Original quantitative research – Analysis of the geographical accessibility of vape shops in the vicinity of Quebec’s secondary and college educational institutions
Health Promotion and Chronic Disease Prevention in Canada
Éric Robitaille, PhD Author reference 1Author reference 2; Pascale Bergeron, MSc Author reference 1; Maxime Houde, MSc Author reference 1Author reference 3
https://doi.org/10.24095/hpcdp.39.8/9.01
This article has been peer reviewed.
Author references:
- Author reference 1
-
Institut national de santé publique du Québec, Montréal, Quebec, Canada
- Author reference 2
-
Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, École de santé publique de l’Université de Montréal, Montréal, Quebec, Canada
- Author reference 3
-
Centre urbanisation culture société, Institut national de la recherche scientifique, Montréal, Quebec, Canada
Correspondence: Éric Robitaille, Institut national de santé publique du Québec, 190 Crémazie Blvd. East, Montréal, Quebec H2E 1P2; Email: eric.robitaille@inspq.qc.ca
Abstract
Introduction: A significant proportion of secondary school students and young adults in Quebec have experimented with electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes). Both personal and environmental factors have been associated with the use of vaping products by youth. Geographical accessibility to the points of sale of these products may be one of these factors. The purpose of this study is to develop a profile of the spatial distribution of stores specializing in the sale of vaping products (vape shops) in the vicinity of secondary schools, colleges and CEGEPs in the province of Quebec.
Methods: We calculated the accessibility of businesses to account for geographical exposure. Analyses were conducted to provide a snapshot of the situation in Quebec and to identify associations between the characteristics of educational institutions and geographical accessibility to vape shops.
Results: A total of 299 vape shops were identified. Colleges are closer to a vape shop (median distance: 1.2 km) than are secondary schools (median distance: 2.3 km). Large private colleges located in urban areas are closer to specialized vape shops. Medium or large private secondary schools located in urban and more advantaged areas are also closer to a specialized vape shop.
Conclusion: This study is a step in developing an understanding of the location of vaping product shops and their geographical accessibility to young people. Important to consider is the geographical accessibility of young people to non-specialized shops that also sell e-cigarettes and then any potential connections between geographical accessibility to such non-specialized shops and the use of vaping products by young people.
Keywords: electronic cigarette, e-cigarette, vaping, Geographic Information System (GIS), school, adolescents, young adults
Highlights
- In Quebec, we identified 299 points of sale specializing in vaping products (vape shops).
- Colleges are closer to a vape shop (median distance: 1.2 km) than secondary schools (median distance: 2.3 km).
- Area deprivation was not associated with the access to points of sale near college-level institutions.
- Quebec students attending private educational institutions, both college and secondary schools, and institutions located in urban areas have greater geographical accessibility to shops specializing in vaping products.
Introduction
Experimentation with electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) is widespread among secondary school students and young adults in Quebec. In 2014–2015, 27% of secondary school students in Quebec reported having used e-cigarettes in their lifetime, a proportion higher than in Canada overall (15% of students), and 8% reported having used them within the last 30 days.Footnote 1 The same trends were observed in 2016–2017.Footnote 2 Of all the 18–24 year olds in Quebec in 2015, 32% had used e-cigarettes in their lifetime and 8% had used them recently.Footnote 1 Moreover, while the regular use of e-cigarettes among non-smoking adults over 35 years of age is a marginal phenomenon, a significant proportion of non-smokers among secondary school students use this product.Footnote 1 Recent longitudinal studies suggest that e-cigarette use among non-smoking youth may be an additional risk factor for smoking initiation.Footnote 3Footnote 4Footnote 5Footnote 6
Both personal and environmental factors have been associated with the use of vaping products by young people.Footnote 7 Some studies suggest that, like tobacco products, geographical accessibility to the point of sale of these products may be one of the factors associated with their use. Access to as well as visibility of tobacco products through points of sale have been associated with their use among youth.Footnote 8,Footnote 9 Some American studies suggest that the same could be true for vaping products.Footnote 10Footnote 11Footnote 12 Recent scientific investigations have focused on improving understanding of the spatial distribution of points of sale for vaping products in the USA,Footnote 13,Footnote 14 particularly in the vicinity of educational institutions.Footnote 10Footnote 11Footnote 12,Footnote 15,Footnote 16
Two US studies examined the impact of the geographical accessibility of the points of sale of vaping products on their use. One of these studies included shops specializing in the sale of vaping products alone (vape shops),Footnote 10,Footnote 11 while the other included both vape shops and tobacco outlets that also sell e-cigarettes.Footnote 12 The results of these analyses indicate a positive association between greater availability in shops selling vaping products that are near schools and the use of these products by students.
In Quebec as well as the rest of Canada, e-cigarettes are sold both in some non-specialized shops (such as convenience stores and gas stations) and in specialized shops (vape shops). In Quebec, points of sale specializing in vaping products, which are not accessible to minors, are authorized to display their products only indoors. However, since these shops remain visible from the outside, frequent exposure to them could provide an incentive for young people to use vaping products, for instance by increasing the perception of the accessibility of these products, a factor associated with e-cigarette use among secondary school students in Canada.Footnote 17 Little data is currently available to capture this exposure in Quebec. Quebec organizations involved in tobacco control and public health have already mentioned the lack of valid information on the location of e-cigarette points of sale.Footnote 18,Footnote 19
An analysis of the spatial distribution of specialized vape shops that are in the vicinity of Quebec educational institutions (secondary schools and colleges / CEGEPsFootnote *) will provide a better understanding of the geographical exposure of young people and young adults to the places where these products are sold. It will represent a first step in the development of knowledge on the geographical accessibility of young people to shops selling vaping products and the potential impact of this accessibility on the use of these products. Our article presents part of this analysis, which will be published in its entirety and available on the Institut national de santé publique du Québec website.Footnote 20
Documenting the presence of specialized vape shops that are in the vicinity of secondary schools is important, as the school is the public place most frequented by adolescents. Colleges and CEGEPs are also attended by a significant proportion of minors, and the young adults who study there are also a priority for prevention of tobacco use in Quebec.Footnote 21 Since November 2017, these post-secondary institutions have been required to have adopted a policy aimed at creating smoke-free environments.
Methods
Two steps were necessary to draw a portrait of geographical accessibility to specialized vaping product stores near educational institutions in Quebec: the development of a georeferenced directory of specialized vaping product shops in Quebec and of a georeferenced directory of educational institutions.
Directory of points of sale
Two main data sources were used to create the Quebec directory of stores specializing in vaping products: a list of stores from the Ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux (MSSS) and a list based on an online search of business directories (via Yelp and Google). Figure 1 illustrates this process.
Figure 1. Steps in building the Quebec directory of points of sale specializing in vaping products
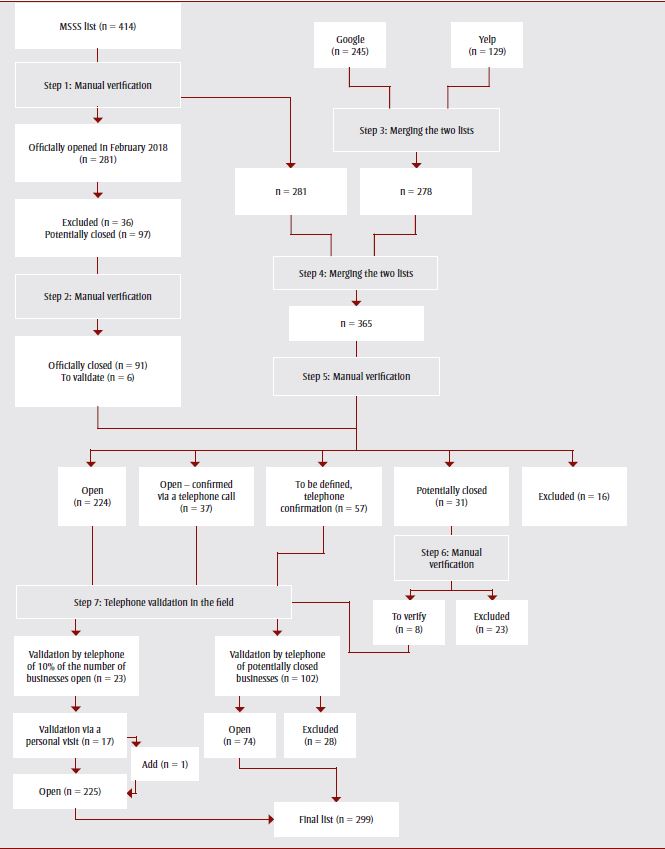
Text Description - Figure 1:Robitaille
The final list of the Quebec directory of stores specializing in vaping products included 299 points of sale. The flowchart depicting the steps of the store selection process is shown in this figure, as follows:
- The first data source was the MSSS list (n= 414), which initiated Step 1: Manual verification, as the list is not updated regularly. Step 1 yielded 281 stores officially opened in February 2018. Of those, 36 were excluded and 97 were potentially closed.
- Step 2: Manual verification involved the verification of the potentially closed stores in Step 1, which resulted in 91 officially closed and 6 to validate.
- The second data source involved the online search engines Google and Yelp. Google yielded 245 results and Yelp yielded 129 results, which initiated Step 3: Merging the two lists for a total of 278.
- Step 4: Merging the two lists involved the addition of the results from both data sources (MSSS list and online search engines), which resulted in a total of 365 stores.
- Step 5: Manual verification resulted in the following: 224 open, 37 open – confirmed via a telephone call, 57 to be defined, telephone confirmation, 31 potentially closed, and 16 excluded.
- Step 6: Manual verification involved the verification of the 31 potentially closed stores from step 5, which resulted in 8 to verify and 23 excluded.
- Step 7: Telephone validation in the field involved the verification of the 224 open stores, 37 open – confirmed via telephone call, 57 to be defined, telephone confirmation (from Step 5) and the 8 potentially closed stores to verify (from Step 6). The telephone validation was conducted as follows: 10% of the number of businesses open (n = 23) underwent validation by telephone. Of those, 17 underwent validation via a personal visit, to which n = 1 was added, for a total of 225 open stores. The potentially closed businesses (n = 102) underwent validation by telephone. Of those, 74 were open and 28 were excluded.
Adding the total number of open stores resulted in the final list of 299 stores.
The list of 414 specialized vape shops supplied by the MSSS includes those that, after the adoption in 2015 of the province's Tobacco Control Act, applied to continue displaying their products inside their place of business, as permitted by the Act for establishments meeting certain criteria.Footnote 22 As this list is not updated regularly, we verified whether the 414 vaping specialty shops were still in business using various online tools (Google Street View, Google, Yelp, Yellow Pages, Facebook, the online search tool of the Registraire des entreprises). In doing so, we reduced the list to 281 stores currently selling vaping products alone (Figure 1).
In the meantime, we conducted an online search to identify specialized vape shops open in Quebec at the time of our study (details of online search available on request), via the Yelp and Google search engines. This methodology is based on the fact that government lists of the shops selling vaping products are rarely up-to-date.Footnote 10,Footnote 13,Footnote 16,Footnote 23 We obtained a list of 278 shops (Figure 1).
We merged these two lists (the MSSS and online search engine lists) and completed a final check of all 365 businesses found using the Google Street View online search engine and the Quebec Registraire des entreprises tool for some businesses, and telephone calls or a field visit for others (Figure 1). This data collection and verification process made it possible to identify 299 Quebec-based points of sale specialized exclusively in selling vaping products at the time of our study. These businesses were then geolocated using the Addresses Quebec website; (n = 273) via their respective address or using Google Earth ; (n = 26).
Directory of institutions
For this analysis, we used files developed by the Ministère de l’éducation et de l’enseignement supérieur (Quebec Department of Education and Higher Education, MEES) that give the location of educational institutions in the Quebec school system to draw up lists of the secondary and college-level educational institutions.
The MEES list of colleges obtained from the Quebec government’s open data website identified 170 colleges at the time of this study, while the list of secondary schools includes 729 schools that were geolocated using their geographic coordinates (provided in the MEES list).
Institutional characteristics
In addition to the level of education (college or secondary school), we used two institutional characteristics in our analyses: the educational system (private or public) and the size of the student population. We also took into account the characteristics of the location of the institutions, namely the level of deprivation of the area in which the institutions are located as well as the rural or urban nature of the region.
Institutions were broken down into four categories based on the size of their student population: very small, small, medium and large.
Each educational institution was assigned a dissemination area identifier based on its location. We linked this information to a material deprivation index used in public health surveillance.Footnote 24 This index is composed of indicators from Statistics Canada’s 2011 National Household Survey: the proportion of people aged 15 and over without a secondary school certificate or diploma; the proportion of people aged 15 and over who are employed; and the average income of people aged 15 and over. We assigned a quintile from the material deprivation indexFootnote 24 to the area in which each educational institution was located. We then divided the institutions into those in advantaged environments (quintiles 1, 2 and 3) and those in disadvantaged environments (quintiles 4 and 5).
We defined the rural or urban character of the area in which the institution was located based on whether it is located within or outside a population centre.Footnote †
Dependent variable
The dependent variable is a measure of geographical accessibility, that is, proximity to points of sale,Footnote 26 and corresponds to the distance (in metres) from an establishment to the nearest vape shop. This distance was calculated on the basis of the road network, using ArcGIS software version 10.5.1 (Esri Canada, Toronto, ON).
Statistical analyses
First, we conducted descriptive analyses in order to obtain the distribution of the variable of interest (distance in metres to the nearest shop) according to the various variables related to the characteristics of the educational institutions and their location. Subsequently, univariate and multivariate generalized linear models were used to measure the associations between the distance to the nearest shop and the characteristics of the institutions. Schools with missing data were excluded from the analysis of generalized linear models in order to use the same samples for model construction.
These statistical analyses were intended to identify associations to extract the type of institution and the category of student population, as these students are more exposed to the presence of a specialized shop near their educational institution.Footnote 27 We used a bottom-up step selection starting from an empty model and adding independent variables. Using the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC), we were able to select the model that best explained the data.Footnote 28 We used a logarithmic function to correct the asymmetry in the distribution of the dependent variable and reduce the weight dedicated to extreme values in the estimate of the parameters of the regression models. Multivariate statistical analyses were performed with SPSS version 19 (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
This study identified 299 points of sale specializing exclusively in vaping prod¬ucts distributed across Quebec (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Spatial distribution of the 299 businesses specializing in the sale of vaping products in Quebec
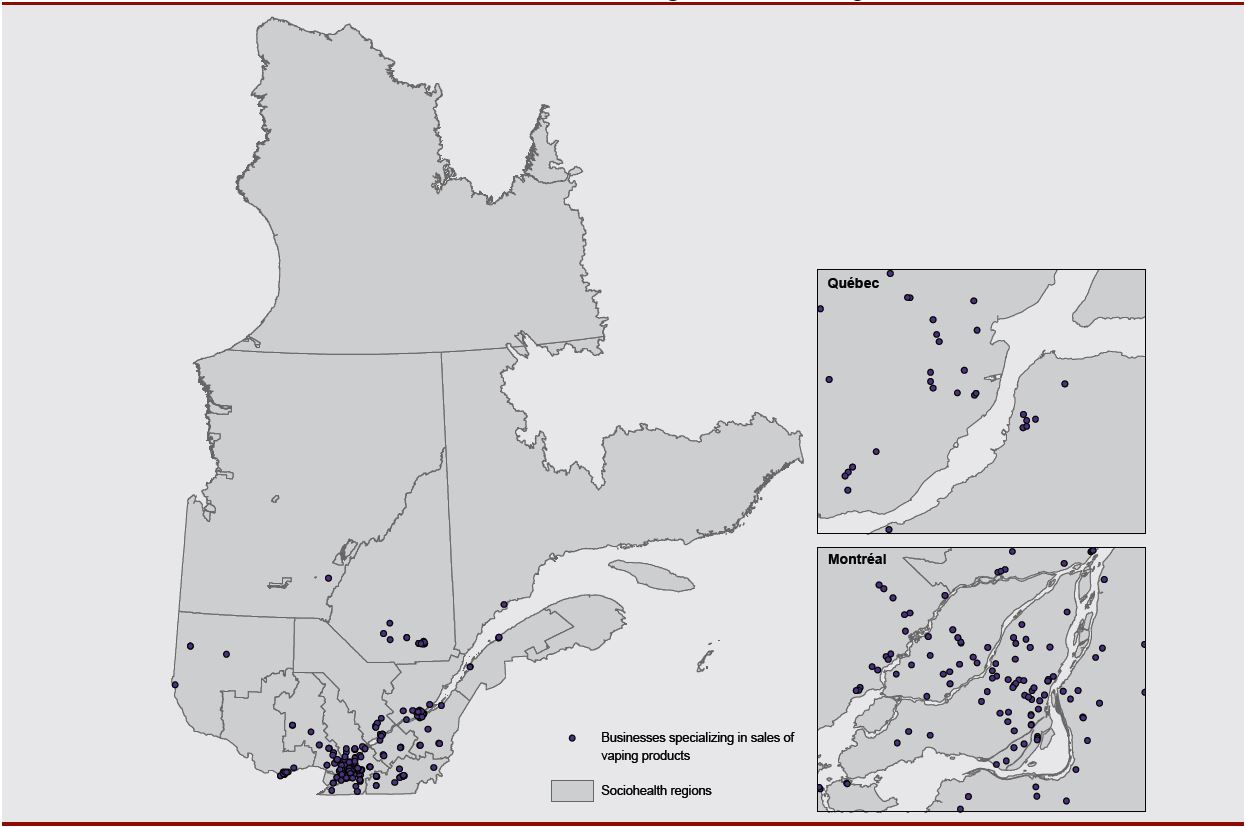
Sources: MSSS, 2017; Yelp, 2018; Google, 2018. Compilation: INSPQ, 2018.
Text Description - Figure 2
| Location number | Postal code | X coordinate | Y coordinate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | G0A 4V0 | −7943084.124511710000000 | 5918642.913591200000000 |
| 2 | J4B 6P5 | −8174593.548616300000000 | 5715038.963427020000000 |
| 3 | H2C 1P8 | −8199740.049535550000000 | 5709783.925348480000000 |
| 4 | J7V 4W7 | −8232910.997549550000000 | 5683910.740677430000000 |
| 5 | J7V 7X4 | −8232744.056368360000000 | 5683807.561150480000000 |
| 6 | J7C 2M5 | −8224670.224461010000000 | 5728597.176530020000000 |
| 7 | G3K 1L2 | −7949366.970929380000000 | 5918402.187769440000000 |
| 8 | J5W 4N7 | −8173446.355898700000000 | 5755578.585306560000000 |
| 9 | G6E 1M8 | −7907713.226943570000000 | 5853440.262322360000000 |
| 10 | H7G 2W2 | −8204180.055037080000000 | 5712908.249710310000000 |
| 11 | J8T 2R9 | −8426565.632271090000000 | 5694676.245181050000000 |
| 12 | H2Z 1S5 | −8189230.430800800000000 | 5701027.602579600000000 |
| 13 | J7E 2W3 | −8218670.739114220000000 | 5723016.038024210000000 |
| 14 | J2K 2Y7 | −8098374.477321810000000 | 5652777.458429940000000 |
| 15 | J7G 2T4 | −8219655.812383850000000 | 5718885.233355940000000 |
| 16 | G6S 1C1 | −8006841.452898270000000 | 5789922.639107780000000 |
| 17 | G8K 2X8 | −8065826.031773620000000 | 6216628.419524580000000 |
| 18 | J1G 1E4 | −7999862.493382070000000 | 5685967.208638910000000 |
| 19 | G7G 2H1 | −7914083.111119190000000 | 6182325.918478710000000 |
| 20 | J7V 2K7 | −8238989.419231300000000 | 5682611.621291990000000 |
| 21 | J7C 4K6 | −8225774.667450220000000 | 5729473.596387220000000 |
| 22 | J1E 2X4 | −8000984.924671770000000 | 5688494.706203130000000 |
| 23 | J2S 4P2 | −8120073.924361320000000 | 5720620.002873380000000 |
| 24 | G6V 6Y8 | −7922871.163226140000000 | 5908894.087273490000000 |
| 25 | J3L 4W7 | −8153723.875193550000000 | 5690911.159802670000000 |
| 26 | J8C 1K1 | −8269016.013843020000000 | 5787766.612446060000000 |
| 27 | J3L 1X3 | −8159775.886110910000000 | 5693482.197731570000000 |
| 28 | H2J 1Y4 | −8190665.585346240000000 | 5705293.611197190000000 |
| 29 | J6E 4R4 | −8175198.407101750000000 | 5784860.380094010000000 |
| 30 | J6W 4P7 | −8198530.524835300000000 | 5732452.357285710000000 |
| 31 | J4K 3S6 | −8181889.956072480000000 | 5703413.375835940000000 |
| 32 | G1G 3Y4 | −7935139.371404420000000 | 5921946.970945900000000 |
| 33 | J3V 5J1 | −8164866.892709470000000 | 5704928.149703250000000 |
| 34 | G9P 1M2 | −8098542.113953270000000 | 5864705.274499960000000 |
| 35 | G9A 4S6 | −8075390.838331470000000 | 5835432.471596150000000 |
| 36 | J2S 6G1 | −8121860.557399430000000 | 5720305.690826950000000 |
| 37 | J2C 5S6 | −8071531.855421920000000 | 5762663.326858940000000 |
| 38 | G7A 2T2 | −7935866.839395150000000 | 5899668.340418470000000 |
| 39 | G7H 5N6 | −7910004.062090190000000 | 6174285.361019300000000 |
| 40 | J7M 1E7 | −8205462.254386230000000 | 5741250.925917790000000 |
| 41 | H2G 1A5 | −8193710.064090690000000 | 5707696.934382130000000 |
| 42 | H2K 4C7 | −8187864.477891350000000 | 5704326.525488040000000 |
| 43 | J1E 2T1 | −8000883.429506130000000 | 5686072.487947280000000 |
| 44 | G5L 1S8 | −7628273.717226690000000 | 6182269.132110170000000 |
| 45 | J0K 2T0 | −8205473.003020780000000 | 5774760.864055810000000 |
| 46 | J8P 1B9 | −8421382.726833760000000 | 5698051.142431130000000 |
| 47 | G3L 1H6 | −7996587.763452360000000 | 5924002.042318580000000 |
| 48 | J1E 3C9 | −7998547.249239210000000 | 5686472.231417160000000 |
| 49 | H1B4A2 | −8182660.354476160000000 | 5723285.291037180000000 |
| 50 | H2X 3K3 | −8188962.102462510000000 | 5702971.871293670000000 |
| 51 | G9N 0A2 | −8098593.142752360000000 | 5869985.260155900000000 |
| 52 | J8X 3J2 | −8214427.566556010000000 | 5717651.603101800000000 |
| 53 | H3H 2P3 | −8190860.237811990000000 | 5699775.652967570000000 |
| 54 | H7S 1M9 | −8207306.609537130000000 | 5711321.377700520000000 |
| 55 | H8N 1T8 | −8196541.704484550000000 | 5689195.367489510000000 |
| 56 | J4J 3X5 | −8180164.036756680000000 | 5705347.627549310000000 |
| 57 | H7M 2P6 | −8206897.663669600000000 | 5716156.291256790000000 |
| 58 | J2G 2V5 | −8095831.288079290000000 | 5684705.035648830000000 |
| 59 | H7T 1L1 | −8210978.791992750000000 | 5708988.933266450000000 |
| 60 | H7M 2P7 | −8206987.268586060000000 | 5716418.399470340000000 |
| 61 | G7A 1C8 | −7935936.146381770000000 | 5895094.793429050000000 |
| 62 | H3H 1M2 | −8190898.466836090000000 | 5699548.401888580000000 |
| 63 | H2H 1J2 | −8190248.588989360000000 | 5705917.471259590000000 |
| 64 | H2B 1H6 | −8198998.979725860000000 | 5711490.819466770000000 |
| 65 | H2G 1L9 | −8192626.101135750000000 | 5707575.690846870000000 |
| 66 | G7K 1E1 | −7915365.646203810000000 | 6173091.079665640000000 |
| 67 | G3K 0R6 | −7948760.657032560000000 | 5919234.868841710000000 |
| 68 | J5W 3E1 | −8173582.430000940000000 | 5752614.261332330000000 |
| 69 | J8V 1E5 | −8432216.047464980000000 | 5698721.555920770000000 |
| 70 | J3B 6S4 | −8154829.177281030000000 | 5667943.435920500000000 |
| 71 | J6K 1C5 | −8206985.771522520000000 | 5678164.117736410000000 |
| 72 | G2M 1K8 | −7937071.658144160000000 | 5924958.583997230000000 |
| 73 | J1H 4S8 | −8003032.490716250000000 | 5684238.129958290000000 |
| 74 | G8L 1X4 | −8040516.883315900000000 | 6254263.051313110000000 |
| 75 | J7V 2L4 | −8239238.940530720000000 | 5682949.503569080000000 |
| 76 | J9H 1A2 | −8441628.359875470000000 | 5683925.048197090000000 |
| 77 | J7R 2L8 | −8225964.574536580000000 | 5709860.386696260000000 |
| 78 | J0T 1T0 | −8334547.908263990000000 | 5846520.185385210000000 |
| 79 | H4N 1C8 | −8200905.594324800000000 | 5705060.338429350000000 |
| 80 | G9N 2J4 | −8097447.493124020000000 | 5869760.245870360000000 |
| 81 | J3G 5P3 | −8149419.163928080000000 | 5710872.820312440000000 |
| 82 | G6G 6K2 | −7939001.789338840000000 | 5796635.528774830000000 |
| 83 | G7X 6L8 | −7931943.112520730000000 | 6176084.035135970000000 |
| 84 | J0N 1H0 | −8216554.314027160000000 | 5742577.810306400000000 |
| 85 | G1M 3H6 | −7931888.148271090000000 | 5912453.874695760000000 |
| 86 | G1J 1Y4 | −7927727.708194090000000 | 5916794.550997230000000 |
| 87 | J5T 2H7 | −8158060.011374000000000 | 5762446.723078540000000 |
| 88 | J3X 1R4 | −8174154.149884640000000 | 5730834.880600140000000 |
| 89 | J1J 2H1 | −8007881.806514290000000 | 5684402.136714570000000 |
| 90 | G1V 1V3 | −7936778.883409780000000 | 5906458.485057660000000 |
| 91 | H7X 2Y9 | −8214677.603535990000000 | 5703975.129551510000000 |
| 92 | G5R 3A9 | −7740799.002852990000000 | 6079148.140488870000000 |
| 93 | J0L 1C0 | −8152798.313465590000000 | 5757638.732013230000000 |
| 94 | J3T 1C4 | −8083607.465668540000000 | 5816948.822766070000000 |
| 95 | G6G 2S4 | −7936607.870165750000000 | 5795514.494340520000000 |
| 96 | H7E 2B5 | −8200823.087899080000000 | 5715200.084634180000000 |
| 97 | J0N 1P0 | −8230030.036232040000000 | 5705910.332567790000000 |
| 98 | G5R 4C2 | −7742101.611737160000000 | 6077688.598783530000000 |
| 99 | G8Y 4R9 | −8080458.374262910000000 | 5834883.435425960000000 |
| 100 | J7K 1Y4 | −8193055.878216380000000 | 5739106.974728190000000 |
| 101 | J6A 2R9 | −8177184.043188930000000 | 5737167.836363170000000 |
| 102 | G1X 1R4 | −7938866.433646970000000 | 5905179.362641050000000 |
| 103 | G1L 3P8 | −7931059.956336440000000 | 5915892.835188770000000 |
| 104 | G3M 2A2 | −7985008.592747890000000 | 5890127.808516180000000 |
| 105 | H7T 1A1 | −8209544.856228840000000 | 5709533.932269610000000 |
| 106 | G1X 1S1 | −7939277.491892260000000 | 5904758.328336060000000 |
| 107 | G1X 1S6 | −7939546.533357010000000 | 5904419.209822820000000 |
| 108 | J6A 2S2 | −8177008.449473490000000 | 5737279.550246160000000 |
| 109 | J8Z 1J1 | −8432023.775340110000000 | 5694626.440885100000000 |
| 110 | H1W 1P9 | −8187079.630838730000000 | 5707425.789198540000000 |
| 111 | H4C 1P3 | −8190816.948350020000000 | 5697550.683844200000000 |
| 112 | J3G 1V1 | −8150495.702237150000000 | 5708068.270668600000000 |
| 113 | J8X 3G8 | −8428740.942233350000000 | 5688939.620501390000000 |
| 114 | H2R 1T3 | −8194763.343372580000000 | 5706548.468367760000000 |
| 115 | G1W 2L2 | −7939355.724188350000000 | 5903171.171572110000000 |
| 116 | J4T 2G2 | −8179085.818519460000000 | 5699232.250174590000000 |
| 117 | J7M 1R7 | −8211564.829478150000000 | 5747155.751342270000000 |
| 118 | G7X 7X2 | −7929916.037592340000000 | 6175617.925520500000000 |
| 119 | J4T 2G3 | −8178995.809116340000000 | 5698992.424674400000000 |
| 120 | H1W 1S1 | −8186957.282064200000000 | 5707862.086911730000000 |
| 121 | J0K 1S0 | −8205072.410577610000000 | 5787234.027643240000000 |
| 122 | J6V 1N5 | −8183374.297241640000000 | 5734510.439420790000000 |
| 123 | G6B2C4 | −7890821.934867610000000 | 5713005.468212960000000 |
| 124 | J9V 1J5 | −8842853.747223610000000 | 5997097.063034410000000 |
| 125 | G7X 0A6 | −7931631.172704880000000 | 6175969.036812970000000 |
| 126 | J2G 2L2 | −8096520.868348790000000 | 5685607.626838380000000 |
| 127 | H7R 1L2 | −8218258.548117450000000 | 5711055.279261990000000 |
| 128 | J2G 3N6 | −8096960.619461230000000 | 5684607.500776540000000 |
| 129 | H2W 1Y3 | −8190706.366999920000000 | 5703259.069077170000000 |
| 130 | H4G 1V3 | −8189393.409117910000000 | 5694842.511113480000000 |
| 131 | G5V 1B7 | −7855094.491333030000000 | 5939031.909897490000000 |
| 132 | J2G 8K1 | −8098369.891785350000000 | 5686993.071962290000000 |
| 133 | J7E 3H2 | −8219909.310107210000000 | 5722589.675974880000000 |
| 134 | J3Y 3M4 | −8175273.570410310000000 | 5702411.611024140000000 |
| 135 | G5L 7Y5 | −7627037.865925880000000 | 6185050.115537450000000 |
| 136 | J3P 4M7 | −8139330.276936240000000 | 5787472.576619010000000 |
| 137 | J9H 6W7 | −8442000.648452110000000 | 5684470.234330190000000 |
| 138 | H1V 1X4 | −8185885.519051640000000 | 5708496.282215470000000 |
| 139 | H4G 1W2 | −8189421.557906050000000 | 5694454.024617650000000 |
| 140 | G1H 2S5 | −7931240.919373120000000 | 5916507.495830460000000 |
| 141 | J5Z 1N9 | −8178647.200952620000000 | 5740994.914334240000000 |
| 142 | J1X 2A9 | −8032155.600752470000000 | 5663512.122153890000000 |
| 143 | G0A 4N0 | −7961151.974094490000000 | 5923577.290184840000000 |
| 144 | G6V 6C5 | −7923650.444726480000000 | 5908789.349292600000000 |
| 145 | J8L 2G8 | −8395385.664298190000000 | 5714584.702616400000000 |
| 146 | G0X 3H0 | −8077653.564564440000000 | 5897239.653701590000000 |
| 147 | J7P 4C1 | −8222997.379473020000000 | 5713623.543365630000000 |
| 148 | G8B 2Y2 | −7975973.332411180000000 | 6198602.576847140000000 |
| 149 | J6N 1X6 | −8223763.657292320000000 | 5671159.978541870000000 |
| 150 | J3B 5L3 | −8155858.847740470000000 | 5671125.426329470000000 |
| 151 | G8P 2X6 | −8277821.262388090000000 | 6431224.947471350000000 |
| 152 | H7K 2Z6 | −8208867.219577940000000 | 5719253.055240570000000 |
| 153 | H7R 1L7 | −8221693.857892310000000 | 5708996.420445360000000 |
| 154 | J7P 4Z8 | −8224075.683136990000000 | 5712988.801696030000000 |
| 155 | J6E 3B3 | −8175484.871119960000000 | 5784419.157966800000000 |
| 156 | J1N 1E8 | −8013902.211307660000000 | 5680430.307337440000000 |
| 157 | G8Y 4Z3 | −8080945.433933380000000 | 5838379.469798530000000 |
| 158 | J2G6N4 | −8098272.289712850000000 | 5686888.441809450000000 |
| 159 | G9N 8G5 | −8096008.829441530000000 | 5871986.491741550000000 |
| 160 | J0S 1H0 | −8256900.862037390000000 | 5635475.437968370000000 |
| 161 | J5C 1L8 | −8189813.112693330000000 | 5683198.118525080000000 |
| 162 | J9X 4P1 | −8796428.805134490000000 | 6147122.303812740000000 |
| 163 | J1N 2K7 | −8014129.882683410000000 | 5679673.348061460000000 |
| 164 | H2T 1R8 | −8192393.130221900000000 | 5704257.992397710000000 |
| 165 | G1P 4B2 | −7940705.700829850000000 | 5912884.145750160000000 |
| 166 | H3W 1X5 | −8196202.453491180000000 | 5698165.544720140000000 |
| 167 | G6V 4Z4 | −7923982.207437270000000 | 5908201.337252420000000 |
| 168 | G1H 6Y8 | −7931513.106419480000000 | 5917808.072706410000000 |
| 169 | G6V 4Z2 | −7923644.765428420000000 | 5908299.358229310000000 |
| 170 | G8Z 4A7 | −8080602.662223740000000 | 5834435.233217170000000 |
| 171 | G1L 2W3 | −7928934.803349920000000 | 5913337.954227790000000 |
| 172 | G8Y 5L5 | −8081396.154718520000000 | 5838791.376020280000000 |
| 173 | J6W 1T5 | −8196936.232849320000000 | 5733060.667759110000000 |
| 174 | J8H 1Y6 | −8274744.021272480000000 | 5725629.795494300000000 |
| 175 | J3G 1P7 | −8151005.103326460000000 | 5708408.448446360000000 |
| 176 | G1M 3E5 | −7931848.943485550000000 | 5913237.233894240000000 |
| 177 | J5R 2L1 | −8180629.950462950000000 | 5687216.205446500000000 |
| 178 | H4A 1W5 | −8194762.561929030000000 | 5696037.698357280000000 |
| 179 | G8Y 1X7 | −8081388.402465280000000 | 5838964.000837730000000 |
| 180 | H3T 1Y8 | −8196080.612932950000000 | 5700366.321276980000000 |
| 181 | G8B 6S9 | −7976177.661432140000000 | 6198741.767751050000000 |
| 182 | J6S 3M1 | −8252432.018775500000000 | 5663034.957595700000000 |
| 183 | H2T 1N6 | −8191512.651179980000000 | 5703874.328787200000000 |
| 184 | J0J 1J0 | −8166070.690171710000000 | 5632893.621599650000000 |
| 185 | J9X 3C2 | −8796282.598813850000000 | 6146533.597154170000000 |
| 186 | J2S 4P4 | −8120115.613316230000000 | 5720785.006475330000000 |
| 187 | G6S 1C9 | −8007691.802365310000000 | 5790245.068708710000000 |
| 188 | H1G 2T6 | −8194979.281873510000000 | 5717444.829325410000000 |
| 189 | J1G 1B9 | −8001152.690672520000000 | 5686020.111024940000000 |
| 190 | G1R 1P7 | −7928126.716989840000000 | 5911123.916841000000000 |
| 191 | J9L 1S8 | −8404106.817669900000000 | 5869418.871491590000000 |
| 192 | G7H 1Z6 | −8039940.750610230000000 | 6192337.740234340000000 |
| 193 | G1M 2T4 | −7931682.367605750000000 | 5911833.888649590000000 |
| 194 | H1P 1H7 | −8191112.408346360000000 | 5715237.749567850000000 |
| 195 | J3B 2M6 | −8157042.291598670000000 | 5669818.355951560000000 |
| 196 | J8P 0B1 | −8424302.362635130000000 | 5699130.404096790000000 |
| 197 | H4E 3J2 | −8192479.783200330000000 | 5693131.458383570000000 |
| 198 | H3W 2T4 | −8198022.432874280000000 | 5700119.052205820000000 |
| 199 | J7Y 4B4 | −8240031.886912010000000 | 5742426.809763730000000 |
| 200 | H2S 2N1 | −8194387.608708180000000 | 5706962.311685190000000 |
| 201 | H8N 1X1 | −8194854.569901900000000 | 5692243.003158370000000 |
| 202 | H2P 1W2 | −8196157.960045840000000 | 5707830.670461350000000 |
| 203 | J2K 2Y2 | −8098192.409382450000000 | 5653388.103478030000000 |
| 204 | G1K 1J6 | −7929570.024631840000000 | 5911356.374949250000000 |
| 205 | G1R 1P9 | −7927948.896038480000000 | 5911298.214407180000000 |
| 206 | G6V 6S5 | −7920236.007537550000000 | 5911899.625487360000000 |
| 207 | J2C 6Y7 | −8072565.813651960000000 | 5764263.266432650000000 |
| 208 | J4Y 1A2 | −8177997.170060100000000 | 5693846.417461990000000 |
| 209 | J1G 1C6 | −8000755.082243210000000 | 5686113.063943450000000 |
| 210 | H7V 2V3 | −8209478.726276350000000 | 5706801.460904830000000 |
| 211 | G1G 4C7 | −7933479.716581660000000 | 5919788.085672910000000 |
| 212 | J5M 2V4 | −8210572.988330320000000 | 5757127.029975440000000 |
| 213 | J4K 2V1 | −8183565.927529760000000 | 5705186.096798200000000 |
| 214 | G1G 4C8 | −7933682.799346310000000 | 5919802.199398290000000 |
| 215 | J0K 1A0 | −8147368.766860010000000 | 5794092.449573130000000 |
| 216 | G7A 2V1 | −7936518.584970550000000 | 5898136.239066010000000 |
| 217 | H2Z 4G2 | −8194547.948412070000000 | 5712515.660249340000000 |
| 218 | J5M 2V4 | −8210639.523433010000000 | 5757312.332639810000000 |
| 219 | G5C 1C7 | −7598654.693205900000000 | 6308375.750149870000000 |
| 220 | G7H 1P9 | −7911006.777737960000000 | 6178375.130200640000000 |
| 221 | J7Y 3S7 | −8239591.195035760000000 | 5747237.771098060000000 |
| 222 | J8P 1H5 | −8415167.508400330000000 | 5699006.084890830000000 |
| 223 | J9P 1T4 | −8659603.177646680000000 | 6124088.536617070000000 |
| 224 | J7N 1N4 | −8248268.351615300000000 | 5733601.145880170000000 |
| 225 | J1E 3J7 | −8000605.327076920000000 | 5688108.288704530000000 |
| 226 | G0A 3C0 | −7897958.223267660000000 | 5944382.365921620000000 |
| 227 | G9A 4H7 | −8075370.695343930000000 | 5835903.740882100000000 |
| 228 | G5Y 5P4 | −7869223.661065360000000 | 5801233.112717970000000 |
| 229 | H2M 1S5 | −8198742.492280170000000 | 5708569.937791150000000 |
| 230 | G1X 4M5 | −7944178.026575930000000 | 5903038.964724820000000 |
| 231 | G2B 3Z6 | −7943350.295781820000000 | 5915526.992822510000000 |
| 232 | J3G 1V7 | −8151917.556473330000000 | 5709616.888935700000000 |
| 233 | J6W 2W5 | −8197819.102732250000000 | 5732707.736572040000000 |
| 234 | H4L 2A7 | −8202229.564111250000000 | 5702794.911248230000000 |
| 235 | J8B 2N4 | −8252504.741422090000000 | 5772409.288043520000000 |
| 236 | J8E 3J8 | −8303910.435574370000000 | 5799288.750831560000000 |
| 237 | G6P 4S2 | −8009373.232046320000000 | 5789580.826661120000000 |
| 238 | G7S 4S9 | −7922574.087686500000000 | 6174095.139639150000000 |
| 239 | G9T 2H2 | −8091883.698299900000000 | 5879608.093074000000000 |
| 240 | G6V 6C1 | −7923925.086670850000000 | 5909351.646231730000000 |
| 241 | J6E 6X6 | −8173651.916341430000000 | 5785616.450966400000000 |
| 242 | G5Y 7G4 | −7867383.864152240000000 | 5799780.852791840000000 |
| 243 | J4B 6G4 | −8176165.781939890000000 | 5712878.920683190000000 |
| 244 | J7P 2V2 | −8223607.622415690000000 | 5712329.846532510000000 |
| 245 | J1S 1J8 | −8014976.143542690000000 | 5712075.689196260000000 |
| 246 | J8Y 3X1 | −8430616.926670160000000 | 5689881.277840790000000 |
| 247 | H9R 5B1 | −8213927.764316900000000 | 5695031.070699580000000 |
| 248 | J3E 2T6 | −8162733.535593580000000 | 5712568.540600130000000 |
| 249 | H7M 2R2 | −8207728.469268100000000 | 5717426.799920340000000 |
| 250 | G8T 6Y1 | −8074669.470200380000000 | 5839952.622912460000000 |
| 251 | J0R 1R0 | −8255136.364910780000000 | 5763522.881691710000000 |
| 252 | J3P 3P8 | −8137343.687576590000000 | 5786841.065266540000000 |
| 253 | J8Y 3Y2 | −8430586.452024560000000 | 5690841.715659160000000 |
| 254 | J2C 4R8 | −8070048.711916370000000 | 5760692.911521470000000 |
| 255 | H7P 1T3 | −8213937.489744700000000 | 5713297.304116300000000 |
| 256 | J0N 1P0 | −8230308.928040220000000 | 5705295.378364160000000 |
| 257 | J0N 1P0 | −8230870.369999920000000 | 5705194.498264970000000 |
| 258 | J8T 8J3 | −8426827.833264080000000 | 5697085.739936030000000 |
| 259 | G1C 5R9 | −7927931.661603130000000 | 5919338.363031220000000 |
| 260 | J0J 1L0 | −8171461.389405670000000 | 5651094.891673710000000 |
| 261 | J6A 2S5 | −8176749.072935060000000 | 5737473.237462650000000 |
| 262 | J8C 2A6 | −8269803.651157660000000 | 5787995.494776570000000 |
| 263 | J8P 1L4 | −8420364.366755720000000 | 5697667.386554900000000 |
| 264 | J6Z 1J2 | −8210669.805037890000000 | 5727069.392490720000000 |
| 265 | H4G 1W8 | −8189509.450904420000000 | 5694022.653676440000000 |
| 266 | H7G 2V1 | −8203276.441520250000000 | 5711595.210002390000000 |
| 267 | J6T 1P3 | −8252514.750061060000000 | 5661643.911377380000000 |
| 268 | J8H 1Y5 | −8274980.567932540000000 | 5725574.293096420000000 |
| 269 | J3A 1M1 | −8157583.041502010000000 | 5673523.771997930000000 |
| 270 | H8R 3G6 | −8198812.011419540000000 | 5688330.723246450000000 |
| 271 | J6A 2W5 | −8174285.908219230000000 | 5740996.502729300000000 |
| 272 | J7C 2J5 | −8222577.426664180000000 | 5726530.005223580000000 |
| 273 | J7Z 5M2 | −8237997.299853290000000 | 5746129.111150800000000 |
| 274 | H1M 2S5 | −8186655.229639730000000 | 5715271.269714140000000 |
| 275 | H1E 3Y1 | −8193034.351531600000000 | 5720409.033843620000000 |
| 276 | G6Z 2C6 | −7926915.850634040000000 | 5898611.112435320000000 |
| 277 | G8T 2T9 | −8073705.279216970000000 | 5839052.473052680000000 |
| 278 | J5L2L1 | −8240815.337211860000000 | 5747873.336045890000000 |
| 279 | J3A 1L2 | −8156236.111663260000000 | 5674242.439855960000000 |
| 280 | J6E 1E5 | −8174892.103203060000000 | 5787083.331173970000000 |
| 281 | H3L 2N5 | −8199783.742079770000000 | 5708101.617524060000000 |
| 282 | J7Z 5N6 | −8238476.470264970000000 | 5747207.865046960000000 |
| 283 | H9R 5M3 | −8218849.424122390000000 | 5695844.788447580000000 |
| 284 | G2L 2X2 | −7941267.161742780000000 | 5919031.692326080000000 |
| 285 | J9L 1T3 | −8403966.006778460000000 | 5869992.005439260000000 |
| 286 | G9P 1NZ | −8098168.273358800000000 | 5864302.629788050000000 |
| 287 | G9A 4N3 | −8077954.286520300000000 | 5832408.060523520000000 |
| 288 | J7K 2L5 | −8195222.702033520000000 | 5737225.622384490000000 |
| 289 | H1P 1Z4 | −8192096.258267460000000 | 5717070.814778460000000 |
| 290 | H1R 2B7 | −8194374.906394880000000 | 5716132.970042150000000 |
| 291 | J3E 1W9 | −8164973.277938920000000 | 5715882.282533280000000 |
| 292 | J7R 2J5 | −8227238.900030400000000 | 5710625.925381070000000 |
| 293 | H1W 1R4 | −8187089.664169030000000 | 5707536.967134930000000 |
| 294 | H2S 3E2 | −8195117.963995920000000 | 5706035.944587470000000 |
| 295 | H4C 1P4 | −8190914.107113200000000 | 5697374.230493480000000 |
| 296 | J5A 1G7 | −8189538.406007090000000 | 5681106.802552830000000 |
| 297 | J0L 1B0 | −8205149.172347060000000 | 5681052.614888510000000 |
| 298 | J5R 0E5 | −8182827.364553630000000 | 5680048.184759270000000 |
| 299 | H9H 5J1 | −8221442.549804540000000 | 5693249.066685380000000 |
For the entire province of Quebec, the median distance of secondary schools to the nearest specialized vape shop is 2278 m (Table 1). More precisely, the median distance is 1993 m for private institutions and 2454 m for public institutions. The shortest median distance to the nearest shop is for educational institutions in advantaged areas (1979 m).
| Secondary schools | Number | Median distance (m) |
Mean distance (m) |
Standard deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | ||||
| Private institution | 169 | 1 993 | 5 452 | 19 051 |
| Public institution | 543 | 2 454 | 47 591 | 145 594 |
| Very small (1–115 students) | 164 | 3 380 | 89 307 | 218 183 |
| Small (118–429 students) | 172 | 3 036 | 42 601 | 103 782 |
| Medium (431–863 students) | 177 | 2 054 | 19 609 | 84 505 |
| Large (868–2540 students) | 176 | 1 970 | 6 506 | 35 341 |
| Environment | ||||
| Advantaged area | 442 | 1 979 | 20 081 | 87 599 |
| Disadvantaged area | 270 | 3 711 | 66 249 | 172 858 |
| Urban | 578 | 1 914 | 15 219 | 60 705 |
| Rural | 134 | 33 492 | 134 076 | 247 027 |
| Combined | 712 | 2 278 | 37 589 | 128 712 |
For the entire province of Quebec, the median distance of secondary schools to the nearest specialized point of sale is 1231 m (Table 2), specifically 1001 m for private educational institutions and 1381 m for public educational institutions. The median distance to the nearest shop is lower for educational institutions located in more advantaged areas (1231 m).
| College | Number | Median distance (m) |
Mean distance (m) |
Standard deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | ||||
| Private institution | 78 | 1 001 | 2 033 | 2 695 |
| Public institution | 92 | 1 381 | 30 624 | 98 290 |
| Very small (5–106 students) | 37 | 942 | 1 406 | 1 261 |
| Small (107–497 students) | 36 | 927 | 47 375 | 138 623 |
| Medium (502–1930 students) | 37 | 1 750 | 27 180 | 70 820 |
| Large (1944–11 062 students) | 36 | 1 122 | 1 236 | 685 |
| Environment | ||||
| Advantaged area | 102 | 1 231 | 12 326 | 44 607 |
| Disadvantaged area | 47 | 1 750 | 36 101 | 122 346 |
| Urban | 152 | 1 077 | 12 100 | 48 727 |
| Rural | 18 | 7 104 | 63 154 | 173 837 |
| Combined | 170 | 1 231 | 17 506 | 73 549 |
Distance to points of sale is treated as a continuous variable in a generalized linear regression model. Medium-sized (versus very small) and large (versus very small) educational institutions as well as urban (versus rural) institutions tend to have a specialized vape shop located closer. Private (versus public) educational institutions, as well as those located in disadvantaged (versus advantaged) areas, are geographically more distant from a vaping product shop (Table 3).
| Log (distance to the nearest point of saleFootnote a, in meters) | Univariate model | Final multivariate model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFootnote a | 95% CI | BFootnote a | 95% CI | |
| Intercepted | – | – | 4.49Footnote *** | 4.35 to 4.64 |
| Characteristics | ||||
| Private institution | Ref. | – | Ref. | – |
| Public institution | 0.34Footnote *** | 0.21 to 0.47 | 0.23Footnote *** | 0.11 to 0.34 |
| Very small | Ref. | – | Ref. | – |
| Small | −0.10 | −0.25 to −0.07 | −0.00 | −0.13 to 0.13 |
| Medium | −0.43Footnote *** | −0.59 to −0.27 | −0.25Footnote *** | −0.38 to −0.11 |
| Large | −0.59Footnote *** | −0.75 to −0.43 | −0.36Footnote *** | −0.50 to −0.28 |
| Environment | ||||
| Urban | Ref. | – | Ref. | – |
| Rural | −1.1Footnote *** | −1.21 to −0.97 | −0.92Footnote *** | −1.04 to −0.79 |
| Advantaged area | Ref. | – | Ref. | – |
| Disadvantaged area | 0.46Footnote *** | 0.35 to 0.57 | 0.21Footnote *** | 0.11 to 0.31 |
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; ref.; reference.
|
||||
Public (versus private), small (versus very small) and medium-sized (versus very small) college institutions are significantly more geographically distant from a vaping product shop. Institutions located in rural areas are significantly further from a vape shop than urban institutions (Table 4).
| Log (distance to the nearest point of saleFootnote a, in meters) | Univariate model | Final multivariate model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFootnote a | 95% CI | BFootnote a | 95% CI | |
| Intercepted | – | – | 3.50Footnote *** | 3.07 to 3.93 |
| Characteristics | ||||
| Private institution | Ref. | – | Ref. | – |
| Public institution | 0.48Footnote *** | 0.22 to 0.74 | 0.51Footnote *** | 0.26 to 0.75 |
| Very small | Ref. | – | Ref. | – |
| Small | −0.42Footnote * | 0.06 to 0.77 | 0.27 | −0.01 to 0.56 |
| Medium | 0.52Footnote ** | 0.17 to 0.88 | 0.20 | −0.10 to 0.51 |
| Large | −0.22 | −0.38 to 0.34 | −0.31 | −0.64 to 0.02 |
| Location | ||||
| Urban | Ref. | – | Ref. | – |
| Rural | −0.86Footnote *** | −1.30 to −0.42 | −0.66Footnote *** | −1.04 to −0.27 |
| Advantaged area | Ref. | – | N/A | N/A |
| Disadvantaged area | 0.19 | −0.09 to 0.47 | N/A | N/A |
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; ref., reference.
|
||||
Discussion
First, our study sought to build a georeferenced directory of specialized vape stores in Quebec, so that we could link them to educational institutions. We found that 299 businesses exclusively selling vaping products were open in Quebec in early 2018. Although a detailed analysis of the evolution of the presence of specialized shops in Quebec was beyond the scope of our study, the development and validation of our database leads us to believe that the number of this type of shop could be decreasing. The MSSS list compiled in 2015, which was used to build our directory, contained 414 businesses, while our final directory contains 299. A decrease in this type of business has been observed elsewhere, particularly in France.Footnote 29 The tightening of the legal framework and the decline of vaping as a fashion trend could be two factors that might explain this decline.
The main objective of our study was to examine, according to various characteristics, the geographical accessibility of specialized vape shops in Quebec that are in the vicinity of educational institutions. This analysis revealed that, in Quebec, colleges had greater accessibility to such specialized shops than did secondary schools. The same situation was observed in the USA: no specialized shop was found within 800 m of secondary schools in New Jersey,Footnote 13 while 30% of all colleges across the USA were located within 1.6 km of a vape shop.Footnote 16 However, the situation appears to vary across the USA: a study in California found that 28% of secondary schools had such a vape shop within an 800 m radius.Footnote 10
A variety of reasons may explain why colleges and CEGEPs in Quebec tend to have greater geographical accessibility to this type of business. One explanation is that college campuses are generally located in more densely populated areas or urban agglomerations, which makes them more likely to be located near any business.
Our analysis also showed that more educational institutions in urban areas than in rural areas are located near specialized vape shops in Quebec. The same situation has been observed in the United States. According to a study conducted across the USA, there is a greater availability of specialized vape shops in urban census areas (0.47 average availability) than in rural areas (0.23 average availability).Footnote 14 According to another US study, greater proximity to speciality shops is associated with urban areas: median distance from the nearest shop is 1.1 miles in the city; 1.9 miles in the suburbs; 6.3 miles in a smaller town or village; and 7.9 miles in rural areas).Footnote 16
Our study revealed that private educational institutions are located closer to specialized vape shops in Quebec. This situation was also observed in the USA: vape shops were more likely to be closer to private colleges (2.6 km for median proximity) than public ones (3.2 km for median proximity). The authors suggested that one of the reasons is that this type of trade potentially targets populations that are more socioeconomically advantaged and therefore more likely to attend private schools.Footnote 16
One of the objectives of our analysis was to examine the proximity of specialized vape shops to educational institutions according to the level of material deprivation of the area. Our analysis revealed that vape stores are closer to secondary schools in advantaged areas, but area deprivation was not associated with accessibility to points of sale in conjunction with colleges.
A similar situation exists in the USA. A study conducted in New Jersey, USA, showed that neighbourhoods with an average median household income—as opposed to the lowest—were more likely to be associated with a higher number of specialized vape shops.Footnote 13 In another study conducted in New Jersey, USA,Footnote 30 more shops (specialized and non-specialized) selling e-cigarettes were identified near schools with fewer students eligible for free school meals than near less advantaged schools.
Some researchers have hypothesized that this type of business potentially targets populations that are more socioeconomically advantaged and yet still have high proportions of smokers.Footnote 16 In fact, the e-cigarette, especially the starting device, is more expensive than tobacco and therefore requires, to a certain extent, more resources. As we have seen, more private educational institutions are located near such shops in Quebec, probably also because a more affluent clientele attends these schools.
It is important to note, however, that across the USA there appears to be a greater availability of specialized vape shops in both urban and rural census areas where fewer people own their own homes, an indicator of lesser socioeconomic advantage. Similarly, the availability of specialized vape stores would be expected to be more prevalent in areas where fewer people have a level of education equal to or higher than college level; however, the associations between the proportion of people living below the poverty line in an area and the availability of vape shops were not significant.Footnote 14
Strengths and limitations
To our knowledge, this is one of the only profiles of the spatial distribution of businesses specializing in the sale of vaping products in Quebec and Canada. The presence of specialized vape shops in the study area was carefully validated (by phone, in person and through the use of various databases). We included several types of schools (private and public, secondary schools and colleges), with variable enrolment. We also took into account the characteristics of the location of these institutions, namely the types of environment (urban or rural, disadvantaged or advantaged). From this point of view, there seems to be an interaction between the urban or rural character and the type of education (private or public), and between the type of education and level of deprivation. Such analysis is beyond the scope of this article, and further research is recommended.
Some limitations should also be mentioned. Specialist vape shops are only a part of e-cigarette business in Quebec: vaping products are also available in other stores, in particular, in convenience stores, tobacconists and gas stations. Unlike specialized vape shops, minors can enter these places, although they cannot legally buy e-cigarettes; and like tobacco products, vaping products must not be visible to customers. Since not all of these businesses sell vaping products, a field visit would have been necessary to identify them, which was beyond the scope of our analysis. Thus, our profile underestimates the true geographical accessibility of points of sale for vaping products to young people near schools.
It would be relevant to continue this analysis to include these points of sale, not least because research in the USA has shown that they are present near schools.Footnote 12,Footnote 15 Moreover, the geographical accessibility of young people to the points of sale of various products (including tobacco and vaping products) can be defined differently from schools: near places of residence or near other places that youth frequent (e.g. sports, cultural and recreational centres). In fact, it is increasingly recognized that research must also include several of these places simultaneously.Footnote 31 Considering only accessibility near schools means that only a portion of the geographical accessibility of young people to the points of sale of these products is taken into account, even if the school is the public place most frequented by young people over the longest period. It would therefore be appropriate to expand on this research given that studies have shown that young people's accessibility to tobacco sales outlets in the vicinity of their homes is associated with the consumption of these products.Footnote 32 Our analysis was not intended to examine the use of vaping products by young Quebecers based on the geographical accessibility of specialized vape shops that are near educational institutions.
Conclusion
Experimentation with e-cigarettes is widespread among young adults in Quebec and among many secondary school students. The factors associated with the use of vaping devices by youth are currently the subject of scientific research. It is possible that geographical accessibility to shops selling these products may be one of these factors, as is the case for tobacco products. As these factors are still largely unknown in Quebec, we have undertaken to provide a snapshot of the geographical accessibility of points of sale specializing in vaping products that are in the vicinity of educational institutions.
Our analysis suggests that specialized vape shops are more easily accessible to students attending college than secondary school. They also appear to be more accessible to students attending private institutions than public ones. For secondary schools, those located in more advantaged areas are closer to a specialized vaping product point of sale. Speciality stores are closer to schools in urban areas than in rural areas.
Future investigations should examine geographical accessibility to all businesses that sell e-cigarettes (such as some convenience stores, tobacco stores and gas stations) and studying the impact of this accessibility on the use of vaping products by young people.
Public health experts agree on the need to limit the use of vaping products among young people in order not to induce nicotine dependence or to provide an incentive for the subsequent use of tobacco products. It is important to continue to improve scientific knowledge about vaping products, their use and marketing and the places where they are sold. In Quebec and Canada overall, legislation has been passed in an attempt to restrict young people’s access to vaping products while allowing adults who want to quit smoking access to them. It is relevant and worthwhile to continue research in this changing regulatory environment.
Acknowledgements
This study was made possible with the financial support of the MSSS.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Authors' contributions and statement
ER and PB designed the project. ER, PB and MH designed the study. MH undertook the data collection. ER and MH conducted the data analysis. ER wrote the manuscript. ER and PB contributed to the synthesis of the data. All the authors contributed to the discussion of the findings and their interpretation, as well as to the writing of the manuscript and approval of its final version. The content and views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Government of Canada.
References
- Footnote 1
-
Lasnier B, Montreuil A. L'usage de la cigarette électronique chez les élèves du Québec et du reste du Canada: 2014–2015. Montréal (QC): Institut national de santé publique du Québec; 2017.
- Footnote 2
-
Health Canada. Detailed tables for the Canadian Student Tobacco, Alcohol and Drugs Survey 2016-17: detailed tables from 2016–2017 [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Health Canada; [modified 2018 Jun 12; cited 2018 Jul 4]. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/canadian-student-tobacco-alcohol-drugs-survey/2016-2017-supplementary-tables.html
- Footnote 3
-
Soneji S, Barrington-Trimis JL, Wills TA et al. Association between initial use of e-cigarettes and subsequent cigarette smoking among adolescents and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(8):788-97. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.1488.
- Footnote 4
-
Hammond D, Reid JL, Cole AG, Leatherdale ST. Electronic cigarette use and smoking initiation among youth: a longitudinal cohort study. CMAJ. 2017;189(43):E1328-36. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.161002.
- Footnote 5
-
Best C, Haseen F, Currie D et al. Relationship between trying an electronic cigarette and subsequent cigarette experimentation in Scottish adolescents: a cohort study. Tob Control. 2018;27:373-8. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2017-053691.
- Footnote 6
-
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Public health consequences of e-cigarettes. Washington (DC): National Academies Press; 2018. Available from: https://www.nap.edu/catalog/24952
- Footnote 7
-
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. E-cigarette use among youth and young adults. A Report of the Surgeon General. Rockville (MD): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; 2016.
- Footnote 8
-
Gwon SH, DeGuzman PB, Kulbok PA, Jeong S. Density and proximity of licensed tobacco retailers and adolescent smoking. J Sch Nurs. 2017;33(1):18-29. doi: 10.1177/1059840516679710.
- Footnote 9
-
Finan LJ, Lipperman-Kreda S, Abadi M, et al. Tobacco outlet density and adolescents' cigarette smoking: a meta-analysis. Tob Control. 2019;28(1):27-33. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2017-0540658.
- Footnote 10
-
Bostean G, Crespi CM, Vorapharuek P, McCarthy WJ. E-cigarette use among students and e-cigarette speciality retailer presence near schools. Health Place. 2016;42:129-36. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2016.09.012.
- Footnote 11
-
Bostean G, Crespi CM, Vorapharuek P, McCarthy WJ. E-cigarette speciality retailers: data to assess the association between retail environment and student e-cigarette use. Data Brief. 2017;11:32-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.12.022.
- Footnote 12
-
Giovenco DP, Casseus M, Duncan DT, Coups EJ, Lewis MJ, Delnevo CD. Association between electronic cigarette marketing near schools and e-cigarette use among youth. J Adolesc Health. 2016;59(6):627-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.08.007.
- Footnote 13
-
Giovenco DP, Duncan DT, Coups EJ, Lewis MJ, Delnevo CD. Census tract correlates of vape shop locations in New Jersey. Health Place. 2016;40:123-8. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2016.05.008.
- Footnote 14
-
Dai H, Hao J, Catley D. Vape shop density and socio-demographic disparities: a US Census tract analysis. Nicotine Tob Res. 2017;19(11):1338-44. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntx063.
- Footnote 15
-
Hahn EJ, Begley K, Gokun Y, Johnson AO, Mundy ME, Rayens MK. Electronic cigarette retail outlets and proximity to schools. Am J Health Promot. 2015;29(6):380-3. doi: 10.4278/ajhp.130627-ARB-335.
- Footnote 16
-
Dai H, Hao J. Geographic density and proximity of vape shops to colleges in the USA. Tob Control. 26(4):379-85. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2016-052957.
- Footnote 17
-
Montreuil A, MacDonald M, Asbridge M, Wild TC, Hammond D, Manske S, et al. Prevalence and correlates of electronic cigarette use among Canadian students: cross-sectional findings from the 2014/15 Canadian Student Tobacco, Alcohol and Drugs Survey. CMAJ Open. 2017;5(2):E460-7. doi: 10.9778/cmajo.20160167.
- Footnote 18
-
Gervais A, Massé R, Jacques M, Tessier S. Montréal sans tabac: mise en œuvre de la Loi sur le tabac 2005–2010: observations et recommandations pour la mise à jour de la Loi: mémoire du directeur de santé publique de Montréal. Montréal (QC): Agence de la santé et des services sociaux de Montréal, Direction de santé publique; 2013. 26 pp.
- Footnote 19
-
Coalition Québécoise pour le contrôle du tabac. La promotion de la cigarette électronique au Québec. Montréal (QC): Coalition Québécoise pour le contrôle du tabac; 2015. Available from: http://www.cqct.qc.ca/Documents_docs/DOCU_2015/DOCU_15_08_16_Promotion_CigaretteElectronique.pdf
- Footnote 20
-
Bergeron P, Robitaille É, Houde M. Accessibilité géographique aux commerces spécialisés en produits de vapotage autour des établissements d'enseignement secondaire et collégial du Québec. Montréal (QC): Institut national de santé publique du Québec; 2019. Available from: https://www.inspq.qc.ca/sites/default/files/publications/2510_accessibilite_commerces_vapotage_etablissements_scolaires-collegial.pdf
- Footnote 21
-
Ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux (MSSS). Le tabagisme chez les jeunes adultes : agir ensemble pour diminuer la prévalence : Rapport du directeur national de santé publique 2017. Québec (QC): MSSS; 2017. Available from: http://publications.msss.gouv.qc.ca/msss/fichiers/2017/17-228-01W.pdf
- Footnote 22
-
Ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux (MSSS). Loi concernant la lutte contre le tabagisme [Internet]. Québec (QC): MSSS; 2017 [cited 2018 Oct 8]. Available from: http://www.msss.gouv.qc.ca/ministere/lois-et-reglements/loi-concernant-la-lutte-contre-le-tabagisme/
- Footnote 23
-
Kim AE, Loomis B, Rhodes B, Eggers ME, Liedtke C, Porter L. Identifying e-cigarette vape stores: description of an online search methodology. Tob Control. 2016;25(e1):e19-23. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2015-052270.
- Footnote 24
-
Gamache P, Hamel D. The challenges of updating the deprivation index with data from the 2011 Census and the National Household Survey (NHS). Montréal (QC): Institut national de santé publique du Québec; 2017. 7 pp.
- Footnote 25
-
Statistics Canada. From urban areas to population centres [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Statistics Canada; 2011 [modified 2017 May 8; cited 2018 Oct 8]. Available from: https://www.statcan.gc.ca/eng/subjects/standard/sgc/notice/sgc-06
- Footnote 26
-
Apparicio P, Gelb J, Dubé AS, Kingham S, Gauvin L, Robitaille É. The approaches to measuring the potential spatial access to urban health services revisited: distance types and aggregation-error issues. Int J Health Geogr. 2017;16:32. doi: 10.1186/s12942-017-0105-9.
- Footnote 27
-
McCullagh P, Nelder JA. Generalized linear models. Boca Raton (FL): Chapman & Hall/CRC; 1989. (Monographs on Statistics & Applied Probability).
- Footnote 28
-
Burnham KP, Anderson DR. Multimodel inference: understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociol Methods Res. 2004;33(2):261-304. doi: 10.1177/0049124104268644.
- Footnote 29
-
Buhagiar R. Le commerce du vapotage s'essouffle [Internet]. La Dépêche du Midi; 2017 [cited 2018 Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.ladepeche.fr/article/2017/02/16/2518145-le-commerce-du-vapotage-s-essouffle.html
- Footnote 30
-
Giovenco DP, Ackerman C, Hrywna M, Delnevo CD. Changes in the availability and promotion of non-cigarette tobacco products near secondary schools in New Jersey, USA. Tob Control. 27(5):578-9. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2017-053800.
- Footnote 31
-
Shareck M, Kestens Y, Vallée J, Datta G, Frohlich KL. The added value of accounting for activity space when examining the association between tobacco retailer availability and smoking among young adults. Tob Control. 2016;25(4):406-12. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2014-052194.
- Footnote 32
-
Finan LJ, Lipperman-Kreda S, Abadi M, et al. Tobacco outlet density and adolescents' cigarette smoking: a meta-analysis. Tob Control. 2019;28(1):27-33. doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2017-054065.
Footnotes
- Footnote 1
-
General and vocational college.
- Footnote 2
-
“A population centre [is] an area with a population of at least 1,000 and a density of 400 or more persons per square kilometre. All areas outside population centres [are] defined as rural areas.”Footnote 25
