FluWatch report: April 19 to April 25, 2015 (Week 16)
Overall summary
- Influenza B continued to be the most common influenza virus circulating in Canada. Detections of influenza B appeared to have peaked in week 12.
- Influenza B is having a greater impact on adults less than 65 years of age, compared to influenza A(H3N2), which predominated earlier in the season.
- Although overall influenza activity in Canada continued to decline, elevated activity was still reported in week 16 (mostly in the Central and Atlantic provinces).
- Fewer influenza hospitalizations were reported this week compared to the previous week. The majority of hospitalizations were due to influenza A and in adults ≥65 years of age.
Are you a primary health care practitioner (General Practitioner, Nurse Practitioner or Registered Nurse) interested in becoming a FluWatch sentinel for the 2014-15 influenza season? Contact us at FluWatch@phac-aspc.gc.ca
On this page
- Influenza/ILI Activity (geographic spread)
- Influenza and Other Respiratory Virus Detections
- Antiviral Resistance
- Influenza Strain Characterizations
- Influenza-like Illness (ILI) Consultation Rate
- Influenza Outbreak Surveillance
- Pharmacy surveillance
- Sentinel Hospital Influenza Surveillance
- Provincial/Territorial Influenza Hospitalizations and Deaths
- Emerging Respiratory Pathogens
- International Influenza Reports

Download the alternative format
(PDF format, 911 KB, 10 pages)
Organization: Public Health Agency of Canada
Date published: 2015-05-01
Related Topics
Influenza/ILI Activity (geographic spread)
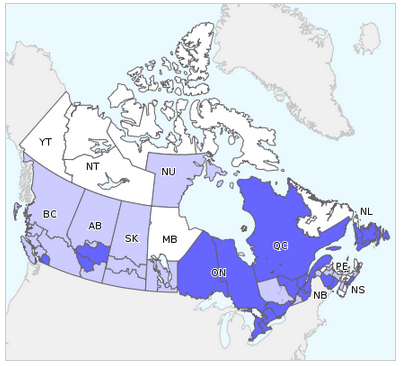
In week 16, no regions reported widespread activity. Twenty regions reported localized activity: BC, AB(2), ON(7), QC(4), NB(2), NS and NL(3). Twenty-three regions reported sporadic activity: in NU, BC(4), AB(3), SK(3), MB(4), QC(2), NB(4), NS(2). Fourteen regions reported no activity activity: in YK, NT(2), NU(2), MB, NB, NS(6), and NL.
Figure 1. Map of overall influenza/ILI activity level by province and territory, Canada, Week 16
Note: Influenza/ILI activity levels, as represented on this map, are assigned and reported by Provincial and Territorial Ministries of Health, based on laboratory confirmations, sentinel ILI rates and reported outbreaks. Please refer to detailed definitions at the end of the report. Maps from previous weeks, including any retrospective updates, are available on the Flu Activity website.
Figure 1 Map of overall influenza/ILI activity level by province and territory, Canada, Week 16 - Text Description
In week 16, no regions reported widespread activity. Twenty regions reported localized activity: BC, AB(2), ON(7), QC(4), NB(2), NS and NL(3). Twenty-three regions reported sporadic activity: in NU, BC(4), AB(3), SK(3), MB(4), QC(2), NB(4), NS(2). Fourteen regions reported no activity activity: in YK, NT(2), NU(2), MB, NB, NS(6), and NL.
Influenza and Other Respiratory Virus Detections
In week 16, the percentage positive for influenza A (1.2%) and B (11.4%) declined from the previous week (Figure 2). Influenza B remained the predominant virus in week 16, representing 90% of influenza detections. Influenza B detections appeared to have peaked in week 12 (761 detections). In the 2013-14 season, influenza B peaked in week 15 (646 detections). More influenza B has been observed to date this season (7,306) compared to the same time during the 2013-14 season (6,104). To date, 83% of influenza detections have been influenza A, and 99% of those subtyped have been A(H3N2) (Table 1). To date this season, detailed information on age and type/subtype has been received for 36,155 cases (Table 2). Adults ≥65 years of age have predominantly been affected by influenza A, accounting for 62% of influenza A detections. Influenza B, while much smaller in numbers, is mainly affecting individuals less than 65 years of age, they account for 59% of influenza B detections.
Figure 2. Number of positive influenza tests and percentage of tests positive, by type, subtype and report week, Canada, 2014-15
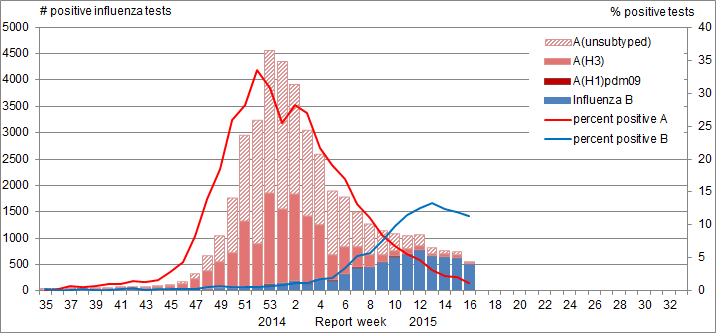
Figure 2 Number of positive influenza tests and percentage of tests positive, by type, subtype and report week, Canada, 2014-15 - Text Description
In week 16, the percentage positive for influenza A (1.2%) and B (11.4%) declined from the previous week.
In week 16, detections for all other respiratory viruses remained similar to, or decreased from, the previous week (figure 3). Overall, the detections of other respiratory viruses have been declining since peaking in week 5.
For more details, see the weekly Respiratory Virus Detections in Canada Report.
Figure 3. Number of positive laboratory tests for other respiratory viruses by report week, Canada, 2014-15
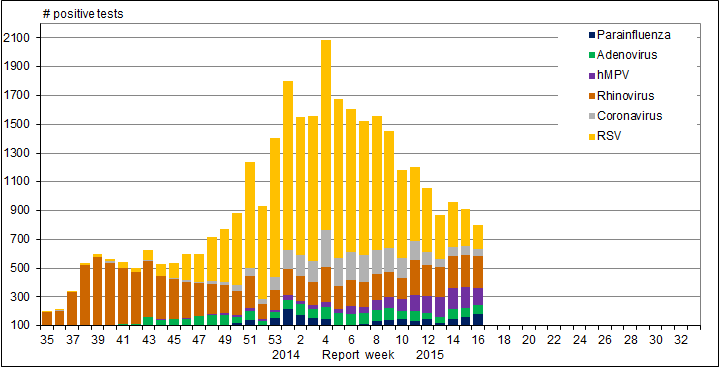 RSV: Respiratory syncytial virus; hMPV: Human metapneumovirus
RSV: Respiratory syncytial virus; hMPV: Human metapneumovirus
Figure 3 Number of positive laboratory tests for other respiratory viruses by report week, Canada, 2014-15 - Text Description
In Week 16, detections for all other respiratory viruses remained similar to, or decreased from, the previous week. Overall, the detections of other respiratory viruses have been declining since peaking in week 5.
| Reporting provincesFootnote 1 | Weekly (April 19 to April 25, 2015) | Cumulative (August 24, 2014 to April 25, 2015) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A | B | Influenza A | B | |||||||
| A Total | A(H1)pdm09 | A(H3) | A Footnote (Uns) | B Total | A Total | A(H1)pdm09 | A(H3) | A(UnS) | B Total | |
| BC | 5 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 21 | 3517 | 28 | 2626 | 863 | 385 |
| AB | 9 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 39 | 3699 | 14 | 3529 | 156 | 844 |
| SK | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 1313 | 0 | 839 | 474 | 238 |
| MB | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 1122 | 0 | 390 | 732 | 165 |
| ON | 17 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 132 | 11131 | 48 | 4698 | 6385 | 1179 |
| QC | 11 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 175 | 11408 | 4 | 422 | 10982 | 3608 |
| NB | 5 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 49 | 1193 | 0 | 192 | 1001 | 484 |
| NS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 511 | 0 | 123 | 387 | 254 |
| PE | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 131 | 1 | 123 | 2 | 1078 |
| NL | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 620 | 0 | 123 | 498 | 41 |
| Canada | 53 | 3 | 23 | 27 | 472 | 34645 | 95 | 13070 | 21479 | 7306 |
| Percentage Footnote 2 | 10.1% | 5.7% | 43.4% | 50.9% | 89.9% | 82.6% | 0.3% | 37.7% | 62.0% | 17.4% |
| Age groups (years) | Weekly April 19 to April 25, 2015 | Cumulative (August 24, 2014 to April 25, 2015) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A | B | Influenza A | B | Influenza A and B | ||||||||
| A Total | A(H1) pdm09 | A(H3) | A Footnote (Uns) | Total | A Total | A(H1) pdm09 | A(H3) | A (UnS) | Total | # | % | |
| <5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 26 | 2087 | 22 | 808 | 1257 | 469 | 2556 | 7.1% |
| 5-19 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 23 | 1782 | 6 | 956 | 820 | 683 | 2465 | 7.1% |
| 20-44 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 33 | 3433 | 16 | 1668 | 1749 | 922 | 4355 | 12.0% |
| 45-64 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 60 | 3859 | 21 | 1656 | 2182 | 1565 | 5424 | 15.0% |
| 65+ | 15 | 0 | 4 | 11 | 132 | 18697 | 15 | 7272 | 11410 | 2531 | 21228 | 58.7% |
| Unknown | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 120 | 0 | 101 | 19 | 7 | 127 | 0.4% |
| Total | 28 | 2 | 9 | 17 | 274 | 29978 | 80 | 12461 | 17437 | 6177 | 36155 | 100.0% |
| PercentageFootnote 2, | 9.3% | 7.1% | 32.1% | 60.7% | 90.7% | 82.9% | 0.3% | 41.6% | 58.2% | 17.1% | ||
Antiviral Resistance
During the 2014-2015 influenza season, the NML has tested 1,317 influenza viruses for resistance to oseltamivir and 1,313 influenza viruses for resistance to zanamivir. All viruses were sensitive to zanamivir and one influenza A(H3N2) virus was resistant to oseltamivir. A total of 1,324 influenza A viruses (99.9%) were resistant to amantadine (Table 3).
| Virus type and subtype | Oseltamivir | Zanamivir | Amantadine | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # tested | # resistant (%) | # tested | # resistant (%) | # tested | # resistant (%) | |
| A (H3N2) | 867 | 1 | 864 | 0 | 1313 | 1312 (99.9%) |
| A (H1N1) | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 12 | 12 (100%) |
| B | 440 | 0 | 439 | 0 | NATable 3 - Footnote * | NA Table 3 - Footnote * |
| TOTAL | 1317 | 1 | 1313 | 0 | 1325 | 1324 |
Influenza Strain Characterizations
During the 2014-2015 influenza season, the National Microbiology Laboratory (NML) has characterized 716 influenza viruses [181 A(H3N2), 14 A(H1N1) and 521 influenza B].
Influenza A (H3N2): When tested by hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assay (n=181), one virus was antigenically similar to A/Texas/50/2012, five showed reduced titers to A/Texas/50/2012 and 175 were antigenically similar to A/Switzerland/9715293/2013, which is the influenza A(H3N2) component recommended for the 2015 Southern Hemisphere influenza vaccine. Additionally, 1,091 A(H3N2) viruses were unable to be tested by HI assay; however, sequence analysis showed that 1,089 belonged to a genetic group that typically shows reduced titers to A/Texas/50/2012.
Influenza A(H1N1): Fourteen A(H1N1) viruses characterized were antigenically similar to A/California/7/2009.
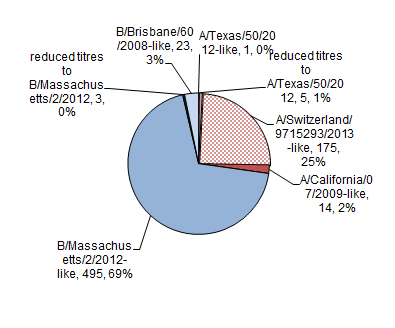
Influenza B: Of the 521 influenza B viruses characterized, 495 viruses were antigenically similar to B/Massachusetts/2/2012, three viruses showed reduced titers against B/Massachusetts/2/2012, and 23 were B/Brisbane/60/2008-like (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Influenza strain characterizations, Canada, 2014-2015, N = 716
The NML receives a proportion of the number of influenza positive specimens from provincial laboratories for strain characterization and antiviral resistance testing. Characterization data reflect the results of haemagglutination inhibition (HAI) testing compared to the reference influenza strains recommended by WHO.
The recommended components for the 2014-2015 northern hemisphere trivalent influenza vaccine include: an A/California/7/2009(H1N1)pdm09-like virus, an A/Texas/50/2012 (H3N2)-like virus, and a B/Massachusetts/2/2012-like virus (Yamagata lineage). For quadrivalent vaccines, the addition of a B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus is recommended.
The WHO has released the recommended composition of the influenza vaccine for the northern hemisphere for the 2015-2016 season. Trivalent vaccines are recommended to contain 1) an A/California/7/2009 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus 2) an A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (H3N2)-like virus, and 3) an B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus(Yamagata lineage). Quadrivalent vaccines are recommended to additionally contain a B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus (Victoria lineage).
Figure 4 Influenza strain characterizations, Canada, 2014-2015, N = 716 - Text Description
| Strain | Number of specimens | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| A/Texas/50/2012-like | 1 | 0% |
| reduced titres to A/Texas/50/2012 | 5 | 1% |
| A/California/07/2009-like | 14 | 2% |
| A/Switzerland/97 15293/2013-like | 175 | 25% |
| B/Massachusetts/2/2012-like | 495 | 69% |
| reduced titres to B/Massachusetts/2/2012 | 3 | 0% |
| B/Brisbane/60/2008-like | 23 | 3% |
Influenza-like Illness (ILI) Consultation Rate
In week 16, the national influenza-like-illness (ILI) consultation rate remained similar to the previous week at 31.9 consultations per 1,000 (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Influenza-like-illness (ILI) consultation rates by report week, compared to the 1996-97 through to 2012-13 seasons (with pandemic data suppressed), Canada, 2014-2015
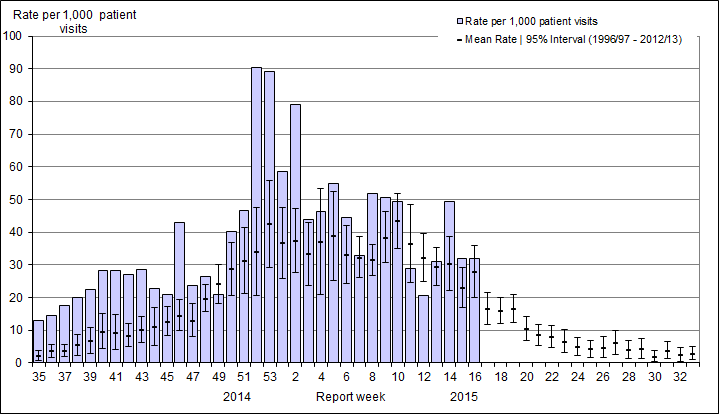
No data available for mean rate for weeks 19 to 39 for the 1996-1997 through 2002-2003 seasons. Delays in the reporting of data may cause data to change retrospectively. The calculation of the average ILI consultation rate over 17 seasons was aligned with influenza activity in each season. In BC, AB, and SK, data is compiled by a provincial sentinel surveillance program for reporting to FluWatch. Not all sentinel physicians report every week.
Figure 5 Influenza-like-illness (ILI) consultation rates by report week, compared to the 1996-97 through to 2012-13 seasons (with pandemic data suppressed), Canada, 2015-16 - Text Description
In week 16, the national influenza-like-illness (ILI) consultation rate remained similar to the previous week at 31.9 consultations per 1,000.
Influenza Outbreak Surveillance
In week 16, 17 new outbreaks of influenza were reported. Similar to previous weeks, the majority of the outbreaks occurred in the Central and Atlantic provinces. Fifteen outbreaks were reported in long-term care facilities (LTCF), and two in institutional or community settings (Figure 6). Among the outbreaks in which the influenza type was known (n=8), six outbreaks were associated with influenza B. To date this season, 1,246 outbreaks in LTCFs have been reported and the majority of those with known subtypes were attributable to A(H3N2). There have been a higher number of reported influenza outbreaks to date this season compared to the same period in previous seasons.
Figure 6: Overall number of new laboratory-confirmed influenza outbreaks by report week, Canada, 2014-2015
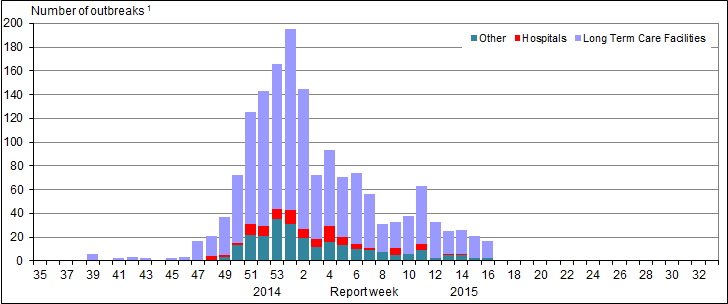
1 All provinces and territories except NU report outbreaks in long-term care facilities. All provinces and territories with the exception of NU and QC report outbreaks in hospitals. Outbreaks of influenza or influenza-like-illness in other facilities are reported to FluWatch but reporting varies between jurisdictions. Outbreak definitions are included at the end of the report.
Figure 6 Overall number of new laboratory-confirmed influenza outbreaks by report week, Canada, 2015-2016 - Text Description
| Report week | Hospitals | Long Term Care Facilities | Other |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 37 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 38 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 39 | 0 | 5 | 1 |
| 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 41 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 42 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 43 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 44 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 45 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 46 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 47 | 0 | 16 | 1 |
| 48 | 3 | 17 | 1 |
| 49 | 2 | 32 | 3 |
| 50 | 2 | 57 | 13 |
| 51 | 9 | 94 | 22 |
| 52 | 8 | 114 | 21 |
| 53 | 9 | 122 | 35 |
| 1 | 12 | 152 | 31 |
| 2 | 8 | 118 | 19 |
| 3 | 6 | 54 | 12 |
| 4 | 13 | 64 | 16 |
| 5 | 7 | 51 | 13 |
| 6 | 4 | 60 | 10 |
| 7 | 2 | 45 | 9 |
| 8 | 0 | 24 | 7 |
| 9 | 6 | 22 | 10 |
| 10 | 0 | 32 | 19 |
| 11 | 5 | 49 | 11 |
| 12 | 0 | 31 | 4 |
| 13 | 1 | 19 | 9 |
| 14 | 1 | 20 | 9 |
| 15 | 0 | 19 | 2 |
| 16 | 0 | 15 | 2 |
Pharmacy surveillance
Pharmacy surveillance for sales of influenza antivirals has ended for the 2014-2015 influenza season (Figure 7).
Figure 7. Proportion of prescription sales for influenza antivirals by age-group and week, Canada, 2014-15
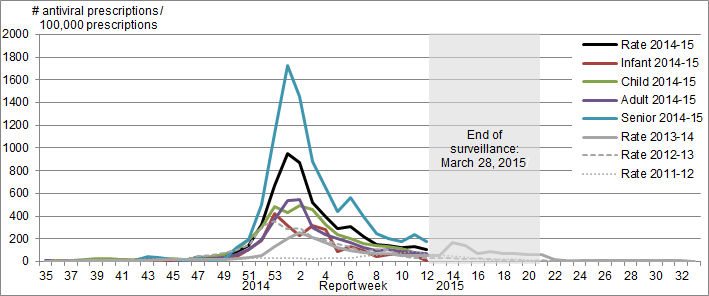
Note: Pharmacy sales data are provided to the Public Health Agency of Canada by Rx Canada Inc. and sourced from major retail drug chains representing over 2,500 stores nationwide (excluding Nunavut) in 85% of Health Regions. Data provided include the number of new antiviral prescriptions (for Tamiflu and Relenza) and the total number of new prescriptions dispensed by Province/Territory and age group. Age-groups: Infant: 0-2y, Child: 2-18y; Adult: 19-64y; Senior: ≥65y
Figure 7 Proportion of prescription sales for influenza antivirals by age-group and week, Canada, 2015-16 - Text Description
Pharmacy surveillance has ended for the 2014-15 season.
Sentinel Hospital Influenza Surveillance
Paediatric Influenza Hospitalizations and Deaths (IMPACT)
In week 16, nine laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated paediatric (≤16 years of age) hospitalizations were reported by the Immunization Monitoring Program Active (IMPACT) network. Seven cases were influenza B (Figure 8a). A greater proportion of cases have been reported with influenza B in recent weeks, following the trend in laboratory detections. Among the reported cases, two (22%) were <2 years of age, six (67%) were 2 to 9 years of age and one (11%) was 10-16 years of age. No ICU cases were reported.
To date this season, 667 hospitalizations have been reported by the IMPACT network, 508 (76%) of which were cases of influenza A. Among cases for which the influenza A subtype was reported, 99% (162/164) were A(H3N2 (Table 4). To date, 82 cases were admitted to the ICU, of which 45 (55%) were 2 to 9 years of age (Figure 9a). A total of 54 ICU cases reported to have at least one underlying condition or comorbidity. Four deaths have been reported.
Note: The number of hospitalizations reported through IMPACT represents a subset of all influenza-associated paediatric hospitalizations in Canada. Delays in the reporting of data may cause data to change retrospectively.
Adult Influenza Hospitalizations and Deaths (PCIRN)
In week 16, 11 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated adult (≥16 years of age) hospitalizations were reported by the PHAC/CIHR Influenza Research Network (CIRN) Serious Outcomes Surveillance (SOS) network. Among the cases in week 16, 8 cases (73%) were in adults over the age of 65 (Figure 8b). One death was reported in week 16 in an adult over the age of 65 years.
To date this season, 2,204 cases have been reported; 1,910 (87%) with influenza A. The majority of cases (81%) were among adults ≥65 years of age (Table 5). One hundred and sixty nine ICU admissions have been reported and 127 cases were adults ≥65 years of age. Among the 169 ICU admissions, 24 were due to influenza B (10 in adults 45 to 64 years of age and 14 in adults over the age of 65). A total of 121 ICU cases (70%) reported to have at least one underlying condition or comorbidity. Of the 118 ICU cases with known immunization status, 39 (33%) reported not having been vaccinated this season. One hundred and thirty-three deaths have been reported, 123 (92%) of the deaths were adults >65 years of age (Figure 9b).
Note: The number of hospitalizations reported through PCIRN represents a subset of all influenza-associated adult hospitalizations in Canada. Delays in the reporting of data may cause data to change retrospectively.
| Age groups | Cumulative (Aug. 24, 2014 to April 25, 2015) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A | B | Influenza A and B | ||||
| A Total | A(H1) pdm09 | A(H3) | AFootnote (Uns) | Total | # (%) | |
| 0-5m | 81 | 0 | 18 | 63 | 10 | 91 (13.6%) |
| 6-23m | 112 | 2 | 35 | 75 | 32 | 144 (21.6%) |
| 2-4y | 125 | 1 | 39 | 85 | 43 | 168 (25.2%) |
| 5-9y | 130 | 0 | 44 | 86 | 45 | 175 (26.2%) |
| 10-16y | 60 | 0 | 25 | 35 | 29 | 89 (13.3%) |
| Total | 508 | 3 | 161 | 344 | 159 | 667 |
| % Footnote 1 | 76.2% | 0.6% | 31.7% | 67.7% | 23.8% | 100.0% |
| Age groups | Cumulative (November 15, 2014 to April 25, 2015) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A | B | Influenza A and B | ||||
| A Total | A(H1) pdm09 | A(H3) | AFootnote (Uns) | Total | # (%) | |
| 16-20 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 (%) |
| 20-44 | 105 | 1 | 55 | 49 | 15 | 120 (5%) |
| 45-64 | 216 | 3 | 98 | 115 | 70 | 286 (13%) |
| 65+ | 1586 | 4 | 760 | 822 | 208 | 1794 (81%) |
| Total | 1910 | 8 | 914 | 988 | 294 | 2204 |
| % Footnote 1 | 87% | 0% | 48% | 52% | 13% | 100% |
Figure 8 - Number of cases of influenza reported by sentinel hospital networks, by week, Canada, 2014-15
8A) Paediatric hospitalizations (≤16 years of age, IMPACT)
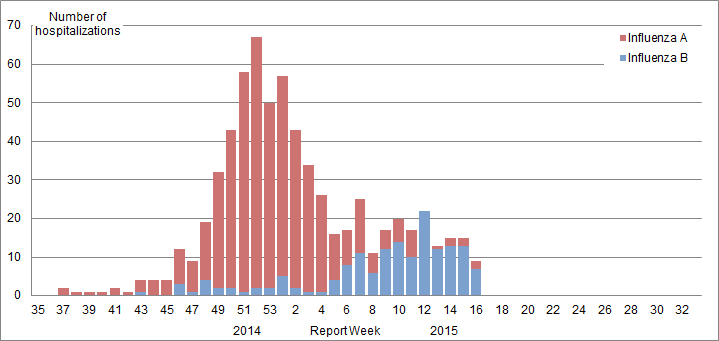
Figure 8A Number of cases of influenza reported by sentinel hospital networks, by week, Canada, 2015-16 - Text Description
| Report week | Influenza A | Influenza B |
|---|---|---|
| 35 | 0 | 0 |
| 36 | 0 | 0 |
| 37 | 2 | 0 |
| 38 | 1 | 0 |
| 39 | 1 | 0 |
| 40 | 1 | 0 |
| 41 | 2 | 0 |
| 42 | 1 | 0 |
| 43 | 3 | 1 |
| 44 | 4 | 0 |
| 45 | 4 | 0 |
| 46 | 9 | 3 |
| 47 | 8 | 1 |
| 48 | 15 | 4 |
| 49 | 30 | 2 |
| 50 | 41 | 2 |
| 51 | 57 | 1 |
| 52 | 65 | 2 |
| 53 | 48 | 2 |
| 1 | 52 | 5 |
| 2 | 41 | 2 |
| 3 | 33 | 1 |
| 4 | 25 | 1 |
| 5 | 12 | 4 |
| 6 | 9 | 8 |
| 7 | 14 | 11 |
| 8 | 5 | 6 |
| 9 | 5 | 12 |
| 10 | 6 | 14 |
| 11 | 7 | 10 |
| 12 | 0 | 22 |
| 13 | 1 | 12 |
| 14 | 2 | 13 |
| 15 | 2 | 13 |
| 16 | 2 | 7 |
Figure 8B - Number of cases of influenza reported by sentinel hospital networks, by week, Canada, 2014-15
8B) Adult hospitalizations (≥16 year of age, PCIRN-SOS)
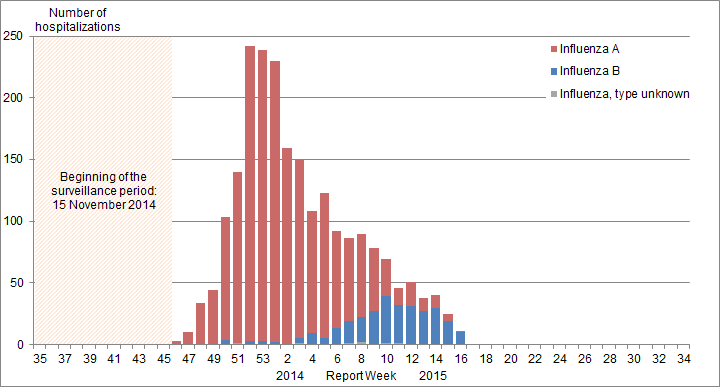 Note: Data for week 46 is based on data collected for 1 day only and do not represent the number of hospitalizations for the entire week.
Note: Data for week 46 is based on data collected for 1 day only and do not represent the number of hospitalizations for the entire week.
Figure 8B Number of cases of influenza reported by sentinel hospital networks, by week, Canada, 2015-16 - Text Description
| Report week | Influenza A | Influenza B | Untyped |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 36 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 37 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 38 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 39 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 40 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 41 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 42 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 43 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 44 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 45 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 46 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 47 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| 48 | 34 | 0 | 0 |
| 49 | 44 | 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 99 | 4 | 0 |
| 51 | 141 | 0 | 1 |
| 52 | 239 | 3 | 0 |
| 53 | 236 | 3 | 0 |
| 1 | 228 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | 160 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 145 | 4 | 1 |
| 4 | 99 | 9 | 0 |
| 5 | 118 | 5 | 0 |
| 6 | 79 | 13 | 0 |
| 7 | 67 | 17 | 1 |
| 8 | 67 | 20 | 2 |
| 9 | 49 | 26 | 0 |
| 10 | 29 | 37 | 1 |
| 11 | 14 | 29 | 1 |
| 12 | 20 | 31 | 0 |
| 13 | 11 | 27 | 0 |
| 14 | 10 | 30 | 0 |
| 15 | 6 | 19 | 0 |
| 16 | 1 | 10 | 0 |
Figure 9 - Percentage of hospitalizations, ICU admissions and deaths with influenza reported by age-group, Canada, 2014-15
9A) Paediatric hospitalizations (≤16 years of age, IMPACT)
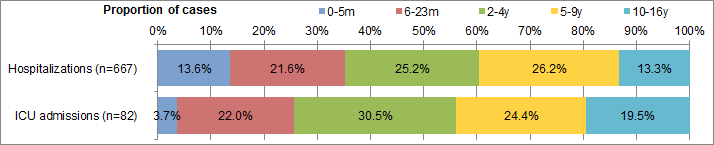
Figure 9A Percentage of hospitalizations, ICU admissions and deaths with influenza reported by age-group, Canada, 2014-15 A) Paediatric hospitalizations (≤16 years of age, IMPACT) - Text Description
| Age-group (years) | Hospitalizations(n=667) | ICU admissions(n=82) |
|---|---|---|
| 0-5m | 13.6% | 3.7% |
| 6-23m | 21.6% | 22.0% |
| 2-4y | 25.2% | 30.5% |
| 5-9y | 26.2% | 24.4% |
| 10-16y | 13.3% | 19.5% |
Figure 9 - Percentage of hospitalizations, ICU admissions and deaths with influenza reported by age-group, Canada, 2014-15
9B) Adult hospitalizations (≥16 year of age, PCIRN-SOS)
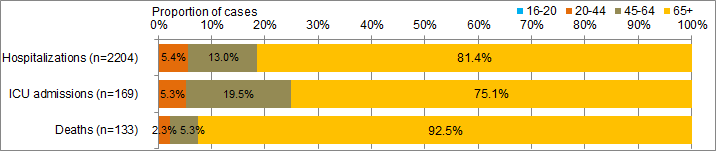
Figure 9B Percentage of hospitalizations, ICU admissions and deaths with influenza reported by age-group, Canada, 2014-15 B) Adult hospitalizations (≥16 year of age, CIRN) - Text Description
| Age-group (years) | Hospitalizations (n=2204) | ICU admissions(n=169) | Deaths (n=133) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16-20 | 0.2% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| 20-44 | 5.4% | 5.3% | 2.3% |
| 45-64 | 13.0% | 19.5% | 5.3% |
| 65+ | 81.4% | 75.1% | 92.5% |
Provincial/Territorial Influenza Hospitalizations and Deaths
In week 16, 99 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations were reported from participating provinces and territoriesootnote *, which is lower than the number reported the previous week. Of the 99 hospitalizations, 63 (64%) were due to influenza A and 63 (64%) were in patients ≥65 years of age.
Since the start of the 2014-15 season, 7,231 hospitalizations have been reported; 6,414 (89%) with influenza A. Among cases for which the subtype of influenza A was reported, 99.4% were A(H3N2). The majority of cases (71%) were ≥65 years of age (Table 6). A total of 375 ICU admissions have been reported to date: 53% (n=199) were in adults ≥65 years of age and 33% (n=123) were in adults 20-64 years. A total of 547 deaths have been reported since the start of the season: four children <5 years of age, four children 5-19 years, 33 adults 20-64 years, and 506 adults ≥65 years of age. Adults 65 years of age or older represent 93% of all deaths reported this season. Detailed clinical information (e.g. underlying medical conditions) is not known for these cases.
| Age groups | Cumulative (24 August 2014 to 25 April, 2015) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A | B | Influenza A and B | ||||
| A Total | A(H1) pdm09 | A(H3) | AFootnote (Uns) | Total | # (%) | |
| 0-4 years | 419 | 2 | 151 | 266 | 61 | 480 (7%) |
| 5-19 years | 277 | 2 | 136 | 139 | 87 | 364 (5%) |
| 20-44 years | 379 | 4 | 229 | 146 | 97 | 476 (7%) |
| 45-64 years | 608 | 7 | 256 | 345 | 112 | 720 (10%) |
| 65+ years | 4675 | 3 | 2217 | 2455 | 440 | 5115 (71%) |
| Unknown | 56 | 1 | 52 | 3 | 20 | 76 (1%) |
| Total | 6414 | 19 | 3041 | 3354 | 817 | 7231 |
| Percentage Footnote 1 | 88.7% | 0.3% | 47.4% | 52.3% | 11.3% | 100.0% |
See additional data on Reported Influenza Hospitalizations and Deaths in Canada: 2009-10 to 2014-15 on the Public Health Agency of Canada website.
Emerging Respiratory Pathogens
Human Avian Influenza
Influenza A(H7N9): Since the last FluWatch report, no new laboratory-confirmed cases of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus were reported by the World Health Organization. Globally to April 30, 2015, the WHO reported a total of 651 laboratory-confirmed human cases with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus, including 225 deaths. Documents related to the public health risk of influenza A(H7N9), as well as guidance for health professionals and advice for the public is updated regularly on the following websites:
Influenza A(H5N6): Since the last FluWatch report, no new cases of human infection with avian influenza A (H5N6) virus from China has been reported by the World Health Organization. Globally to April 23, 2015, the WHO has been informed of a total of three cases of avian influenza A (H5N6) virus, including two deaths.
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)
Since the last FluWatch report, four new laboratory-confirmed cases of MERS-CoV have been reported by the World Health Organization. Globally, from September 2012 to April 30, 2015, the WHO has reported a total of 1,110 laboratory-confirmed cases of infection with MERS-CoV, including 422 deaths. All cases have either occurred in the Middle East or have had direct links to a primary case infected in the Middle East. The public health risk posed by MERS-CoV in Canada remains low (see the PHAC Assessment of Public Health Risk) and for the latest global risk assessment posted by the WHO on February 5, 2015: WHO MERS-CoV.
Documents related to the public health risk of MERS-CoV, as well as guidance for health professionals and advice for the public is updated regularly on the following websites:
Avian Influenza A(H5)
The Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) is continuing its investigation into the second outbreak of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N2 virus in Oxford County, Ontario. To date, there has been three infected commercial premises. Individual quarantines and Avian Influenza Control Zones have been established. No human cases have been reported. Avian influenza viruses do not pose risks to food safety when poultry and poultry products are properly handled and cooked. Avian influenza rarely affects humans that do not have consistent contact with infected birds. Further information on the outbreak is provided on the following CFIA website:
International Influenza Reports
- World Health Organization influenza update
- World Health Organization FluNet
- WHO Influenza at the human-animal interface
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention seasonal influenza report
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control - epidemiological data
- South Africa Influenza surveillance report
- New Zealand Public Health Surveillance
- Australia Influenza Report
- Pan-American Health Organization Influenza Situation Report
FluWatch definitions for the 2014-2015 season
Abbreviations: Newfoundland/Labrador (NL), Prince Edward Island (PE), New Brunswick (NB), Nova Scotia (NS), Quebec (QC), Ontario (ON), Manitoba (MB), Saskatchewan (SK), Alberta (AB), British Columbia (BC), Yukon (YT), Northwest Territories (NT), Nunavut (NU).
Influenza-like-illness (ILI): Acute onset of respiratory illness with fever and cough and with one or more of the following - sore throat, arthralgia, myalgia, or prostration which is likely due to influenza. In children under 5, gastrointestinal symptoms may also be present. In patients under 5 or 65 and older, fever may not be prominent.
ILI/Influenza outbreaks
- Schools:
-
Greater than 10% absenteeism (or absenteeism that is higher (e.g. >5-10%) than expected level as determined by school or public health authority) which is likely due to ILI.
Note: it is recommended that ILI school outbreaks be laboratory confirmed at the beginning of influenza season as it may be the first indication of community transmission in an area. - Hospitals and residential institutions:
- two or more cases of ILI within a seven-day period, including at least one laboratory confirmed case. Institutional outbreaks should be reported within 24 hours of identification. Residential institutions include but not limited to long-term care facilities ( LTCF) and prisons.
- Workplace:
- Greater than 10% absenteeism on any day which is most likely due to ILI.
- Other settings:
- two or more cases of ILI within a seven-day period, including at least one laboratory confirmed case; i.e. closed communities.
Note that reporting of outbreaks of influenza/ILI from different types of facilities differs between jurisdictions.
Influenza/ILI activity level
1 = No activity: no laboratory-confirmed influenza detections in the reporting week, however, sporadically occurring ILI may be reported
2 = Sporadic: sporadically occurring ILI and lab confirmed influenza detection(s) with no outbreaks detected within the influenza surveillance region Footnote †
3 = Localized:
- evidence of increased ILIFootnote * and
- lab confirmed influenza detection(s) together with
- outbreaks in schools, hospitals, residential institutions and/or other types of facilities occurring in less than 50% of the influenza surveillance regionFootnote †
4 = Widespread:
- evidence of increased ILIFootnote * and
- lab confirmed influenza detection(s) together with
- outbreaks in schools, hospitals, residential institutions and/or other types of facilities occurring in greater than or equal to 50% of the influenza surveillance regionFootnote †
Note: ILI data may be reported through sentinel physicians, emergency room visits or health line telephone calls.
We would like to thank all the Fluwatch surveillance partners who are participating in this year's influenza surveillance program.