Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS): Design and methods
On this page
- Using whole genome sequencing for antimicrobial resistance prediction for Salmonella
- Recent Design and Methods document
- All Design and Methods documents
- Did you find what you were looking for?
Using whole genome sequencing for antimicrobial resistance prediction for Salmonella
CIPARS is transitioning from using broth microdilution to whole genome sequencing (WGS) for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) determination. With WGS, AMR is predicted based on the presence of genes, as compared to broth microdilution which measures the growth of bacteria in the presence of increasing concentrations of antimicrobials. Validation tests performed by the National Microbiology Laboratory found that the prediction of AMR from WGS for Salmonella is accurate and reliable (Bharat et al., 2022).
With this transition comes changes in how CIPARS reports ciprofloxacin resistance in Salmonella. With broth microdilution bacteria are classified as either susceptible, intermediate, or resistant depending on the lowest concentration of antimicrobial needed to inhibit growth. However, with WGS, the ciprofloxacin "resistance" genes do not discriminate between "resistant" and "intermediate", and findings are therefore reported as 1) "non-susceptible" (intermediate and resistant classification based on the presence of resistance genes) or 2) "susceptible" (based on the absence of resistance genes).
It is important to note that the percentage of ciprofloxacin "non-susceptible" Salmonella (determined using WGS) may be higher than in previous reports where the percentage of ciprofloxacin "resistant" Salmonella (determined using broth microdilution) was reported (Figure 1). Going forward, a component of this transition will include harmonizing WGS data with previous broth microdilution data for comparison of historical trends with current AMR surveillance findings.
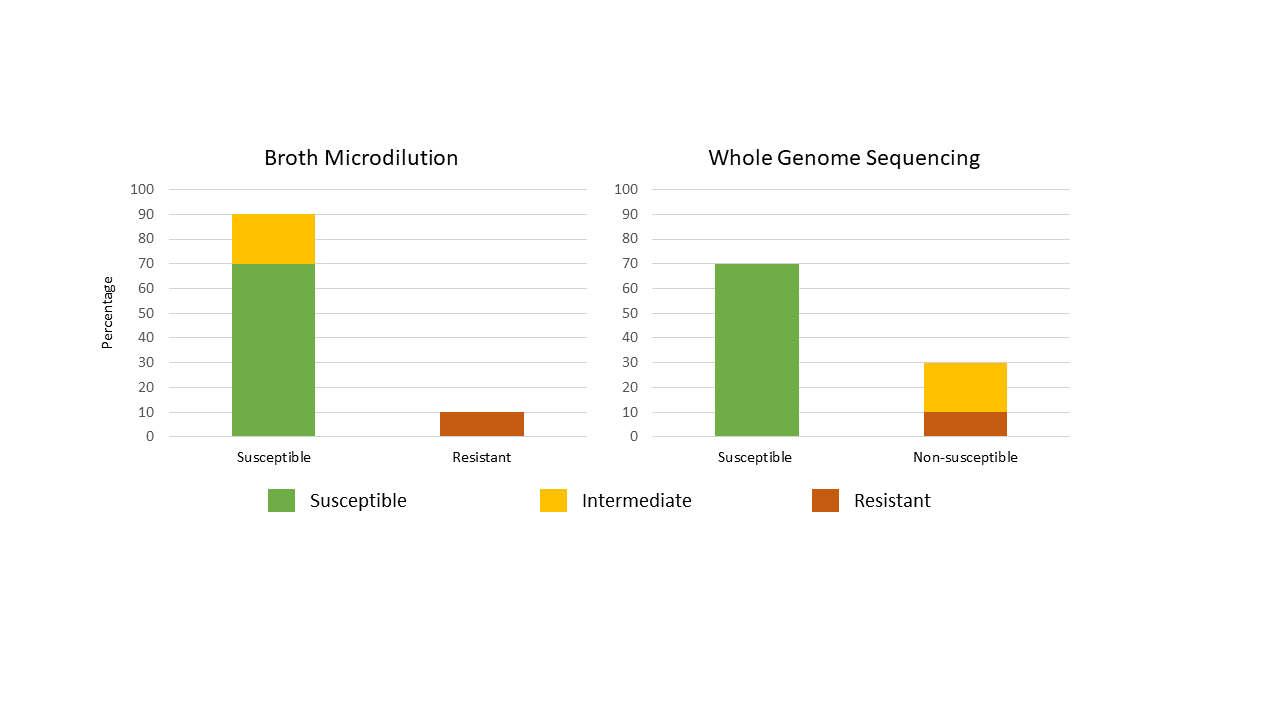
Figure 1 - Text description
| Method | Findings | Percentage of susceptible isolates | Percentage of intermediate isolates | Percentage of resistant isolates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broth microdilution | Susceptible | 70 | 20 | NA |
| Resistant | NA | NA | 10 | |
| Whole genome sequencing | Susceptible | 70 | NA | NA |
| Non-susceptible | NA | 20 | 10 | |
| Not applicable: NA | ||||
Work cited:
Recent Design and Methods document
This document describes the design and methods used for all antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial use surveillance components for a recent surveillance year
All Design and Methods documents
These documents describe the design and methods used for all antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial use surveillance components for all surveillance years, since the beginning of CIPARS in 2002
| Surveillance year | Document title |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 2019 Design and Methods |
| 2018 | 2018 Design and Methods |
| 2017 | 2017 Design and Methods |
| 2016 | 2016 Design and Methods: see Chapter 5 in the 2016 Annual Report |
| 2015 | 2015 Design and Methods: see Chapter 5 in the 2015 Annual Report |
| 2014 | 2014 Design and Methods: see Appendix in the 2014 Annual Report |
| 2013 | 2013 Design and Methods: see the 2013 Chapter 1. Design and Methods |
| 2012 | 2012 Design and Methods: see the 2012 Chapter 1. Design and Methods |
| 2011 | 2011 Design and Methods: no annual report was published in 2011 |
| 2010 | 2010 Design and Methods: see Appendix A in the 2010 Annual Report |
| 2009 | 2009 Design and Methods: see Appendix A in the 2009 Annual Report |
| 2008 | 2008 Design and Methods: see Appendix A in the 2008 Annual Report |
| 2007 | 2007 Design and Methods: see Appendix A in the 2007 Annual Report |
| 2006 | 2006 Design and Methods: see Appendix A in the 2006 Annual Report |
| 2005 | 2005 Design and Methods: see Appendix A in the 2005 Annual Report |
| 2004 | 2004 Design and Methods: see Appendix B in the 2004 Annual Report |
| 2003 | 2003 Design and Methods: see Appendix B in the 2003 Annual Report |
| 2002 | 2002 Design and Methods: see Appendix B in the 2002 Annual Report |
Did you find what you were looking for?
To obtain additional information, please contact us by email: cipars-picra@phac-aspc.gc.ca