Lyme disease surveillance in Canada: Annual edition 2019 (infographic)
Download in PDF format
(PDF format, 1,177 Kb, 1 page)
- Organization: Public Health Agency of Canada
- Date published: October 2023
What is Lyme disease?
- Lyme disease is a bacterial infection transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick.
- Early clinical manifestations can present as flu-like symptoms including joint pain and/or bull's eye rash. If untreated, individuals may experience cardiac and neurologic manifestations and arthritis.
What is the risk?
- Lyme disease is the most frequently reported vector-borne disease in Canada.
- The greatest risk of acquiring Lyme disease occurs in regions where populations of ticks carrying the bacteria, Borrelia burgdorferi, have become established.
Who's at greater risk?
- Children aged 5-14 years
- Adults aged 55-79 years
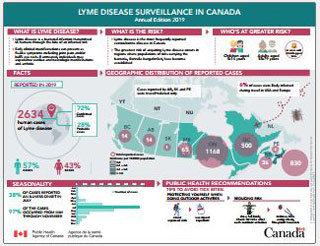
Facts reported in 2019
- 2,634 cases of Lyme disease were reported, of which 72% were confirmed cases and 28% probable cases
- 57% cases were males
- 43% cases were females
Geographic distribution of reported cases
| Province | Number of reported Lyme disease cases |
|---|---|
| British Columbia | 14 |
| Alberta | 14 |
| Saskatchewan | 1 |
| Manitoba | 65 |
| Ontario | 1,168 |
| Quebec | 500 |
| New Brunswick | 36 |
| Nova Scotia | 830 |
| Prince Edward Island | 6 |
| Newfoundland & Labrador | 0 |
| Yukon | 0 |
| Northwest Territories | 0 |
| Nunavut | 0 |
Cases reported by Alberta, Saskatchewan and Prince Edward Island were travel−related only. 6% of reported cases were likely infected during travel in the USA or Europe.
Seasonality
- 38% of cases reported illness onset in July
- 97% of the cases occurred from May through November
Public health recommendations: Tips to avoid tick bites
Protecting yourself when doing outdoor activity:
- cover exposed skin
- use insect repellent
Reducing risk:
- do a full-body check for ticks after each outdoor activity
- remove ticks using clean, fine-tipped tweezers