Importing, exporting or transhipping consumer products and cosmetics: Guide
Disclaimer
This policy and its associated documents are intended to provide guidance and do not supersede, limit or alter the Act or regulations. In case of any discrepancy between this policy and the legislation, the legislation will prevail.
Table of Contents
- 1. Purpose
- 2. Scope
- 3. Policy objective
- 4. What is importing or exporting for commercial purposes?
- 5. Import into Canada: Importing requirements of consumer products or cosmetics into Canada for commercial purposes
- 6. Export from Canada: Exporting consumer products or cosmetics from Canada for commercial purposes
- 7. Tranship through Canada: Transhipping consumer products or cosmetics through Canada
- Appendix A – Glossary
- Appendix B – Consumer products with specific regulatory requirements and their associated guides
- Appendix C – References
About this document
1. Purpose
This policy provides general information to any person – an individual or an organization that is involved in the import, export or transhipment of consumer products and cosmetics for commercial purposes. It describes Health Canada's position about this subject within the context of the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and the Food and Drugs Act and it may help you to understand your responsibilities with respect to products you move into and out of Canada for commercial purposes. However, it is not intended to provide legal advice to you regarding those responsibilities. If you have questions about your responsibilities under those Acts, you should seek advice from a legal professional.
Are you an importer?
In general, an importer is a person or entity that brings consumer products or cosmetics into Canada from another country (including from the United States). Depending on the specifics of a case, an importer may be an individual or business that:
- crosses the Canadian border with the products.
- causes or directs the goods to be imported into Canada.
- directly receives the products entering Canada from another country.
Note: An 'Importer of record', 'Non-resident importer' or 'Foreign importer' will not be treated as an Importer carrying on the activity of Import as described above.
Are you an exporter?
In general, an exporter is an entity that moves consumer products or cosmetics out of Canada into another country. It includes an individual or an organization that:
- crosses the Canadian border with the products.
- sends or ships the products abroad.
- sells or advertises the products over the internet and ships to a foreign jurisdiction from Canada.
2. Scope
The information in this policy is directed towards an individual or an organization that imports, exports or tranships consumer products and cosmetics through Canada for commercial purposes.
-
Consumer products are regulated under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA) and its regulations, and are defined as:
"Consumer product means a product, including its components, parts or accessories that may reasonably be expected to be obtained by an individual to be used for non-commercial purposes, including for domestic, recreational and sports purposes, and includes its packaging."
Examples include consumer chemicals, sporting equipment, home furnishings, lighters and matches, mattresses and children's products such as cribs, strollers, toys, sleepwear and pacifiers.
- Cosmetics are regulated under the Food and Drugs Act (FDA) and its Cosmetic Regulations. A Cosmetic is defined as:
"Cosmetic includes any substance or mixture of substances manufactured, sold or represented for use in cleansing, improving or altering the complexion, skin, hair or teeth, and includes deodorants and perfumes."Examples include perfume, deodorant, shampoo, tooth whiteners, shaving cream, lipstick, hair dyes, soaps, moisturizers, self-tanning products, nail polish and nail polish remover. It does not include cosmetics or grooming products for animals. Most pet grooming products intended for use on animals are considered consumer products and regulated under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and its regulations.
This policy provides general information on import, export and transhipments under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and its regulations and the provisions of the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations. Other federal legislation may impose additional requirements on importers, exporters, and trans-shippers of consumer products and cosmetics, but they are not covered in this document.
The scope of this policy does not include:
- products described in Section 4 of the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (excluding cosmetics).
- consumer products for research purposes.
- cosmetics for lab testing, use in a clinical trial or for research purposes.
- consumer products or cosmetics exclusively for personal use.
Note: Consumers bringing products across the border into Canada should be aware that some consumer products are not allowed into Canada by law, even if they are for personal use. For more information, see Bringing Consumer Products into Canada.
3. Policy objective
The vast majority of consumer products and cosmetics in the Canadian market are imported. Verifying the safety of these products is important to the Government of Canada. Therefore, the objective of this policy is to:
- familiarize an individual or an organization that imports, exports or tranships consumer products or cosmetics with the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and the Food and Drugs Act and their obligations under these Acts and their regulations;
- communicate Health Canada's expectations of any person or business that imports, exports or tranships consumer products and cosmetics for commercial purposes; and
- provide another tool to assist Health Canada staff to administer the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and the Food and Drugs Act in a fair, consistent and effective way across Canada.
Refer to the following parts of this document for information specific to importing, exporting or transhipping goods:
- Part 4 – What is 'importing' or 'exporting' for commercial purpose?
- Part 5 – Import into Canada
- Part 6 – Export from Canada
- Part 7 – Tranship through Canada
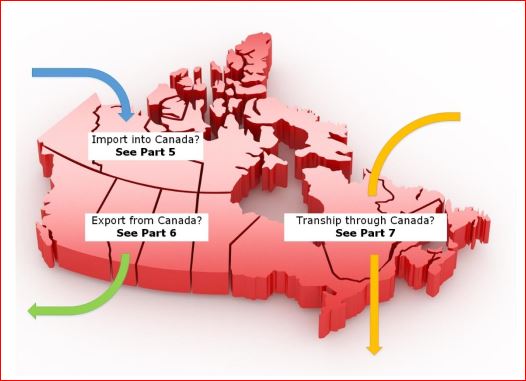
Text Description:
Refer to the appropriate section of this document for details on the different requirements for any individual or organization who imports, exports or tranships consumer products or cosmetics in Canada for commercial purposes.
Guidance
4. What is 'importing' or 'exporting' for commercial purposes?
Health Canada takes the position that the import or export of a consumer product or a cosmetic product for the following purposes constitutes the import or export of those products for a commercial purpose:
- for sale or distribution by a retailer, distributor or other commercial establishment, including independent sales contractors;
- for distribution within a supply chain (e.g., at any point from import to consumer);
- for supply or distribution of products free of charge, such as donations or promotional giveaways;
- for advertising at trade shows;
- for small businesses that sell new products or second hand products from a recurring flea market stall, rotating fairs, bazaars;
- for advertising or selling through online storefronts or e-commerce platforms, including those found on online auction websites or online classified ad websites;
- in a shipment that is sent with advertising or promotional materials, such as pamphlets.
In addition, for cosmetics, Health Canada takes the position that the following activities involving a cosmetic constitute the import or export of that product for a commercial purpose:
- for a professional to use in their practice. Professionals include beauticians, hairdressers, estheticians, dermatologists, medical doctors, dentists and dental hygienists.
- a shipment that:
- is part of a series of repeat shipments, is received within a 90-day period of at least one other shipment in that series, contains the same cosmetic products for use by the same person at the same address as at least one other shipment received within a 90-day period, and the contents of these at least two shipments exceeds a 90-day supply in total; or
- contains more than a 90-day supply of the cosmetic products in the shipment taking into account, among other things, directions for use.
The above list is not exhaustive. Health Canada may use other indicators and factors to determine commercial purpose (as described in the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act - section 4). For example, Health Canada may take into account the level of involvement in an organized supply chain for a product, or the use of business-like practices in supplying products.
Note: A 90 day supply is based on, among other things, the directions for use of the product.
5. Import into Canada: Importing requirements of consumer products or cosmetics into Canada for commercial purposes
Consumer products
Consumer products imported for commercial purposes are regulated under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and its regulations.
You may import consumer products into Canada, if the product:
- is not prohibited in Canada (see CCPSA Schedule 2);
- does not pose a "danger to human health or safety";
- meets the requirements in the applicable regulations or standards (see Appendix B for a list of product-specific regulations);
- has not been ordered — through a written notice — by Health Canada to be recalled;
- has not been voluntarily recalled in Canada;
- is not subject of a measure, a written order or one that is under review by Health Canada.
As an importer of consumer products, you are required to:
- Ensure the imported products meet the conditions above
- Provide information and assistance to Health Canada Inspectors
- Report to Health Canada, potential or known, health or safety incidents and product defects of consumer products you import (Canada Consumer Product Safety Act - Section 14). For example, recalls or measures initiated for health or safety reasons must be reported to Health Canada. Incidents must also be reported within a certain time period. Please refer to the Guidance on Mandatory Incident Reporting under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act.
- Prepare and keep documents to ensure a consumer product imported by you can be traced throughout the supply chain, in the event that a danger must be addressed (Canada Consumer Product Safety Act - Section 13). Records must be kept for a certain period of time. Please refer to the Guidance on Preparing and Maintaining Documents under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act
- Provide tests or studies to Health Canada of consumer products you import, if requested (Canada Consumer Product Safety Act - Section 12).
- Carry out a recall of consumer products you import when ordered by Health Canada to do so (Canada Consumer Product Safety Act - Section 31). Please refer to the Guidance on voluntarily recalling consumer products or cosmetics in Canada
For some consumer products, specific product requirements are set out in regulations (see Appendix B for a list of product-specific regulations). These regulations may outline product, label or packaging specifications or make reference to an existing standard.
Beyond complying with the requirements listed in any specific regulations, it is the importer's responsibility to ensure the products they import do not present a "danger to human health or safety" (see Industry Guidance - "Danger to Human Health or Safety" Posed by Consumer Products). Importers may also reference published guidelines from Health Canada or another relevant organization (e.g. regulators in other jurisdictions, industry associations, etc.).
Cosmetics
Cosmetics imported for a commercial purpose must meet the requirements of the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations.
If you intend to import cosmetics into Canada for commercial purposes, as per Section 16 of the Food and Drugs Act, no person shall sell any cosmetic that:
- (a) has in or on it any substance that may cause injury to the health of the user when the cosmetic is used,
- (i) according to the directions on the label or accompanying the cosmetic, or
- (ii) for such purposes and by such methods of use as are customary or usual therefor;
- (b) consists in whole or in part of any filthy or decomposed substance or of any foreign matter; or
- (c) was manufactured, prepared, preserved, packaged or stored under unsanitary conditions.
In addition, as an importer, you must meet the following obligations relating to:
- Ingredients;
- Cosmetic Notification Form;
- Appropriate claims or classification; and
- Labelling.
1. Ingredients
To determine if an ingredient is safe for use in cosmetics, Health Canada applies evidence-based decision making and focuses on reducing any risks to consumers if an ingredient poses a hazard. The Cosmetic Ingredient Hotlist (Hotlist) is an administrative tool that includes a list of ingredients that may be prohibited or restricted in cosmetics and also gives information about warnings and cautionary statements.
Health Canada uses the Hotlist to communicate to industry, stakeholders and the public that certain substances – when present in a cosmetic may:
- a) contravene the general prohibition found in Section 16 of the Food and Drugs Act;
- b) contravene a provision of the Cosmetic Regulations; or
- c) need to meet certain restrictions.
In addition, the Hotlist communicates that the presence of certain substances, or their use under certain conditions, may make the product unsuitable for classification as a cosmetic under the Food and Drugs Act.
Cosmetics containing ingredients described as prohibited or restricted on the Hotlist may result in shipments being refused entry into Canada or removed from sale.
2. Cosmetic Notification Form
All cosmetics sold in Canada must be notified to Health Canada, through the online Cosmetic Notification Form. The importer and manufacturer must notify Health Canada within 10 days of selling a cosmetic product in Canada.
Cosmetic imports for commercial purposes should contain the unique Cosmetic Number issued by Health Canada on import documents for easy verification.
For more information on the cosmetic notification process, see the Guide for Cosmetic Notifications.
Failure to notify Health Canada about a cosmetic product may result in Health Canada initiating compliance and enforcement actions in relation to that product.
3. Appropriate claims or classification
A cosmetic product cannot make therapeutic claims or pest control claims on the product label, advertisements, the product website, or elsewhere. Therapeutic claims are only allowed on drugs or natural health products, while pest control claims are only allowed on pest control products. Products with therapeutic claims or pest control claims must obtain appropriate market authorization before they can be sold in Canada.
When deciding whether to place claims on your products, you may want to take into account the general information set out in the following documents:
- Guidelines for The Non-prescription and Cosmetic Industry Regarding Non-therapeutic Advertising and Labelling Claims
- Guidance Document: Classification of Products at the Cosmetic-Drug Interface
4. Labelling
All cosmetics must be labelled in accordance with:
- The Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations.
To comply with these requirements, cosmetic labels must include:
- an ingredient list – using the International Nomenclature for Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) system;
- the identity of the product, in English and French;
- contact information (i.e. telephone number, email address, website, etc.) where consumers can direct their questions about the cosmetic;
- warnings or cautions, if applicable, in English and French; and
- directions for safe use of the product, if applicable, in English and French according to federal requirements.
There may be additional labelling requirements, cosmetics must also comply with other applicable legislation, such as The Consumer Packaging and Labelling Act and Regulations and the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (CEPA).
For details, see the Industry Guide for the labelling of cosmetics.
Advance Notice of Importation (ANI) Process for Cosmetics
It is prohibited to import cosmetic products into Canada for sale if their sale would contravene the Food and Drugs Act or the Cosmetic Regulations (refer to Section 5 of the Cosmetic Regulations). However, under Section 9 of the Cosmetic Regulations importers are allowed to import for sale a non-compliant cosmetic provided the following conditions are met:
- The importer provides advance notice by email to the Health Canada regional office corresponding to the province or territory of the importer's place of business; and
- The product is relabelled or modified as required to enable its sale to be lawful in Canada within 3 months of import.
For more information on Section 9 of the Cosmetic Regulations, see Health Canada's Advance Notice of Importation Process for cosmetics and drugs. Health Canada's approach to compliance and enforcement activities, including in relation to consumer products and cosmetics, is described in this document in Part 8 - Guiding Principles.
The submission of an Advance Notice of Importation (ANI) Form does not guarantee that importations of cosmetics will be allowed entry into Canada.
6. Export from Canada: Exporting consumer products or cosmetics from Canada for commercial purposes
If you are exporting consumer products or cosmetics from Canada for commercial purposes, then you must ensure that the products you intend to export are not only compliant with the requirements of the country you are shipping to, but also compliant with the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and its regulations and the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations, which set out rules concerning the export from Canada of:
- consumer products and cosmetics manufactured in Canada for export;
- consumer products and cosmetics that are imported into Canada for export only;
- cosmetics that are imported under the Advance Notice of Importation Process, for export.
Health Canada's approach to compliance and enforcement activities is described in this document in Part 8 - Guiding Principles.
An individual or an organization exporting consumer products and cosmetics from Canada is responsible for taking the necessary steps to ensure that the exported products do not contravene the law of the destination country.
7. Tranship through Canada: Transhipping consumer products or cosmetics through Canada
Consumer products
The Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and its regulations apply to consumer products transhipped through Canada. Transhipped products are not for consumption in Canada. As is the case with all consumer products, Health Canada's approach to compliance and enforcement activities concerning consumer products transiting through Canada is outlined in this document in Part 8 – Guiding Principles.
Cosmetics
The Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations do not apply to cosmetics transhipped through Canada provided that they satisfy the following conditions of exemption under Section 38 of the Food and Drugs Act:
- the cosmetics are manufactured or prepared outside of Canada;
- the cosmetics are imported solely for the purpose of export and not sold for use in Canada; and they
- meet any other prescribed requirements.
Cosmetics while in transit through Canada under Section 38 of the Food and Drugs Act cannot undergo any activities regulated under the Food and Drugs Act and the Cosmetic Regulations. These activities include:
- Sale or distribution;
- Manufacturing or fabrication;
- Packaging or labelling;
- Testing; or
- Storage – unless still in bond in a Canada Border Services Agency's (CBSA) storage facility for transhipments.
The following examples help to illustrate these requirements.
Example 1:
My company wants to have a shipment of cosmetics pass through Canada from country A on its way to country B for logistical reasons.
- Question: Do these cosmetics need to comply with the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations?
- Answer: This would be considered transhipment. If the conditions for transhipment are met, as described above, the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations would not apply to this shipment.
Example 2:
My Canadian company wants to import cosmetic products into my warehouse for foreign export. I want to re-label my cosmetics while they are in Canada. The products will not be sold to Canadians. Upon receiving orders from foreign clients, my company will fulfill the orders and export the cosmetics to my foreign clients.
- Question: Do my products need to comply with the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations?
- Answer: In this scenario, the company in Canada is conducting activities regulated under the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations (labelling and selling). As a result, the shipment would not be a permissible transhipment. Therefore, the products being imported must meet the requirements of the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations or be brought into compliance with the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations in accordance with Section 9 of the Cosmetic Regulations. This approach prevents the import into Canada of non-compliant cosmetics to protect the health and safety of Canadians, even if they are intended to be exported out at a later time.
Health Canada's approach to compliance and enforcement activities, in relation to consumer products and cosmetics, is described in this document in Part 8 – Guiding Principles.
Additional information
8. Guiding principles
The Consumer Product Safety Program's (CPSP) approach to compliance and enforcement actions is set out in Health Canada's Compliance and Enforcement Policy Framework. A wide range of compliance and enforcement actions and tools are available to enable the program to choose the level of intervention that is the most appropriate for the situation. Generally, CPSP will consider various circumstances, including:
- the danger posed to the health and safety of Canadians;
- the likelihood that the issue will occur again;
- the compliance history of the regulated party;
- the behaviour of the company or person, including the degree of cooperation offered by the company or person;
- the need to maintain public confidence; and
- the effective use of Health Canada's resources.
9. Roles and responsibilities
Health Canada, regulated parties and consumers all have roles and responsibilities in relation to consumer products and cosmetics.
Government of Canada's role
Health Canada's Consumer Product Safety Program (CPSP) is responsible for the administration and enforcement of the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and its regulations for consumer products, as well as the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations for cosmetics.
The CPSP works closely with the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) to monitor the movement of consumer products or cosmetics into and out of Canada. Together, they take steps to:
- identify imported products that do not meet the requirements of the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and the Food and Drugs Act; and
- provide Canadians with information to help them make informed decisions in relation to the importation of these products.
At the border, CBSA border officers may detain any consumer product or cosmetic that they suspect do not comply with Canadian law. The CBSA may contact the CPSP to assess whether the products that have been detained comply with the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and the Food and Drugs Act. In these situations, CPSP may:
- inspect or examine the products;
- have the products analyzed at a lab or assessed for their potential to harm the health or safety of Canadians; and/or
- contact the owner of the products or authorised agent for copies of relevant records or documents that are required under the Acts and regulations (including test reports).
Depending on the outcome of the CPSP's assessment, CBSA may take the following actions with the products:
- release;
- refuse entry into Canada; or
If the products are refused entry or seized, CPSP and/or the CBSA will notify the owner (importer and exporter) in writing of the decision. Health Canada and the CBSA are not responsible for loss, damage or expense for products that are refused or seized.
Section 26 of the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act states that a product that has been seized by Health Canada will be forfeited to the crown if:
- within 60 days after the seizure, no person is identified as its owner or as the person entitled to possess it;
- within 60 days after the day on which the owner or the person entitled to possess it was notified of the seized products' release, but the owner or the person entitled to possess it does not claim it; or
- the owner or the person entitled to possess it consents to forfeit the seized product.
Once forfeited, Health Canada may store, move, dispose or destroy the seized product at the expense of its owner.
General information about the activities Health Canada and the CBSA can perform at the border can be found in the Administration of Health Canada Acts and Regulations Related to Certain Controlled, Prohibited or Regulated Goods.
Industry's role
Industry (that is, importers, exporters, and other supply chain partners) have a responsibility to ensure products meet the requirements outlined in the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act and its regulations, and the Food and Drugs Act and its Cosmetic Regulations.
Industry should include information with the shipment that shows the products in the shipment meet the applicable requirements of these Acts and regulations. For example, Health Canada recommends that industry include the unique Cosmetic Number – assigned by Health Canada – with the shipment of cosmetics.
Consumer's role
Consumers are responsible for maintaining and protecting their health and safety and the health and safety of those around them through the appropriate use of consumer products or cosmetics. Consumers are strongly encouraged to familiarize themselves with how to use products safely and only to buy products from reputable sources or suppliers.
Subscribe and stay informed about product safety alerts and recalls or report an incident involving a consumer product or cosmetic.
Consumers bringing products across the border into Canada should be aware that some consumer products are not allowed into Canada by law, even if it is for personal use (See Bringing Consumer Products into Canada).
Buying consumer products and cosmetics online may expose consumers and their families to potential risks. Learn how to minimize risk when buying these products online.
10. Contact us
Health Canada and the Canada Border Services Agency may be contacted at the following coordinates:
Health Canada's Consumer Product Safety Program
Enquiries related to consumer products
Email: cps-spc@hc-sc.gc.ca
Phone: 1-866-662-0666 (toll-free within Canada and the United States)
Enquiries related to cosmetics
E-mail: cosmetics@hc-sc.gc.ca
Phone: 1-866-662-0666 (toll-free within Canada and the United States)
Canada Border Services Agency
Border Information services
Phone: 1-800-461-9999 (toll-free, calls within Canada)
Appendices
Appendix A – Glossary
Acronyms
- CPSP:
- Consumer Product Safety Program
- CCPSA:
- Canada Consumer Product Safety Act
- CBSA:
- Canada Border Services Agency
- FDA:
- Food and Drugs Act
- CR:
- Cosmetic Regulations
Terms
- Advertisement (Section 2, CCPSA) – includes a representation by any means for the purpose of promoting directly or indirectly the sale of a consumer product.
- Advertisement (Section 2, FDA) – advertisement includes any representation by any means whatever for the purpose of promoting directly or indirectly the sale or disposal of any food, drug, cosmetic or device.
- Business-like practices (FAQ, CCPSA) – would include managing inventory, record keeping (including issuing receipts or invoices) and receiving payments in a commercial manner (including through invoices, business accounts or credit card terminals).
- Commercial purpose (Section 4, 5) – Involving one of more of the following activities: manufacturing, importation, packaging, storing, advertising, selling, labelling, testing or transportation of a consumer product.
- Consumer product (Section 2, CCPSA) – means a product, including its components, parts or accessories, that may reasonably be expected to be obtained by an individual to be used for non-commercial purposes, including for domestic, recreational and sports purposes, and includes its packaging.
- Cosmetic (Section 2, FDA) – includes any substance or mixture of substances manufactured, sold or represented for use in cleansing, improving or altering the complexion, skin, hair or teeth, and includes deodorants and perfumes.
- Cosmetic Number (Guide for Cosmetic Notifications) – The Cosmetic Number is a unique identifier assigned by Health Canada. Once the CNF is processed, a CN will be assigned and sent to the notifier via email. This CN should also be used in any correspondence with Health Canada related to a product. This is equivalent to the "CNF number" used prior to 2013.
- Drug (Section 2, FDA) – drug includes any substance or mixture of substances manufactured, sold or represented for use in
- (a) the diagnosis, treatment, mitigation or prevention of a disease, disorder or abnormal physical state, or its symptoms, in human beings or animals,
- (b) restoring, correcting or modifying organic functions in human beings or animals, or
- (c) disinfection in premises in which food is manufactured, prepared or kept
- Exporter – determining who the exporter is and who is subject to which requirements under the CCPSA and regulations will be made on a case by case basis. For the purpose of this policy, exporters may move goods into Canada or moves consumer products or cosmetics out of Canada into another country. It includes a person that sends product across the Canadian border or a person in Canada who sends or ships a consumer products or cosmetics abroad. It also includes a person in Canada who sells or advertises products to another country over the Internet.
- Export – for the purposes of this policy, export includes, in addition to the sending or transporting of consumer products or cosmetics abroad, the sale or advertising over the Internet of consumer products or cosmetics to a foreign jurisdiction.
Note: for foreign companies exporting products to Canada, they should verify their products meet the relevant requirements for products being imported into Canada. - Import (Section 2, CCPSA) – means to import into Canada.
- Importer – for the purpose of this policy, "importer" is a person who brings consumer product or cosmetic (for the purpose of selling it, Section 2, Cosmetic Regulations) into Canada from another country, including the United States. An importer may also be a person that crosses the Canadian border with the products, a person that causes or directs the goods to be imported into Canada, or a person in Canada who directly receives the products entering Canada from another country. Health Canada does not recognize the terms "importer of record", "non-resident importer" or "foreign importer" as being importers under the CCSPA or FDA and Cosmetic Regulations.
Determining who the importer is will be made on a case by case basis.
- Manufacture (Section 2, CCPSA) – includes produce, formulate, repackage and prepare, as well as recondition for sale.
- Manufacturer (Section 2, Cosmetic Regulations) – the Canadian manufacturer of a cosmetic who sells a cosmetic under their own or a trademark, design, trade name, or other name they own or control;
- Responsible person in Canada acting on behalf of a manufacturer who is not in Canada; or
- If no one in Canada meets the definition of the "manufacturer", the importer or any person who manufactures or processes the cosmetic in Canada is considered the manufacturer.
- Measure (Section 32, CCPSA) – any action necessary to remedy a non-compliance or to address or prevent a danger to human health or safety and include: Stopping the manufacturing, importation, packaging, storing, advertising, selling, labelling, testing or transportation of the consumer product or causing any of those activities to be stopped.
- Natural Health Product (Section 1, Natural Health Products Regulations) – means a substance set out in Schedule 1 or a combination of substances in which all the medicinal ingredients are substances set out in Schedule 1, a homeopathic medicine or a traditional medicine, that is manufactured, sold or represented for use in
- (a) the diagnosis, treatment, mitigation or prevention of a disease, disorder or abnormal physical state or its symptoms in humans;
- (b) restoring or correcting organic functions in humans; or
- (c) modifying organic functions in humans, such as modifying those functions in a manner that maintains or promotes health.
However, a natural health product does not include a substance set out in Schedule 2, any combination of substances that includes a substance set out in Schedule 2 or a homeopathic medicine or a traditional medicine that is or includes a substance set out in Schedule 2.
- Package (Section 2, FDA) – includes anything in which any food, drug, cosmetic or device is wholly or partly contained, placed or packed.
Note: this excludes consolidation and deconsolidation. - Person (Section 2, CCPSA & FDA) – means an individual or an organization as defined in section 2 of the Criminal Code.
- Pest Control Product (Section 2, Pest Control Products Act) – pest control product means:
- (a) a product, an organism or a substance, including a product, an organism or a substance derived through biotechnology, that consists of its active ingredient, formulants and contaminants, and that is manufactured, represented, distributed or used as a means for directly or indirectly controlling, destroying, attracting or repelling a pest or for mitigating or preventing its injurious, noxious or troublesome effects;
- (b) an active ingredient that is used to manufacture anything described in paragraph (a); or
- (c) any other thing that is prescribed to be a pest control product (produit antiparasitaire).
- Sell (Section 2, CCPSA) – includes offer for sale, expose for sale or have in possession for sale — or distribute to one or more persons, whether or not the distribution is made for consideration (eg. payment) — and includes lease, offer for lease, expose for lease or have in possession for lease.
- Sell (Section 2, FDA) – includes offer for sale, expose for sale, have in possession for sale and distribute, whether or not the distribution is made for consideration, eg. payment.
- Therapeutic claims (See "Health Claims" on Canada.ca) are a type of disease risk reduction claims about the treatment, or mitigation of a disease or health-related condition or about restoring, correcting or modifying body functions (e.g. "Skin cleanser removes toxins").
- Transhipment – goods that pass through Canada where the journey begins and ends beyond the borders of Canada. Goods transhipped through Canada, while in transit are not released into Canada and/or do not undergo any activity – such as labeling, storing, further finishing – while in transit through Canada.
- Written Order –An order, in the form of a written notice ordering a person to recall their product (Section 31, CCPSA), to take measures (Section 32, CCPSA) or directing any person who manufactures or imports a consumer product for commercial purposes to conduct tests or studies and to compile information where deemed necessary to verify compliance or prevent non-compliance with the CCPSA or its regulations and to submit these in the time and manner specified in the order (Section 12, CCPSA).
Appendix B – Consumer products with specific regulatory requirements and their associated guides
In addition to the product specific regulatory requirements below, in all cases, products you bring into Canada cannot pose a "danger to human health or safety".
To see the most up-to-date Regulations under the authority of the CCPSA, please visit the CCPSA Justice Canada webpage and scroll down to the heading "Regulations made under this Act".
Appendix C – References
Laws
Policies and guidance document
- Canada Consumer Product Safety Act Quick Reference Guide
- Compliance and Enforcement Policy
- Bringing Consumer Products into Canada
- Guidance on Preparing and Maintaining Documents under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act (CCPSA) - Section 13
- Industry Guide on Mandatory Reporting under the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act - Section 14 "Duties in the Event of an Incident"
- D-Memo for CPS (D-19-9-1) The Administration of Health Canada Acts and Regulations Relating to Certain Controlled, Prohibited or Regulated Goods (2017-01-24)
- Frequently Asked Questions for the Canada Consumer Product Safety Act
- Industry Guide for the labelling of cosmetics
- Industry Guidance - "Danger to Human Health or Safety" Posed by Consumer Products
Incident reporting and notification form
Other