Appendix A: Human Antimicrobial Drug Use Report 2012/2013 – Methods for data collection and analysis
Human Antimicrobial Drug Use Report 2012/2013
- Table of Contents
- Contributors
- Executive Summary
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- What's New in the 2012/2013 Report
- 1. Physician Diagnosis Data
- 2. Pharmacy Dispensation Data
- 3. Hospital Purchasing Data
- Appendix A – Methods for Data Collection and Analysis
- Appendix B – Additional Physician Diagnosis Data
- Appendix C – Additional Pharmacy Dispensation Data
- Appendix D – Additional Hospital Purchasing Data
Appendix A – Methods for Data Collection and Analysis
Physician Diagnosis Data
The Canadian Disease and Therapeutic Index (CDTI) is a quarterly profile that provides information about the patterns and treatments of disease encountered by office-based physicians (specialists and general practitioners, including those with offices in hospitals). These data are presented over three geographic regions in Canada: West (British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba), Central (Québec and Ontario), and East (New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island).
The sample of physicians represents all major specialties across Canada. Data from 652 physicians were available in 2013, and projection methods were used to extrapolate data to a universe of approximately 55,092 physicians in Canada. Data on physician prescription/recommendations were extracted from the IMS Health Canada database.
For four consecutive quarters, each physician in the CDTI group maintains a practice diary describing information on every patient visit during a randomly selected 48-hour period within the quarter. Information includes patient age and gender, reason for visit, diagnosis, name(s) of the treatment(s) recommended or discussed (including drugs, referrals, environmental, behavioural, or dietary changes, etc.), desired therapeutic effect(s), and the presence of concomitant therapies. If a patient presents to a doctor's office for multiple "diseases", the practitioner will generate one form for each disease. If a person visits multiple times for the same "disease", it is counted in the system separately every time. CDTI data were used to determine the most common diagnoses, defined by the International Classification of Diseases Ninth Revision System (ICD-9), and associated with antimicrobial drug mentions for sampled physicians.
The total number of antimicrobial recommendations and number of diagnoses per 10,000 individuals for a given year, age or region was obtained by dividing by the size of the population in thousands during that year, age group and region (Table A.1 and Table A.2).
Some limitations and caveats should be considered for assessing data from the CDTI dataset:
- The drugs listed are those that the physician has written or recommended and do not represent actual prescriptions dispensed by pharmacists or products consumed by the patient, as information on patient compliance was not available.
- Although diagnoses are listed for each visit, diagnoses are not necessarily made at the visit in question, as previous diagnoses are recorded for chronic conditions.
- The data does not include patient visits to primary care nurses.
- Visit counts do not translate into number of patients (multiple visits per individual are possible, as well as multiple diagnoses per individual)
- Drug recommendations are not necessarily tied to a prescription, as samples may be given by the practitioner. Similarly, patients may choose not to fill a prescription.
- Physicians also record drugs 'previously ordered and continued' for the diagnosis, which would not necessarily tie to a prescription dispensed.
- Some drug therapy and diagnosis is under-represented due to self-medication (i.e. over-the-counter products).
- Reliability of the data is dependent on sampling error, so caution should be taken when interpreting those disease categories with a small sample size.
Data is only available at the regional level, where fluctuations may be more or less obvious and specific information for individual provinces could not be determined.
Hospital Purchasing Data
The Canadian Drugstore and Hospital Purchases Audit (CDH) measures the dollar value and unit volume of pharmaceutical and diagnostic products purchased by nearly all Canadian retail pharmacy outlets and hospitals excluding those in the Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. Information was collected from a representative sample of over 2,750 retail pharmacy outlets, and over 650 hospitals. A method of geographical projection was used to create projection factors for a "universe" of approximately 9,000 drugstores and over 750 hospitals to reflect all Canadian purchases (including non-participating stores). Data on drug purchases were extracted from the IMS Health Canada database, which included sales from manufacturers and wholesalers. For the purposes of this report, only data on hospital purchases were included in the analyses as pharmacy information was presented using the CompuScript data.
Only information regarding antimicrobials for systemic use was included in the analysis. Defined daily doses (DDDs) were determined according to the World Health Organization's Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. For erythromycin ethylsuccinate, all tablets were classified as erythromycin ethylsuccinate tablets (2g) and all forms other than tablets were classified as erythromycin (1g). For oral pediazole, the DDD for sulfonamides, combinations with other antibacterials (excl. trimethoprim) (2 g) was used. For oral administration of penicillin G, the DDD for benzylpenicillin by parenteral route (3.6 g) was used. Where a DDD was not available for both routes of administration, the available DDD was used (e.g., for benzylpenicillin, kanamycin).
The total amount of active ingredient was obtained by multiplying the number of extended units (real or corrected) by the strength of the product in grams. For combination drugs, the active ingredients of all antimicrobial components were summed to obtain the total number of active ingredients. However, the amount of active ingredient used in the calculation of the total number of DDDs for combination drugs included only the compounds from which the DDDs were derived. For example, for drugs composed of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, only the total number of grams of sulfamethoxazole was used to compute the number of DDDs.
The total number of DDDs per 1,000 inhabitant-days for a given year was obtained by summing all DDDs for each antimicrobial drug and each year.
This number was further divided by the size of the population in thousands during that year, divided by the number of days in that year (365 or 366). The total number of active ingredients (kg) and total cost per 1,000 inhabitants (for oral and parenteral antimicrobials combined) was obtained by dividing the total number of active ingredients or the total cost by the population size in thousands for each year. The cost was then adjusted for inflation using the Bank of Canada Inflation Calculator Footnote 1. Population data were obtained from updated and preliminary post-census estimates based on the results of the 2001 Census. The use of metronidazole was added in 2005.
The limitations and caveats that should be considered with the CDH dataset include the following:
- The data is estimated and is not census data.
- Limited tracking of specific niche markets (due to low volume and/or unique distribution).
- A small number of products may be excluded due to confidentiality (if they are only sold in one outlet).
- Some data may be excluded to reflect true market trends (i.e. large stockpiling transactions that occur prior to a potential epidemic).
- Direct sales for a specific manufacturer may not be available leading to underestimation of a product (higher incidence in the hospital than in drug store purchases).
- The provinces of Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland and Labrador were grouped due to the small volume within each province.
- Changes made to the databases are made to the last 72 months only and outside the five year period it is considered a closed dataset as updates cannot be made.
- Hospital patient days or number of hospital beds was not available for this data; general population information was used for developing rates of purchasing.
Data for CCS, CDH, and CDTI datasets were analyzed using SAS v. 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) and Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Cor., Redmond, WA, USA).
Population sizes used for analysis of all datasets.
| Province | Population (000's) | |
|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2013 | |
| British Columbia | 4,599.8 | 4,638.2 |
| Alberta | 3,924.6 | 4,061.0 |
| Saskatchewan | 1,098.6 | 1,119.5 |
| Manitoba | 1,263.5 | 1,278.2 |
| Ontario | 13,564.0 | 13,688.6 |
| Québec | 8,182.6 | 8,255.5 |
| New Brunswick | 767.5 | 766.6 |
| Nova Scotia | 958.4 | 953.6 |
| Prince Edward Island | 147.2 | 147.3 |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | 534.3 | 534.3 |
| Canada | 35,040.5 | 35,442.9 |
| Province | Population (000) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-5 | 6-11 | 12-17 | 18-39 | 40-59 | 60-64 | 65+ | |
| British Columbia | 267.2 | 268.7 | 302.8 | 1351.3 | 1345.6 | 294.0 | 808.6 |
| Alberta | 315.6 | 281.1 | 280.9 | 1373.0 | 1126.1 | 199.2 | 485.2 |
| Saskatchewan | 87.8 | 80.3 | 82.8 | 342.4 | 294.2 | 60.8 | 171.3 |
| Manitoba | 95.6 | 92.7 | 99.3 | 381.0 | 343.8 | 70.3 | 195.5 |
| Ontario | 864.3 | 873.9 | 958.5 | 4027.0 | 3966.7 | 789.6 | 2208.5 |
| Québec | 535.6 | 480.0 | 504.3 | 2392.7 | 2365.7 | 521.8 | 1455.4 |
| New Brunswick | 43.5 | 44.0 | 49.0 | 201.9 | 230.9 | 53.7 | 143.5 |
| Nova Scotia | 52.6 | 52.7 | 60.9 | 257.4 | 284.8 | 65.6 | 179.7 |
| Prince Edward Island | 8.9 | 9.2 | 10.3 | 38.4 | 43.2 | 10.1 | 27.1 |
| Newfouldland and Labrador | 29.4 | 30.8 | 33.0 | 138.7 | 164.8 | 40.0 | 97.6 |
| Canada | 2300.5 | 2213.4 | 2381.8 | 10503.8 | 10165.7 | 2105.2 | 5772.5 |
Appendix B – Additional Physician Diagnosis Data
| Diagnostic Class | Total diagnoses | Number of diagnoses / 10,000 inhabitants |
Antimicrobial recommendations(N) | Number of antimicrobial recommendations / 10,000 individuals |
Percentage of diagnoses with antimicrobial recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acne | 2,137,030 | 609.87 | 535,210 | 152.74 | 25.04 |
| Acute bronchitis | 2,547,010 | 726.88 | 1,961,240 | 559.71 | 77.00 |
| Acute sinusitis | 1,626,800 | 464.26 | 1,427,640 | 408.43 | 87.76 |
| Chronic bronchitis | 1,175,000 | 335.33 | 837,670 | 239.06 | 71.29 |
| Chronic sinusitis | 1,319,090 | 376.45 | 676,670 | 193.11 | 51.30 |
| Disease of the gastrointestinal system | 19,616,280 | 5,598.18 | 1,163,000 | 33.90 | 5.93 |
| Diseases of the ear | 9,054,310 | 2,583.96 | 2,425,050 | 692.07 | 26.78 |
| Injuries and poisonings | 13,093,100 | 3,736.56 | 419,120 | 119.61 | 3.20 |
| Lower UTI or Cystitis | 4,715,880 | 1,345.84 | 3,173,210 | 905.58 | 67.29 |
| Other diseases of the genitourinary system | 14,987,530 | 4,277.20 | 1,451,450 | 414.22 | 9.68 |
| Other respiratory tract infections | 16,063,670 | 4,584.32 | 1,059,120 | 302.26 | 6.59 |
| Other skin and soft tissue infections | 15,835,440 | 4,519.19 | 644,330 | 183.88 | 4.07 |
| Pneumonia | 1,443,120 | 411.84 | 1,184,910 | 338.15 | 82.11 |
| SSTIs | 2,731,830 | 779.62 | 1,780,290 | 508.07 | 65.17 |
| Symptoms and ill-defined conditions | 21,925,630 | 6,257.23 | 401,270 | 114.52 | 1.83 |
| Upper respiratory tract infections | 11,172,760 | 3,188.53 | 3,664,680 | 1,045.84 | 32.80 |
| TOTAL | 28,921,9210 | 8,2538.61 | 23,543,270 | 6,718.88 | 8.14 |
Diagnostic classes were removed from this table if they represented < 1% of antimicrobial mentions in 2013. These classes were: complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium; congenital anomalities; diseases of the central nervous system; diseases of the circulatory system; diseases of the sense organs; endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and immunity diseases; musculoskeletal diseases; neoplasms; perinatal conditions; supplementary classifications; and upper UTI or pyelonephritis |
|||||
Appendix C – Additional Pharmacy Dispensation Data
Table C.1: Anatomical Therapeutic Group (ATC) classification of antimicrobials used in Canada 2000 – 2013
| Therapeutic Group | ATC Class | Antimicrobials |
|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | J01GA & J01GB |
amikacin |
| gentamicin | ||
| streptomycin | ||
| tobramycin | ||
| Amphenicols | J01BA | chloramphenicol |
| Beta-lactamase sensitive & resistant penicillins | J01CE & J01CF |
cloxacillin |
| flucloxacillin | ||
| penicillin g | ||
| penicillin v | ||
| Carbapenems | J01DH | ertapenem |
| imipenem and cilastatin | ||
| meropenem | ||
| First-generation cephalosporins | J01DB | cefadroxil |
| cefazolin | ||
| cephalexin | ||
| Macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins | J01FA & J01FF |
azithromycin |
| clarithromycin | ||
| clindamycin | ||
| erythromycin | ||
| lincomycin | ||
| spiramycin | ||
| Methenamine | J01XX | methenamine mandelate |
| Other antibacterials | J01X | colistin |
| J01XX | daptomycin | |
| A07AA | fidaxomicin | |
| J01XX | fosfomycin | |
| J01XC | fusidic acid | |
| J01XX | linezolid | |
| J01XD | metronidazole | |
| J01XE | nitrofurantoin | |
| J01XA | vancomycin |
| Therapeutic Group | ATC Class | Antimicrobials |
|---|---|---|
| Other cephalosporins and penems | J01DD & J01DE |
cefepime |
| cefixime | ||
| cefotaxime | ||
| ceftazidime | ||
| ceftriaxone | ||
| Penicillins with extended spectrum | J01CA | amoxicillin |
| amoxicillin and enzyme inhibitor | ||
| ampicillin | ||
| piperacillin | ||
| piperacillin and tazobactam | ||
| ticarcillin and clavulanic acid | ||
| Quinolone antibacterials | J01MA | ciprofloxacin |
| levofloxacin | ||
| moxifloxacin | ||
| norfloxacin | ||
| ofloxacin | ||
| Second-generation cephalosporins | J01DC | cefaclor |
| cefoxitin | ||
| cefprozil | ||
| cefuroxime | ||
| Sulfonamides | J01EC | sulfadiazine |
| sulfamethoxazole | ||
| sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim | ||
| Tetracyclines | J01AA | doxycycline |
| minocycline | ||
| tetracycline | ||
| tigecycline | ||
| Trimethoprim | J01EA | trimethoprim |
| Antimicrobial | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | RankFootnote * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 53,614 | 52,547 | 50,610 | 50,700 | 49,441 | 51,585 | 52,318 | 52,402 | 53,862 | 55,080 | 57,380 | 62,915 | 61,327 | 61,685 | 1 |
| Amoxicillin and enzyme inhibitor | 7,148 | 7,296 | 7,113 | 7,470 | 7,470 | 8,389 | 8,931 | 9,744 | 10,512 | 10,989 | 9,660 | 12,894 | 13,877 | 15,424 | 4 |
| Ampicillin | 1,374 | 1,179 | 968 | 861 | 739 | 611 | 547 | 473 | 427 | 400 | 376 | 345 | 319 | 285 | 26 |
| Azithromycin | 1,788 | 2,208 | 2,504 | 2,825 | 2,667 | 2,911 | 2,873 | 2,799 | 2,865 | 2,912 | 2,878 | 3,811 | 3,826 | 3,251 | 12 |
| Cefadroxil | 546 | 599 | 641 | 695 | 707 | 730 | 821 | 875 | 926 | 983 | 874 | 779 | 1,049 | 1,151 | 21 |
| Cefazolin | 161 | 237 | 286 | 1,018 | 22 | ||||||||||
| Cefixime | 441 | 413 | 372 | 321 | 275 | 282 | 275 | 303 | 322 | 338 | 422 | 458 | 493 | 554 | 25 |
| Cefprozil | 2,427 | 2,833 | 3,274 | 3,901 | 4,377 | 4,589 | 4,536 | 4,183 | 4,109 | 4,095 | 4,092 | 4,188 | 3,695 | 3,328 | 11 |
| Ceftriaxone | 44 | 54 | 62 | 103 | 29 | ||||||||||
| Cefuroxime | 4,490 | 3,922 | 3,218 | 2,959 | 2,675 | 2,739 | 2,604 | 2,595 | 2,571 | 2,601 | 2,263 | 2,565 | 2,504 | 2,694 | 14 |
| Cephalexin | 16,148 | 16,697 | 17,717 | 18,988 | 19,606 | 20,855 | 22,160 | 22,479 | 23,123 | 22,635 | 22,384 | 24,258 | 24,867 | 25,875 | 2 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 12,754 | 12,005 | 11,843 | 12,319 | 12,618 | 12,943 | 13,817 | 14,426 | 14,693 | 14,270 | 14,741 | 15,220 | 14,850 | 14,235 | 6 |
| Clarithromycin | 12,402 | 12,693 | 12,060 | 12,833 | 12,724 | 14,490 | 15,251 | 16,125 | 16,552 | 16,935 | 16,727 | 17,635 | 16,748 | 14,572 | 5 |
| Clindamycin | 3,289 | 3,590 | 3,896 | 4,272 | 4,442 | 4,500 | 4,977 | 5,304 | 5,551 | 5,563 | 6,154 | 6,175 | 6,120 | 6,149 | 9 |
| Cloxacillin | 8,351 | 8,004 | 7,376 | 7,135 | 6,596 | 5,861 | 5,605 | 5,159 | 4,775 | 4,378 | 5,489 | 4,036 | 3,562 | 3,071 | 13 |
| Doxycycline | 844 | 819 | 797 | 815 | 818 | 862 | 929 | 1,027 | 1,116 | 1,164 | 1,396 | 1,541 | 1,657 | 1,789 | 17 |
| Erythromycin | 10,698 | 8,686 | 6,898 | 6,278 | 5,220 | 4,444 | 3,959 | 3,422 | 3,296 | 2,699 | 2,553 | 1,758 | 1,652 | 1,382 | 19 |
| Levofloxacin | 1,495 | 2,022 | 1,840 | 1,874 | 1,877 | 1,677 | 1,535 | 1,474 | 1,483 | 1,424 | 1,347 | 1,390 | 1,359 | 1,377 | 20 |
| Metronidazole | 4,808 | 4,927 | 5,127 | 5,238 | 5,311 | 5,564 | 5,588 | 5,789 | 5,921 | 6,349 | 6,395 | 6,528 | 6,645 | 8 | |
| Minocycline | 2,177 | 2,250 | 2,317 | 2,388 | 2,396 | 2,429 | 2,469 | 2,440 | 2,462 | 2,345 | 2,543 | 2,454 | 2,218 | 2,102 | 15 |
| Moxifloxacin | 35 | 486 | 846 | 1,120 | 1,231 | 1,478 | 1,828 | 2,046 | 2,049 | 2,094 | 2,075 | 2,133 | 1,971 | 1,786 | 18 |
| Nitrofurantoin | 935 | 982 | 1,020 | 1,073 | 1,152 | 1,211 | 1,324 | 1,390 | 1,503 | 1,625 | 1,740 | 1,862 | 1,975 | 1,992 | 16 |
| Norfloxacin | 2,518 | 2,466 | 2,349 | 2,227 | 2,080 | 1,919 | 1,791 | 1,597 | 1,480 | 1,311 | 1,223 | 1,119 | 950 | 839 | 23 |
| Penicillin V | 15,199 | 14,363 | 13,831 | 13,906 | 13,037 | 13,377 | 13,308 | 13,056 | 12,663 | 12,492 | 11,579 | 10,194 | 9,727 | 9,038 | 7 |
| Piperacillin and tazobactam | 239 | 247 | 204 | 697 | 24 | ||||||||||
| Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim | 29,691 | 26,988 | 24,482 | 22,972 | 20,493 | 18,856 | 18,520 | 18,102 | 18,154 | 18,208 | 18,187 | 18,079 | 16,903 | 16,713 | 3 |
| Tetracycline | 11,084 | 10,088 | 9,465 | 8,685 | 7,823 | 7,405 | 6,868 | 6,217 | 5,836 | 5,741 | 3,120 | 3,918 | 4,098 | 3,840 | 10 |
| Trimethoprim | 316 | 297 | 310 | 307 | 288 | 266 | 266 | 261 | 242 | 257 | 257 | 256 | 259 | 237 | 27 |
| Vancomycin | 26 | 28 | 32 | 41 | 70 | 79 | 76 | 84 | 85 | 88 | 193 | 213 | 188 | 231 | 28 |
| TOTAL | 208,984 | 205,654 | 196,701 | 197,214 | 190,648 | 193,974 | 196,013 | 195,644 | 197,731 | 197,508 | 197,185 | 207,773 | 203,720 | 202,581 | |
Antimicrobials were removed from this table if they represented <0.05% of mass of active ingredient dispensed in 2013. These are: amikacin, bacampicillin, cefaclor, cefepime, cefotaxime, cefoxitin, ceftazidime, ceftobiprole, cephradine, chloramphenicol, colistin, daptomycin, demeclocycline, dicloxacillin, ertapenem, erythromycin ethylsuccinate, fidaxomicin, flucloxacillin, fosfomycin, fusidic acid, gatifloxacin, gemifloxacin, gentamicin,grepafloxacin, imipenem and cilastatin, kanamycin, lincomycin, linezolid, meropenem, methenamine hippurate, methenamine mandelate, nalidixic acid, neomycin, ofloxacin, oxacillin, penicillin g, piperacillin, pivampicillin, pivmecillinam, spiramycin, streptomycin, sulfadiazine, sulfadiazine and trimethoprim, sulfamethizole, sulfamethoxazole, sulfapyridine, sulfisoxazole, sulfonamides, combinations with other antibacterials (excl. trimethoprim), telithromycin, ticarcillin and clavulanic acid, tigecycline, tobramycin, and trovafloxacin. |
|||||||||||||||
| Antimicrobial | C.-B. | Alb. | Sask. | Man. | Ont. | Qc | N.-B. | N.-É. | I.-P.-É. | T.-N.-L. | RankFootnote * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicilline | 141.35 | 178.84 | 236.37 | 186.62 | 188.57 | 99.12 | 150.73 | 168.80 | 161.62 | 262.68 | 1 |
| Amoxicilline et inhibiteur enzymatique | 21.37 | 30.36 | 21.48 | 26.70 | 18.78 | 31.74 | 24.96 | 25.42 | 71.68 | 49.54 | 8 |
| Ampicilline | 0.38 | 0.24 | 4.54 | 0.25 | 0.59 | 0.15 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 2.15 | 6.38 | 26 |
| Azithromycine | 29.81 | 52.17 | 73.27 | 84.93 | 70.44 | 52.08 | 76.48 | 57.36 | 65.04 | 83.07 | 4 |
| Céfadroxil | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 12.53 | 0.66 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 23 |
| Céfixime | 6.42 | 8.62 | 2.34 | 3.39 | 5.78 | 5.20 | 4.05 | 5.79 | 11.92 | 9.73 | 19 |
| Cefprozil | 0.57 | 12.09 | 4.37 | 7.72 | 20.06 | 20.82 | 7.35 | 15.03 | 4.87 | 0.49 | 14 |
| Céfuroxime | 10.62 | 8.34 | 8.46 | 4.96 | 8.65 | 5.57 | 25.78 | 16.82 | 7.13 | 28.60 | 16 |
| Céfalexine | 59.57 | 62.16 | 98.50 | 65.44 | 53.21 | 15.90 | 57.65 | 64.12 | 62.76 | 77.14 | 5 |
| Ciprofloxacine | 59.12 | 61.70 | 52.36 | 59.02 | 48.81 | 80.99 | 50.25 | 50.74 | 57.23 | 122.44 | 3 |
| Clarithromycine | 55.32 | 71.73 | 40.38 | 36.78 | 63.73 | 61.51 | 67.14 | 51.90 | 66.98 | 93.65 | 2 |
| Clindamycine | 21.74 | 28.76 | 32.90 | 19.53 | 22.05 | 19.67 | 23.91 | 22.58 | 18.61 | 22.57 | 10 |
| Cloxacilline | 6.25 | 6.11 | 11.82 | 12.86 | 6.16 | 4.53 | 5.01 | 6.84 | 12.01 | 12.56 | 18 |
| Doxycycline | 26.91 | 19.21 | 52.74 | 14.13 | 11.66 | 10.66 | 18.46 | 28.68 | 28.19 | 21.80 | 12 |
| Érythromycine | 5.87 | 3.79 | 16.83 | 5.60 | 2.83 | 1.02 | 3.26 | 6.51 | 21.87 | 5.74 | 22 |
| Lévofloxacine | 1.55 | 11.53 | 2.55 | 14.33 | 10.83 | 7.96 | 2.53 | 10.03 | 7.62 | 2.83 | 17 |
| Métronidazole | 19.41 | 22.06 | 22.53 | 19.74 | 19.49 | 16.21 | 20.24 | 21.24 | 18.03 | 25.85 | 11 |
| Minocycline | 12.58 | 21.14 | 6.06 | 14.49 | 8.68 | 24.41 | 12.98 | 15.27 | 9.81 | 14.48 | 15 |
| Moxifloxacine | 13.88 | 10.11 | 12.58 | 6.43 | 13.95 | 25.05 | 20.50 | 10.53 | 25.84 | 13.85 | 13 |
| Nitrofurantoïne | 43.75 | 27.91 | 48.00 | 21.72 | 41.49 | 17.96 | 33.64 | 44.77 | 27.83 | 26.93 | 6 |
| Norfloxacine | 0.64 | 3.22 | 0.26 | 0.60 | 8.07 | 0.72 | 15.37 | 2.59 | 7.62 | 7.03 | 21 |
| Pénicilline V | 23.57 | 26.54 | 15.87 | 24.55 | 19.26 | 32.44 | 29.54 | 24.49 | 26.50 | 27.12 | 9 |
| Sulfaméthoxazole et triméthoprime | 28.04 | 30.12 | 52.33 | 38.60 | 29.04 | 20.92 | 38.14 | 44.97 | 50.62 | 49.15 | 7 |
| Tétracycline | 4.58 | 3.20 | 4.94 | 4.63 | 7.08 | 2.35 | 2.90 | 4.35 | 10.08 | 4.36 | 20 |
| Triméthoprime | 0.73 | 1.05 | 2.63 | 0.78 | 1.90 | 3.84 | 2.19 | 0.89 | 0.63 | 2.12 | 24 |
| Vancomycine | 0.66 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 2.11 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 0.22 | 25 |
| TOTAL | 595.63 | 702.33 | 825.61 | 674.84 | 683.00 | 579.78 | 700.15 | 704.22 | 779.58 | 972.23 | |
Antimicrobials were removed from this table if they represented <0.05% of prescribing in 2012. These are: amikacin, cefaclor, cefazolin, cefepime, cefotaxime, cefoxitin, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, chloramphenicol, colistin, daptomycin, ertapenem, erythromycin ethylsuccinate, fidaxomicin, fosfomycin, fusidic acid, gentamicin, imipenem and cilastatin, lincomycin, linezolid, meropenem, methenamine mandelate, ofloxacin, penicillin g, piperacillin, piperacillin and tazobactam, spiramycin, streptomycin, sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, ticarcillin and clavulanic acid, tigecycline, and tobramycin. |
|||||||||||
| Antimicrobial | BC | AB | SK | MB | ON | QC | NB | NS | PEI | NF | RankFootnote * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 4.03 | 5.17 | 6.62 | 5.62 | 5.44 | 3.28 | 4.92 | 5.13 | 4.84 | 8.11 | 1 |
| Amoxicillin and enzyme inhibitor | 0.76 | 1.05 | 0.70 | 0.99 | 0.70 | 1.17 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 2.28 | 1.74 | 7 |
| Ampicillin | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 26 |
| Azithromycin | 0.72 | 0.98 | 1.16 | 1.33 | 1.20 | 0.74 | 1.13 | 0.86 | 0.79 | 1.24 | 5 |
| Cefadroxil | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.16 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 24 |
| Cefixime | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 21 |
| Cefprozil | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 16 |
| Cefuroxime | 0.45 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 1.26 | 0.76 | 0.29 | 1.36 | 12 |
| Cephalexin | 1.13 | 1.23 | 1.89 | 1.24 | 1.07 | 0.31 | 1.23 | 1.38 | 1.33 | 1.62 | 6 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 1.13 | 1.22 | 1.07 | 1.17 | 1.04 | 1.23 | 1.01 | 1.12 | 1.10 | 3.24 | 4 |
| Clarithromycin | 2.32 | 3.11 | 1.59 | 1.58 | 2.66 | 2.64 | 3.07 | 2.32 | 2.91 | 4.27 | 2 |
| Clindamycin | 0.38 | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.42 | 11 |
| Cloxacillin | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 19 |
| Doxycycline | 1.97 | 1.52 | 4.06 | 1.32 | 1.06 | 0.76 | 1.17 | 1.67 | 1.63 | 1.53 | 3 |
| Erythromycin | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.64 | 0.20 | 20 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.04 | 0.29 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 18 |
| Metronidazole | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.34 | 17 |
| Minocycline | 0.86 | 1.39 | 0.31 | 0.83 | 0.68 | 0.97 | 0.80 | 1.16 | 0.69 | 0.93 | 8 |
| Moxifloxacin | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.35 | 0.59 | 0.50 | 0.26 | 0.65 | 0.33 | 13 |
| Nitrofurantoin | 0.96 | 0.69 | 1.18 | 0.55 | 0.93 | 0.36 | 0.86 | 1.11 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 9 |
| Norfloxacin | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 22 |
| Ofloxacin | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 25 |
| Penicillin V | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.40 | 0.54 | 0.47 | 14 |
| Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.95 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 0.32 | 0.73 | 0.83 | 1.02 | 1.11 | 10 |
| Tetracycline | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.48 | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.71 | 0.39 | 15 |
| Trimethoprim | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 23 |
| TOTAL | 17.20 | 20.21 | 22.63 | 18.12 | 18.70 | 14.96 | 20.24 | 20.15 | 21.88 | 29.24 | |
Antimicrobials were removed from this table if they represented <0.05% of prescribing in 2012. These are: amikacin, cefaclor, cefazolin, cefepime, cefotaxime, cefoxitin, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, chloramphenicol, colistin, daptomycin, ertapenem, erythromycin ethylsuccinate, fidaxomicin, fosfomycin, fusidic acid, gentamicin, imipenem and cilastatin, lincomycin, linezolid, meropenem, methenamine mandelate, ofloxacin, penicillin g, piperacillin, piperacillin and tazobactam, spiramycin, streptomycin, sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, ticarcillin and clavulanic acid, tigecycline, and tobramycin. |
|||||||||||
Figure C.1. Defined daily doses and cost per 1,000 inhabitant-days, by antimicrobial class and province, 2013
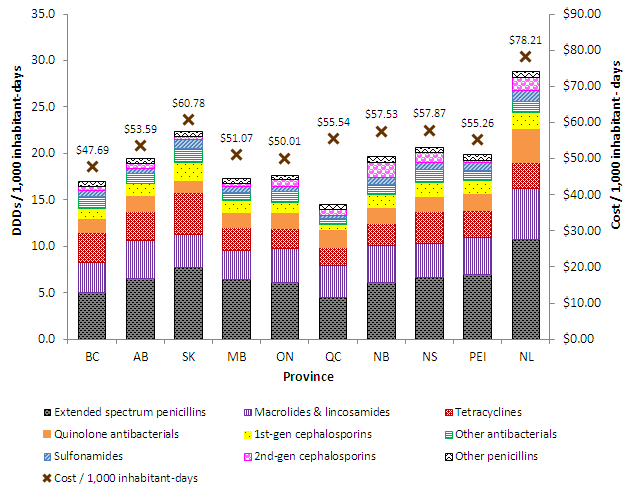
| Antimicrobial Therapeutic Class | BC | AB | SK | MB | ON | QC | NB | NS | PEI | NL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extended spectrum penicillins | 5.01 | 6.52 | 7.67 | 6.38 | 6.10 | 4.52 | 6.09 | 6.59 | 6.98 | 10.70 |
| Macrolides & lincosamides | 3.23 | 4.13 | 3.56 | 3.11 | 3.61 | 3.40 | 3.98 | 3.71 | 3.98 | 5.46 |
| Tetracyclines | 3.27 | 3.14 | 4.49 | 2.47 | 2.16 | 1.89 | 2.34 | 3.47 | 2.87 | 2.85 |
| Quinolone antibacterials | 1.42 | 1.70 | 1.34 | 1.62 | 1.72 | 1.99 | 1.81 | 1.61 | 1.83 | 3.67 |
| 1st-gen cephalosporins | 1.17 | 1.29 | 1.98 | 1.31 | 1.10 | 0.58 | 1.32 | 1.46 | 1.41 | 1.72 |
| Other antibacterials | 1.24 | 1.01 | 1.45 | 0.84 | 1.19 | 0.62 | 1.15 | 1.42 | 1.10 | 1.19 |
| Sulfonamides | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 0.53 | 0.30 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 1.14 |
| 2nd-gen cephalosporins | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.75 | 0.63 | 1.63 | 1.01 | 0.25 | 1.42 |
| Other penicillins | 0.46 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.50 | 0.58 | 0.67 |
| Cost / 1,000 inhabitant-days | 47.69 | 53.59 | 60.78 | 51.07 | 50.01 | 55.54 | 57.53 | 57.87 | 55.26 | 78.21 |
Figure C.2. Cost per DDD dispensed by retail pharmacies in Canada, by province (oral antimicrobials 2000 – 2009, oral and parenteral antimicrobials 2010 – 2013)

| Province | Cost per Defined Daily Dose | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | |
| BC | 3.11 | 3.15 | 3.32 | 3.39 | 3.34 | 3.27 | 3.15 | 3.08 | 3.10 | 3.11 | 3.18 | 2.98 | 2.90 | 2.79 |
| AB | 3.55 | 3.56 | 3.56 | 3.56 | 3.56 | 3.51 | 3.28 | 3.20 | 3.23 | 3.21 | 3.36 | 3.18 | 2.97 | 2.72 |
| SK | 2.86 | 2.84 | 2.87 | 2.92 | 2.79 | 2.68 | 2.57 | 2.51 | 2.57 | 2.68 | 2.78 | 2.71 | 2.65 | 2.71 |
| MB | 2.96 | 2.99 | 3.08 | 3.17 | 3.24 | 3.15 | 3.06 | 3.05 | 3.19 | 3.17 | 3.20 | 3.03 | 3.00 | 2.94 |
| ON | 4.11 | 3.99 | 4.03 | 4.13 | 4.06 | 4.03 | 3.67 | 3.50 | 3.45 | 3.45 | 3.36 | 3.05 | 2.89 | 2.82 |
| QC | 4.63 | 4.70 | 4.87 | 4.82 | 4.75 | 4.61 | 4.36 | 4.14 | 3.89 | 3.84 | 3.92 | 3.68 | 3.57 | 3.79 |
| NB | 3.78 | 4.01 | 4.00 | 4.04 | 4.00 | 3.93 | 3.62 | 3.41 | 3.33 | 3.32 | 3.44 | 3.32 | 3.24 | 2.90 |
| NS | 3.83 | 3.90 | 3.89 | 3.96 | 3.79 | 3.68 | 3.42 | 3.27 | 3.27 | 3.30 | 3.32 | 3.09 | 2.89 | 2.79 |
| PEI | 3.29 | 3.25 | 3.14 | 3.17 | 3.10 | 3.11 | 3.11 | 2.91 | 2.75 | |||||
| PEI & NL | 3.38 | 3.46 | 3.56 | 3.52 | 3.32 | |||||||||
| NL | 3.16 | 3.06 | 3.03 | 3.04 | 3.10 | 3.10 | 3.01 | 2.84 | 2.68 | |||||
Appendix D – Additional Hospital Purchasing Data
| Antimicrobial | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | RankFootnote * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 1,262.73 | 1,167.00 | 1,103.41 | 1,066.42 | 1,173.60 | 1,013.37 | 971.34 | 973.26 | 1,044.73 | 1,100.21 | 1,159.93 | 1,197.41 | 1,263.35 | 10 |
| Amoxicillin and enzyme inhibitor | 272.44 | 328.61 | 406.08 | 451.77 | 540.86 | 620.94 | 478.72 | 503.34 | 586.48 | 590.87 | 722.51 | 819.71 | 830.83 | 14 |
| Ampicillin | 2,275.11 | 1,341.79 | 1,295.13 | 1,318.27 | 2,050.84 | 2,210.65 | 1,357.88 | 1,118.16 | 1,056.24 | 988.52 | 982.71 | 953.45 | 947.68 | 13 |
| Azithromycin | 159.98 | 189.22 | 228.95 | 213.18 | 226.51 | 193.11 | 239.10 | 261.23 | 296.26 | 281.07 | 330.47 | 414.45 | 462.08 | 16 |
| Cefadroxil | 12.45 | 14.20 | 17.80 | 23.45 | 22.55 | 25.60 | 28.60 | 32.35 | 40.55 | 31.35 | 35.25 | 37.70 | 42.70 | 37 |
| Cefazolin | 3,927.45 | 4,228.99 | 4,278.14 | 4,128.03 | 4,151.53 | 3,896.28 | 4,428.73 | 4,570.26 | 4,864.67 | 4,589.91 | 4,575.73 | 4,691.44 | 4,060.75 | 5 |
| Cefixime | 36.78 | 39.46 | 35.86 | 24.04 | 28.32 | 29.68 | 37.16 | 42.55 | 53.93 | 57.10 | 72.61 | 95.15 | 97.04 | 28 |
| Cefotaxime | 593.37 | 628.39 | 731.14 | 765.77 | 782.82 | 847.58 | 838.68 | 567.25 | 545.93 | 317.48 | 286.02 | 255.05 | 195.22 | 21 |
| Cefoxitin | 7,653.08 | 11,208.45 | 12,789.57 | 12,594.00 | 10,113.11 | 9,756.92 | 9,705.48 | 8,560.82 | 10,350.01 | 7,870.20 | 7,797.13 | 6,257.71 | 4,614.48 | 3 |
| Cefprozil | 37.45 | 40.56 | 55.23 | 66.29 | 51.42 | 46.98 | 50.41 | 52.04 | 68.47 | 60.29 | 55.28 | 52.39 | 49.75 | 31 |
| Ceftazidime | 410.93 | 567.86 | 457.12 | 455.27 | 716.59 | 512.58 | 155.81 | 157.84 | 151.19 | 153.87 | 149.39 | 156.56 | 142.80 | 25 |
| Ceftriaxone | 272.36 | 438.53 | 615.62 | 722.56 | 789.33 | 843.65 | 999.33 | 1,215.56 | 1,499.93 | 1,528.40 | 2,942.70 | 9,146.01 | 16,794.88 | 2 |
| Cefuroxime | 1,089.74 | 916.64 | 730.68 | 616.70 | 554.66 | 386.42 | 347.27 | 298.97 | 297.41 | 226.61 | 257.25 | 232.23 | 223.04 | 19 |
| Cephalexin | 1,077.73 | 1,123.48 | 1,226.69 | 1,239.41 | 1,362.13 | 1,664.34 | 1,094.83 | 1,084.37 | 1,097.21 | 1,003.52 | 1,101.53 | 1,160.27 | 1,212.72 | 11 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 1,741.41 | 1,598.12 | 1,653.27 | 1,702.93 | 1,538.76 | 1,631.67 | 1,643.50 | 1,636.99 | 1,617.46 | 1,433.96 | 1,453.08 | 1,507.31 | 1,710.37 | 6 |
| Clarithromycin | 355.57 | 333.38 | 311.45 | 300.86 | 304.33 | 294.18 | 298.57 | 301.95 | 317.24 | 265.43 | 275.68 | 248.88 | 192.19 | 23 |
| Clindamycin | 604.30 | 588.49 | 556.90 | 515.76 | 547.73 | 866.25 | 919.12 | 907.78 | 919.97 | 857.34 | 882.35 | 867.61 | 1,413.53 | 8 |
| Cloxacillin | 1,626.03 | 1,550.90 | 1,517.02 | 1,454.70 | 1,413.03 | 1,336.41 | 1,311.96 | 1,256.98 | 1,396.81 | 1,243.30 | 1,329.25 | 1,329.24 | 1,292.02 | 9 |
| Doxycycline | 47.45 | 34.43 | 43.96 | 49.59 | 44.68 | 48.50 | 80.55 | 131.47 | 86.95 | 93.17 | 116.76 | 97.32 | 106.73 | 27 |
| Ertapenem | 0.80 | 8.38 | 20.35 | 33.89 | 43.04 | 64.27 | 86.45 | 102.15 | 143.79 | 167.09 | 183.08 | 24 | ||
| Erythromycin | 263.94 | 276.17 | 297.10 | 201.32 | 208.89 | 184.92 | 179.84 | 162.23 | 149.82 | 115.86 | 133.60 | 98.43 | 82.77 | 29 |
| Gentamicin | 88.41 | 72.14 | 53.52 | 34.70 | 49.82 | 91.12 | 88.95 | 78.21 | 68.12 | 63.98 | 59.54 | 57.36 | 47.85 | 32 |
| Imipenem | 301.09 | 936.85 | 1,083.44 | 215.78 | 296.05 | 265.70 | 278.19 | 254.51 | 261.83 | 242.36 | 793.08 | 1,359.70 | 1,103.93 | 12 |
| Levofloxacin | 458.34 | 484.23 | 456.58 | 412.38 | 366.77 | 315.89 | 312.81 | 317.94 | 349.00 | 302.70 | 337.08 | 319.98 | 307.28 | 17 |
| Linezolid | 3.97 | 10.73 | 13.22 | 15.39 | 24.60 | 27.18 | 33.57 | 39.74 | 44.07 | 39.22 | 41.07 | 48.22 | 44.41 | 33 |
| Meropenem | 142.66 | 246.43 | 243.12 | 261.20 | 227.46 | 355.53 | 400.38 | 457.76 | 548.19 | 538.70 | 558.06 | 546.10 | 591.24 | 15 |
| Metronidazole | 1,018.43 | 399.58 | 151.55 | 147.95 | 134.03 | 131.81 | 129.19 | 119.69 | 93.22 | 99.37 | 138.97 | 117.30 | 122.68 | 26 |
| Moxifloxacin | 22.13 | 49.42 | 83.88 | 174.51 | 260.60 | 351.58 | 374.02 | 375.16 | 378.35 | 331.27 | 329.58 | 307.01 | 257.35 | 18 |
| Nitrofurantoin | 50.21 | 57.58 | 58.91 | 67.74 | 70.77 | 71.73 | 69.92 | 66.99 | 67.81 | 77.14 | 85.07 | 85.83 | 81.50 | 30 |
| Penicillin G | 9,399.67 | 7,545.75 | 8,955.94 | 10,892.43 | 10,820.07 | 9,585.90 | 9,734.76 | 10,263.17 | 10,550.84 | 10,101.52 | 9,816.04 | 8,005.56 | 4,382.57 | 4 |
| Penicillin V | 502.00 | 595.70 | 618.66 | 544.61 | 505.85 | 534.06 | 292.51 | 315.65 | 359.91 | 220.94 | 403.77 | 239.56 | 218.07 | 20 |
| Piperacillin and enzyme inhibitor | 1,898.13 | 1,230.91 | 2,312.65 | 3,043.18 | 4,046.54 | 4,636.79 | 5,741.59 | 6,324.86 | 8,862.18 | 9,234.08 | 13,477.90 | 27,751.54 | 40,097.01 | 1 |
| Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim | 1,991.11 | 1,672.59 | 1,758.77 | 1,627.06 | 1,670.46 | 1,719.65 | 1,602.25 | 1,559.30 | 1,611.91 | 1,496.04 | 1,525.65 | 1,522.47 | 1,509.31 | 7 |
| Tetracycline | 107.75 | 104.65 | 89.23 | 77.08 | 75.10 | 73.30 | 89.73 | 87.58 | 95.03 | 40.45 | 49.53 | 46.43 | 43.28 | 35 |
| Ticarcillin and enzyme inhibitor | 1,106.35 | 2,490.13 | 2,209.10 | 925.15 | 876.93 | 1,003.16 | 920.27 | 967.73 | 757.74 | 717.90 | 310.54 | 122.69 | 42.82 | 36 |
| Tobramycin | 62.26 | 57.53 | 27.23 | 18.54 | 27.94 | 58.29 | 62.04 | 57.01 | 54.45 | 51.30 | 47.53 | 47.16 | 43.78 | 34 |
| Vancomycin | 1,982.13 | 3,237.72 | 859.70 | 235.89 | 266.05 | 188.14 | 164.14 | 175.93 | 227.34 | 228.61 | 304.30 | 262.04 | 194.94 | 22 |
| TOTAL | 44,156.45 | 46,947.12 | 48,747.87 | 47,897.84 | 47,211.50 | 46,488.19 | 45,997.73 | 45,558.15 | 51,053.92 | 46,866.71 | 53,255.74 | 70,792.27 | 85,148.84 | |
Antimicrobials were removed from this table if they represented <0.05% of mass of active ingredient purchased in 2013. These are: amikacin, bacampicillin, cefaclor, cefepime, cefotetan, ceftizoxime, ceftobiprole, cephalothin, chloramphenicol, colistin, daptomycin, demeclocycline, doripenem, fosfomycin, gatifloxacin, gemifloxacin, lincomycin, methenamine hippurate, methenamine mandelate, minocycline, nalidixic acid, netilmicin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, piperacillin, pivampicillin, pivmecillinam, quinupristin/dalfopristin, spiramycin, streptomycin, sulfadiazine, sulfadiazine and trimethoprim, sulfonamides, combinations with other antibacterials (excl. trimethoprim), telithromycin, tigecycline, trimethoprim, and trovafloxacin. |
||||||||||||||
| Antimicrobial | BC | AB | SK | MB | ON | QC | NB | NS | PEI & NL | RankFootnote * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 7 |
| Amoxicillin and enzyme inhibitor | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 12 |
| Ampicillin | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 18 |
| Azithromycin | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 6 |
| Cefadroxil | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 39 | |||||
| Cefazolin | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 5 |
| Cefixime | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 24 |
| Cefotaxime | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 31 |
| Cefoxitin | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.40 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 8 |
| Cefprozil | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 33 |
| Ceftazidime | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 37 |
| Ceftriaxone | 0.36 | 0.73 | 0.16 | 0.67 | 0.29 | 0.24 | 0.61 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 2 |
| Cefuroxime | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 21 |
| Cephalexin | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 15 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 4 |
| Clarithromycin | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 17 |
| Clindamycin | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 16 |
| Cloxacillin | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 13 |
| Daptomycin | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 35 |
| Doxycycline | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 9 |
| Ertapenem | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 26 |
| Erythromycin | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 29 |
| Gentamicin | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 23 |
| Imipenem | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.05 | <0.01 | 0.49 | 0.14 | 20 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 14 |
| Linezolid | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 36 |
| Meropenem | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 22 |
| Metronidazole | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.04 | <0.01 | 30 |
| Minocycline | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 32 |
| Moxifloxacin | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 11 |
| Nitrofurantoin | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 19 |
| Norfloxacin | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 38 |
| Penicillin G | 1.45 | 1.17 | 1.18 | 1.21 | 1.11 | 0.68 | 0.94 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 1 |
| Penicillin V | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 28 |
| Piperacillin and enzyme inhibitor | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 3 |
| Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 10 |
| Tetracycline | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 34 |
| Vancomycin | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 27 |
| TOTAL | 3.51 | 3.16 | 3.17 | 4.65 | 2.50 | 2.42 | 3.15 | 3.06 | 3.27 | |
Antimicrobials were removed from this table if they represented <0.05% of DDDs in 2012. These are: amikacin, cefaclor, cefepime, chloramphenicol, colistin, doripenem, fosfomycin, lincomycin, methenamine mandelate, ofloxacin, piperacillin, spiramycin, streptomycin, ticarcillin and enzyme inhibitor, tigecycline, and trimethoprim. |
||||||||||
| Antimicrobial | BC | AB | SK | MB | ON | QC | NB | NS | PEI & NL | RankFootnote * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 10 |
| Amoxicillin and enzyme inhibitor | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 14 |
| Ampicillin | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | <0.01 | 12 |
| Azithromycin | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 16 |
| Cefadroxil | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 38 | |||||
| Cefazolin | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 5 |
| Cefepime | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 39 | |
| Cefixime | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 30 |
| Cefotaxime | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.03 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 20 |
| Cefoxitin | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 4 |
| Cefprozil | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 33 |
| Ceftazidime | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 25 |
| Ceftriaxone | 0.26 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.41 | 2 |
| Cefuroxime | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 23 |
| Cephalexin | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 11 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 7 |
| Clarithromycin | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 21 |
| Clindamycin | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 13 |
| Cloxacillin | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9 |
| Doxycycline | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 29 |
| Ertapenem | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 24 |
| Erythromycin | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 28 |
| Gentamicin | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 32 |
| Imipenem | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.06 | <0.01 | 0.72 | 0.20 | 8 |
| Levofloxacin | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 17 |
| Linezolid | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 35 |
| Meropenem | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 15 |
| Metronidazole | 0.00 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 27 |
| Moxifloxacin | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 18 |
| Nitrofurantoin | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.00 | <0.01 | 31 |
| Penicillin G | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 3 |
| Penicillin V | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 22 |
| Piperacillin | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 34 |
| Piperacillin and enzyme inhibitor | 0.43 | 0.35 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 1.02 | 0.72 | 1.85 | 0.84 | 1.09 | 1 |
| Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 6 |
| Ticarcillin and enzyme inhibitor | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 26 | ||
| Vancomycin | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 19 |
| TOTAL | 1.82 | 1.72 | 1.76 | 3.54 | 1.97 | 1.91 | 3.18 | 2.74 | 2.74 | |
Antimicrobials were removed from this table if they represented <0.05% of mass of active ingredient purchased in 2012. These are: amikacin, cefaclor, chloramphenicol, colistin, daptomycin, doripenem, fosfomycin, lincomycin, methenamine mandelate, minocycline, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, spiramycin, streptomycin, tigecycline, and trimethoprim. |
||||||||||