Archived Farm to Fork: FoodNet Canada 2015 Results
Download the alternate format
(PDF format, 239 KB, 1 pages)
Organization: Public Health Agency of Canada
Type: Infographic
ISBN: 978-0-660-08752-8
Published: 2017-10-27
Related topics
Public health and food safety partners working together to identify the primary sources of major enteric pathogens that are contributing to human illness by looking for these common pathogens across the farm-to-fork continuum: food, animal, and the environment.
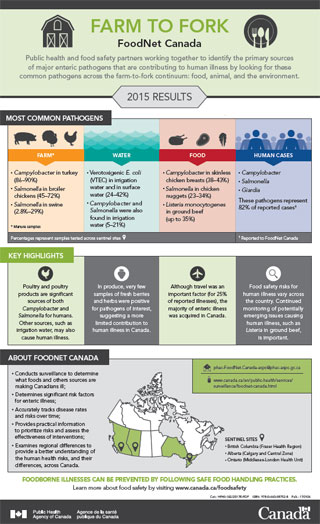
Most common pathogens
Percentages represent samples tested across sentinel sites.
FarmFootnote 1 Footnote 2
- Campylobacter in turkey (86-90%)
- Salmonella in broiler chickens (45-72%)
- Salmonella in swine (2.8%-29%)
WaterFootnote 2
- Verotoxigenic E. coli (VTEC) in irrigation water and in surface water (24-42%)
- Campylobacter and Salmonella were also found in irrigation water (5-21%)
FoodFootnote 2
- Campylobacter in skinless chicken breasts (38-43%)
- Salmonella in chicken nuggets (23-34%)
- Listeria monocytogenes in ground beef (up to 35%)
Human cases
- Campylobacter
- Salmonella
- Giardia
These pathogens represent 82% of reported cases.Footnote 3
Key highlights
Poultry and poultry products are significant sources of both Campylobacter and Salmonella for humans. Other sources, such as irrigation water, may also cause human illness.
In produce, very few samples of fresh berries and herbs were positive for pathogens of interest, suggesting a more limited contribution to human illness in Canada.
Although travel was an important factor (for 25% of reported illnesses), the majority of enteric illness was acquired in Canada.
Food safety risks for human illness vary across the country. Continued monitoring of potentially emerging issues causing human illness, such as Listeria in ground beef, is important.
About FoodNet Canada
- Conducts surveillance to determine what foods and others sources are making Canadians ill.
- Determines significant risk factors for enteric illness.
- Accurately tracks disease rates and risks over time.
- Provides practical information to prioritize risks and assess the effectiveness of interventions.
- Examines regional differences to provide a better understanding of the human health risks, and their differences, across Canada.
Sentinel sites
- British Columbia (Fraser Health Region)
- Alberta (Calgary and Central Zone)
- Ontario (Middlesex-London Health Unit)
Foodborne illnesses can be prevented by following safe food handling practices. Learn more about food safety by visiting www.canada.ca/foodsafety.
- Footnote 1
-
Manure samples
- Footnote 2
-
Percentages represent samples tested across sentinel sites
- Footnote 3
-
Reported to FoodNet Canada.