptability. The GMPs should be consulted for further information on the manufacturing requirements for packaging infant formula. Additional information on the premarket submission process for food packaging is also available in Health Canada's guidance document on packaging materials.
4.12 Directions for preparation, use and storage
As per Sections B.25.046 (2) (k), B.25.057 (1) (e) and (2) (e) (for infant formula) and Sections B.25.011 (l), B.25.020 (e) and (f) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, the directions for the preparation, use and storage of an infant formula or human milk fortifier must be included in the label text provided as part of the premarket submission package, as detailed below.
4.12.1 Directions for preparation and use
The purpose of providing appropriate instructions in the label text is to reduce the risk of foodborne illness in infants. The directions for preparing and using the infant formula or human milk fortifier can include diagrams or pictograms. For powdered infant formula, these instructions should align with Health Canada's guide on preparing and handling powdered infant formula. For powdered infant formulas and human milk fortifiers, refer to Codex Alimentarius Commission in the CXC 66-2008 Code of Hygienic Practice for Powdered Formulae for Infants and Young Children.
The directions for preparation and use for infant formula should include:
- A general statement on how to safely prepare formula, such as 'Your baby's health depends on carefully following preparation instructions. Proper hygiene, preparation, dilution, handling (or use) and storage are important when preparing infant formula';
- Instructions on initial preparation including proper hand washing and ensuring that formula is prepared in a clean environment. Possible wording includes 'Wash hands and counters thoroughly with soap and water before preparing infant formula';
- Instructions on sterilization of bottles and preparation tools such as 'Wash bottles, nipples, caps, rings, can opener and all preparation tools, then boil for at least 5 minutes at a rolling boil'. For powdered infant formula, instructions on the additional water used to prepare the infant formula should be included. For example, 'Boil additional water for formula at a rolling boil at least 2 minutes. After cooling water to 70°C, required amount of water can be added into a sterilized bottle';
- A statement about testing the temperature of prepared infant formula prior to feeding to prevent scalding the infant's mouth. Prepared formula should be cooled to room or body temperature. One way to ensure proper temperature is testing the temperature of the formula on the caregiver's wrist. Possible wording includes 'Place a drop of formula onto the inside of your wrist. If you do not feel a temperature difference, the formula temperature is just right'.
For human milk fortifiers, the following safety precautions should be included:
- Use under medical supervision only;
- Not intended for feeding low-birth-weight infants after they reach a weight of 3600 g (approximately 8 lb.) unless otherwise directed by a health care professional;
- Additional iron may be necessary.
For human milk fortifiers, a statement similar to the following should be included 'Tolerance to enteral feedings should be confirmed by offering small volumes of unfortified human milk. Once enteral feeding is well-established, (product name) can be added to human milk. A chart similar to Table 1 should also be included:
| Additional Calories Desired | Human Milk | Human Milk Fortifier | Approximate Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
x Calories/ y mL |
z mL |
Packaging type (e.g., 1 packet) |
w mL |
Examples |
|||
2 Calories/ 30 mL |
50 mL |
1 packet |
55 mL |
4 Calories/ 30 mL |
25 mL |
1 packet |
30 mL |
4.12.2 Storage
Instructions on how to properly store infant formulas or human milk fortifiers before and after opening the containers/package should include information on temperature, exposure to light or heat and the length of time that the containers can be safely stored. Statements such as 'Do not freeze' or 'keep frozen' and 'Avoid excessive heat' should be included as well, if applicable.
Once prepared, infant formula, or human milk fortifier in human milk, can spoil quickly. Length of time that these can be used after preparation should be included. Possible wording includes: 'Either feed immediately or cover and store in refrigerator at 2-4°C (35-40°F) for no longer than 24 hours. Do not use prepared formula if it is unrefrigerated for more than 1 hour'.
4.13 Label text
As per Sections B.25.046 (2) (l) and B.25.048 (2) (f) (for infant formula) and Sections B.25.011 (m) and B.25.015 (2) (f) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, the written text of all labels, including package inserts, to be used in connection with the infant formula or human milk fortifier must be provided to Health Canada as part of the premarket submission.
Sections B.25.057 and B.25.020 of the FDR set out the labelling requirements for infant formula and human milk fortifier, respectively. The formula should also comply with general food labelling regulations. The CFIA's Food Labelling for Industry guidance document should be consulted for more information on general food labelling requirements.
Section B.25.020 (1), (2) and (3) of the FDR lists specific information required for inner and outer human milk fortifier labels:
- Information found in B.25.020 (1) (a) through (i) is required to be on the outer label of the human milk fortifier;
- Information found in B.25.020 (1) (h) and (i) is required to be on the inner label of the human milk fortifier;
- If the human milk fortifier does not have an outer label, information in B.25.020 (1) (a) through (i) is required to be on the inner label. In this scenario, the information in B.25.020 (1) (e) and (f) [the directions for storage, use and preparation] may be located in a leaflet that is affixed/ attached to the immediate container.
The written text of all labels, including package inserts, to be used in connection with the infant formula or human milk fortifier must be provided as part of the premarket submission. Electronic copies should be sent to Health Canada's Food and Nutrition Directorate SMIU at smiu-ugdi@hc-sc.gc.ca as soon as they are available after sending in a premarket submission. The electronic copies provided should allow for magnification, such that all text is legible.
Warning statements
Important safety information should be clearly listed under a bolded, all caps warning header, WARNING.
There should be a safety warning about the risks associated with heating and reheating infant formula in the microwave such as, 'Never heat formula in a microwave oven. Serious burns can result.' The label text must include a warning about priority food allergens that may have come into contact with the infant formula or human milk fortifier.
To ensure safety of use for human milk fortifiers, the product label should also include:
- The potential renal solute load (PRSL) of the fortified human milk (as consumed);
- Osmolality of the fortified human milk (as consumed).
Infant formula advisory
It is highly recommended that labelling include the words 'Important Notice' followed by a statement on the superiority of breastfeeding. This direction aligns with the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes, to which Canada is a signatory.
Infant formula indications for use
Some specialty infant formulas are indicated for infants with certain medical conditions. Indications for use identify products that are meant for the dietary management of medical conditions. Examples of appropriate indications for use that have been accepted for infant formula include:
- For the dietary management of colic due to cow's milk protein allergy;
- Hypoallergenic, for the dietary management of infants with cow's milk allergy;
- Thickened with rice starch, for feeding infants who spit up frequently.
Any proposed new indication for use of an infant formula must be supported by clinical studies performed with the specific infant formula being notified. These specialty formulas and their accompanying indications for use are reviewed by Health Canada during the premarket submission review process.
Lactose free infant formula claims must be accompanied by information on the finished product specification for lactose which should be ≤10 mg/100 kcal. In Canada, all milk-based lactose free infant formulas are labelled with a contraindication statement against the use of these formulas in infants with galactosemia.
Human milk fortifier indications for use
Examples of appropriate indications for use that have been accepted for human milk fortifiers include:
- Designed for premature infants as a nutritional supplement to be added to human milk;
- For premature and low-birth-weight infants fed human milk;
- This human milk fortifier is formulated for preterm and low-birth-weight infants as a nutritional supplement to be added to human milk.
As with specialty formula, any proposed new indication for use must be substantiated by clinical studies performed with the specific human milk fortifier being notified and will be reviewed by Health Canada during the premarket submission review process.
4.14 Signed submission
As per Sections B.25.046 (2) (m) and B.25.048 (2) (g) (for infant formula) and Sections B.25.011 (n) and B.25.15 (2) (g) (for human milk fortifier) of the FDR, the name, title and dated signature of the contact person responsible for the infant formula or human milk fortifier premarket submission must be included.
4.15 Scientific rationale for new human milk fortifier or major change
As per Sections B.25.011 (e) and B.25.15 (2) (c) of the FDR, a rationale for the purpose and use of the new human milk fortifier or one that has undergone a major change must be submitted.
5.0 Foreign reviews
When conducting a premarket review of a new infant formula or human milk fortifier, or a major change, Health Canada could also consider other relevant information, such as information provided to, or obtained from, a foreign regulator, or post-market data from another jurisdiction. While such information is not required under the premarket submission, information from another regulator relating to the approval of an infant formula or human milk fortifier, or a major change, in a foreign jurisdiction may help to streamline Health Canada's review process.
For any questions on the use of information from a foreign regulator or post-market data, manufacturers are encouraged to contact Health Canada at bns-bsn@hc-sc.gc.ca.
6.0 References to breastmilk
The International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes (Code), to which Canada is a signatory, outlines labelling principles that promote clear labelling regarding the appropriate use of an infant formula while promoting breastfeeding. Comparing infant formula to breastmilk, including comparisons of the levels of a nutrient in infant formula to the levels of the same nutrient in breastmilk, is contrary to the message embodied in the Code.
Health Canada strongly urges the infant formula industry to support and implement the principles of the Code. In addition, the CFIA's guidance, Labelling requirements for infant foods, infant formula and human milk provides information about acceptable claims and aligns with certain principles set out in the Code. For example, highlighting an ingredient in infant formula as a key component of breastmilk is considered misleading as many components in breastmilk are equally important.
7.0 Glossary and abbreviations
This section provides a glossary of key terms and abbreviations used in this guide.
7.1 Glossary
Batch
A specific quantity of infant formula intended to have uniform character and quality within specified limits, which is produced according to a single manufacturing order and which may constitute the whole or a part of a lot.
Lot
A quantity of infant formula produced under identical conditions, all packages of which bear a lot number that identifies the production during a particular time interval from a particular 'line' or other critical processing unit. It may be defined by a time period (e.g., from sanitation to sanitation) or some other processing measure. It is often associated with a number and enables tracing of the constituent parts or ingredients as well as labour and equipment records involved in the manufacturing of an infant formula. This enables manufacturers and other entities to perform quality control checks, calculate expiration dates, and issue corrections or recall information to subsets of the production output.
Nutritional adequacy
An infant formula is nutritionally adequate if it promotes acceptable growth and development in infants when consumed in accordance with the directions for use. Clinical trial evidence is often used to determine whether a given infant formula is nutritionally adequate.
Premarket submission
The FDR requires that manufacturers notify Health Canada prior to the marketing of any new infant formula or human milk fortifier or of an infant formula or human milk fortifier that has undergone a major change in formulation, manufacturing or packaging. Sections B.25.046 and B.25.048 of the FDR specify the information that must be presented in the premarket submission for infant formula, and for human milk fortifiers in Section B.25.011 and B.25.015.
Premix
A combination of ingredients containing two or more nutrients as specified on the label, which is compounded in a manufacturing operation distinct from the processing of the final product.
Safety
A reasonable certainty of no harm (US Food and Drug Administration, Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, Section 409).
7.2 Abbreviations
- CFIA
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency
- FDA
- Food and Drugs Act
- FDR
- Food and Drug Regulations
- GMP
- Good Manufacturing Practice
- HACCP
- Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point
- HMF
- Human Milk Fortifier
- IF
- Infant Formula
- LSRO
- Life Sciences Research Office
- NIFI
- New Infant Food Ingredient
- PCP
- Preventive Control Plan
- PRSL
- Potential Renal Solute Load
- SFCA
- Safe Food for Canadians Act
- SFCR
- Safe Food for Canadians Regulations
- SMIU
- Submission Management and Information Unit
Appendix 1. Examples of minor and major changes, per category
A minor change to an infant formula (IF) or human milk fortifier (HMF) is any change that does not meet the regulatory definition of a major change as described in section B.25.001 of the Food and Drug Regulations (FDR). A minor change is not expected to introduce a safety risk to the product or affect its nutrient availability. Examples of such changes, which are not reviewed through premarket notification by Health Canada, include the use of previously approved packaging materials, and certain updates to product labelling. The table below presents a non-exhaustive list of minor changes compared to major changes per category, provided as guidance to stakeholders. It is the manufacturer's responsibility to ensure that any minor change does not impact the quality or safety of the product.
| Category | Examples of Major Change | Examples of Minor Change |
|---|---|---|
Ingredients |
|
|
Finished Product Specifications |
|
|
Label |
|
|
Manufacturing |
|
|
Packaging |
|
|
|
||
It is the manufacturer's responsibility to ensure that a change meets the criteria of a minor change before deciding not to submit an application. It is important to note that it is the manufacturer's responsibility to ensure their products continue to comply with the Food and Drug Regulations and the Food and Drug Act, in addition to the Safe Food for Canadians Act and Safe Food for Canadians Regulations.
For additional questions regarding the difference between minor and major changes for IF and HMF, please contact the Food and Nutrition Directorate's Submission Management and Information Unit (SMIU) at smiu-ugdi@hc-sc.gc.ca.
Appendix 2a. Verification checklist for infant formula submissions – new
| Administrative information | ||
|---|---|---|
Submission content |
Yes (√) |
Rationale for No |
Cover letter provided |
||
Title of the submission indicated |
||
Completed checklist attached |
||
Contact information provided (company name, full postal address, contact name, telephone number, email address) |
||
Electronic version of the submission |
||
If applicable, previous reference submission # and date on letter: |
||
| Information required under Part B of the Food and Drug Regulations | ||
|---|---|---|
New infant formula submission |
Yes (√) |
Rationale for No |
Name under which it will be sold or advertised for sale (FDR B.25.046.2 a) |
||
Name and address of the principal place of business of the manufacturer (FDR B.25.046.2 b) |
||
Names and addresses of each establishment in which it is manufactured (FDR B.25.046.2 c) |
||
List of all ingredients, stated quantitatively (FDR B.25.046.2 d) |
||
Specifications for nutrient, microbiological and physical quality for the ingredients and for the new infant formula (FDR B.25.046.2 e) |
||
Details of quality control procedures respecting the testing of the ingredients and of the new infant formula (FDR B.25.046.2 f) |
||
Details of the manufacturing process and quality control procedures used throughout the process (FDR B.25.046.2 g) |
||
Results of tests carried out to determine the expiration date of the new infant formula (FDR B.25.046.2 h) |
||
Evidence relied on to establish that the new infant formula is nutritionally adequate to promote acceptable growth and development in infants when consumed in accordance with the directions for use (FDR B.25.046.2 i) |
||
Description of the type of packaging to be used (FDR B.25.046.2 j) |
||
Directions for use (FDR B.25.046.2 k) |
||
Written text of all labels (bilingual coloured mock ups are preferred), including package inserts, to be used in connection with the new infant formula (FDR B.25.046.2 l) |
||
Name and title of the person who signed the submission and the date of signature (FDR B.25.046.2 m) |
||
Appendix 2b. Verification checklist for infant formula submissions – major change
| Administrative information | ||
|---|---|---|
Submission content |
Yes (√) |
Rationale for No |
Cover letter provided |
||
Title of the submission indicated |
||
Completed checklist attached |
||
Contact information provided (company name, full postal address, contact name, telephone number, email address) |
||
Electronic version of the submission |
||
| Information required under Part B of the Food and Drug Regulations | ||
|---|---|---|
Submissions related to a major change to an existing infant formula |
Yes (√) |
Rationale for No |
Name under which it will be sold or advertised for sale (FDR B.25.048.2 a) |
||
Name and address of the principal place of business of the manufacturer (FDR B.25.048.2 b) |
||
Description of the major change (FDR B.25.048.2 c) |
||
Evidence relied on to establish that the infant formula is nutritionally adequate to promote acceptable growth and development in infants when consumed in accordance with the directions for use (FDR B.25.048.2 d) |
||
Evidence relied on to establish that the major change has had no adverse effect on the infant formula (FDR B.25.048.2 e) |
||
Written text of all labels, including package inserts, to be used in connection with the new infant formula (bilingual coloured mock ups are preferred) (FDR B.25.048.2 f) |
||
Name and title of the person who signed the submission and the date of signature (FDR B.25.048.2 g) |
||
Appendix 3a. Verification checklist for human milk fortifier submissions – new
| Administrative information | ||
|---|---|---|
Submission content |
Yes (√) |
Rationale for No |
Cover letter provided |
||
Title of the submission indicated |
||
Completed checklist attached |
||
Contact information provided (company name, full postal address, contact name, telephone number, email address) |
||
Electronic version of the submission |
||
If applicable, previous reference submission# and date on letter: |
||
Information required under Part B of the Food and Drug Regulations |
||
New human milk fortifier submission |
Yes (√) |
Rationale for No |
Name under which it will be sold or advertised for sale (FDR B.25.011 a) |
||
Name and address of the principal place of business of the manufacturer (FDR B.25.011 b) |
||
Names and addresses of each establishment in which it is manufactured (FDR B.25.011 c) |
||
List of all ingredients, stated quantitatively (FDR B.25.011 d) |
||
Scientific rationale for the formulation (FDR B.25.011 e) |
||
Specifications for nutrient, microbiological and physical quality for the ingredients and for the new human milk fortifier (FDR B.25.011 f) |
||
Details of quality control procedures respecting the testing of the ingredients and of the new human milk fortifier (FDR B.25.011 g) |
||
Details of the manufacturing process and quality control procedures used throughout the process (FDR B.25.011 h) |
||
Results of tests carried out to determine the expiration date of the new human milk fortifier (FDR B.25.011 i) |
||
Evidence relied on to establish that the new human milk fortifier is nutritionally adequate to promote acceptable growth and development in infants when consumed in accordance with the directions for use (FDR B.25.011 j) |
||
Description of the type of packaging to be used (FDR B.25.011 k) |
||
Directions for use (FDR B.25.011 l) |
||
Written text of all labels (bilingual coloured mock ups are preferred), including package inserts, to be used in connection with the new human milk fortifier (FDR B.25.011 m) |
||
Name and title of the person who signed the submission and the date of signature (FDR B.25.011 n) |
||
Appendix 3b. Verification checklist for human milk fortifier submissions – major change
| Administrative information | ||
|---|---|---|
Submission content |
Yes (√) |
Rationale for No |
Cover letter provided |
||
Title of the submission indicated |
||
Completed checklist attached |
||
Contact information provided (company name, full postal address, contact name, telephone number, email address) |
||
Electronic version of the submission |
||
| Information required under Part B of the Food and Drug Regulations | ||
Submissions related to a major change to an existing human milk fortifier |
Yes (√) |
Rationale for No |
Name under which it will be sold or advertised for sale (FDR B.25.015.2 a) |
||
Name and address of the principal place of business of the manufacturer (FDR B.25.015.2 b) |
||
Description of the major change (FDR B.25.015.2 c) |
||
Evidence relied on to establish that the human milk fortifier is nutritionally adequate to promote acceptable growth and development in infants when consumed in accordance with the directions for use (FDR B.25.015.2 d) |
||
Evidence relied on to establish that the major change has had no adverse effect on the human milk fortifier (FDR B.25.015.2 e) |
||
Written text of all labels, including package inserts, to be used in connection with the new human milk fortifier (bilingual coloured mock ups are preferred) (FDR B.25.015.2 f) |
||
Name and title of the person who signed the submission and the date of signature (FDR B.25.015.2 g) |
||
Appendix 4. Flow chart for approval of a novel food or new infant food ingredient (NIFI)
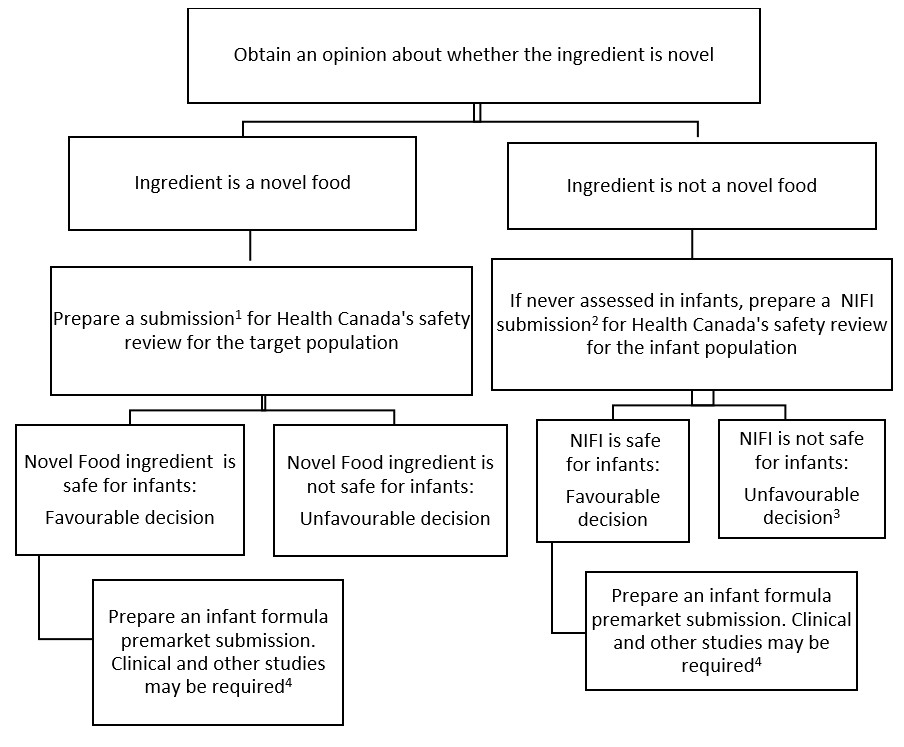
Figure 1 - Text description
PENDING
Reference 1 For information on the requirements for a novel food submission, consult Health Canada's Guidelines for the Safety Assessment of Novel Foods.
Reference 2 For information on the requirements for a NIFI submission, see Section 2.3.3 of this guide.
Reference 3 An unfavourable decision would result in closure of the submission. A new submission would be required.
Reference 4 For further information on clinical testing, consult Health Canada’s Growth and Tolerance Clinical Trial Protocol - Healthy Term Newborn Infants
Appendix 5. Nutrient requirement template for preterm infant formula or fortifier with human milk (as fed) per 100 kcal
NOTE: Single value indicates a minimum recommendation. Value in a square bracket has been reported as the calculated value in respective citation.
- MACRONUTRIENTS
| Nutrient | FDR requirements | International expert recommendations | Nutritional profile | Specification | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Unit | ESPGHAN (2010)Reference 1 | Tsang, et. al. (2005)Reference 2 >1000 g BW | LSRO (2002)Reference 3 | WHOReference 4 >1000 g BW (stabilization to term)Footnote a | Koletzko, et.al. (2014)Reference 5 | Min | Max | ||
Protein |
g |
1.8 – 4 |
3.2 – 4.1Footnote b |
2.6 – 3.8 |
2.5 – 3.6 |
[2.5 – 3.0] |
3.2 – 4.1 |
|||
Fat |
g |
3.3 – 6 |
4.4 – 6.0 |
4.1 – 6.5 |
4.4 – 5.7 |
[3.8 – 5.7] |
4.4 – 6.0 |
|||
- LA |
g |
0.5 |
0.350 – 1.400 |
0.462 – 1.309 |
[0.350 – 1.425]Footnote c |
NS |
0.350 – 1.400 |
|||
- ALA |
g |
NS |
0.050 |
NS (1 – 4 E% per kg/day) |
0.077 – 0.228 (1.75 – 4% of total fatty acids) |
NS |
0.050 |
|||
- LA:ALA |
- |
NS |
5 – 15 |
5 – 15 |
6 – 16 |
NS |
NS |
|||
- ARA |
g |
NS |
0.016 – 0.039 |
0.022 |
[0 – 0.034] Footnote d |
NS |
0.032 – 0.041 |
|||
- DHA |
g |
NS |
0.011 – 0.027 |
0.016 |
[0 – 0.020]Footnote e |
NS |
0.050 – 0.055 |
|||
Carbohydrate |
g |
NS |
10.5 – 12 |
5.4 – 15.5 |
9.6 – 12.5 |
[6.3 – 12.9] |
10.5 – 12 |
|||
- VITAMINS AND MINERALS
| Nutrient | FDR requirements | International expert recommendations | Nutritional profile | Specification | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Unit | ESPGHAN (2010)Reference 1 | Tsang, et. al. (2005)Reference 2 >1000 g BW | LSRO (2002)Reference 3 | WHOReference 4 >1000 g BW (stabilization to term)Footnote a | Koletzko, et.al. (2014)Reference 5 | Min | Max | ||
Vitamin A |
IU |
250 – 500 |
1200 – 2467 |
538 – 1364 |
680 – 1267 |
583 – 1250 |
1217 – 3333 |
|||
mcg RE |
-- |
[360 – 740] |
[162 – 410] |
[204 – 380] |
[175 – 375] |
[365 – 1000] |
||||
Vitamin D |
IU |
40 – 100 |
800 – 1000Footnote f per day |
115 – 364 |
75 – 270 |
[400 – 800]Footnote f per day |
100 – 350 from milk only |
|||
Vitamin E |
IU |
0.6 |
[3.0 – 15] |
4.6 – 10.9 |
[3.0 – 12] |
[5.0 – 10.0] |
[3.0 – 15] |
|||
mg α-TE |
-- |
2 – 10 |
[3.1 – 7.3] |
2 – 8 Footnote g |
[3.4 – 6.7] |
2 – 10 |
||||
Vitamin K |
mcg |
8 |
4 – 25 |
6.2 – 9.1 |
4 – 25 |
[6.7 – 8.3] |
4 – 25 |
|||
Vitamin C |
mg |
8 |
10 – 42 |
13.8 – 21.8 |
8.3 – 37 |
[5 – 8] |
18 – 50 |
|||
Thiamine |
mcg |
40 |
125 – 275 |
138 – 218 |
30 – 250 |
[33 – 42] |
127 – 273 |
|||
Riboflavin |
mcg |
60 |
180 – 365 |
192 – 327 |
80 – 620 |
[300 – 383] |
181 – 364 |
|||
Vitamin B6 |
mcg |
35 |
41 – 273 |
115 – 191 |
30 – 250 |
[15]Footnote h |
45 – 273 |
|||
Vitamin B12 |
mcg |
0.15 |
0.08 – 0.7 |
0.23 – 0.27 |
0.08 – 0.7 |
[0.15]Footnote f |
0.09 – 0.73 |
|||
Niacin |
mcg |
250 |
345 – 5000 |
2800 – 4400 |
550 – 5000 |
[720] |
900 – 5000 |
|||
Pantothenic acid |
mcg |
300 |
300 – 1900 |
900 – 1500 |
300 – 1900 |
[667 – 1083] |
450 – 1900 |
|||
Folic acid |
mcg |
4 |
32 – 90 |
19 – 45 |
30 – 45 |
[50]Footnote f |
32 – 91 |
|||
Biotin |
mcg |
2 |
1.5 – 15 |
2.8 – 5.5 |
1.0 – 37 |
[1.3] |
1.5 – 15 |
|||
Choline |
mg |
12 |
7 – 50 |
11.1 – 25.5 |
7 – 23 |
NS |
7.3 – 50 |
|||
Inositol |
mg |
NS |
4 – 48 |
25 – 74 |
4 – 44 |
NS |
4 – 48 |
|||
Taurine |
mg |
NS |
NS |
3.5 – 8.2 |
5 – 12 |
NS |
NS |
|||
Carnitine |
mg |
NS |
NS |
2.2 – 2.6 |
2 – 5.9 |
NS |
NS |
|||
Calcium (Ca) |
mg |
50 |
110 – 130 |
77 – 200 |
123 – 185 |
[134 – 200] |
109 – 182 |
|||
Phosphorus (P) |
mg |
25 |
55 – 80 |
46 – 127 |
82 – 109 |
[65 – 98] |
55 – 127 |
|||
Ca:P |
-- |
1.2 – 2 |
NS |
NS |
1.7 – 2.0:1 |
NS |
NS |
|||
Magnesium |
mg |
6 |
7.5 – 13.6 |
NS |
6.8 – 17 |
[4.1 – 8.1] |
7.5 – 13.6 |
|||
Sodium |
mg |
20 – 60 |
63 – 105 |
53 – 105 |
39 – 63 |
[48 – 77] |
63 – 105 |
|||
Potassium |
mg |
80 – 200 |
60 – 120 |
60 – 106 |
60 – 160 |
[81 – 114] |
71 – 177 |
|||
Chloride |
mg |
55 – 150 |
95 – 161 |
82 – 226 |
60 – 160 |
[74 – 118] |
95 – 161 |
|||
Iron |
mg |
0.15 |
1.8 – 2.7 |
1.538 – 3.636 |
1.7 – 3.0 |
[1.7 – 2.5] |
1.8 – 2.7 |
|||
Zinc |
mg |
0.5 |
1.0 – 1.8 |
0.769 – 2.727 |
1.1 – 1.5 |
[0.42 – 0.67] |
1.3 – 2.3 |
|||
Copper |
mcg |
60 |
90 – 120 |
92 – 136 |
100 – 250 |
[58 – 101] |
90 – 210 |
|||
Manganese |
mcg |
5 |
6.3 – 25 |
0.5 – 6.8 |
6.3 – 25 |
[0.5 – 0.9] |
0.9 – 13.6 |
|||
Iodine |
mcg |
5 |
10 – 50 |
7.7 – 54.5 |
6 – 35 |
[26 – 53] |
9 – 50 |
|||
Selenium |
mcg |
NS |
4.5 – 9 |
1.0 – 4.1 |
1.8 – 5.0 |
[2.6 – 3.9] |
4.5 – 9 |
|||
Chromium |
mcg |
NS |
0.027 – 1.12 |
0.08 – 2.05 |
NS |
0.04 – 0.08 |
0.027 – 2.045 |
|||
Molybdenum |
mcg |
NS |
0.27 – 4.5 |
0.23 – 0.27 |
NS |
0.16 – 0.32 |
0.27 – 4.5 |
|||
Fluoride |
mcg |
NS |
1.4 – 55 |
NS |
0 – 25 |
NS |
1.4 – 55 |
|||
- NUCLEOTIDES
| Nutrient | FDR requirements | International expert recommendations | Nutritional profile | Specification | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Unit | ESPGHAN (2010)Reference 1 | Tsang, et. al. (2005)Reference 2 >1000 g BW | LSRO (2002)Reference 3 | WHOReference 4 >1000 g BW (stabilization to term)Footnote a | Koletzko, et.al. (2014)Reference 5 | Min | Max | ||
Total Nucleotides |
mg |
NS |
NS |
NS |
NS |
NS |
NS |
|||
AMP |
mg |
NS |
NS |
0.27 – 0.73 |
NS |
NS |
NS |
|||
CMP |
mg |
NS |
NS |
1.6 – 3.7 |
NS |
NS |
NS |
|||
GMP |
mg |
NS |
NS |
0.03 – 0.54 |
NS |
NS |
NS |
|||
UMP |
mg |
NS |
NS |
0.69 – 0.9 |
NS |
NS |
NS |
|||
Abbreviations
- ALA
- Alpha-linolenic acid
- AMP
- Adenosine monophosphate
- ARA
- Arachidonic acid
- BW
- Body weight
- Ca:P
- Calcium to phosphorous ratio
- CMP
- Cytosine monophosphate
- DHA
- Docosahexaenoic acid
- g
- gram
- GMP
- Guanosine monophosphate
- LA
- Linoleic acid
- LSRO
- Life Sciences Research Office
- Max
- Maximum
- mcg
- microgram
- mg
- milligram
- Min
- Minimum
- NS
- None specified
- PUFA
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- RE
- Retinol equivalents
- TE
- Tocopherol equivalents
- UMP
- Uridine monophosphate
- WHO
- World Health Organization.
References
- Reference 1
-
Agostoni C, Buonocore G, Carnielli VP, De Curtis M, Darmaun D, Decsi T, et al. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: commentary from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010:50. 85-91.
- Reference 2
-
Tsang RC, Uauy R, Koletzko B, Zlotkin S. Nutrition of the preterm infant, Scientific basic and practical guidelines. Cincinnati, OH: Digital Educational Publishing Inc. 2005.
- Reference 3
-
Klein CJ. Nutrient requirements for preterm infant formulas. J Nutr 2002;132:1395S-577S.
- Reference 4
-
Tudehope D. et al. Nutritional Needs of the Micropreterm Infant March 2013, Volume 162, Issue 3, Supplement, Pages S72–S80
- Reference 5
-
Koletzko B, Poindexter B, Uauy R. Nutritional Care of Preterm Infants: Scientific Basis and Practical Guidelines. Karger, 2014:99-120
Footnotes
- Footnote a
-
Calculated based on the average of the maximum and minimum energy recommendations for the indicated population; 120 kcal/kg/d for stabilization to term.
- Footnote b
-
3.6 – 4.1 g / 100 kcal for infants < 1 kg BW; 3.2 – 3.6 g/100 kcal for infants 1 - 1.8 kg BW
- Footnote c
-
Total fatty acids: 8% (minimum) and 25% (maximum)
- Footnote d
-
A minimum recommendation for ARA was not established. Maximum: 0.6% of total fatty acids with the further stipulation that the ARA:DHA is within the range of 1.5-2.0 : 1
- Footnote e
-
A minimum recommendation for DHA was not established. Maximum: 0.35% of total fatty acids with the further stipulation that the ARA:DHA is within the range of 1.5-2.0 : 1
- Footnote f
-
Recommendation given per day, independent of body weight and energy intake
- Footnote g
-
The ratio of vitamin E to PUFA (mg α-TE per g PUFA) should exceed 1.5 (mg α-TE/g PUFA)
- Footnote h
-
Recommendation per gram protein fed
Appendix 6. Suggested template for finished product specification data, infant formula
| Nutrients (unit) | Label Claim | Release Limits | FDR (1990) | LSRO 1998 | Codex Stan 72-1981 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| per 100 ml | per 100 kcal | Min per 100 kcal | Min % label claim | Max per 100 kcal | Max % label claim | MIN per 100 kcal | MAX per 100 kcal | MIN per 100 kcal | MAX per 100 kcal | MIN per 100 kcal | MAX per 100 kcal | |
| Energy (kcal) | --- |
--- |
63 |
71 |
60 |
70 |
||||||
| Protein (g) | 1.8 |
4 |
1.7 |
3.4 |
1.8 |
3 |
||||||
| Total carbohydrate (g) | --- |
--- |
9 |
13 |
9 |
14 |
||||||
| Total Fat (g) | 3.3 |
6 |
4.4 |
6.4 |
4.4 |
6 |
||||||
| Linoleic acid (LA) (mg. % fat) | 500 |
--- |
350 |
2240 |
300 |
1400Footnote * |
||||||
| Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (mg, % fat) | --- |
--- |
77 |
256 |
50 |
--- |
||||||
Arachidonic acid (ARA) (mg/100kcal) |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
||||||
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (mg, % fat) |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
0.5%Footnote * |
||||||
Carnitine (mg) |
--- |
--- |
1.2 |
2 |
1.2 |
--- |
||||||
Taurine (mg) |
--- |
--- |
0 |
12 |
--- |
12 |
||||||
Nucleotides (mg) |
--- |
--- |
0 |
16 |
--- |
--- |
||||||
Choline (mg) |
12 |
--- |
7 |
30 |
7 |
|||||||
Inositol (mg) |
--- |
--- |
4 |
40 |
4 |
|||||||
Vitamin A (IU) |
250 |
500 |
200 |
500 |
200 |
600 |
||||||
Vitamin D (IU) |
40 |
100 |
40 |
100 |
40 |
100 |
||||||
Vitamin E (IU) |
0.6 |
--- |
0.7 |
7.5 |
0.7 |
|||||||
Vitamin K (mcg) |
8 |
--- |
1 |
25 |
4 |
|||||||
Vitamin B1 - Thiamin (mcg) |
40 |
--- |
30 |
200 |
60 |
300Footnote * |
||||||
Vitamin B2 - Riboflavin (mcg) |
60 |
--- |
80 |
300 |
80 |
500Footnote * |
||||||
Vitamin B3 - Niacin (mcg) |
250 |
--- |
550 |
2000 |
300 |
1500Footnote * |
||||||
Vitamin B5 - Pantothenic acid (mcg) |
300 |
--- |
300 |
1200 |
400 |
2000Footnote * |
||||||
Vitamin B6 - Pyridoxin (mcg) |
35 |
--- |
30 |
130 |
35 |
175Footnote * |
||||||
Vitamin B12 - Cobalamin (mcg) |
0.15 |
--- |
0.08 |
0.7 |
0.1 |
1.5Footnote * |
||||||
Folic acid (mcg) |
4 |
--- |
11 |
40 |
10 |
|||||||
Biotin (mcg) |
2 |
--- |
1 |
15 |
1.5 |
|||||||
Vitamin C (mg) |
8 |
--- |
6 |
15 |
10 |
|||||||
Calcium (mg) |
50 |
--- |
50 |
140 |
50 |
140Footnote * |
||||||
Phosphorus (mg) |
25 |
--- |
20 |
70 |
25 |
100Footnote * |
||||||
Magnesium (mg) |
6 |
--- |
4 |
17 |
5 |
|||||||
Iron (mg) |
0.15 |
--- |
0.2 |
1.65 |
0.45 |
--- |
||||||
Zinc (mg) |
0.5 |
--- |
0.4 |
1 |
0.5 |
1.5Footnote * |
||||||
Manganese (mcg) |
5 |
--- |
1 |
100 |
1 |
100Footnote * |
||||||
Copper (mcg) |
60 |
--- |
60 |
160 |
35 |
120Footnote * |
||||||
Iodine (mcg) |
5 |
--- |
8 |
35 |
10 |
|||||||
Sodium (mg) |
20 |
60 |
25 |
50 |
20 |
60 |
||||||
Potassium (mg) |
80 |
200 |
60 |
160 |
60 |
180 |
||||||
Chloride (mg) |
55 |
150 |
50 |
160 |
50 |
160 |
||||||
Selenium (mcg) |
--- |
--- |
1.5 |
5 |
1 |
|||||||
Ratio LA:ALA |
--- |
--- |
6 |
16 |
5 |
15 |
||||||
Ratio Calcium:Phosphorus |
1.2 |
2 |
1.1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
||||||
Ratio Vitamin B6:Protein (mcg/g) |
15 |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
||||||
Ratio alpha-tocopherol:linoleic acid (IU/g) |
0.6 |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
--- |
||||||
|
||||||||||||
Appendix 7. Suggested template for stability data, infant formula
PRODUCT NAME: |
Research or Commercial Batch: |
Temperature: |
||||||||||||||||||
Other product name (if applicable): |
Batch Number: |
Proposed Shelf Life: |
||||||||||||||||||
Packaging Type: |
||||||||||||||||||||
0 month (initial time point) |
X month (middle time point) |
X month (final time point) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Label Claim | Data Points | Data Points | Data Points | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients (unit) | per 100 ml | per 100 kcal | per 100 kcal | AVERAGE | % Label Claim | per 100 kcal | AVERAGE | % Label Claim | per 100 kcal | AVERAGE | % Label Claim | per 100 kcal | AVERAGE | % Label Claim | per 100 kcal | AVERAGE | % Label Claim | per 100 kcal | AVERAGE | % Label Claim |
Energy (kcal) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Protein (g) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Total carbohydrate (g) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Total Fat (g) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Linoleic acid (LA) (mg, % fat) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (mg, % fat) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Arachidonic acid (ARA) (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (mg, % fat) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Carnitine (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Taurine (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Nucleotides (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Choline (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Inositol (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin A (IU) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin D (IU) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin E (IU) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin K (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin B1 - Thiamin (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin B2 - Riboflavin (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin B3 - Niacin (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin B5 - Pantothenic acid (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin B6 - Pyridoxin (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin B12 - Cobalamin (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Folic acid (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Biotin (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Vitamin C (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Calcium (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Phosphorus (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Magnesium (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Iron (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Zinc (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Manganese (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Copper (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Iodine (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Sodium (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Potassium (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Chloride (mg) |
||||||||||||||||||||
Selenium (mcg) |
||||||||||||||||||||